
Control is a measure taken to mitigate a regulatory reporting risk. Control measures help an organization to avoid risks that may otherwise hamper a business due to inconsistency in reporting. Controls are defined to ensure that the data elements used for various business processes are accurate in value and obtained in time.
Topics:
· Control Creation through Batches
The controls identified for risk mitigation can be recorded and stored in a repository. This section helps in capturing Controls, and also assesses their effectiveness in avoiding the risks of reporting.
Control effectiveness establishes the confidence factor in data elements and their values.
· Quality Controls: They are used to assess data accuracy.
Controls are defined on data elements based on the defined DQ rules. The effectiveness of these controls can be automatically assessed based on the DQ execution facts.
NOTE:
To view an issue and create an action, the user must be mapped to the following issue and action groups ACTNANLST, ISSUEADMN, ISSUEANLST, ISSASR, ACTASR, ACTVIEWER, ISSAPR in addition to other Control related groups.
The following are the types of Data Quality Checks and their definitions:
Table 5: Data Quality Checks
Data Quality Check |
Definition |
Blank Value Check |
Identifies if the base column is empty considering the blank space. |
Column Reference/Specific Value Check |
Compares the base column data with another column of the base table or with a specified direct value by using a list of pre-defined operators. |
Data Length Check |
Checks for the length of the base column data by using a minimum and maximum value, and identifies if it falls outside the specified range |
Duplicate Check |
Is used when a combination of the column is unique and identifies all duplicate data of a base table in terms of the columns selected for the duplicate check |
List of Value Check |
It can be used to verify values where a dimension/master table is not present. This check identifies if the base column data does not match with a value or specified code in a list of values. |
NULL Value Check |
Identifies if ‘NULL’ is specified in the base column. |
Referential Integrity Check |
Identifies all the base column data that has not been referenced by the selected column of the referenced table. Here, the user specifies the reference table and columns. |
Range Check |
Identifies if the base column data falls outside a specified range of a Minimum and Maximum value. |
The controls are specific to reports. The DQs are defined in the DQ_CHECK_MASTER and DQ_GROUP_MAPPING tables.
NOTE:
The DQ rules are defined based on the Stage Table and Column mapped to a particular report.
All the users are required to be mapped to DGSAUTHGRP, DGSADMINGRP, and DGSANALYSTGRP groups along with their respective individual groups.
The following is the user role for control viewer:
· Control Viewer: This allows the user to view an issue and create an action.
Perform the following steps to create a Control through Batches:
1. For control creation, the FSI_DGS_CONFIGURATION table has to be seeded first.
NOTE:
In the N_LOOKUP_VALUE column, you can modify the values in the CREATOR and the OWNER fields.
Figure 24: Control Creation through Batches

2. Execute the batch DGS_DQ_CTL_BATCH, this batch contains the entire task that needs to be executed for control. See the OFS Data Governance Run Chart.
Pre-Requisites
· For performing Control Assessment, the Control Execution Details must be present.
· Execution Details can be DQ or User Defined Parameters related.
· The DQ-related parameters are available by default if DQ executions are done for that control.
Generate Assessments
Execute the batch DGS_DQ_CTL_BATCH, this batch has the entire task, which needs to be executed for control. See the OFS Data Governance Run Chart.
To view the controls, follow these steps:
1. From Financial Services Data Governance for US Regulatory Reporting window navigate to Controls.
Figure 25: Controls

The Control summary window is displayed. After you execute the batch DGS_DQ_CTL_BATCH, the Control summary window displays the stage tables for which the controls are defined. It also displays the assessments and open issues if any.
Figure 26: Data Governance Controls

2. Select a stage
table and then click  View Controls to view the details.
View Controls to view the details.
3. For example, the stage table “Stage Investment” and control “Instrument Code in Stage Investments” is selected here.
Figure 27: Data Governance Controls – Stage investments

4. Click Properties, to view the control properties.
Figure 28: Data Governance Controls – Properties

The control information is displayed:
— Name: Name of the control
— Type: Type of the Control – Quality Control
— Methodology: Method used – OFSAA Method
— Financial Accuracy Check: Yes or No
— Owner: Name of the Owner
— Comments: Add comments if any
5. Click Data Quality, to view the DQ information on which the control is created.
Figure 29: Data Governance Controls – Data Quality

