3Signals
Signals
In earlier releases, Siebel order management functions and function calls were handled locally by the code in the calling object or business component. In this release, every interaction between C/OM components occurs through an API invocation that you can configure or redirect. These API invocations are called signals. A signal is a request to perform a business function.
Each API invocation supports a configurable set of input arguments. The API is handled by a series of business service methods and workflows that you define using the Administration - Order Management screen, then the Signals view.
This chapter includes the following topics:
About the Signals Mechanism
Within Siebel order management, you use the Signals mechanism to invoke configurable business logic. Signals are used to hold together all the C/OM services, and they are used to call external services. You configure signals in the run-time client.
Nearly all buttons and engines within Siebel order management invoke business logic by raising a signal. The business logic invoked comes in the form of one or more business service methods or workflows.
Signals are versioned objects. The numbering assigned to a signal version means that a new version of a signal can be developed while you are using the current version in the same production environment.
A signal action property specifies the business service or workflow to invoke when the signal is raised. Signal action parameters are the input arguments to signal action workflows or business service methods.
Components of the Signals Mechanism
The following figure shows how a signal created using the Administration - Order Management screen, then the Signals view is routed through a signal dispatcher to invoke a business service method or workflow.
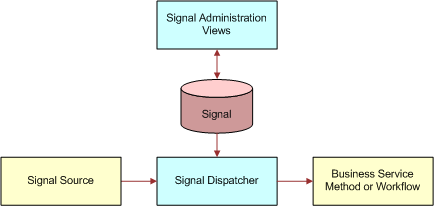
Signals Administration
Administer signals using the Administration - Order Management screen, then the Signals view. Use the Signals view for creating new signals, working with existing signals, and releasing signals into production. In the Versions list applet, click the Work Space hyperlink to access the Actions and Properties tabs, and the Parameters list applet, for the selected signal.
Signal Dispatcher
Signals are dispatched by the Context Service business service. The Context Service business service reads and caches signal definitions, and then when a business component raises the signal, Context Service executes the appropriate business service or workflow.
For more information about the Context Service business service, see Variable Maps and Context Service Business Service.
Signal Sources
All applications supported by the Siebel order management infrastructure can be sources of signals. A signal can be invoked by any C/OM business component. Signals are not supported on non-C/OM business components.
Signals are invoked through the standard InvokeMethod call. If the method is not handled by logic or script on the source business component, then the signal dispatcher (Context Service business service) is invoked to handle the signal.
Signal Actions
A signal action can be either a business service method or a workflow. By setting the Service Type field using the Administration - Order Management screen, Signals, and then the Actions view, you define whether the action is a business service method or a workflow.
Creating Signal Actions
You create and modify signal actions in the Signals view. You can set the sequence for a group of actions, set input arguments for actions, and set filter values that determine when an action executes. Use the following procedure to create and modify signal actions.
The Signals view lists and describes all the standard signals that are available in your Siebel Business Application. The following table lists some of the signals that are relevant to order management and pricing administration.
| Signal Name | Description |
|---|---|
ApproveItem |
Invoked by clicking Generate Approvals in quote, order, and agreement views. Reprices and then generates approval requests for the current line item. |
CalculatePriceAndCheckEligibility |
Invoked by Add Item and Verify. Performs Pricing and Eligibility on selected rows. |
CalculatePrice |
Invoked by clicking Reprice or selecting a product for a line item. Establishes context, calls the pricing procedure, and then synchronizes any updates back to the database. |
CalculatePriceAll |
Invoked by clicking Reprice All. Establishes context, calls the pricing procedure, and then synchronizes any updates back to the database. |
CalculatePriceExternal |
This signal is called when a user calls the method CalculatePriceExternal for the Pricing Manager business service; it is used to calculate the price of a product externally. |
CalculatePrice_eSales |
Invoked by clicking Reprice in Siebel eSales. Establishes context, calls the pricing procedure, and then synchronizes any updates back to the database. |
CalculatePriceAll_eSales |
Invoked by clicking Reprice All in Siebel eSales. Establishes context, calls the pricing procedure, and then synchronizes any updates back to the database. |
CalculatePrice_Configurator |
Invoked by clicking Reprice in Siebel Configurator. Establishes context, calls the pricing procedure, and then synchronizes any updates back to the CP instance. |
CheckEligibility |
Invoked by the Verify Eligibility Status menu item on the line items applet. Executes the eligibility procedure for the current line item. |
CheckEligibilityAll |
Not invoked out-of-the-box. Executes the eligibility procedure for all line items. |
CopyOrder |
Invoked when copying Order records. |
CopyQuote |
Invoked when copying Quote records. |
