Understanding Constituent Web Services
Note: Campus Solutions offers two different types of web services to support Constituent functions. This section covers asynchronous web services. For information on synchronous Constituent web services based on the system's Entity Registry functionality, see Using Entity Registry Based Constituent Web Service Operations.
For information about setup, functional, and technical implementation considerations when you use Search/Match directly between two systems, see Understanding CS-to-HCM Integration.
In general, a web service is a collection of operations that enable software to utilize a resource. The official web service definition can describe almost any standard for exchanging data over the internet, but in common usage the term refers to the exchange of XML messages that follow the SOAP standard using the same HTTP protocol as a web browser. A simple definition of a web service is an internet application programming interface (API) that's self-describing and can work between various programming languages. The constituent web service was developed to be used in a manner consistent with common web services.
The constituent web service manages information about a constituent. A constituent can be a prospect, applicant, student, faculty member, or any other person of interest to your institution. The web service allows the Campus Solutions database to communicate with virtually any other external system, regardless of the technology supporting that system. Prior to web service standards it was difficult to connect systems on disparate technologies, such as operating systems, database platforms, and application architectures. Web service standards make it possible for computer systems on virtually any technology platform to integrate with minimal effort.
Institutions can use constituent web services to integrate constituent data between Campus Solutions and other external systems. The constituent web service:
Notifies integrated systems when new constituents in Campus Solutions are created or when their information is changed.
External systems can use this notification to synchronize their version of the constituent or to perform processing based on the changed data.
Allows integrated systems to update a constituent's information in Campus Solutions, such as adding a new address or changing the constituent's name.
Allows integrated systems to retrieve a constituent's detailed information.
Enables Campus Solutions users to run Search/Match against an external constituent repository, such as a data hub.
Constituent web service information flow diagram
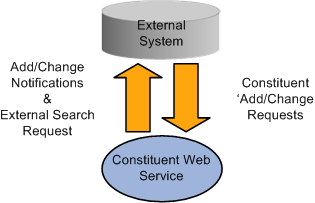
Institutions can use the web service to integrate to a variety of administrative and academic systems that comprise the higher education ecosystem. For example, the service can be used to integrate to a data hub (MDM), housing system, human resources, parking system, learning management system, and general purpose registry. Large institutions often deploy hundreds of such systems.
Messaging between the systems is done via synchronous or asynchronous interactions. In a synchronous interaction, the source system issues a request to the target system and then waits until a response is received. Asynchronous interactions involve the source system issuing a request to the target system and not waiting for any response, but instead immediately continuing with processing. The request is assumed to have been received by the target system and to have been processed successfully. Asynchronous requests don't receive a response from the target system. This model assumes that the underlying messaging middleware guarantees the delivery of the request to the target system.
The PeopleSoft Campus Solutions Constituent Web Services Developer's Guide provides the technical details of web services as well as configuration and messaging.
The data that comprises the constituent message includes the core person data contained in the PERSON_BASIC_SYNC message, the Campus Solutions extension data contained in the PERSON_SA message, and affiliations data.
Messaging
Constituent web services uses three types of messaging. The system generates outbound messages when a constituent's data is changed in Campus Solutions. A change in any data element in the constituent message definition raises this condition. The system publishes the constituent message so that any interested external system can be informed. The system generates inbound messages when a constituent's data is updated in an external system that is integrated with Campus Solutions. When a third-party or external system needs to query the Campus Solutions database to view data, the system generates a query message. This is a synchronous inbound request/response get service, in which a third party raises a query or data request and the Campus Solutions system delivers a response that contains the requested data details.
Constituent web services delivers the following messages, which are defined using PeopleTools Integration Broker:
SCC_CONSTITUENT_SYNC (Outbound)
SCC_PERSON_SYNC (Outbound)
SCC_CONSTITUENT_IN_SYNC_DS (Inbound)
SCC_GET_CONSTITUENT_REQ_DS (Inbound)
SCC_GET_CONSTITUENT_RES_DS (Query)
Note: If you implement Campus Solutions and a separate instance of PeopleSoft Human Capital Management, read the relevant documentation about CS-HCM Integration to understand the setup, functional, and technical implementation considerations. See:
Monitoring Integrations Using the Integrity Utility
See Information Center: CS-HCM Integration for PeopleSoft Enterprise Campus Solutions in My Oracle Support (ID 2091799.2).
See:
PeopleTools: Integration Broker