The DQ information is displayed:
— DQ Name: Name of the DQ contributing to the control
— DQ Weight: Weight of the DQ contributing to the control. In case there is one DQ the number is 100. If there are more than one the number is divided to make it 100.
— Attribute: Name of the attribute on the entity column where the DQ is defined.
— Entity: Name of the stage table name.
6. Click Assessments, to view the Control Assessments.
Figure 30: Data Governance Controls – Assessments

The control assessment information is displayed:
— Effectiveness Score: Control Assessment Score
— Effectiveness Rating: Control Assessment Rating. It can be Ineffective or Effective depending on the effectiveness score.
— Effectiveness Status: Control Assessment Status
— Execution Date: Assessment date and time
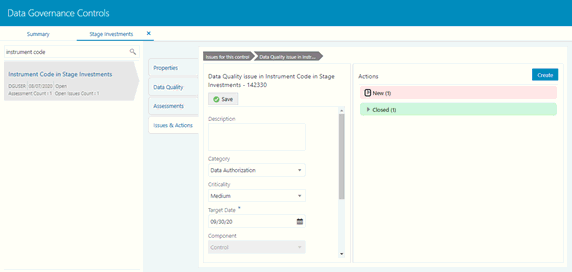
7. Click Issues & Actions to view the system-generated issues created for control. To edit a system-generated issue, see section Editing an Issue.
Figure 31: Data Governance Controls – Issues & Actions

To edit an issue, follow these steps:
1. From Financial Services Data Governance for US Regulatory Reporting window navigate to Controls.
2. Select a stage
table and then click  View Controls to view the details.
View Controls to view the details.
3. Click Issues & Actions. The system-generated issues for this control are displayed.
Figure 32: Data Governance Controls – Issues & Actions

4. Click the required issue to edit.
Figure 33: Data Governance Controls – Issues & Actions

5. Enter the Description.
6. Select the Category from the drop-down list:
§ Data Authorization
§ Data Privacy
§ Data Security
§ Data Accuracy
§ Data Availability
7. Select the Criticality:
§ High
§ Medium
§ Low
8. Choose the
Target Date from the Calendar
 .
.
9. Enter Comments if any.
10. Select a file or drag and drop a file to Attach a document.
11. Click Save. A confirmation message is displayed: Issue is saved successfully. This creates an issue for the particular action.
The Issue Owner creates the required Actions for the system-generated Issue. Additionally, the Issue Owner is the Data Adjustment Creator.
To create a new action for the system-generated Issue, follow these steps:
1. From the Financial Services Data Governance Studio window, navigate to Controls.
2. Select a stage
table and then click  View
Controls to view the details.
View
Controls to view the details.
3. Click Issues & Actions. The Issus for this control is displayed with the details.
Figure 34: Data Governance Controls – Issues & Actions

