The Order Fulfillment Process
PeopleSoft Inventory is delivered with the ability to handle one-step order fulfillment or multi-step order fulfillment. There are many options to tailor the steps in PeopleSoft fulfillment to match your work environment. Orders can be fulfilled in one step, several steps, or any combination in between based on the complexity of your shipping operations. You can use different steps in different parts of your organization.
The following diagram illustrates the possible fulfillment steps and corresponding fulfillment states that you might use in your environment:
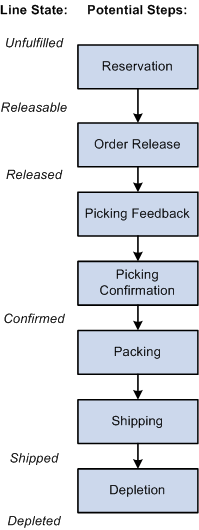
PeopleSoft Inventory tracks order demand lines throughout the fulfillment process and displays fulfillment state information on multiple pages and components. Demand lines processed in PeopleSoft Inventory have one of these fulfillment states:
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
Pending |
The line is either incomplete, invalid, or on hold. Lines in a Pending state are ignored by fulfillment processes. There is one exception to this rule, work order from PeopleSoft Maintenance Management are in the Pending state throughout to fulfillment process. |
Unfulfilled |
The line has been entered. The demand line's quantity could be partially or fully soft-reserved, promised, pre-allocated, or lot-allocated but the line has not been released downstream to the next order fulfillment step. |
Releasable |
The line is ready to be released to picking. The line can be soft-reserved, promised, pre-allocated, lot-allocated, or simply set to the releasable state. |
Released |
The line has been associated with a pick batch ID and released for picking. The line can be allocated or remain soft-reserved, promised, lot-allocated, or simply released for picking. |
Confirmed |
The Picking Confirmation process has subtracted the quantity picked for the order line from quantity balances at the material storage location level and has staged the demand line for shipping. The business unit level available balance has been updated but the on-hand balance has not yet been decreased. |
Shipped |
The quantity shipped has been recorded for the line. |
Depleted |
The Deplete On Hand Qty (Depletion) process has subtracted the quantity shipped from quantity balances at the business unit level and has inserted the shipping transaction into the TRANSACTION_INV table for costing. |
Canceled |
The line has been canceled in PeopleSoft Order Management or PeopleSoft Inventory. Sales order lines must be canceled using the Order Entry Form component in PeopleSoft Order Management. After the fulfillment stage indicated on the Demand Change Configuration feature, it must also be canceled on the Cancel/Hold Stock Requests page in PeopleSoft Inventory. All unshipped non-sales orders must be canceled in the Cancel/Hold Stock Requests page. |
During implementation of PeopleSoft Inventory, you must tailor the steps in PeopleSoft fulfillment to match your work environment. The following fulfillment steps can be combined or eliminated based on the needs of your environment.
Reservation
The reservation processes complete three tasks:
Reserve inventory stock to items defined as soft-reserve.
Promise stock to items defined as Available-to-Promise (ATP) items.
Move demand lines from the unfulfilled state to the releasable state once they have met the requirements of the applicable reservation and backorder rules. During this task, the backorder decision may be made, allowing for the creation or cancellation of the backorder. Depending on the applicable backorder rule, the backorder decision may be delayed until shipping time.
Each task can be performed independently. For example, a reservation process might reserve available quantity to a demand line and still keep it in the unfulfilled state because it did not meet the criteria of the reservation rules to be set to the releasable state. In addition, a reservation process can simply release demand lines downstream with no type of reservation if the item is not defined for soft-reserve or promise or if the reservation and backorder rules instruct the process to release a shortage downstream. A demand line can stay in the unfulfilled state and be partially or fully soft-reserved or promised.
Reservations can be initiated several different ways:
The Reserve Materials process launched directly from the process page, a link on another page, or by auto-processing.
The online reservations program launched from sales order entry in PeopleSoft Order Management or material stock request (MSR) entry in PeopleSoft Inventory. The online reservations program gives immediate feedback about the quantities reserved or promised and the releasable state.
For material stock requests (MSRs), you choose the method used at order entry time; the online reservations process or the Reserve Materials process.
