S9 AF/pCSCF Topology Hiding is concerned with hiding the identities of a Protected Network's AF/pCSCFs, as well as the number of AF/pCSCFs in the network, when it exchanges messages with Untrusted Networks. An AF/pCSCF identity is embedded in the Origins-Host and Session-ID AVPs sent in Request messages and the Origin-Host AVP sent in Answer messages. This capability is associated with the Diameter Rx application message set.
S9 AF/pCSCF topology hiding is concerned with Rx messages when AF/pCSCF is deployed in proxy mode. If PCRF is deployed in client/server mode for Rx messages, then S9 AF/pCSCF TH Configuration Set should be enabled for the protected network. If S9 AF/pCSCF TH is enabled (for example, if vPCRF is proxying AF/pCSCF messages to hPCRF), then only AAR/STR and RAA/ASA have S9 PCRF TH applied.
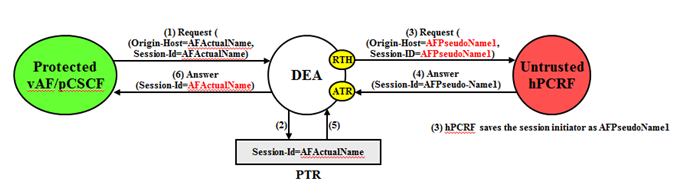
AF/pCSCF identities are hidden by replacing the actual host name portion of the Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs with AF/pCSCF pseudo-host name. The Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs may have different AF/pCSCF host names. A unique pseudo name must be created for each AF/pCSCF in a Protected Network. When the vAF/pCSCF initiates a transaction to the hPCRF, the hPCRF saves the vAF/pCSCF's identity for use in subsequent hPCRF-to-vAF/pCSCF transactions. This vAF/pCSCF's pseudo-host name must not only be unique, but the DEA must be able to convert the vAF/pCSCF's pseudo-name to an actual vAF/pCSCF host name for these subsequent hPCRF to vAF/pCSCF transactions.
To hide the number of AF/pCSCFs in a network, each AF/pCSCF is assigned either a random or fixed number of pseudo-host names (the maximum is defined by an S9 AF/pCSCF TH Configuration Set attribute called Maximum Pseudo-Host Names per AF/pCSCF). This procedure of creating randomized AF/pCSCF pseudo-host names and assigning them to actual pseudo-host names is performed by the GUI and used by DRL. The TH Host Names MO allows DRL to map a Protected-AF/pCSCF actual-host name to a set of AF/pCSCF pseudo-host names and map an AF/pCSCF pseudo-host name received from an Untrusted network to a Protected-AF/pCSCF actual-host name.
Protected-vAF/pCSCF to Untrusted-hPCRF Transactions
When AF/pCSCF and PCRF are in a Protected Network and AF/pCSCF uses vPCRF in proxy mode to communicate Rx messages initiated by vAF/pCSCF to hPCRF in Untrusted Network, then S9 AF/pCSCF TH is used to hide AF/pCSCF host names to Untrusted Network.
For Protected-vAF/pCSCF to Untrusted-hPCRF Rx Diameter transactions, S9 AF/pCSCF TH is concerned with the following topology information and restoral issues:
- The AVPs containing an AF/pCSCF's actual-host name in Request message must be hidden with one of the pseudo-host names assigned to the AF/pCSCF at TH trigger point RTH
- The Untrusted Network's PCRF (hPCRF in this case) saves the subscriber's location using the Origin-Host AVP contents containing a pseudo-host name. This action has the following impact:
- In subsequent hPCRF-vAF/pCSCF transactions (for example, RAR/ASR), the vAF/pCSCFis addressed by on of its pseudo-host names requiring a pseudo-to-actual name restoral
- All vAF/pCSCF-to-hPCRF transactions associated with a particular session must use the same vAF/pCSCF pseudo-host name. The Session is identified by Session-ID AVP, a mandatory AVP in all S9/RX messages.
Note:
Although the Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs both have actual AF/pCSCF host names, the may be different. Because Rx is a session based application, actual AF/pCSCF host names must be restored in subsequent hPCRF-vAF/pCSCF transactions. Hence the Origin-Host and Session-ID AVPs must be selected from the Actual Host Names TH Host Names.
- The hPCRF sends an Answer response to the transaction with the Session-ID received in the Request (containing an AF/pCSCF pseudo-host name). Because the Session-ID value returned in the Answer must match the Request, the AF/pCSCF pseudo-host name in the Session-ID AVP must be replaced with its corresponding value received in the Request message. This value is restored at TH trigger point ATR. This requires saving the host name portion of the Session-ID AVP value in the PTR. This host name restoral procedure is not required for Answers initiated by internal nodes as these Answer responses are based upon the original Request message content.
An example of a Protected-vAF/pCSCF to Untrusted-hPCRF Diameter transaction is shown in
Figure 10-21.
To ensure all Rx messages for the same session are modified using the same pseudo-name, Session-ID AVP can be used as a key to select a Pseudo Host Name for an Actual Host Name.
