5Data Mapping Using Scripts
Data Mapping Using Scripts
This chapter describes the process of using the Siebel eScript Data Mapping to convert your external data to the Siebel format and your Siebel data to your external data specifications. It contains the following topics:
Overview
You can accomplish your data transformation requirements in Siebel by using the Data Transformation Function or Siebel Data Mapper, as illustrated in the following figure.
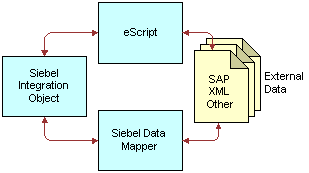
For customers who want to do data mapping within Siebel applications, Siebel applications now support two data mapping solutions—Siebel Data Mapper and Siebel eScript Data Mapping. Siebel Data Mapper has a declarative interface and requires no programming skills. Siebel eScript Data Mapping uses scripts programmed in eScript as data maps.
Data maps defined using Siebel Data Mapper are easy to maintain and upgrade. These maps also perform better than eScript Data Maps. Because Siebel Data Mapper is based on a declarative interface, it does not have the full flexibility and power that the data mapping using eScript has. Siebel Data Mapper should suffice for most integration needs except some complex mapping situations requiring aggregation, joins, or programmatic flow control.
The following checklist outlines the main steps required to accomplish your data transformation requirements using the Data Transformation Functions.
| Checklist | |
|---|---|
| □ |
Define integration objects in Siebel Tools—one to represent Siebel objects and another to represent external data. For details, see Integration Platform Technologies: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration. |
| □ |
Set up the Data Transformation Map. For details, see Setting Up a Data Transformation Map. |
| □ |
Write the Siebel eScript code to perform the data transformation. For details, see To write a script for the DTE business service. |
EAI Data Transformation
The Siebel Data Transformation Functions are a framework for building data transformation maps. Data transformation maps act as import and export filters, preparing data from an external system for entry into Siebel applications and preparing data in Siebel applications for export.
Data transformation maps are created as business services using Siebel eScript. You invoke them as part of an EAI workflow process.
A data transformation map reads data from an input structure and transfers it to an output structure, transforming it along the way. The map developer creates a custom eScript function to do the transformation. The Data Transformation Functions provide a convenient way to read the input data and generate results. They also provide a framework for invoking your map functions, handling errors, and accessing other EAI resources.
Setting Up a Data Transformation Map
Using the workspace in Siebel Tools, you can create your data transormation map in a business service and you can deliver these changes into the runtime repository. You can organize your maps in many different ways. Each business service you create can contain one or more maps. You can, in fact, use several business services to organize a large number of maps into logical groups.
To define a data transformation business service in Siebel Tools
In Siebel Tools, create a new business service associated with a locked project.
Choose the CSSEAIDTEScriptService class for the business service.
Double-click the Business Services Methods folder and add the method Execute.
Select the Business Service Method Arg folder and add the arguments for the Execute method. For a list of arguments and their description, see DTE Business Service Method Arguments. The arguments to include are:
MapName
An input argument. Select one of SiebelMessage, XMLHierarchy, or MIMEHierarchy as the argument name, based on the type of input.
An output argument. Required if the output object is a different type than the input argument. Select one of SiebelMessage, XMLHierarchy, or MIMEHierarchy as the argument name.
Note: If the input and output types are the same then the same argument entry is used for both.OutputType
InputType(Optional). This is required only when passing the business service input property set to the map function without interpretation. This is done by specifying the InputType as ServiceArguments.
Note: Most transform maps use SiebelMessage for both the input and output arguments. This is for mapping one integration object to another. For details, see DTE Business Service Method Arguments.
Once you have created the business service you need to write the Siebel eScript code to perform the data transformation.
To write a script for the DTE business service
In Siebel Tools, select the business service you want to contain the transformation map.
Right-click, then choose Edit Server Scripts
Choose eScripts as the scripting language if you are prompted to select a scripting language.
In the (declarations) procedure of the (general) object, add the line:
#include "eaisiebel.js"
In the Service_PreInvokeMethod function of the service, change the function to the following:
function Service_PreInvokeMethod (MethodName, Inputs, Outputs) { return EAIExecuteMap (MethodName, Inputs, Outputs); }Your data transformation map is run as a business service invoked from a workflow process. Business service scripts have a standard entry point, Service_PreInvokeMethod. Although the script environment provides you with a boilerplate function by this name, you need to modify it, as described in the preceding steps, to include the call to the EAIExecuteMap function.
The MethodName must be Execute and is used by Siebel Workflow. The name of your function is the name you supply for the MapName argument to the Execute method.
Inputs is the input message from workflow containing service arguments—for example, MapName and Output Integration Object Name—and the integration message to be transformed. Outputs is the argument used to return data—for example, Siebel Message. MapName specifies the map function to be executed and must be the name of one of the functions you defined in the business service.
For examples of DTE business services, select the Business Service object in Siebel Tools, and then query for CSSEAIDTEScriptService in the Class field in the Object List Editor.
DTE Business Service Method Arguments
The following information presents the arguments for the Execute method of the DTE business services.
| Name & Display Name | Data Type | Type | Optional | Storage Type | PickField | PickList |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
MapName Map Name |
String |
Input |
No |
Property |
- |
- |
InputType Input Type |
String |
Input |
No |
Property |
Value |
EAI Message Type PickList |
OutputType Output Type |
String |
Input |
No |
Property |
Value |
EAI Message Type PickList |
SiebelMessage Siebel Message |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
Yes |
Hierarchy |
- |
- |
MIMEHierarchy MIME Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
Yes |
Hierarchy |
- |
- |
XMLHierarchy XML Hierarchy |
Hierarchy |
Input/Output |
Yes |
Hierarchy |
- |
- |
You can set the following arguments in Siebel Tools:
MapName. The name of the eScript function to call to perform the transformation.
InputType. The type of input object to pass to the transformation function. The value will be one of SiebelMessage, MIMEHierarchy, XMLHierarchy, or ServiceArguments. This argument is required only when you use ServiceArguments as the value. When ServiceArguments is used the business service, PropertySet is passed to the map function without interpretation.
OutputType. The type of the output object to pass to the transformation function. The types are the same as the ones for Input Type.
SiebelMessage. You use this argument when the input or output object or both are SiebelMessage. SiebelMessage is used when converting to or from an integration object, and is the correct choice when mapping one integration object to another. Your map function is passed two objects of type CSSEAIIntMsgIn and CSSEAIIntMsgOut. These objects are for the SiebelMessage that is the input to the transformation and the SiebelMessage that is produced by the transformation, respectively.