For sales orders, online reservations is initiated if the Reserve at Save check box has been selected on the Order Management Definition component for the order management business unit.
The online reservations program launched from a work order in PeopleSoft Maintenance Management. The work order reservation rule defined within PeopleSoft Maintenance Management determines when the work order demand line is reserved. To override the reservation rule setting and reserve immediately, you can use the Reserve button on the Work Order- Schedules: Inventory page in PeopleSoft Maintenance Management.
The Inventory_Reservation EIP.
The Fulfillment Workbench with the action of reserve.
The Shortage Workbench can be used to soft-reserve or promise stock online and set lines to the releasable state. You can also use the workbench to unreserve or unpromise stock and set the demand line back to the unfulfilled state.
At the end of the Reserve Materials process or the Fulfillment Requests process, the Unreserved Demand Lines Report (INS6400) can be generated to allow viewing of all demand lines that did not pass reservations processing.
Order Release
This step is a process that releases demand lines for picking by moving the line from the releasable state to the released state. On the Order Release process, you can select the Create Allocations action to allocate stock for the demand line (push pick plan). An allocation means that quantity in a specific material storage location has been reserved for a particular demand line. You can also choose to not create an allocation, requesting that the Order Release process just make suggestions (pull pick plan) without allocating stock at the material storage location level. The default value for allocation can be defined at the inventory business unit level for all order release processes using the Setup Fulfillment-Order Release page. In addition, the Order Release process can generate:
An SQR picking plan report for printing.
An electronic picking extract file for electronic data collection devices.
The Shipping Order Release EIP is an outbound service operation that sends the demand lines to a warehouse management system (WMS) for picking. Data can also be sent to a third-party system to produce RFID tags.
Bar code labels, carton labels, and item usage labels on the printed or electronic picking plan.
Note: A material storage location's on-hand quantity and reserved or allocated quantity are maintained on the PHYSICAL_INV record.
Picking Feedback
Once you have physically picked the stock, enter picking results. When you have released demand lines to picking with an allocation, then the system assumes that you picked from the material storage locations specified in the hard allocation. You must enter exceptions to the allocations on the pick batch ID before confirming the pick results. When you have released demand lines to picking without an allocation, then the system does not know where to pull the stock from. In this case, you must enter all the picking results with the material storage locations used. The picking results can be entered into PeopleSoft Inventory by using:
The Material Picking Feedback page to enter the results manually.
The Inventory Picking inbound EIP and process to record results recorded on electronic data collections devices.
The Fulfillment Workbench with the action of pick confirm.
The Inventory Pick Confirm EIP.
The Shipping Notification EIP to receive picking results from a warehouse management system (WMS).
Once picking results have been entered, the demand lines are marked for confirmation.
Picking Confirmation
Once picking results have been entered, use the Picking Confirmation process to:
Move the demand lines from the released state to the confirmed state.
Decrease the onhand quantities for the appropriate material storage locations and prepares the demand lines for shipment processing. For push picking plans, the Picking Confirmation process also relieves the allocations created by the Order Release process.
The Picking Confirmation process can be launched directly from the process page, a link on the Material Picking Feedback page, or by auto-processing.
Packing
After running the Picking Confirmation process and before shipping orders, you can pack stock into shipping containers. The PeopleSoft Inventory packing feature enables you to create multiple levels of shipping containers and to keep track of how each container is packed. Shipping container information is listed on packing lists, advanced shipping notices (ASN), and is stored for historical inquiry purposes.
You can also use the Shipping Request transaction or the Pick Confirm transaction to create shipping containers. In addition, you can create shipping containers earlier in the fulfillment process by using the electronic data collection shipping container transactions to create single-level containers during picking. The electronic data collection transactions enable you to convert storage containers into shipping containers for tracking purposes.
To pack stock into shipping containers, use:
The Packing Session component.
The Inventory Shipping Container EIP to receive shipping container data packed by a third-party application, such as, electronic data collection systems and warehouse management systems.
Shipping
In the shipping business process, demand lines are moved from any previous fulfillment state to the shipped state. The process also includes assigning demand lines to a shipping ID, entering or changing shipping information, generating backorders, and creating the necessary shipping documents.