For Protected-vAF/pCSCF to Untrusted-hPCRF Rx transactions, S9 Af/pCSCF topology hiding is only required on Request messages at topology hiding point RTH which meet the following criteria:
- The message was a candidate for topology hiding as defined by topology trigger point RTH and
- S9 AF/pCSCF TH is enabled for the Protected Network (S9 PCRF TH Configuration Set is assigned to the Protected Network) and
- The Request message is a member of the Rx message set and was initiated by an AF/pCSCF and
- The Origin-Host and/or Session-ID AVPs in the Request contain an actual AF/pCSCF host name assigned to the Protected Network via the S9 AF/pCSCF TH Configuration Set.
For Protected-vAF/pCSCF to Untrusted-hPCRF transactions, AF/pCSCF topology information restoral is only performed on Answer messages which meet the following criterion:
- At TH Trigger Point ATR, the AF/pCSCF TH ATR flag in the PTR associated with the Answer message is set to Enabled.
Untrusted-hPCRF to Protected-vAf/pCSCF Transactions
When an Untrusted-hPCRF initiates a transaction to a Protected-vAF/pCSCF, it is most likely addressed to one of the vAF/pCSCF pseudo-host names that the hPCRF saved in a previous vAF/pCSCF-to-hPCRF transaction for which S9 AF/pCSCF TH was applied. For Untrusted-hPCRF to Protected-vAF/pCSCF Diameter transactions (RAR, ASR, and so on), S9 AF/pCSCF TH is concerned with the following topology information hiding and resotral issues:
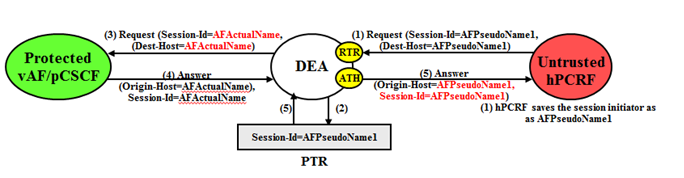
- The Destination-Host AVP contains a vAF/pCSCF pseudo-host name. This pseudo-host name must be replaced with the vAF/pCSCF's actual-host name at TH trigger point RTR. It's perfectly acceptable that an Untrusted-hPCRF to Protected-vAF/pCSCF Request message does not contain a vAF/pCSCF pseudo-host name. If the Destination-Host AVP value does not match a Pseudo-Host entry in the TH Host Name table , then no host name conversion is required and the Request message is routed as normal. Destination-Host name conversion is performed to prevent the following problems:
- Certain vAF/pCSCFs do not accept messages that do not contain its actual host name
- Diameter routing problems associated with pseudo-host names. For example, DRL Implicit Routing currently only works with actual host names (for example, the FQDN assigned to the Peer Node and used for the Capabilities Exchange procedure (CER/CEA)).
- The host portion of Session-ID AVP containing a vAF/pCSCF pseudo-host name must be replaced back with vAF/pCSCF's actual host name at TH trigger point RTR
- An Origin-Host AVP containing an vAF/pCSCF's actual-host name in the Answer response from the Protected- vAF/pCSCF must be hidden with one of the pseudo-host names assigned to that vAF/pCSCF. This is done at TH trigger point ATH.
- Session-ID AVP containing an vAF/pCSCF's actual-host name in the Answer response from the Protected-vAF/pCSCF must be hidden with one of the pseudo-host names assigned to that vAF/pCSCF. This is done at TH trigger point ATH.
An example of an Untrusted-hPCRF to Protected- vAF/pCSCF Diameter transaction is shown in
Figure 10-22.
For Untrusted-hPCRF to Protected-vAF/pCSCF transactions, S9 AF/pCSCF TH is only invoked on Request messages at topology trigger point RTR which meet the following criteria:
- Message was a candidate for topology hiding as defined by topology trigger point RTR and
- S9 AF/pCSCF TH is enabled for the Protected Network (S9 AF/pCSCF TH Configuration Set is assigned to the Protected Network) and
- The Request message is a member of the Rx message set and was initiated by a AF/pCSCF and
- The Destination-Host AVP or host portion of Session-ID AVP contains a AF/pCSCF pseudo-host name that is assigned to the Protected Network as determined from the internal AF/pCSCF TH Pseudo-Host Name
- Message was a candidate for topology hiding as defined by topology trigger point ATH
- S9 AF/pCSCF TH is enabled for the Protected Network (S9 AF/pCSCF TH Configuration Set is assigned to the Protected Network)
- The Answer message is a member of the Rx message set and was initiated by a AF/pCSCF
- The Origin-Host AVP or host portion of Session-ID AVP contains an actual AF/pCSCF host name that is assigned to the Protected Network via the S9 AF/pCSCF TH Configuration Set
Protected-hPCRF to Untrusted-vAF/pCSCF Transactions
When AF/pCSCF and PCRF are in untrusted network and AF/pCSCF uses vPCRF in proxy to communicate Rx messages initiated by vAF/pCSCF to hPCRF in protected network, then S9 PCRF TH is used to hide PCRF host names to untrusted network.
Untrusted-vAF/pCSCF to Protected-hPCRF Transactions
When AF/pCSCF and PCRF are in untrusted network and AF/pCSCF uses vPCRF in proxy to communicate Rx messages initiated by hPCRF in protected network to vAF/pCSCF, then S9 PCRF TH is used to hide PCRF host names to untrusted network.