3XML Representation of Property Sets
XML Representation of Property Sets
This chapter discusses the XML representation of property sets and the mapping between property sets and XML. It also discusses the elements and attributes naming conversion performed by the XML Converter. It includes the following topics:
Mapping Between Property Sets and XML
An arbitrary property set hierarchy can be serialized to XML and an XML document can be converted to a property set hierarchy using the XML Converter business service. This service is used by the Business Service Simulator screen to save property set inputs and outputs to a file from eScript.
Each part of a property set object has a corresponding XML construct. The following table shows the mappings between parts of a property set hierarchy and their XML representation.
Table Property Set to XML Mappings
| Property Set Component | XML Representation |
|---|---|
PropertySet |
Element |
PropertySet Type |
Element name (if Type is not specified, then the element name is set to PropertySet) |
PropertySet Value |
Element Character Data |
Property name |
Attribute name |
Property value |
Attribute value |
Child Property Set |
Child element |
Element and Attribute Naming
The property set Type (which maps to an XML element name) and the names of individual properties (which map to XML attribute names) do not necessarily follow the XML naming rules. For example, a name can include characters such as a space, a quote, a colon, a left parenthesis, or a right parenthesis that are not allowed in XML element or XML attribute names. As a result, you must perform some conversion to generate a valid XML document.
When creating an XML document from a property set hierarchy, the XML Converter will make sure that legal XML names are generated. There are two different approaches provided to handle name translation. The approach is determined by the EscapeNames user property on the XML Converter service. This user property can be either True or False.
True. If EscapeNames is True, instances of illegal characters are converted to an escape sequence that uses only legal characters. For example, a space is converted to the characters _spc. When an XML document is parsed to a property set hierarchy, the escape sequences are converted back to the original characters. For example, the name Account (SSE) becomes Account_spc_lprSSE_rpr.
The following table shows the escape sequences that are used by the XML Converter.
Table XML Converter Escape Sequences
Character in Property Set Description Generated Escape Sequence Space
_spc
_
Underscore
_und
“
Double Quote
_dqt
‘
Single Quote
_sqt
:
Colon
_cln
;
Semicolon
_scn
(
Left Parenthesis
_lpr
)
Right Parenthesis
_rpr
&
Ampersand
_amp
,
Comma
_cma
#
Pound symbol
_pnd
/
(Forward) slash
_slh
?
Question Mark
_qst
<
Less Than
_lst
>
Greater Than
_grt
Illegal characters
Other illegal characters not listed in this table
_<Unicode character code>
False. If EscapeNames is False, the XML Converter removes illegal characters. These characters include the space ( ), double quote ("), single quote('), semicolon (;), left parenthesis ((), right parenthesis ()), and ampersand (&). For example, the XML Converter changes the name Account (SSE) to AccountSSE.
Note: These conversions are not reversible: the original names cannot be obtained from the XML names.
If a property set instance does not have a value for its Type member variable, the XML Converter uses the name PropertySet for the corresponding element’s name.
Property Set Examples and Their XML Representation
The following is examples of different types of property sets that are available and their XML representation:
An Arbitrary Property Set
<?Siebel-Property-Set> <PropertySet> <Person> Jack </Person> </PropertySet>
<?Siebel-Property-Set EscapeNames="true"><PropertySet><SiebelMessage MessageID="1- 111" IntObjectFormat="Siebel Hierarchical" MessageType="Integration Object" IntObjName="Sample Account"><ListOfSample_spcAccount>...</ ListOfSample_spcAccount></SiebelMessage></PropertySet>
<?Siebel-Property-Set><PropertySet><_XMLHierarchy><Account><Contact>...</ Contact></Account><_XMLHierarchy></PropertySet>
The following illustrates an example property set hierarchy and the XML that would be generated for each component of the hierarchy. The XML was generated with the EscapeNames user property set to True.
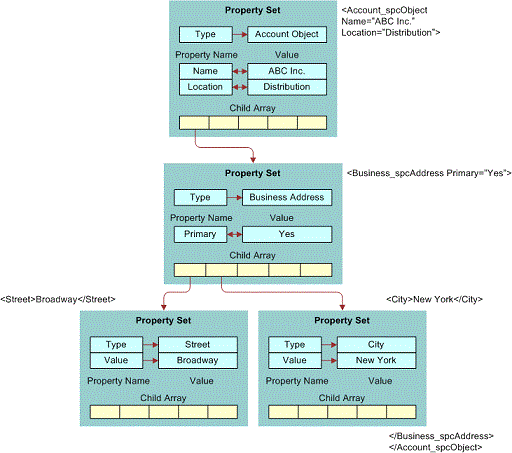
Properly Formatted Property Sets
Property sets are used internally to represent Siebel EAI data. A property set is a logical memory structure that is used to pass the data between business services.
To benefit from using the XML Converter, be sure that any code you use, such as eScript or Siebel VB, correctly represents property sets within Siebel Business Applications for the XML Converter Business Service. This includes necessary arguments and values. An example of such code is:
Set Inputs = TheApplication.NewPropertySet
REM Fill in Siebel Message Header
Inputs.SetType "SiebelMessage"
Inputs.SetProperty "MessageId", ""
Inputs.SetProperty "MessageType", "Integration Object"
Inputs.SetProperty "IntObjectName", "Sample Account"
Set svc = theApplication.GetService("EAI XML Converter")
Set XMLInputs = theApplication.NewPropertySet
Set XMLOutputs = theApplication.NewPropertySet
XMLInputs.AddChild Inputs
svc.InvokeMethod "PropSetToXML", XMLInputs, XMLOutputs