MIMEHierarchy. You use this argument if either the input or output object or both are MIMEHierarchy. MIMEHierarchy is used when converting to or from MIME Hierarchy objects. Your map function is passed two object types; CSSEAIMimeMsgIn for the MIMEHierarchy that is the input to the transformation and CSSEAIMimeMsgOut for the MIMEHierarchy that is produced by the transformation. MIME Hierarchy objects are defined by the EAI MIME Doc Converter business service. For details on the EAI MIME Doc Converter, see Integration Platform Technologies: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.
XMLHierarchy. You use this argument if either the input or output object or both are XMLHierarchy. XMLHierarchy is used when converting to or from XML Hierarchy objects. Your map function is passed an object of type XML Property Set for both input and output XMLHierarchy. XML Hierarchy objects are defined by the XML Hierarchy Converter business service. For details on XML Hierarchy Converter, see XML Reference: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration.
Map Functions
A map function has the following signature:
function MapFnName (objectIn, objectOut)
The function name signified by MapFnName is the name of your transformation function. It is the value passed as the MapName argument to the business service. The Input Type and Output Type business service arguments determine the types of the objectIn and objectOut arguments and default to the type Integration Message. You should name these arguments according to type. For example, to use the default values, you would specify a function that transforms one integration object to another as:
function MapFnName (intMsgIn, intMsgOut)
If you define a function that transforms an XML property set to an integration object, you might specify it as:
function MapFnName (xmlPropSetIn, intMsgOut)
The arguments to these functions are contained within the input and output arguments to the business service’s Service_PreInvokeMethod function. The EAIExecuteMap function—called by Service_PreInvokeMethod—interprets the arguments and passes them to MapFnName. MapFnName reads from the input object and writes to the output object using the appropriate API for each type of object.
If you define a function to access input integration object, you might specify it as:
function myMapFn (ObjectIn, ObjectOut) {
inIntObj = ObjectIn.GetIntObj(); //Get Integration Object
//Iterate over all Integration Object Instances
while (inIntObj.NextInstance()) {
//Get the Primary Component which is called "Order Entry - Orders"
primaryIntComp = inIntObj.GetPrimaryIntComp("Order Entry - Orders");
//Iterate over all instances of Primary Component
while (primaryIntComp.NextRecord()) {
OrderId = primaryIntComp.GetFieldValue ("Id");
//Get component "Order Entry - Line Items" which is child of "Order Entry - Orders"
comp = primaryIntComp.GetIntComp ("Order Entry - Line Items");
//Process component similar to primary component
while (comp.NextRecord()) {
OrderItemId = comp. GetFieldValue ("Id");
And to define a function to create output integration object, you might specify it as:
function myMapFn (ObjectIn, ObjectOut) {
outIntObj = ObjectOut.CreateIntObj("Sample Order");
while (Need new integration object instances) {
outIntObj.NewInstance();
//Create Primary Component which is called "Order Entry - Orders"
primaryIntComp = outIntObj.CreatePrimaryIntComp("Order Entry - Orders");
while (Need new instances of primary int component) {
primaryIntComp.NewRecord();
primaryIntComp.SetFieldValue ("Id", OrdertemId);
//Create component Order Item which is child of Order
comp = primaryIntComp.CreateIntComp ("Order Entry - Order Items");
//Process component similar to primary component
while (need new instances of component) {
comp.NewRecord();
comp. SetFieldValue ("Id", OrdertemId);
EAIExecuteMap() Method
This method executes a user-defined data transformation function. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
EAIExecuteMap(methodName, inputPropSet, outputPropSet)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
methodName |
The business service method should be Execute. |
inputPropSet |
Input message and service arguments. |
outputPropSet |
Output message and service arguments. |
Returns
CancelOperation or ContinueOperation. The Service_PreInvokeMethod function should return the value returned by the EAIExecuteMap.
Usage
Data Transformation Functions
The data transformation API consists of global functions and classes that represent the different parts of input and output data. The data transformation functions are implemented as Siebel eScript. You must use Siebel eScript to create your data transformation maps.
Three different high-level data types are supported:
Siebel Messages. See Siebel Message Objects and Methods.
MIME Messages. See MIME Message Objects and Methods.
XML Property Sets. See XML Property Set Functions.
The data type is determined by the InputType and OutputType arguments, as described in DTE Business Service Method Arguments.
Siebel Messages are the most common data type, and they are represented at the highest level by an Integration Message message. See Siebel Message Objects and Methods.
It is also possible to operate directly on the business service input and output property sets. This is accomplished by specifying the InputType or OutputType as ServiceArguments. In this case the business service property set arguments are passed directly to the map function. The standard property set functions can be used to access them.
Siebel Message Objects and Methods
A Siebel Message is a message containing the data of individual integration object instances. It is hierarchically structured and composed of several different types of objects.
The data transform API uses several different eScript classes to represent a Siebel Message:
An integration message. This represents the high-level message container. See Integration Message Objects.
An integration object. See Integration Object Objects.
A primary integration component. See Primary Integration Component Objects.
Integration components. See Integration Component Objects.
Each of these parts of a Siebel Message has two classes: one for input and one for output. Each class provides methods for specific purposes.
Integration Message Objects
The integration message is the high-level piece of a message. The workflow process passes the integration message to the Data Mapping Engine as input. The Data Mapping Engine returns another message as output. The integration message object provides access to workflow arguments, integration message arguments, and the integration object that is contained in the message.
The following integration message objects are provided:
CSSEAIIntMsgIn
CSSEAIIntMsgOut
CSSEAIIntMsgIn
This object represents an integration message that is open for reading. The object provides GetArgument and GetIntObj methods.
GetArgument() Method
This method gets the value of a business service argument. For example, this could get the name of a map function in the business service. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
GetArgument(name [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of a business service argument. |
defaultIfNull |
Returned if a service argument of the specified name does not exist. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Returned if the service argument is set to an empty string. |
Returns
String or null.
Usage
Use this method to get the value of an argument passed to the business service. For example, if the MapName argument passed to the business service is MapExtOrderToOrder, the call:
intMsgIn.GetArgument("MapName");
returns the name of the map, MapExtOrderToOrder, passed to the business service.
If the named argument does not exist, null is returned. If the named argument exists but the value is the empty string, the empty string is returned. You can use the defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty optional arguments to change this behavior.
The arguments defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty are optional; however, if you specify defaultIfEmpty, you must also specify the defaultIfNull argument.
GetIntObj() Method
This method returns an instance of the integration object and opens it for reading. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetIntObj(name)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of an integration object in the active integration message. |
Returns
CSSEAIIntObjIn Integration Object
Usage
An integration object instance is always returned even if the integration object does not exist. Call the returned object’s Exist method to test for this before calling other methods on the object. An error is raised if an integration object is present but the name is not correct.
GetAttachmentCount() Method
This method returns the number of attachments in the input integration message.
Syntax
GetAttachmentcount()
Returns
The number of attachments in the input integration message.