To move orders to the shipped state, you can use any of the following methods:
The Shipping/Issues component.
The Ship and Invoice process page.
The Fulfillment Workbench with the actions of pick confirm, front-end ship, or ship.
The Pick Confirm EIP.
The Picking Confirmation process page.
The Front End Shipping Request process page.
Important! Front end shipping does not support shipping staged date-controlled items.
Note: Shipping kits can degrade performance.
The Inventory Front End Shipping EIP.
The Shipping Request process page.
The Inventory Shipping EIP.
Depletion
The Deplete On Hand Quantity (Depletion) process completes the final step in order fulfillment by; reviewing all the demand lines that have been shipped, depleting the Inventory business unit for the shipped stock (that is, reducing the on-hand balance and removing the soft-reserve for shipped materials), creating the costing records in the transaction history table (TRANSACTION_INV), and changing the demand lines state to depleted. Once this process has been run, the demand lines cannot be unshipped. The Deplete On Hand Quantity process can be launched directly from the process page, the Shipping/Issues component, the Express Issues page, or by auto-processing.
An allocation occurs when an item quantity in a specific material storage location (MSL) within the inventory business unit has been reserved for a particular demand line. Allocation usually occurs when the Order Release process is run, moving the demand line from the Releasable fulfillment state to the Released state. However, allocations can take place earlier in the demand fulfillment cycle; this is called pre-allocation.
PeopleSoft Inventory defines the following types of allocations:
Standard Allocation: Refers to an allocation that is created within the picking fulfillment step; that is, when the demand line is moved to the Released fulfillment state.
Pre-Allocation: Refers to an allocation to a MSL that is created before the picking fulfillment step; that is, while the demand line is in the Unfulfilled or Releasable state. Pre-allocations can occur when pegged stock is putaway in the inventory business unit or when you pre-allocate stock to a demand line.
Lot-Allocation: Refers to allocating a specific lot ID to fulfill a lot-controlled item on a demand line. This is a type of pre-allocation since it takes place when the demand line is in the Unfulfilled or Releasable fulfillment state. It differs from other pre-allocations in that the demand line is allocated to a particular lot ID.
The following diagram illustrates the possible fulfillment steps that you might use for a pre-allocated or lot-allocated demand line:
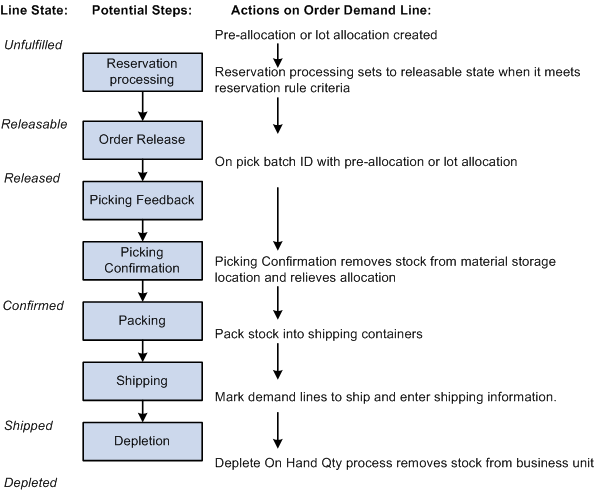
Pre-Allocation
A pre-allocation occurs when a demand line is allocated to inventory stock while the demand line is still in the Unfulfilled or Releasable fulfillment state. A pre-allocation can be created by:
The pegging feature.
The Allocation Workbench.
The Create/Update Stock Request component.
The Shortage Workbench.
For sales orders, the Order Entry Form component within PeopleSoft Order Management.
The Inventory Create Stock Request EIP (Enterprise Integration Point) or the Inventory Reservation EIP
Lot-Allocated Items
For lot-controlled items, you can create a lot allocation. The lot allocation is created when a specific lot has been allocated to a particular demand line. Lot allocations reserve quantity at the business unit item, lot, and material storage location levels. You can allocate lots to orders using the:
Order Entry Form component in PeopleSoft Order Management.
Create/Update Stock Request component in PeopleSoft Inventory.
