Administering the Average Cost Methods
This topic provides an overview of the administration of the average cost methods.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
CM_COST_ADJ |
Adjust perpetual weighted averages for items. ChartField security can be applied to this page. |
|
|
ChartField Overrides Page |
CM_COST_ADJ2 |
Replace the ChartField combinations that are defined in the account distribution setup. |
|
CM_COST_ADJ_RETRO |
Adjust retroactive perpetual weighted averages for items. ChartField security can be applied to this page. |
For average costing, you can select one of three costing methods:
Term |
Definition |
|---|---|
Periodic Weighted Average |
The weighted average is calculated only once, at the end of the period. All depletions during that period use this same average. Run the Transaction Costing process (within the Cost Accounting Creation process) with a Cost Mode of Regular to calculate end-of-period averages. There is no cost adjustment page for periodic averages. |
Perpetual Weighted Average |
The weighted average is calculated at each putaway. The average cost that is applied to depletions could fluctuate throughout the period. |
Retroactive Perpetual Weighted Average |
The weighted average is calculated after each putaway, just like the perpetual average method; however, this weighted average cost is calculated at the end of the period and applied retroactively to the depletions. This method enables you to value each individual transaction by using the current perpetual average cost at depletion time, yet delay the calculation of the average until the end of a period, when more cost information is likely to be captured for a more accurate average cost. Run the Transaction Costing process (within the Cost Accounting Creation process) with a Cost Mode of Regular to calculate retroactive perpetual average. |
Based on the entry in the Cost Element Option field of the Cost Profiles page, the perpetual average costing methods can combine all costs into the primary cost element and calculate one average cost per item or break out the averages by cost element.
When the items are defined as average-cost items, the Transaction Costing process (within the Cost Accounting Creation process):
Values all receipts (putaways) at the purchase order price or the cost of production.
Values all depletions by using the periodic weighted average, the perpetual weighted average, or the retroactive perpetual average method. The choice of cost flow method on the cost profile page does not impact the weighted average calculations, but it is necessary for the system background processes.
To apply purchase price variances and exchange rate variances to the perpetual average cost items, select the Apply Perpetual Average Adjs check box on the Transaction Costing process page. Putaways and depletions are adjusted for the difference between the PO price and the voucher price (price variance) and also any difference in the exchange rate that is used on the PO and the voucher (ERV). To delay calculation of the price and exchange rate variances, do not select the Apply Perpetual Average Adjs check box when running the Transaction Costing process.
For periodic weighted average items, no variances are computed. This method assumes that the invoices are matched, posted, and extracted within the same period that the PO is entered. When the Transaction Costing process is run, it picks up the invoice costs for putaway and average cost calculations. If the invoice costs are not available, then the PO costs are used but no variance later updates the average cost calculations for delayed invoice costs. The frequency of the periodic average computation is controlled by running the Transaction Costing process in Regular mode. When the Transaction Costing process is run in Mid Period mode, periodic averages are not computed and depletion transactions are not costed. The accounting for these transactions is postponed.
The cost of an average cost item can also be manually adjusted by using the Adjust Average Cost page and the Adjust Retro Costs page. When the system is running in a live environment, you may need to manually adjust an item's average cost due to entry errors, variances, and other causes. You can increase or decrease the item's cost, or you can establish a new average cost for an item.
The Adjust Average Cost page and the Adjust Retro Costs page write the perpetual average adjustments to the average cost table, CM_PERPAVG_COST, and the average cost adjustment table, CM_COST_ADJB, where they are picked up by the Accounting Line Creation job.
All periodic average cost items are updated on the CM_PERDAVG_COST record during the Transaction Costing process whenever there is a receipt or depletion of any periodic averaged item. Each update puts a new row in the table, and all other previous rows are marked inactive, so only one row for the business unit and item ID is active. There is no cost adjustment page for periodic cost.
Note: Manual adjustments do not change the average cost that is stored in the AVERAGE_COST_MAT field of the BU_ITEMS_INV record. This field is appears in the Avg Matl Cost field of the Define Business Unit Item-General: Common page.
Use the Adjust Average Cost page (CM_COST_ADJ) to adjust perpetual weighted averages for items.
ChartField security can be applied to this page.
Navigation:
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Adjust Average Cost page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
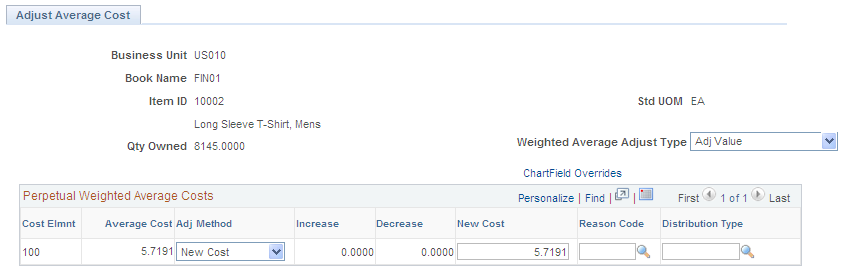
Use this page to adjust an item's current perpetual weighted average cost based on the business unit, cost book, item ID, and cost elements. The cost adjustment and inventory revaluation are processed by the Accounting Line Creation job. Entries on this page impact the average purchase price value displayed on the Define Business Unit Item - General: Common page.
