Schedule Assessment Thresholds Pane
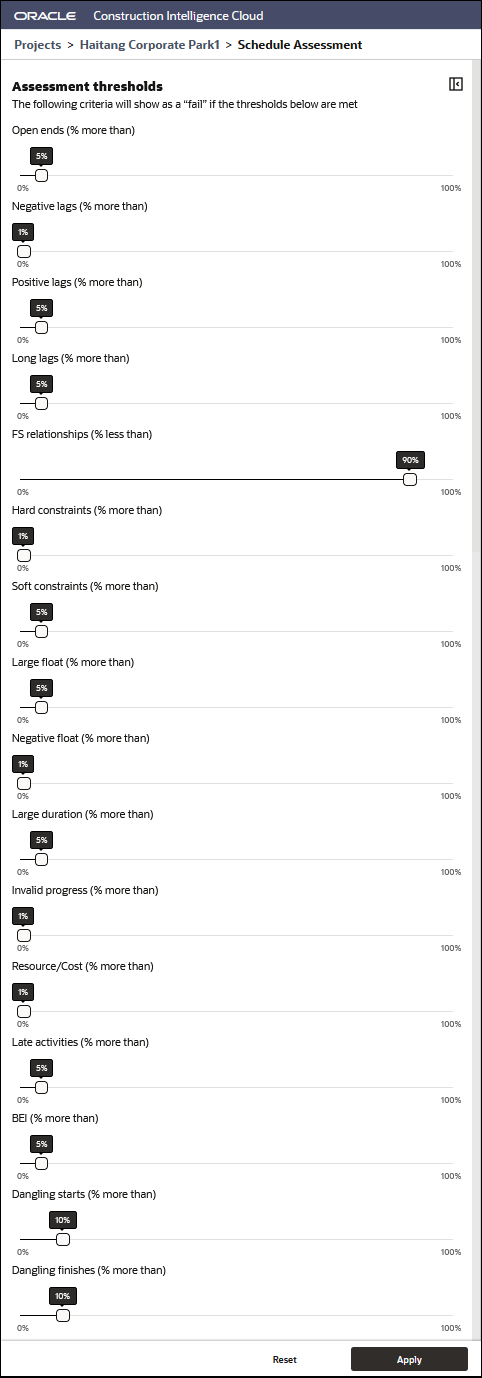
The following metrics are displayed:
- Baseline Execution Index (BEI): This metric determines how many activities are behind or ahead of schedule against the baseline.
- Dangling starts: A start date for an activity that is not tied to another activity. It implies that the activity can start indefinitely earlier without impacting any preceding activities.
- Dangling finishes: A finish date for an activity that is not tied to another activity. It implies that the activity can finish indefinitely later without impacting any successive activities.
- Finish to Start relationships: This metric identifies incomplete tasks containing each relationship type. Since Finish-to-Start (FS) relationship is the most logical, it should account for at least 90% of the relationship types being used. The check counts uses the number of Start-to-Start (SS), Finish-to-Finish (FF) and Start-to-Finish (SF) relationship types to work out the % of Finish-to-Start (FS) relationship types.
It is calculated as: % of FS Relationship Types = (number of logic links with FS Relationships / number of logic links) x 100
- Hard constraints: This metric counts the number of hard constraints used in the incomplete tasks. Hard constraints may prevent the schedule from being logic-driven and should be used sparingly. The number of tasks with hard constraints shouldn't exceed 5%.
It is calculated as: Hard Constraint % = (Total number of incomplete tasks with hard constraints / Total number of incomplete tasks) x 100
- Invalid progress: This metric looks at incomplete tasks that have no actual dates in the future beyond the status date and no forecast dates in the past before the status date. There should not be any invalid dates in the schedule.
- Large duration: This metric looks at incomplete tasks that have a baseline duration greater than 44 working days and a baseline start date within the detail planning period or rolling wave. This helps to determine whether you can break a task into two or more tasks or leave it as a single task. The number of tasks with the higher duration should not exceed 5%.
It is calculated as: High Duration % = (Total # of incomplete tasks with high duration / Total # of incomplete tasks) x 100
- Large float: This metric counts incomplete tasks with a total float greater than 44 working days. This may indicate missing predecessors / successors.
It is calculated as: High Float % = (Total # of incomplete tasks with high float / Total # of incomplete tasks) x 100.
- Late activities: This metric identifies tasks that have finished late compared to the baseline. It helps to identify how well the schedule is meeting the baseline plan and is a good check to gauge whether the project will finish on time.
It is calculated as: Missed % = (# of tasks with actual/forecast finish date past baseline date / # of tasks with baseline finish dates on or before status date) x 100.
- Long Lags: Relationships with a lag duration greater than 352 hours.
- Negative float: This metric counts incomplete tasks with total float less than 0 working days. These tasks should have an explanation and corrective action plan.
It is calculated as: Negative Float % = (Total # of incomplete tasks with negative float / Total # of incomplete tasks) x 100.
- Negative lags: This metric identifies incomplete tasks that have logic links with leads (negative lag) in predecessor relationships. Ideally, there should not be any leads as they distort total float.
It is calculated as: Leads % = (number of logic links with leads / number of logic links) x 100
- Open ends: The number of tasks without predecessors and/or successors. It should not exceed 5% of the total activities.
It is calculated as: (number of tasks with missing logic / number of incomplete tasks) x 100
- Positive lags: The number of activities with a lag as a predecessor should not be more than 5% of the total activities.
- Resource / Cost: This metric reports on all tasks that have a duration greater than zero and have currency or hours assigned. Some projects may not have resources loaded directly into the schedule. If they are loaded into the schedule, then this metric uses the following formula to identify missing resources:
Missing Resource % = (Total # of incomplete tasks with missing resource / Total # of incomplete tasks) x 100.
- Soft constraints: Constraints that do not prevent activities being moved. It should be less than 5%.
Related Topics
Assessment Criteria for Your Project
Comparing Your Project Metrics
Last Published Tuesday, December 24, 2024