GetAttachment() Method
This method returns the attachment specified by the index. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetAttachment(index)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
index |
The index of the attachment to return. |
Returns
The attachment (a PropertySet) specified by the index. The index is zero based. Returns null if index is out of bounds.
GetAttachmentByCID() Method
This method retrieves an attachment based on the Content Identifier (CID).The following table presents the parameter for this method.
GetAttachmentByCID(cid)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cid |
The Content Identifier of the attachment. |
Returns
The attachment (a PropertySet) specified by the CID. Returns null if there is no attachment with the specified CID.
CSSEAIIntMsgOut
This object represents an output integration message that is open for writing. The object provides CreateIntObj and SetArgument methods:
CreateIntObj() Method
This method creates a new integration object. The following information presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
CreateIntObj(name)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
Creates a new integration object and adds it to the integration message. |
Returns
CSSEAIIntObjOut Output Integration Object
Usage
An integration message can contain only one integration object, so multiple calls to this method on one integration message raises an error. The name must agree with the business service argument OutputIntObjName, if that argument is passed to the service.
SetArgument() Method
This method sets the value of a business service argument. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
SetArgument(name, value)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of an argument in the active business service. |
value |
The string value corresponding to the argument named by the name parameter. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
You can call the SetArgument method to establish the value of a given output argument for the business service method invocation.
SetAttachmentSource() Method
This method establishes the source object to copy attachment objects from. The source object must be a CSSEAIIntMsgIn, CSSEAIMimeMsgIn, or other object implementing the GetAttachmentByCID method. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
SetAttachmentSource(source)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
source |
The attachment source. |
CopyAttachment() Method
This method copies an attachment from the attachment source to the output integration object. The attachment is referenced by the MIME Content Identifier (CID). The attachment source must be established by calling CSSEAIIntMsgOut.SetAttachmentSource before calling this method. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
CopyAttachment(cid)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cid |
MIME content identifier. |
Returns
The attachment copy is returned as a property set. This method returns null if the attachment source does not contain an attachment with the specified CID.
Integration Object Objects
The integration object contains one or more integration components. The following integration object objects are provided:
CSSEAIIntObjIn
CSSEAIIntObjOut
CSSEAIIntObjIn
This object represents an input integration object, open for reading, that is contained in the integration message. The integration object has a name and contains zero or more instances of actual integration objects. Integration object instances are accessed one at a time, similar to accessing database records. Each instance has a primary integration component that contains data and every subordinate integration components. This object provides the Exists, FirstInstance, GetPrimaryIntComp, and NextInstance methods.
Exists() Method23
This method checks to see if the integration object is actually present in the input data. It takes no parameters.
Syntax
Exists()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Call Exists after retrieving the integration object from the integration message. If the integration object was found and is open for reading, the Exists method returns true.
FirstInstance() Method
This method moves to the first integration object instance and sets it as the active instance.
Syntax
FirstInstance()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
The FirstInstance method returns true if the instance exists, false otherwise.
GetPrimaryIntComp() Method
This method returns the primary integration component of the active instance of the integration object. The following information presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetPrimaryIntComp(name)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of a primary integration component in the active integration object instance. |
Returns
CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompIn Input Primary Integration Component
Usage
Gets the primary integration component of the active instance of the integration object and opens it for input.
This method always returns an input primary integration component object, even if the component does not exist. Call the Exists method on the returned object to test for this condition. If there is no active instance, a call to this method raises an error.
NextInstance() Method
This method moves a pointer to the next logical integration object instance in the active integration message.
Syntax
NextInstance()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Moves to the next integration object instance and makes it the active instance. This method returns true if the instance exists, or false if there are no more instances. If neither the NextInstance or the FirstInstance method has been called previously, the NextInstance method moves to the first instance in the message.
CSSEAIIntObjOut
This object represents an output integration object, open for writing, that is contained in the integration message. It provides CreatePrimaryIntComp and NewInstance methods as an interface to the output integration object.
CreatePrimaryIntComp() Method
This method creates a new primary integration component. The following information presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
CreatePrimaryIntComp(name)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
Assigned as the name of the Primary Integration Component. |
Returns
CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompOut Primary Integration Component, open for output
Usage
Use the Exists method to test for existence of the integration object instance, then create a new integration object instance and set it as the active instance, using the NewInstance method. You must perform these tasks before calling the CreatePrimaryIntComp() method.
NewInstance() Method
This method creates a new instance of an integration object and makes it the active instance.
Syntax
NewInstance()
Returns
Not applicable
Primary Integration Component Objects
A primary integration component represents the integration component contained within an integration object instance. It has a name and contains records with data from actual integration components. Each record may have fields and subordinate integration components.
The following primary integration component objects are provided:
CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompIn
CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompOut
CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompIn
This object represents the input primary integration component, open for reading. Your data transformation maps can use this object’s methods to traverse integration components. This object provides Exists, FirstRecord, GetFieldValue, GetIntComp, and NextRecord methods:
Exists() Method
This method checks to see if the primary integration component is actually present in the input data. It takes no parameters.
Syntax
Exists()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Call Exists after retrieving the primary integration component with the CSSEAIIntObjIn.GetPrimaryIntComp method, and before invoking the primary integration component’s other methods.
If the primary integration component was found and is open for reading, the Exists method returns true.
FirstRecord() Method
This method moves a pointer to the first component record in the primary integration component.
Syntax
FirstRecord()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Moves to the first integration component record and sets it as the active record. This method returns true if the record exists, false if the integration component has no records.
GetFieldValue() Method
This method returns the value of the primary integration component field from the active record. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
GetFieldValue(name [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of a primary integration component field. |
defaultIfNull |
Optional. Sets the default value if the field does not exist. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Optional. Sets the default value if the field is set to an empty string. |
Returns
String or null
Usage
A null value is returned if the active record does not contain the field. Otherwise, a string containing the value in the field is returned. If there is no active record, this method raises an error.
If the named argument does not exist, null is returned. If the named argument exists but the value is the empty string, the empty string is returned. You can use the defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty optional arguments to change this behavior.
The arguments defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty are optional; however, if you specify defaultIfEmpty, you must also specify the defaultIfNull argument.
GetIntComp() Method
This method returns the named integration component from the active record and opens it for input. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetIntComp(name)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of an integration component in the active record. |
Returns
CSSEAIIntCompIn Input Integration Component
This method always returns an input integration component object, even if the component does not exist. Call the Exists method on the returned object to test for this condition. If there is no active record, a call to this method raises an error.
NextRecord() Method
This method moves a pointer to the next logical record in the active integration component.
Syntax
NextRecord()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Moves to the next record and makes it the active record. Returns true if the record exists, or false if there are no more records. Moves to the first record if neither the NextRecord method nor the FirstRecord method has been called previously.
CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompOut
This object represents the output primary integration component. You can use the object’s methods to create output integration components and records and to copy input data records to output data records. This object provides CopyFieldValue, CreateIntComp, NewRecord, SetCopySource, and SetFieldValue methods.
CopyFieldValue() Method
This method sets the value of a field in the active record to the value of a field in the current source record. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
CopyFieldValue(targetName, sourceName [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
targetName |
Name of the field to set in the output integration component. |
sourceName |
Name of the field to retrieve from the input integration component. |
defaultIfNull |
Optional value that specifies what should be inserted into the target, if the source field does not exist. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Optional value that specifies what to use as a source value if the source field is empty. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
Use this method to copy a field from an input integration component to the output primary integration component. You could achieve the same results by calling the GetFieldValue method on the input component and the SetFieldValue on the output component; however, using CopyFieldValue is easier.
You must call the SetCopySource method first to specify the source integration component. CopyFieldValue uses the active records of the input and output components of the active integration component.
If the integration component is not set with the SetCopySource method first, a call to the CopyFieldValue method raises an error. An error also occurs if either input or output component does not have an active record.
If you set the copy source using the following statement:
outIntComp.SetCopySource (inIntComp);
the following two statements are equivalent:
outIntComp.SetFieldValue("Fld-A", inIntComp.GetFieldValue("X"));
outIntComp.CopyFieldValue("Fld-A", "X");
Using the second convention is convenient if you are copying many fields between the same components.
CreateIntComp() Method
This method creates a new integration component. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
CreateIntComp(name [, createNow])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of the new integration component. |
createNow |
Defaults to true. This is an optional parameter. By default, the underlying data object is created in the output data object at the time this method is called. To change this behavior, specify the optional createNow argument as false. If you specify createNow as false, the underlying data object is not created until you make the first NewRecord call on the newly created integration component. |
Returns
CSSEAIIntCompOut. Output Integration Component
Usage
Use this method to create a new integration component, open it for writing, and add it to the active record of the integration component.
NewRecord() Method
This method creates a new record in a primary integration component.
Syntax
NewRecord()
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
This method adds a new primary integration component record and makes it the active record.
SetCopySource() Method
This method establishes the integration component from which a field value will be copied. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
SetCopySource(IntComp)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IntComp |
The integration component object—either CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompIn or CSSEAIIntCompIn. |
Returns
Not applicable
Call this method before a call to the CopyFieldValue method.
This method sets the value of the named field in the active integration component record. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
SetFieldValue(name, value)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of a field in the active record of the primary integration component. |
value |
The string value to be put into the field given in the name parameter. |
Returns
Not applicable
Both the name and value arguments should be strings.
The field is not set if the value is null. This method provides no return value.
This method raises an error if called while there is no active record.
Integration Component Objects
An integration component object represents integration components. The following integration component objects are provided:
CSSEAIIntCompIn
CSSEAIIntCompOut
CSSEAIIntCompIn
This object represents the input integration component, open for reading. You can use the object’s methods to traverse actual integration components and to retrieve data from those integration components. This object provides Exists, FirstRecord, GetFieldValue, GetIntComp, and NextRecord methods.
Exists() Method
This method checks to see if the integration component is actually present in the input data. It takes no parameters.
Syntax
Exists()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Call Exists after retrieving the integration component from its parent object using the GetIntComp method, and before invoking the integration component’s other methods.
If the integration component is found and is open for reading, the Exists method returns true.
FirstRecord() Method
This method moves a pointer to the first component record in the integration component.
Syntax
FirstRecord()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Moves to the first integration component record and sets it as the active record. This method returns true if the record exists, false if the integration component has no records.
GetFieldValue() Method
This method returns the value of the integration component field from the active record. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
GetFieldValue(name [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of an integration component field. |
defaultIfNull |
Optional. Value to return if the field does not exist. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Optional. Value to return if the field is set to an empty string. |
Returns
String or null
Usage
A null value is returned if the active record does not contain the field. Otherwise, a string containing the value in the field is returned. If there is no active record, this method raises an error.
If the named argument does not exist, null is returned. If the named argument exists but the value is the empty string, the empty string is returned. You can use the defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty arguments to change this behavior.
GetIntComp() Method
This method returns the integration component from the active record and opens it for input. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
GetIntComp(name)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of an integration component in the active record. |
Returns
CSSEAIIntCompIn Input Integration Component
This method always returns an input integration component object, even if the component does not exist. Call the Exists method on the returned object to test for this condition.
NextRecord() Method
This method moves a pointer to the next logical record in the active integration component.
Syntax
NextRecord()
Returns
Boolean
Usage
Moves to the next record and makes it the active record. Returns true if the record exists, or false if there are no more records. Moves to the first record if neither the NextRecord method nor the FirstRecord method has been called previously.
CSSEAIIntCompOut
This object represents the output integration object, open for writing. You can use this object’s methods to create new output integration components and to copy or set actual data in the records of the integration components. This object provides CopyFieldValue, CreateIntComp, NewRecord, SetCopySource, and SetFieldValue methods.
CopyFieldValue() Method
This method sets the value of a field in the active record to the value of a field in the current source record. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
CopyFieldValue(targetName, sourceName [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
targetName |
Name of the field to set in the output integration component. |
sourceName |
Name of the field to retrieve from the input integration component. |
defaultIfNull |
Optional value that specifies what should be inserted into the target, if the source field does not exist. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Optional value that specifies what to use as a source value if the source field is empty. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
Use this method to copy a field from an input integration component to the output integration component. You could achieve the same results by calling the GetFieldValue method on the input component and the SetFieldValue on the output component; however, using CopyFieldValue is easier.
You must call the SetCopySource method first to specify the source integration component. CopyFieldValue uses the active records of the input and output components of the active integration component.
If the integration component is not set with the SetCopySource method first, a call to the CopyFieldValue method raises an error. An error also occurs if either input or output component does not have an active record.
If you set the copy source using the following statement:
outIntComp.SetCopySource(inIntComp);
the following two statements are equivalent:
outIntComp.SetFieldValue("Fld-A", inIntComp.GetFieldValue("X"));
outIntComp.CopyFieldValue("Fld-A", "X");
Using the second convention is convenient if you are copying many fields between the same components.
CreateIntComp() Method
This method creates a new integration component. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
CreateIntComp(name [, createNow])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of the new integration component. |
createNow |
Defaults to true. This is an optional parameter. By default, the underlying data object is created in the output data object at the time this method is called. To change this behavior, specify the optional createNow argument as false. If you specify createNow as false, the underlying data object is not created until you make the first NewRecord call on the newly created integration component. |
Returns
CSSEAIIntCompOut. Output Integration Component
Usage
Use this method to create a new integration component, open it for writing, and add it to the active record of the integration component.
This method raises an error if you call it without an active integration component record. Use the NewRecord method to create a new record and set the active record.
