2Overview of Support for XML in Siebel Business Applications
Overview of Support for XML in Siebel Business Applications
This chapter provides an overview of support for Extensible Markup Language (XML) in Siebel Business Applications. It includes the following topics:
About XML
XML is the industry standard for precisely representing data from virtually any source, stored in virtually any format. In appearance, it is similar to HTML, but while HTML explains a document in terms of how it should display data in a Web browser, XML is the data (or more precisely, the data from an application represented as XML).
This data can be from an application screen, sometimes called a screen scraping, it can be the output from a database, or it can be an application executed using processing instructions that run Oracle’s Siebel eScript, for example.
There are also technologies that explain XML documents. These are known as metadata because the data within these documents is used to describe and format the information in an XML document. Examples of metadata documents include XSDs (XML Schema Definitions), DTDs (Document Type Definitions), and XDRs (XML Data Reduced), which are supported by Siebel Business Applications.
Siebel CRM Integration and XML
Siebel Business Applications support for XML allows you to communicate with any Siebel application or external application that can read and write XML (either arbitrary XML or Siebel XML, also known as the Siebel Message format).
XML documents are delivered directly to and from Siebel Business Applications, or through middleware using any of the supported transports: HTTP, IBM WebSphere MQ, File, and so on. XML communicated in this way can query the Siebel Database, upsert (update or insert) data, synchronize the two systems, delete data, or execute a workflow process.
Objects from various systems, such as Siebel business objects and Oracle application data, can be represented as Siebel integration objects.
Siebel CRM can also communicate bidirectionally with Web services using Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP), and Representational State Transfer (REST) through Siebel Application Integration (SAI) for Oracle Fusion Middleware. For details, see Integration Platform Technologies: Siebel Enterprise Application Integration and Siebel Application Integration for Oracle Fusion Middleware Guide.
Unable to create the Business Service ‘EAI XML Converter.’ The XML parser is included by default in the full installation.
XML Integration Objects
The Integration Object type of XML is available within Siebel Business Applications to represent externally defined XML documents, where the object’s XML representation is compliant with the XSD or DTD supplied by your trading partner or external system. This type of integration object supports a representation of XML documents.
Bidirectional Data Flow
The following shows the bidirectional progress of XML documents into and out of Siebel Business Applications.
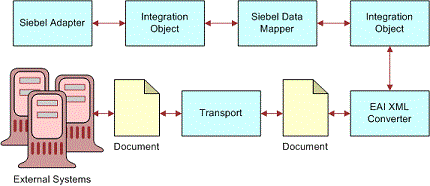
Metadata Support for XML
For sending and receiving information for Siebel Objects in an XML format between Oracle and external systems, Oracle supports the metadata representations for XML known as XSDs (XML Schema Definitions), DTDs (Document Type Definitions), and XDRs (XML Data Reduced, a Microsoft specification). Support for XSDs and DTDs gives you a way to communicate with external systems using externally defined XML documents, instead of having to use the Siebel XSD and DTD format.
The Siebel application includes a Schema Generator wizard to assist in the creation of XML Integration Objects, using an externally defined XSD or DTD. The XSD and DTD are used to map data between the Siebel application and an external integration object, and to transform data, as needed. These tasks are conducted using the Siebel Data Mapper.
Special Characters in XML Documents
Special characters should be represented in accordance with XML standards for those characters in order for them to be correctly interpreted within Siebel Business Applications. Also, specify the character set you are using if it is not UTF-8 (the default).
Special (Escape) Characters
The EAI XML Converter can handle special characters for inbound and outbound XML, as shown in the following. Non-Siebel XML should already handle special characters before integrating into the Siebel application. Special characters are indicated by enclosing the text for the character between an ampersand (&) and a semicolon (;). Also, if the XML is passed in a URL, then URL encoding of special characters is required as shown in the following table.
Table XML Escape Characters (Character Entities)
| Character | Entity | URL Encoded |
|---|---|---|
< |
< |
%26lt%3B |
> |
> |
%26gt%3B |
& |
& |
%26amp%3B |
“ |
" |
%26quot%3B |
' |
' |
%26apos%3B |
Unicode Character (Decimal) |
	 |
%26%2309%3B |
Unicode Character (Hex) |
° |
%26%23x00B0%3B |
Date |
Must follow the ISO 8601 format |
Not applicable |
Declaring the Character Set in Use
You must include the following parameter in the XML version declaration of your XML, XSD, or DTD document to declare the character set in use, if it is not the default of UTF-8:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="US-ASCII"?>
Supported character sets include but are not limited to ASCII, UTF-8, UTF-16 (Big or Small Endian), UCS4 (Big or Small Endian), EBCDIC code pages IBM037 and IBM1140 encodings, ISO-8859-1, and Windows-1252. This means that the XML parser can parse input XML files in these encodings.
The following encodings can be used in the XML declaration:
US-ASCII
UTF-8
ISO-10646-UCS-4
ebcdic-cp-us
ibm1140
ISO-8859-1
windows-1252
The character set declaration encoding must appear after the version declaration. For example: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="US-ASCII"?>
The output can be in one of the following XML encodings:
UTF-8
UTF-16
Local Code Page