Get Config Item Price |
Called when the user calls the GetConfigItemPrice method of the Pricing Manager business service; it is used to get the price of a configurable item externally. |
Get Product List Price |
Called when the user calls the GetProductListPrice method of the Pricing Manager business service; it is used to get the product list price of the product, as well as other price list field values (for example, MSRP Price and Cost). |
GetUserProdPrice |
Calculates the list price and net price for a list of products using the login user profile as context. |
MergeIntoOnePackage |
Invoked by the Package menu item in quote, order, and agreement views. Calls the ISS Package Product Service to combine the selected line items into a package; it then reprices the package. |
OrderTemplate |
Invoked by clicking Add Items in the Catalog or Favorites list applet. Calls the ISS Template Service to copy line items from favorites in to the shopping cart. |
OrderTemplateCopy |
Invoked by the ISS Template Service to copy template line items to the current order. |
OrderTemplateSelectItems |
Invoked by the ISS Template Service to copy template line items from the available product applet to the current order. |
Product Recommendation Signal |
Invoked by a product selection or by a current line item change. Calls the Product Recommendation Driver Workflow to generate and display product recommendation messages. |
QuotesAndOrdersValidate |
Invoked by clicking the Verify button on a Header or Line Item. On Header: runs Pricing and Eligibility, verifies promotions, validates data rules, and validates CP. On Line Item: checks eligibility and validates CP. |
QuoteTemplateCopy |
Invoked by the ISS Template Service to copy template line items to the current quote. |
QuoteTemplateSelectItems |
Invoked by the ISS Template Service to copy template line items from the available product applet to the current quote. |
SetFieldValue |
Invoked whenever a field value changes in the quote, order or agreement header, or line items. Triggers various processing depending on the field changed. |
SpreadDiscount |
Invoked by clicking Spread in the spread discount pop-up applet. Calls the Spread Discount Driver Workflow Process to query the selected line items and spread the specified discount. |
SpreadDiscount - All |
Invoked by clicking Spread in the spread discount pop-up applet when Type is set to All. Calls the Spread Discount Driver Workflow Process to query all the line items and spread the specified discount. |
VerifyItem |
Invoked by clicking the Verify button or menu item in quotes, orders or agreements. Calls workflows to reprice and check eligibility. Then calls the FINS Validator business service to execute validation rules. |
To create and modify signal actions
Navigate to the Administration - Order Management screen, then the Signals view.
In the Signals list applet, select an existing signal to modify, or create a new signal record.
Lock the signal by checking the Locked Flag box.
This locks the object for your user ID.
If you are creating a new signal, give it a name and description, and then save the record.
In the Versions list applet, click the Work Space link to drill down to the Actions list applet.
In the Actions list applet, create a new action, or select an existing signal action.
Complete the fields.
Set the Sequence field value to reflect the sequence number of a particular action relative to other actions for the signal.
Set the Service Type field to specify whether the action is a business service method or a workflow:
If you specified that the signal action is a workflow, enter the workflow’s name in the Service Name field and enter “RunProcess” in the Service Method field.
If you specified that the signal action is a business service method, enter the business service name in the Service Name field and enter the method name in the Service Method field.
(Optional) Set filter fields for the action as described in the table that follows.
Filter fields limit the execution of a signal action. The action occurs only if all filter field values specified match the current situation.
Filter Field Allowed Values Description Application Name
Any “Application” repository object name
Used to define industry-specific or channel-specific logic.
Mode
Any string from the ISS_MODE LOV
Must match the value of the Mode user property on the business component (such as Quote, Order, Asset or Agreement).
Instance Type
Any string from the ISS_INSTANCE_TYPE LOV
Must match the integration component name from the integration object specified in the business component “Instance Uniform Name EAI Object:[Current Business Object]” user property, for example, “Header”, “Line Item”, or “Payments”.
Fields
A semi-colon-separated list of field names (example: “Account; Product; Net Price”)
The business component fields for which the action is executed. The action occurs if the active field in the calling business component appears in the list.
Condition
A Siebel logical expression that returns TRUE or FALSE.
If the condition is not empty, the action is only invoked when the condition returns TRUE.
(Optional) In the Parameters list applet (at the end), enter input arguments for the action.
As an example, parameters for the CalculatePrice signal are listed in the following table:
Input Argument Example Value CPScope
Whole
RowScope
Selected
SubPSPWFName
Pricing Procedure - Default
Variable Map - Context
Default Pricing Variable Map - Context
Variable Map - Row Set
Default Pricing Variable Map - Row Set
(Optional) You can specify a CanInvoke check by completing the fields in the Properties list applet. See Modifying Signal Properties for Signal Actions.