SetCopySource() Method
This method establishes the integration component from which a field value will be copied. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
SetCopySource(IntComp)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
IntComp |
The integration component object—either CSSEAIPrimaryIntCompIn or CSSEAIIntCompIn. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
Call this method before calling the CopyFieldValue method.
SetFieldValue() Method
This method sets the value of the named field in the active integration component record. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
SetFieldValue(name, value)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of a field in the active record of the integration component. |
value |
The string value to be put into the field given in the name parameter. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
Both the name and value arguments should be strings.
The field is not set if the value is null. This method provides no return value.
This method raises an error if called while there is no active record.
MIME Message Objects and Methods
Siebel EAI represents MIME documents using a property set format. This is the format used by the EAI MIME Doc Converter Business Service. The objects and methods described here provide access to this property set format, and are intended for use in conjunction with transforming pieces of the MIME message to and from Siebel Integration Messages.
The following MIME message objects are provided:
CSSEAIMimeMsgIn
CSSEAIMimeMsgOut
CSSEAIMimeMsgIn
This object represents an input MIME Message, open for reading. The MIME message is in the property set format generated by the EAI MIME Doc Converter. The object consists of a series of MIME parts forming the different pieces of the message.
This object provides GetArgument, GetPartCount, GetPart, GetPartByCID, GetAttachmentByCID, and GetXMLRootPart methods.
GetArgument() Method
This method gets the value of a business service argument. For example, this could get the name of a map function in the business service. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
GetArgument(name [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of a business service argument. |
defaultIfNull |
Returned if a service argument of the specified name does not exist. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Returned if the service argument is set to an empty string. |
Returns
String or null
Usage
Use this method to get the value of an argument passed to the business service. For example, if the MapName argument passed to the business service is MapExtOrderToOrder, the call:
intMsgIn.GetArgument("MapName");
returns the name of the map, MapExtOrderToOrder, passed to the business service.
If the named argument does not exist, null is returned. If the named argument exists but the value is the empty string, the empty string is returned. You can use the defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty optional arguments to change this behavior.
The arguments defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty are optional; however, if you specify defaultIfEmpty, you must also specify the defaultIfNull argument.
GetPartCount() Method
This method returns the number of parts in the MIME message. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetPartCount()
Returns
This method returns the number of parts in the MIME message.
GetPart() Method
GetPart(index)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
index |
Index of the MIME part to return. |
Returns
Property set. Returns the part, a property set, specified by the index. The index is zero based. Returns null if the index is out of bounds.
GetPartByCID() Method
Retrieve a MIME part based on the MIME Content Identifier (CID).The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetPartByCID(cid)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cid |
MIME Content Identifier to retrieve. |
Returns
Returns null if there is no part with the specified CID.
GetAttachmentByCID() Method
The same functionality as CSSEAIMimeMsgIn.GetPartByCID. Supports using a CSSEAIMimeMsgIn as an attachment source for copying attachments to output objects. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
GetAttachmentByCID(cid)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cid |
MIME Content Identifier to retrieve. |
Returns
The attachment (a property set) specified by the CID. Returns null if there is no attachment with the specified CID.
Finds the first MIME part that is an XML message in property set format and returns the root element of the XML document. The XML message must be in property set format as produced by the XML Hierarchy Converter Business Service. An error is raised is the XML message is not found. The method is intended for use with MIME messages that consist of an XML message and a series of related attachments. The property set returned is consistent with what XPSGetRootElement returns, and can be accessed with the XML Property Set functions. See XML Property Set Functions.
Syntax
GetXMLRootPart()
Returns
MIME body part representing an XML document.
CSSEAIMimeMsgOut
This object represents an output MIME message, open for writing. This object provides SetArgument, CreateXMLPart, SetAttachmentSource, and CopyAttachment methods:
SetArgument() Method
This method sets the value of a business service argument. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
SetArgument(name, value)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
name |
The name of an argument in the active business service. |
value |
The string value corresponding to the argument named by the name parameter. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
You can call the SetArgument method to establish the value of a given output argument for the business service method invocation.
CreateXMLPart() Method
This method is similar to XPSCreateRootElement. See XPSCreateRootElement(). CreateXMLPart() Method creates an XML MIME part and adds it to the MIME document. The property set representing the XML root element is returned. The property set returned can be populated using the XML Property Set functions. See XML Property Set Functions.The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
CreateXMLPart(xmlRootTagName)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlRootTagName |
The name you want to supply as the root element name in the XML document. |
Returns
Property set
SetAttachmentSource() Method
This method establishes the source object from which to copy attachment objects. The source object must be a CSSEAIIntMsgIn, CSSEAIMimeMsgIn, or other object implementing the GetAttachmentByCID method.The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
SetAttachmentSource(source)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
source |
The attachment source. |
CopyAttachment() Method
This method copies an attachment from the attachment source to the output MIME message object. The attachment is referenced by the MIME Content Identifier (CID). The attachment copy, a property set, is returned. The attachment source must be established by calling CSSEAIMimeMsgOut.SetAttachmentSource before calling this method. The following table presents the parameter for this method.
Syntax
CopyAttachment(cid)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
cid |
MIME Content Identifier of the attachment to copy. |
Returns
Property set. This method returns null if the attachment source does not contain an attachment with the specified CID.
Attachments and Content Identifiers in MIME Messages
A MIME message contains one or more parts, each representing a separate piece of the message. One common use of multipart MIME messages is to include attachments with a message.
Each MIME body part has an optional Content Identifier (CID) used to identify it. The Content Id is part of the MIME part header, for example:
--unique_boundary_123 Content-Type : image/jpeg Content-ID : <001110.102215@abc.com>
Then the CID is 001110.102215@abc.com. The CID is usually referenced from another part of the MIME message. A common scheme is to use an XML document as the main part of the MIME message, and use Content Ids to reference the other attachments in the message. The following is an example of a MIME message with attachment.
MIME-Version: 1.0
Content-Type: multipart/related;
boundary="unique_boundary_123";
type="application/xml"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary
--unique_boundary_123
Content-Type: application/xml; charset="UTF-8"
Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE Memo SYSTEM "Memo.dtd">
<Memo>
<To>All Employees</To>
<Subject>Map and Directions</Subject>
<Body>Maps to company headquarters are attached.</Body>
<ListOfAttachments>
<Attachment>
<URI>cid:001110.102203@oracle.com</URI>
<Filename>largemap.jpg</Name>
</Attachment>
<Attachment>
<URI>cid:001110.102211@oracle.com</URI>
<Filename>detailmap.jpeg</Filename>
</Attachment>
</ListOfAttachment>
</Memo>
--unique_boundary_123
Content-Type: image/jpeg
Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary
Content-ID: <001110.102203@oracle.com>
[... Raw JPEG Image ...]