Note: Negative quantities are acceptable, but the unit cost cannot be negative. A message appears if this situation arises.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Qty Owned (quantity owned) |
Inventory is classified as owned, nonowned, or consigned. If inventory is nonowned, it is not considered a part of the inventory value for the business unit; nonowned inventory does not affect costing, and in this case, the average cost. The owned quantity for an item is used to recalculate average cost. Consigned inventory from a supplier becomes owned inventory when it is consumed; at that time, it is included in average cost recalculation. |
Weighted Average Adjust Type |
Options are: Adj Value (adjustment value): Enter a new inventory value for the specified item. The adjustment is processed by the Accounting Line Creation process by using the value adjustment transaction (transaction group 205). Accounting entries are created to record the change in inventory valuation. The adjustment transaction records the difference between the old and the new weighted average cost for the current owned quantity on hand for the entire business unit. If the inventory business unit requires location accounting, the process writes an average cost adjustment transaction for each owned storage area containing a nonzero balance of the item. Change Avg (change average): Enter a new current average cost for the specified item. This option does not result in accounting entries, but the transaction is stored in the database for record keeping purposes. For example, assume that the balance of the item in PeopleSoft Inventory (average cost multiplied by on-hand quantity) does not agree with the item's net balance in PeopleSoft General Ledger. Upon investigation, you discover that the general ledger (GL) balance is correct. Perhaps it is adjusted by using a manual journal entry. The change average option provides a method to change the average cost for perpetual inventory records. |
ChartField Overrides |
Select to change ChartField information, or you can select a SpeedType Key and the ChartField information appears as the default from the SpeedType. The SpeedType Key field only appears if SpeedType level is selected on the Inventory Definition - Business Unit Options page. |
Adjustment Method |
To adjust the average cost of an item, you have three options: Increase: The amount that you enter in the Increase field is added to the current average cost. Decrease: The amount that you enter in the Decrease field is subtracted from the current average cost. Enter the amount as a positive number. New Cost: The amount that you enter in the New Cost field replaces the current average cost. |
Distribution Type |
(Optional) User-defined codes that are a subset of transaction groups. This enables you to break down a transaction group into customized categories which can use different ChartFields by distribution type from the distribution accounting rules. |
Use the Average Cost Adjustment/PPV report to view adjustments that this page creates.
Note: ChartField security can be applied to this page.
Use the Adjust Retro Costs page (CM_COST_ADJ_RETRO) to adjust retroactive perpetual weighted averages for items.
ChartField security can be applied to this page.
Navigation:
Enables you to update or add an average cost for the item in the retroactive perpetual average record. The entry is inserted into the actual cost table. The Transaction Costing process (in the regular Cost Mode) then recalculates the correct average for every depleted depletion transaction.
Field or Control |
Description |
|---|---|
Qty Owned (quantity owned) |
Inventory is classified as owned, nonowned, or consigned. If inventory is nonowned, it is not considered a part of the inventory value for the business unit; nonowned inventory does not affect costing, and in this case, the retroactive perpetual average cost. The owned quantity for an item is used to recalculate the retroactive perpetual average cost. Consigned inventory from a supplier becomes owned inventory when it is consumed; at that time, it is included in perpetual average cost recalculation. |
Weighted Average Adjust Type |
The options are: Adj Value (adjustment value): Enter a new inventory value for the specified item. The adjustment is processed by the Transaction Costing process and the Accounting Line Creation process by using the value adjustment transaction (transaction group 205). Accounting entries are created to record the change in inventory valuation. The adjustment transaction records the difference between the old and the new perpetual weighted average cost for the current owned quantity on hand for the entire business unit. If the inventory business unit requires location accounting, the process writes an average cost adjustment transaction for each owned storage area containing a nonzero balance of the item. Change Avg (change average): Enter a new current average cost for the specified item. This option does not result in accounting entries, but the transaction is stored in the database for record keeping purposes. For example, assume that the balance of the item in PeopleSoft Inventory (average cost multiplied by on-hand quantity) does not agree with the item's net balance in PeopleSoft General Ledger. Upon investigation, you discover that the GL balance is correct. Perhaps it is adjusted by using a manual journal entry. The Change Average option provides a method to change the average cost for perpetual inventory records. |
ChartField Overrides |
Select to change ChartField information, or you can select a SpeedType Key and the ChartField information appears as the default from the SpeedType. The SpeedType Key field only appears if SpeedType level is selected on the Inventory Definition - Business Unit Options page. |
Adjustment Method |
To adjust the average cost of an item, you have three options: Increase: The amount that you enter in Increase Cost By is added to the current average cost. Decrease: The amount that you enter in Decrease Cost By is subtracted from the current average cost. Enter the amount as a positive number. New Cost: If there is no current perpetual average for this item, then you can enter an amount in theNew Cost field. This new cost is applied to the beginning of the period. |
Distribution Type |
(Optional) User-defined codes that are a subset of transaction groups. This enables you to break down a transaction group into customized categories which can use different ChartFields by distribution type from the distribution accounting rules. |
Note: ChartField security can be applied to this page.