4. Click the required issue. The Actions pane is displayed.
Figure 35: Data Governance Controls – Actions
5. To create an action, in the Actions section click Create.
Figure 36: Data Governance Controls – New Actions
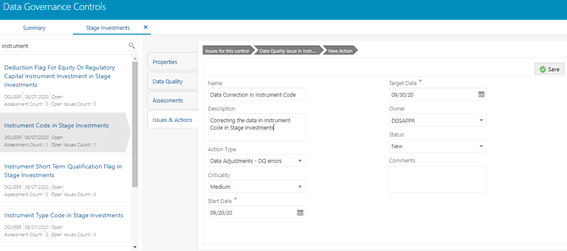
6. Enter the Name and Description.
7. Select the Action Type from the drop-down list:
a. Data Adjustments - DQ errors
b. Data Adjustments - Others
c. Data Adjustments - Regulatory Reporting
d. Reconciliation Adjustments
e. Others
8. Select the Criticality:
a. High
b. Medium
c. Low
9. Choose the
Start Date and Target Date from the Calendar  . Action
start and target date must be within the Issue target date.
. Action
start and target date must be within the Issue target date.
10. Select the action Owner name from the drop-down list.
11. Select the Status from the drop-down list:
a. New
b. InProgress
c. Closed
12. Enter Comments if any and click Save. A confirmation message is displayed: Action saved successfully. This creates an action for the particular issue.
NOTE:
Based on the Action Type, the Data Adjustment details page is displayed during the Data Adjustments process for DQ errors or any other errors.
13. Select a file or drag and drop a file to Attach a document.
14. When a new action is created, it is listed under the Actions section under New status of the Issue. In the Status field, the issue can be closed when it is resolved. It is then moved to Closed status.
Figure 37: Data Governance Controls – New Actions
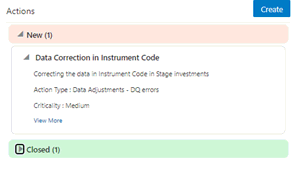
15. After an action
is created, it is possible to create Data Adjustments.
See section Data Adjustments
for details.
Data Quality checks are grouped under the following types:
· Data Quality Errors – Percentage of records that have failed the data quality checks.
· Data Quality Warning Flag - Percentage of records that have passed but have a warning flag.
· Data Quality Information Flags - Percentage of records that are passed but have an information flag.
· Defaults - Percentage of records that are defaulted.
Configure the following parameters in the DGS application to evaluate the Data Quality effectiveness:
· Threshold Score
· DQ Weight percentage
· Parameter Weight Percentage
Threshold Score
The threshold score is the value configured to compare with the computed Total Control Score to evaluate the effectiveness or ineffectiveness of the Data Quality control.
Table 6: Threshold Score
Sl No. |
Threshold Configuration |
Weight |
1 |
Threshold Score |
50 |
DQ Weight Percentage
This value is configured based on the number of data quality checks mapped to a data quality control. For example, if there are four data quality checks mapped, then the data quality weight percentage is as displayed as follows:
Table 7: DQ Weight Percentage
Sl No. |
Control ID |
Data Quality ID |
Weight |
1 |
865675 |
E1_STC_STLMT_DAT_01 |
25% |
E1_STC_STLMT_DAT_02 |
25% |
||
E1_STC_STLMT_DAT_03 |
25% |
||
E1_STC_STLMT_DAT_04 |
25% |
Parameter Weight Percentage
Data quality checks are tagged as Error/Warning/Information/Default and each of these is given a weightage. The values are configurable from the DGS application.
Table 8: Parameter Weight Percentage
Sl no. |
Data Quality Type |
Weight |
1 |
Data Quality Errors |
20 |
2 |
Data Quality Warning Flag |
30 |
3 |
Data Quality Information Flags |
25 |
4 |
Defaults |
25 |
Step 1.
Compute the DQ Failure Percentage for every single Data Quality in each Data Quality Type
DQ Failure - DQ1 Error = (Failed Record Count/Total Scan Record)*100
DQ Failure - DQ1 Warning = (Failed Record Count/Total Scan Record)*100
DQ Failure - DQ1 Information = (Failed Record Count/Total Scan Record)*100
DQ Failure - DQ1 Default = (Failed Record Count/Total Scan Record)*100
Step 2.
Compute the Cumulative Control Score
Control Score is the sum of DQ Failure * Parameter Weight for a DQ for each of the DQ Type multiplied into DQ Weight Parameter. Similarly, compute for each DQ is mapped to a DQ control. For Cumulative Control, Score adds Control Score for each DQ in a DQ control and then divides by 100.
Cumulative Control Score =
[[DQ1 Error * Parameter Weight] + [DQ1 Warning * Parameter Weight] +
[DQ1 Info * Parameter Weight] + [DQ1 Defaults * Parameter Weight] *
DQ1 weight] +
[[DQn Error * Parameter Weight] + [DQn Warning * Parameter Weight] +
[DQn Info * Parameter Weight] + [DQn Defaults * Parameter Weight] *
DQn weight]] / 100
Step 3.
For each Data Quality control, the Total Control Score is computed as:
Total Control Score = 100 minus (Cumulative Control Score)
If the Total Control Score is equal to or above the Threshold Score, then the control is effective, and if below the Threshold Score it is Ineffective.
Data Quality Control Evaluation with GL Recon Validation
In case GL Recon Application is installed and measure data quality checks have financial validation check set as ‘Y’ then effective or ineffective evaluation is as follows:
Table 9: Data Quality Control Evaluation with GL Recon Validation
Sl No. |
Data Quality Control Validation |
Status |
1 |
IF GL Recon is installed, all reconciliations are passed, and the Total Control score is equal to or above the configured threshold |
Control Effective |
2 |
IF GL Recon is installed, any reconciliations fail, and the Total Control score is above the configured threshold. |
Control Ineffective |
3 |
IF GL Recon is installed, all reconciliations are passed, and the Total Control score is below the configured threshold. |
Control Ineffective |
4 |
IF GL Recon is installed, any reconciliations fail, and the Total Control score is below the configured threshold. |
Control Ineffective |