--unique_boundary_123
Content-Type: image/jpeg
Content-Transfer-Encoding: binary
Content-ID: <001110.102211@oracle.com>
[... Raw JPEG Image ...]
--unique_boundary_123-
XML Property Set Functions
Siebel EAI represents XML documents using the property set format. While Siebel EAI does not always require using the property set format, this representation is used by EAI Business Services such as the EAI XML Converter. The functions described in this section provide a simple interface for manipulating XML documents using the property set format.
High-Level Property Set Functions
These functions are used to manipulate the high-level property set passed to the Map function.
XPSGetRootElement()
This function returns the property set representing the root element of the XML document. If the root element is not present, the system raises an error. The following information presents the parameter for this function.
Syntax
XPSGetRootElement(xmlPropSetIn)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSetIn |
The name of the property set representing the root element of the XML document. |
Returns
Property set
Usage
Use this function to return the root element of an XML document.
XPSCreateRootElement()
This function creates the root element in an output XML document and returns the property set representing it. The element tag in the XML document is set to the value of the tagName argument. The following information presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSCreateRootElement(xmlPropSetOut, tagName)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSetOut |
The output property set. |
tagName |
The name you want to supply as the root element name in the XML document. |
Returns
Property set
Usage
Use this function to create the root element of an XML document that represents a property set. Because the root element does not directly map to a component in the property set, you can give it any representative name.
As an example of how the XPSGetRootElement() and XPSCreateRootElement() functions work, consider the following XML document:
<?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE LETTER SYSTEM "letter.dtd"> <letter> <from>Mary Smith</from> <to>Paul Jones</to> <text>Hello!</text> </letter>
The root element is <letter>. The property set for the <letter> element can be retrieved from the input property set using EAIXPS_GetRootElement, or it can be created in the output property set using EAIXPS_CreateRootElement.
A map function that converts a letter to a memo might start with the following code:
function ConvertLetterToMemo (xmlPropSetIn, xmlPropSetOut)
{
var xmlLetter = XPSGetRootElement (xmlPropSetIn);
var xmlMemo = XPSCreateRootElement (xmlPropSetOut, "memo");
... Code to fill in the 'memo' from the 'letter' ...
}
XML Element Accessors
These functions provide access to elements represented by property sets. The following information presents the parameter for this function.
XPSGetTagName()
Retrieves the tag name of an XML element.
Syntax
XPSGetTagName (xmlPropSet)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The output property set. |
Returns
String. If xmlPropSet is null, XPSGetTagName returns null.
XPSSetTagName()
This function sets the tag name of an XML element. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSSetTagName (xmlPropSet, tagName)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The property set. |
tagName |
The name you want to supply as the current element name in the XML document. |
Returns
String
XPSGetTextValue()
This function returns the text value of an XML element as a string. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSGetTextValue (xmlPropSet [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The output property set. |
defaultIfNull |
Specify a value to override the null default value that results if xmlPropSet is null. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Specify a value to override an empty string ("") contained in xmlPropSet. |
Returns
String or null
Usage
If xmlPropSet is null then null is returned. You can use the optional defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty arguments to override null and empty string ("") return values. An element’s text value is the text between an XML element's start and end tags, excluding child elements.
XPSSetTextValue()
This function sets the text value of an XML element. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSSetTextValue (xmlPropSet, text)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The property set. |
text |
A string you want inserted between start and end tags of an XML element. |
Returns
Not applicable
Usage
The text argument should be a string. An element’s text value is the text between the element’s start and end tags, excluding child elements.
XPSGetAttribute()
This function retrieves an element’s attribute of the given name and returns it as a string. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSGetAttribute (xmlPropSet, name [, defaultIfNull [, defaultIfEmpty]])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The output property set. |
name |
The name you want to supply as the root element name in the XML document. |
defaultIfNull |
Specify a value to override the null default value that results if xmlPropSet is null. |
defaultIfEmpty |
Specify a value to override an empty string ("") contained in xmlPropSet. |
Returns
String
Usage
A null value is returned if xmlPropSet is null or the element does not have the named attribute. The optional defaultIfNull and defaultIfEmpty arguments can be used to override null and empty string ("") return values.
XPSSetAttribute()
This function sets an element attribute value. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSSetAttribute (xmlPropSet, name, value)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The output property set. |
name |
Attribute name. |
value |
String value you want to supply as the attribute value. |
Returns
String
Usage
No action is taken if any of the arguments are null.
XPSGetChildCount()
This function returns the number of children of an element. The following table presents the parameter for this function.
Syntax
XPSGetChildCount(xmlPropSet)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The property set. |
Returns
Number
Usage
All children of an element are also elements.
XPSGetChild()
This function returns the nth child element as specified by the index. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSGetChild(xmlPropSet, index)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The property set. |
index |
Number, starting at zero, of child elements of another element in an XML document. |
Returns
Property set
Usage
Child elements are specified using a zero-based index. A value of null is returned if the index is invalid.
XPSFindChild()
This function returns the first child element with the tagName. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSFindChild (xmlPropSet, tagName)
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The property set. |
tagName |
An XML element tag that signifies the first child element of another XML element. |
Returns
Property set.
Usage
A value of null is returned if there is no child with the specified tag name.
XPSAddChild()
This function creates a new child element with the tagName and appends it to the list of xmlPropSet’s children. The following table presents the parameters for this function.
Syntax
XPSAddChild (xmlPropSet, tagName [, textValue])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
xmlPropSet |
The property set. |
tagName |
The name you want to give to the new child element. |
textValue |
Optional. Sets the text value of the new element. |
Returns
Property set
Examples
The following example converts a <letter> to a <memo>.
The input XML document is:
<letter from="Mary Smith" to="Paul Jones"> <text>Hello!</text> </letter>
The conversion function converts this to a memo format, as follows:
<memo> <type>Interoffice Memo</type> <header> <from>Mary Smith</from> <to>Paul Jones</to> </header> <body>Hello!</body> </memo>
The map function that performs this conversion is:
function ConvertLetterToMemo (xmlPropSetIn, xmlPropSetOut)
{
var letter = XPSGetRootElement (xmlPropSetIn);
var memo = XPSCreateRootElement (xmlPropSetOut, "memo");
XPSAddChild (memo, "type", "Interoffice Memo");
var header = XPSAddChild (memo, "header");
XPSAddChild (header, "from", XPSGetAttribute (letter, "from"));
XPSAddChild (header, "to", XPSGetAttribute (letter, "to"));
XPSAddChild (memo, "body", XPSGetTextValue (XPSFindChild (letter, "text")));
}
EAI Value Maps
EAI Value Maps correlate Siebel data values with external data values.