Allocate Lots component in PeopleSoft Inventory.
The Allocation Workbench in PeopleSoft Inventory
The Inventory Create Stock Request EIP (Enterprise Integration Point) or the Inventory Reservation EIP.
Enable lot allocation by selecting the Allow Lot Allocation check box on the Inventory Definition-Business Unit Options page.
Note: The LOT_CONTROL_INV record provides a business unit view of lot quantities by summarizing quantity information for lot-controlled items recorded in the PHYSICAL_INV record.
Note: You cannot lot-allocate any demand lines that have been pre-allocated. You cannot lot-allocate demand lines that have an open peg, nor lines that have been pre-allocated due to a peg.
See Creating a Lot Allocation.
A soft reservation means that part of the business unit's total available quantity for the item has been reserved for an order demand line and cannot be consumed by other orders staged for fulfillment processing. With soft reservations, you process only those orders for which you have sufficient onhand stock to fulfill. You can reserve items marked for soft-reservation processing using a reservations process.
To manage short-supply situations, you can require that soft-reserved items be reserved only online from the Shortage Workbench using the Reserve Online check box on the Setup Fulfillment-Reservation page or the Setup Item Fulfillment page.
Note: The business unit's available quantity and reserved quantity are maintained on the BU_ITEMS_INV record.
Orders can be released directly from an unfulfilled state, bypassing the reservations process. Soft-reserved items released in this manner are treated as shortages by the Order Release process if sufficient inventory is not available at the business unit level. If the Order Release Shortage option allows the release of shortages then any available quantity is reserved and the order is released. If no shortages exist, then the full quantity is reserved and the order released.
The following diagram illustrates the possible fulfillment steps that you might use for a soft-reserved item. This item can be allocated during the Order Release process or just keep the soft-reservation applied during reservations processing:
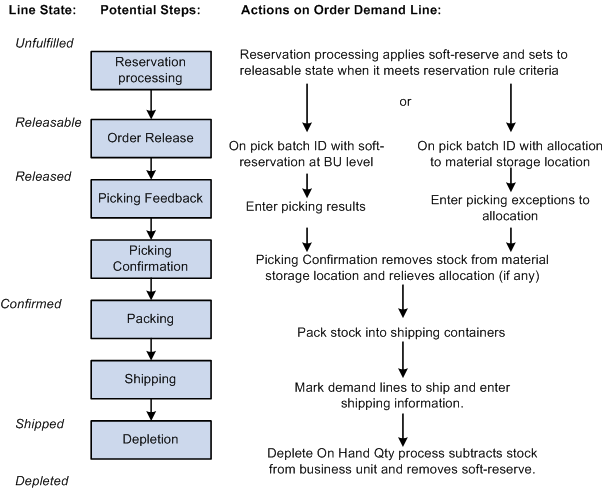
A promised order line is a demand line for which a scheduled shipment date has been promised based on Available to Promise (ATP) calculations of future supply and demand. Quantity for promised items is not soft-reserved or allocated (subtracted from the business unit or material storage location's available quantity) until the demand line has been allocated by the Order Release process or confirmed as picked by the Picking Confirmation process. You can promise items marked for ATP processing using a reservations process.
Orders can be released directly from an unfulfilled state, bypassing the reservations process. ATP items released in this manner are promised and released if inventory is available at the material storage location level. Normal ATP rules are not followed as this is considered an exception situation.
The following diagram illustrates the possible fulfillment steps that you might use for an ATP item The reservations process promises stock to fulfill the order and the Order Release process can (optionally) apply an allocation:

Items can be defined for no reserve, promise, or lot-allocation. Using this method, the system does not tie up available stock in the business unit until the picking stage. This is especially useful for items that are plentiful and rarely experience shortages.
Note: For non-soft reserve, non-ATP items, you have the option to skip the reservation process by adding the orders in the releasable state. Use the Non-Soft Reserved State field on the Setup Fulfillment page to choose this option.
The following diagram illustrates the possible fulfillment steps that you might use for non-soft reserve, non-ATP item. The reservations process applies no soft-reserve and the Order Release process can optionally apply an allocation. Without an allocation, you must enter the picking results before running the Picking Confirmation process:
