Adding a Policy with Custom Actions
You can define a custom action and include it as part of a policy action. For example, you can write a custom action to perform external health checks on provisioned environments or run OCI REST API calls.
Custom actions are supported for Environment and Repository Artifact policy objects, and scheduled or event-based policy types. The allowed parameters depend upon the policy object.
|
Parameter Type |
Parameter |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Define Source: Select one of these options. If you select more than one you receive an error when you save the page. |
PeopleCode Handler (Application Class) |
Available for Repository Artifact and Environment policy objects. See the following sections for more details on using PeopleCode Handler. |
|
Inline Commands |
Available for Environment policy objects and life-cycle events. To use inline commands for custom actions set Policy Object to Environment and Policy Type to Event. Enter one or more comma-separated commands. For Linux nodes the commands will be interpreted as shell (.sh) commands. For Windows nodes the commands will be interpreted as batch (.bat) commands. This is not applicable for Delete event. |
|
|
Repository File |
Available for Environment policy objects and life-cycle events. Upload the file to the Repository before creating the policy action. See Upload Custom Scripts Page. To use an uploaded repository file for custom actions set Policy Object to Environment and Policy Type to Event. |
|
|
Set Execution Content. Enter the content needed to run the custom action. |
Input (JSON) |
Available for Repository Artifact and Environment policy objects. If used with the Repository File parameter, you can use predefined variables to set environment variables. See Using Environment Variables with Custom Actions Based on Repository Files or Command Lines. |
|
Operating System |
Available for Environment policy objects and life-cycle events. Select Linux or Windows. |
|
|
Node Type |
Available for Environment policy objects and life-cycle events. Select Database, DBSystem, Middle Tier, Full Tier, Search Stack, or PeopleSoft Client. This is optional. If the Operating System is specified and Node Type is not specified, all nodes of the chosen operating system will be used. |
The following guidelines apply to custom actions:
Ensure that custom scripts exit with the correct status so that the proper script processing status is propagated to Cloud Manager. This ensures that the correct status is shown on the environment card.
Custom actions based on Repository Files or Command Line(s) are not supported for Stop events.
Custom actions based on Repository Files or Command Line(s) are not supported for schedule-based policies.
Custom actions based on Repository Files are not applicable when the Policy Object is Repository Artifact.
If a custom action based on Repository Files or Command Line(s) is associated with a Delete event, the script will run locally on Cloud Manager. For other events, the script is run remotely, on the managed environment node.
As part of policy processing of custom actions based on Repository Files, Cloud Manager sets environment variables that will be available in the custom script being run.
Cloud Manager sets the following environment variables as part of a Custom Action:
|
Environment Variable |
Description |
|---|---|
|
PSFT_ADDED_NODE |
Identify a newly-added node. This is supported only for Add Node policies. |
|
PSFT_LIFE_CYCLE_EVENT_NAME |
Event name for which the action is triggered. |
|
PSFT_POLICY_NAME |
Policy name |
See Upload Custom Scripts Page for a list of the environment variables set by Cloud Manager during custom action processing and examples of using the environment variables.
You can target the implementation of a custom script or command line(s) on specific environment nodes by setting the following variables in the Input (JSON) field:
|
Environment Variable |
Allowed Values |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
MIDTIER_TYPE |
|
This variable is only applicable if the NodeType selected on the Policy Action Parameter page is Middle Tier or if Node Type is left blank. Use this variable to target Middle Tier nodes for specific domain combinations. If this variable is not supplied then all Middle Tier nodes are selected for a particular operating system type. |
|
INSTANCE |
|
This variable is applicable to Middle Tier, Search Stack, and PeopleSoft Client. For Middle Tier, this variable will be used along with MIDTIER_TYPE for node selection. This variable will not be applicable for DBsystems, Database, or Full Tier as the Number of Instance will always be one in those cases. |
This example illustrates the Policy Action Parameters dialog box with Input (JSON) using the INSTANCE and MIDTIER_TYPE environment variables.
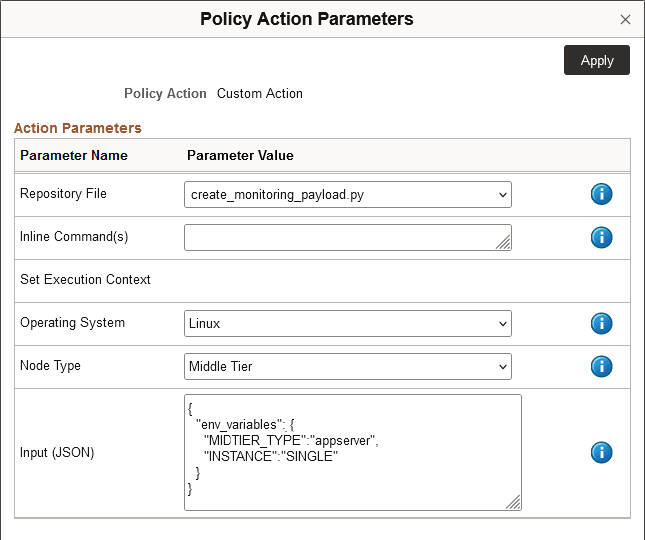
Here is an example of using the delivered environment variables. The Policy Action Parameters page includes these entries:
Repository File = Python file (create_monitoring_payload.py)
Node Type = Middle Tier
Operating System = Linux
Input (JSON) includes MIDTIER_TYPE = appserver and INSTANCE = SINGLE
The environment variables in the Input (JSON) directs the script to act on a single Linux Middle Tier node that has only an application server.
Cloud Manager delivers a PeopleSoft application class, ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler, which acts as the superclass for any custom policy action handler class. You are responsible for writing the processing logic for the custom action.
To set up a policy for a custom action, define a PeopleCode application class extending from the class ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler. When the policy is run, a predefined method of the instance of the handler class is invoked.
See the product documentation PeopleTools: PeopleCode API Reference, Understanding Application Classes on Oracle Help Center at https://docs.oracle.com/en/applications/peoplesoft/peopletools/index.html.
You can create a policy with multiple actions that combines several custom actions, or a mixture of custom actions and predefined actions, in sequence.
The base PeopleSoft application class is structured with input and output methods. When you set up a policy with multiple actions they are run one after another in the order you define. This gives you the option to write a series where the output from one policy action is passed to the next policy action as input.
Use Application Designer, which is included with the PeopleSoft Client, to write the PeopleCode application class.
To install a PeopleSoft Client:
Subscribe to the Interaction Hub (IH) download channel in the Repository.
Create a template to deploy the PeopleSoft Interaction Hub 9.1 database on a PUM topology.
Note: The IH image should be based on the same PeopleTools release as the current Cloud Manager update image.
The delivered PUM topology includes a PeopleSoft Client node on Microsoft Windows.
Create an environment from the IH template.
Make a note of the Windows Client IP on the Environment Details page in the PeopleSoft Client section.
Use RDP to connect to the PeopleSoft Client.
To determine the IP address of the PeopleSoft Client, go to the Environment Details page for the environment. Click Refresh Metadata and then select Diagrammatic View. Hold the mouse pointer over the PSoft Client box and look for the public ip in the table.
Follow the instructions in the product documentation to use Application Designer.
See the product documentation PeopleTools: PeopleCode Developer's Guide on Oracle Help Center at https://docs.oracle.com/en/applications/peoplesoft/peopletools/index.html.
Here is the definition of ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler class. Descriptions of the methods are included as comments (marked by /* at the beginning of the comment and */ at the end).
When you define the policy action for custom actions, you are required to provide input in JSON format. The contents in the Input (JSON) field is then passed as input through the "Execute" method (in bold font).
The SavePolicyActionOutput (in bold font) API can be used to save the policy action output, which can be seen from the Policy Monitor page. If you combine multiple custom actions, the method GetPreviousPolicyActionOutput (in bold font) is used to read the output produced by the previous custom policy action.
/***
*** Custom policy action handler classes should extend from this class and implement the Execute method.
*** Policy governance framework will invoke the Execute method of the handler class while executing the policy
***/
class CustomActionHandler
method CustomActionHandler();
/* Property that can be used by subclasses to set a description for the custom handler class */
property string description;
protected
method GetPolicyObjectName(&policyInstanceObj As string) Returns string;
method GetPolicyArtifactId(&policyInstanceObj As string, &policyArtifactObj As string) Returns string;
method SavePolicyActionOutput(&policyInstanceObj As string, &policyArtifactObj As string, &output As string);
method GetPreviousPolicyActionOutput(&policyInstanceObj As string, &policyArtifactObj As string) Returns string;
method Execute(&policyInstanceObj As string, &policyArtifactObj As string, &handlerInputObj As string);
private
instance object &policyUtils;
end-class;
method CustomActionHandler
&policyUtils = CreateJavaObject("com.peoplesoft.pa.cl.governance.policyengine.PolicyUtils");
%This.description = "";
end-method;
/***
*** Description: Get the policy object name of the executed policy
*** Parameters:
*** &policyInstanceObj : JSON representation of the policy instance object containing policy instance metadata
***/
method GetPolicyObjectName
/+ &policyInstanceObj as String +/
/+ Returns String +/
Local string &policyObjectName = "";
Local JsonParser &jParser = CreateJsonParser();
Local boolean &ret = &jParser.Parse(&policyInstanceObj);
Local JsonObject &policyInstanceJsonObj = &jParser.GetRootObject();
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_object_name") Then
&policyObjectName = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_object_name");
End-If;
Return &policyObjectName;
end-method;
/***
*** Description: Get the policy artifact id associated with the executed policy
*** Parameters:
*** &policyInstanceObj : JSON representation of the policy instance object containing policy instance metadata
*** &policyArtifactObj : JSON representation of the policy artifact object associated with the executed policy
***/
method GetPolicyArtifactId
/+ &policyInstanceObj as String, +/
/+ &policyArtifactObj as String +/
/+ Returns String +/
Local string &policyArtifactId = "";
Local string &policyObjectName = %This.GetPolicyObjectName(&policyInstanceObj);
Local JsonParser &jParser = CreateJsonParser();
Local boolean &ret = &jParser.Parse(&policyArtifactObj);
Local JsonObject &policyArtifactJsonObj = &jParser.GetRootObject();
/* We are handling only environment artifacts for now */
If &policyObjectName = "Environment" And
&policyArtifactJsonObj.IsExist("name") Then
&policyArtifactId = &policyArtifactJsonObj.GetAsString("name");
End-If;
If &policyArtifactId = "" And
&policyArtifactJsonObj.IsExist("Product") And
&policyArtifactJsonObj.IsExist("Release") Then
&policyArtifactId = &policyArtifactJsonObj.GetAsString("Product") | "_" | &policyArtifactJsonObj.GetAsString("Release");
End-If;
Return &policyArtifactId;
end-method;