If you are:
Sending and receiving data, you can create inbound and outbound maps for the same data
Receiving data only, you need only to define an inbound map
Sending data only, you need only to define an outbound map
Consider an example of how EAI Value Maps provide correlations between Siebel applications and the SAP R/3 system. SAP country codes, which are represented as two-character codes, are different from Siebel country codes, represented by the country name spelled out. An EAI Value Map provides a lookup table that lists these two sets of data side by side.
The EAI Value Map entries are stored in the EAI Value Map table. You can view and administer this table from the EAI Value Maps view in the Administration-Integration screens in the Siebel client. The Siebel client groups the entries logically based on the Type and Direction columns.
The following image shows the entries form two logical groupings, with entries for the Siebel inbound and Siebel outbound entries.
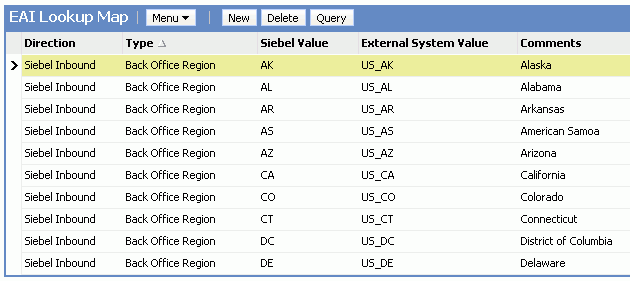
The Direction field determines the direction of the mapping and is either Siebel Outbound or Siebel Inbound. In a Siebel Outbound mapping, the Siebel Value field is the lookup key; the External System Value is the translation. In a Siebel Inbound mapping, the External System Value field is the lookup key; the Siebel Value is the translation.
You can add, remove, or modify entries in the Type group on the EAI Lookup Map view in the Siebel client. The EAI_LOOKUP_MAP_TYPE list of values defines type values. You can modify the list from the Application Administration views in the Siebel client.
The data transformation methods include an interface to EAI Value Maps for translating the codes of one database to another. You use the EAIGetValueMap function to obtain an interface to the mappings of specific Type-Direction pairs. You use the interface object’s Translate method to find specific keys in the Type-Direction map and retrieve the translated values.
EAIGetValueMap Function
You use the following statement in your Siebel eScript code to return a value map:
EAIGetValueMap (type, direction [,unmappedKeyHandler])
This object returns a value map for translating lookup keys using the Type-Direction combination.
The type argument is a string found in the Type field of the EAI Value Map table.
The direction argument must be either Siebel Inbound or Siebel Outbound string values.
A call to this function returns a CSSEAIValueMap object.
You can use the optional unmappedKeyHandler argument to control the behavior of the Translate method when it gets keys that do not have mappings in the table. The unmappedKeyHandler argument can be either a literal value or a function. If you pass a literal value, it is used as the default value. Otherwise, if you pass a function, the method calls that function, then uses the value returned by the function.
The unmappedKeyHandler defaults to an empty string ("").
EAILookupSiebel Search Function
This function returns an EAI Value Map, with inbound direction that has the external value matching the value in the []. The general format for this function is as follows:
EAILookupSiebel ("EAI Value Type",[Source field that lookup will be based on]).
EAILookupExternal Search Function
This function returns an EAI Value Map, with outbound direction that has the Siebel value matching the value in the []. The general format for this function is as follows:
EAILookupExternal ("EAI Value Type",[Source field that lookup will be based on]).
CSSEAIValueMap Translate Method
The CSSEAIValueMap object has one method: Translate. The Translate method takes one argument, as follows:
Translate (key)
The Translate method looks up the key value in the EAI Value Map and returns the translated value. The EAIGetValueMap call establishes the set of mappings for the translation using the type and direction arguments. The call looks for the key in either the Siebel Value column or in the External System Value column, depending on the value of the type argument.
If the type is Siebel Outbound, the method returns the key found in the Siebel Value column. The translated value is in the External System Value column.
If the type is Siebel Inbound, the method returns the key found in the External System Value column. The translated value is in the Siebel Value column.
If key is null then the return value is null.
If key is an empty string, the lookup is performed.
If there is no mapping, an empty string is returned.
If a nonempty string does not have a mapping, the unmappedKeyHandler value specified in the call to the EAIGetValueMap function is used to determine the translation.
EAIGetValueMap unmappedKeyHandler Argument
The unmappedKeyHandler provides a flexible mechanism for handling cases where keys are not found in the EAI Value Map. In most situations, you can use literal values for defaults or you can use one of several predefined handler functions. However, you can also provide your own handler function.
The technique you use for handling unmapped values depends on the data being mapped.
Typical strategies include:
Use the empty string as the translation.
This is the default strategy. It clears the field if the data is being imported into your Siebel application. To follow this approach, omit the unmappedKeyHandler argument or pass it as an empty string. For example:
var langMap = EAIGetValueMap("SAP Language","Siebel Inbound","");This example looks up a nonexistent language code and returns an empty string. For example:
var translatedValue= langMap.Translate ("ABC"); // returns an empty stringUse
nullas the translation.This technique makes the result unspecified rather than empty. For data imported to Siebel applications, this keeps the existing value from being overridden when performing updates. Use
nullas the unmappedKeyHandler — for example:var langMap = EAIGetValueMap("SAP Language","Siebel Inbound", null);Use a literal string as the translation.
Specify the string as the unmappedKeyHandler. For example:
var langMap = EAIGetValueMap("SAP Language","Siebel Inbound", "Unknown Language");Raise an error.
This may be the best strategy if the Value Map should contain mappings for every key. You can use the EAIValueMap_NoEntry_RaiseError function. For example:
var langMap = EAIGetValueMap ("SAP Language", "Siebel Inbound", EAIValueMap_NoEntry_RaiseError);Use the untranslated value.
The predefined function EAIValueMap_NoEntry_ReturnLookupKey implements this strategy. For example:
var langMap = EAIGetValueMap ("SAP Language", "Siebel Inbound", EAIValueMap_NoEntry_ReturnLookupKey);Trying to look up a nonexistent language code (for example, ABC) will return the original key. For example:
var translatedValue = langMap.Translate ("ABC"); // returns "ABC"
You can also write a custom handler function. You need to write a function taking three arguments: key, type, and direction. The value your function returns is used as the translation. For example:
function MyUnmappedLangHandler (key, type, direction)
{
return ("Unknown Language: " + key);
}
var langMap = EAIGetValueMap ("SAP Language", "Siebel Inbound",
MyUnmappedLangHandler);
// Lookup a nonexistent language code.
var translatedValue = langMap.Translate ("ABC"); // returns "Unknown Language: ABC"
EAIGetValueMap() Method
This method retrieves objects for the required Type-Direction mapping. The following information presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
EAIGetValueMap(type, direction [, unmappedKeyHandler])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
type |
Specifies the type of transformation map. |
direction |
A string specifying the direction of the message. The possible values are: "Siebel Inbound" "Siebel Outbound" |
unmappedKeyHandler |
Specifies the value to pass to the map for an unmapped key. Can be an empty string, null, a literal, or the name of a predefined function. |
Returns
An object you can use to access the EAI Value Maps.