Navigate back to the Signals list applet.
Click the Release New Version button to release the signal version.
If you are creating a new signal action, create a button, script or workflow to invoke the signal. See Invoking Signals from Controls and Custom Script.
Test the signal.
You test the signal by triggering the appropriate event.
Note: After releasing a new version, you must start a new user session (by logging out and logging in again) to test the latest version.Using Application Deployment Manager (ADM), promote the updated signal definition to the production environment. For information about using ADM, see Siebel Application Deployment Manager Guide.
Modifying Signal Properties for Signal Actions
Signal properties are similar to user properties on repository objects. Signal properties are name-value pairs used to configure processing. In this release, the only supported use of signal properties is to provide a CanInvoke check.
To modify signal properties for a Can Invoke check
(Optional) You can specify a CanInvoke check by completing the fields in the Properties list applet as follows:
Name. CanInvoke:[Mode]
Value. A Boolean expression using one of the following:
Business component fields. The expression can be comprised of real business fields or pseudo business fields supported by Context Service. Allowed fields include the following:
Field Comment [$IsNewRecordPending]
None
[$HasActiveRow]
None
[$IsInQueryMode]
None
[$CanUpdate]
Returns ‘Y’ or ‘N’
[$GetType]
Returns instance type such as ‘Line Item’, ‘Header’, ‘XA’
Profile attributes. As an example, the following table shows a properties setting for the SetFieldValue signal:
Property Example Attributes CanInvoke:Any
GetProfileAttr('Block Variable Map Operations')='N' OR GetProfileAttr('Block Variable Map Operations') IS NULL
Example of Signal Properties Settings for a Can Invoke Check
An example of the fields set for a CanInvoke check is listed in the following table.
| Name | Value |
|---|---|
CanInvoke:Any |
[Account Id] is not null |
CanInvoke:Quote |
[Status] = LookupValue('ORDER_STATUS', 'Open') |
[Status] = LookupValue('ORDER_STATUS', 'Open') instead of [Account Id] is not null.
Invoking Signals from Controls and Custom Script
Siebel order management business components route unrecognized InvokeMethod calls to the Context Service business service’s RaiseSignal method. All business components of class CSSBCOrderMgmtBase, CSSBCPecBase, and their subclasses, support this routing.
You can invoke signals from controls, such as buttons. You can also invoke signals from a script.
Invoking Signals from a Button
Use the following procedure to invoke signals from a button.
To invoke a signal from a button
In Web Tools, create or open a workspace and then navigate to Object Explorer.
To use the workspace dashboard, see Using Siebel Tools.
Click Applet and then locate the applet you must modify.
Expand the applet list in Object Explorer and click Control.
Set the MethodInvoked property of the control to the signal name.
Save your changes using the gear icon and submit the workspace for delivery.
Invoking Signals from a Script
Use the following procedure to invoke signals from a script.
To invoke a signal from a script
Access the Siebel Script Editor in Siebel Tools by selecting the affected object in the Object Explorer.
Right-click the object, and choose Edit Scripts.
Modify the script to execute the InvokeMethod method on the appropriate C/OM business component, passing the signal name as the MethodName input argument.
For example:
pQuoteBC.InvokeMethod("Calculate Tax");
Using Recursion with Signals
Recursion of signals is supported, but you cannot use recursive variable map APIs such as GetRowSet and SyncRowSet in recursed signals. If your recursive signal calls recursive variable map APIs, you will receive an error message. When this happens, you must revisit the definition of the signal and make modifications to make sure these variable map APIs are not involved (for example, you might remove GetRowSet and SyncRowSet, or instead add a CanInvoke method to skip the signal).
Recursive variable map APIs are not supported because these APIs read data from, or write data to, the database. This kind of recursive read and write is not safe.
For details on how to use signal properties and profile attributes when making sure your recursion works properly with signals, see Modifying Signal Properties for Signal Actions.
Migrating Signals Between Environments
Signals can be moved between environments, such as from the development environment to the test environment, by using the Application Deployment Manager (ADM). For information about using ADM, see Siebel Application Deployment Manager Guide.
You can also export a specific version of a signal using the Export Version applet menu in the Signal Version list applet. To import a signal, navigate to the Administration - Products screen, then the Joint Workspace view. This is a joint workspace for all types of versioned objects (signals, variable maps, products, product attributes, and so on). For more information about import and export, see Siebel Product Administration Guide.