Usage
Use this method at the beginning of a script function to retrieve objects for the required Type-Direction mapping. Then call the object’s Translate method to get the translation of a code from the map table as needed within the function.
Exception Handling Considerations
There are three categories of errors you might encounter in the data transformation area of your integration. These categories are:
Siebel errors. Errors signaled by the built-in facilities that execute a map; for example, run-time Siebel eScript errors, business service invocation errors, BusComp errors, and errors in the data transformation functions.
Siebel errors are fatal, terminating execution of the map immediately.
The business service returns an error code other than OK. No specific error code is guaranteed, and they are not intended for workflow branching. Workflow processes can branch on the indication of an error occurrence, but not on a specific code.
The CSSService error stack will contain useful error information. In particular, data transformation function errors will generate error stacks describing the particular error.
User errors. Errors signaled in custom maps using the EAIRaiseErrorCode call. These are similar to Siebel Framework errors, except that the map developer selects the error code and uses them for workflow branching.
User errors are fatal, terminating execution of the map immediately.
The service returns the error code specified in the call to EAIRaiseErrorCode. Your workflow can branch on this code.
Available error codes are those in the Workflow generic error set.
You specify the entire error text for these generic errors in the call to EAIRaiseErrorCode.
You can use the function EAIRaiseError to raise an error without specifying a particular error code.
Map status flags. The map developer can use the SetArgument method to set custom status information in the output property set. For example, you can use the SetArgument method to indicate that a required field is missing. This can be used for workflow branching, if desired. This mechanism is independent of calls made to EAIRaiseError.
Error Codes and Error Symbols
All errors each have an error code, which is a unique integer. A subset of errors also each have an error symbol. An error symbol is a text string that allows you to reference specific error codes in Siebel Workflow and in Siebel eScript. Errors that do not have an error symbol cannot be used for branch decisions and cannot be raised as user errors.
Error codes returned by a data transformation service may or may not have an associated error symbol. User errors will have error symbols. Currently, errors generated by Data Transformation Functions have error symbols. Errors occurring outside the data transformation framework often will not have error symbols.
Data Transformation Error Processing
This section describes how the Data Transformation Functions handle errors, and how the high-level error code returned by the data transformation business service invocation is determined.
Framework errors occurring outside the Data Transformation Context. These errors are passed through without change to the CSSService script invocation mechanism. That mechanism takes control and returns an error of its choice. For example, if your map invokes a BusComp and the BusComp signals an error, an exception is thrown that will be ignored by the Data Mapping Engine but passed to the CSSService script invocation mechanism, which sets up the error state and returns an error from the business service invocation.
Framework errors generated by Data Transformation Functions. These are caught by an exception handler that sets up the state in the output PropertySet and passes control to the CSSEAIDTEScriptService class. CSSEAIDTEScriptService sets the error code on the business service as in the state, transforming error symbols to error codes in the process. Error symbols are specific to the failure.
User errors. These are processed the same way as errors generated by the Data Transformation Functions, except that you specify the error symbols and error text in your maps.
Exception Handling Functions
When writing your data transformation scripts, you can use the following functions to handle error conditions:
EAIRaiseError
EAIRaiseErrorCode
EAIFormatMessage
EAIRaiseError() Method
This method raises a fatal error and terminates the script. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
EAIRaiseError(msg [, formatParameters])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
msg |
Error message text from the Data Mapping Engine. |
formatParameters |
Optional string arguments inserted in the return value in the positions specified by the positional arguments in the msg parameter. A maximum of nine format parameters are allowed. |
Usage
You can provide format parameters to format the message text. For details, see EAIFormatMessage() Method.
EAIRaiseErrorCode() Method
This method raises a fatal error, terminates the script, and returns an error symbol that it receives from the business service.
Syntax
EAIRaiseErrorCode(errorSymbol, msg)
Usage
You can use this function when you want to pass an error symbol to a workflow as an indication to branch on an exception. If you are not branching on the specific error code in your workflow, use EAIRaiseError instead.
EAIFormatMessage() Method
This method formats strings that have position-independent arguments. The following table presents the parameters for this method.
Syntax
EAIFormatMessage(msg [, formatParameters])
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
msg |
A string that contains positional arguments. The substitution operation replaces the percent sign followed by a digit with the corresponding format parameter. |
formatParameters |
Optional string arguments inserted in the return value in the positions specified by the positional arguments in the msg parameter. A maximum of nine format parameters are allowed. |
Returns
A string of the formatParameters argument values in the positions specified by the positional arguments included in the msg parameter.
Usage
You can use this function to generate messages from strings that are translated and whose positions have changed as a result of the translation.
Example
EAIFormatMessage("Data: '%2', '%3', '%1'", "A", "B", "C")
returns the string:
"Data: 'B', 'C', 'A'"
Sample Siebel eScript
This section provides a sample Siebel eScript map for transforming data from a Siebel Account to SAP to retrieve an order list. The map is used to convert between Oracle’s Siebel Account object and the equivalent SAP R/3 objects.
function GetSAPOrderStatus_SiebelToBAPI (inputMsg, outputMsg)
{
/* Input Objects' Integration Components:
* Order Object (Order - Get SAP Order Status (Siebel))
* Order
*
* Output Object's Integration Components:
* BAPI Import (Order - Get SAP Order Status (BAPI Input))
* Import Parameters
*/
/*
* Set up EAI Lookup objects
*/
/*
* Set up EAI Input Message objects
*/
var iOrderObj; // Siebel Order instance
var iOrderComp; // Order
/*
* Set up EAI Output Message objects
*/
var oGSObj; // BAPI instance
var oGSImportComp; // Import Parameters
/*
* Find and create high-level integration object
*/
iOrderObj = inputMsg.GetIntObj ("Order - Get SAP Order Status
(Siebel)");
oGSObj = outputMsg.CreateIntObj ("Order - Get SAP Order
Status
(BAPI Input)");
/*
* Read int object instances from EAI message
*/
while (iOrderObj.NextInstance ())
{
/*
* Create "Get Status" object
*/
oGSObj.NewInstance ();
/*
* Read "Order" component
*/
iOrderComp = iOrderObj.GetPrimaryIntComp ("Order");
oGSImportComp = oGSObj.CreatePrimaryIntComp
("Import Parameters");
if (iOrderComp.NextRecord ())
{
/*
* Write "Import Parameters" component
*/
oGSImportComp.NewRecord ();
oGSImportComp.SetCopySource (iOrderComp);
oGSImportComp.CopyFieldValue ("SALESDOCUMENT",
"Integration Id");
}
}
}