/***
*** Description: Save the policy action output. Policy action output can be seen from Policy Monitor page.
*** Parameters:
*** &policyInstanceObj : JSON representation of the policy instance object containing policy instance metadata
*** &policyArtifactObj : JSON representation of the policy artifact object associated with the executed policy
*** &output : Output generated for the policy action execution
***/
method SavePolicyActionOutput
/+ &policyInstanceObj as String, +/
/+ &policyArtifactObj as String, +/
/+ &output as String +/
Local string &policyInstanceId = "";
Local string &policyObjectName = "";
Local string &jobId = "";
Local JsonParser &jParser = CreateJsonParser();
Local boolean &ret = &jParser.Parse(&policyInstanceObj);
Local JsonObject &policyInstanceJsonObj = &jParser.GetRootObject();
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_object_name") Then
&policyObjectName = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_object_name");
End-If;
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_instance_id") Then
&policyInstanceId = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_instance_id");
End-If;
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_action_jobid") Then
&jobId = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_action_jobid");
End-If;
&policyUtils.updatePolicyActionOutput(&policyInstanceId, &policyObjectName, &policyArtifactObj, &jobId, &output);
end-method;
/***
*** Description: Get output of previous policy action
*** NOTE: At present, we will return output from the previous custom policy action (if any). Defined policy actions currently does not produce any output as such.
*** This API is given a generic name, so that when we allow output from defined policy actions (in future), we can re-use the same API
*** Parameters:
*** &policyInstanceObj : JSON representation of the policy instance object containing policy instance metadata
*** &policyArtifactObj : JSON representation of the policy artifact object associated with the executed policy
*** Returns the output of previous policy action as a string. Empty string if previous policy action is not found or if it does not produce any output
***/
method GetPreviousPolicyActionOutput
/+ &policyInstanceObj as String, +/
/+ &policyArtifactObj as String +/
/+ Returns String +/
Local string &output = "";
Local string &policyInstanceId = "";
Local string &policyObjectName = "";
Local string &jobId = "";
Local JsonParser &jParser = CreateJsonParser();
Local boolean &ret = &jParser.Parse(&policyInstanceObj);
Local JsonObject &policyInstanceJsonObj = &jParser.GetRootObject();
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_object_name") Then
&policyObjectName = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_object_name");
End-If;
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_instance_id") Then
&policyInstanceId = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_instance_id");
End-If;
If &policyInstanceJsonObj.IsExist("policy_action_jobid") Then
&jobId = &policyInstanceJsonObj.GetAsString("policy_action_jobid");
End-If;
&output = &policyUtils.getPreviousPolicyActionOutput(&policyInstanceId, &policyObjectName, &policyArtifactObj, &jobId);
Return &output;
end-method;
/***
*** Description: Custom policy action handler classes should implement this method. This method will be invoked while executing the policy action
*** Parameters:
*** &policyInstanceObj : JSON representation of the policy instance object containing policy instance metadata
*** &policyArtifactObj : JSON representation of the policy artifact object associated with the executed policy
*** &handlerInputObj : JSON representation of the input provided in the policy action parameters, while defining the policy
***/
method Execute
/+ &policyInstanceObj as String, +/
/+ &policyArtifactObj as String, +/
/+ &handlerInputObj as String +/
end-method;
Here are definitions for the parameters included in the Execute and SavePolicyActionOutput methods:
|
Parameter Name |
Parameter Definition |
Example |
|---|---|---|
|
policyInstanceObj |
JSON string representation of policy instance (implemented policy) details. The following attributes are available in the JSON object:
|
|
|
policyArtifactObj |
JSON string representation of the policy artifact associated with the policy instance (executed policy) The following attributes are available in the JSON object:
|
|
|
handlerInputObj |
JSON string representation of the input defined for the custom policy action. This is the input added in the policy action parameter dialog box. |
none |
This is an example of a PeopleCode application class for a custom policy action, EmailNotificationHandler, which sends email notifications during policy processing.
Before invoking the policy, the user must set up OCI Notification and update the Notification Topic OCID in Cloud Manager Infrastructure Settings page.
See Infrastructure Settings Page.
All custom policy action handler classes should implement the "Execute" method. This method will be invoked when the policy runs.
import ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler;
class EmailNotificationHandler extends ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler
method EmailNotificationHandler();
method Execute(&policyInstanceObj As string, &policyArtifactObj As string, &handlerInputObj As string);
end-class;
method EmailNotificationHandler
%Super = create ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler();
%This.description = "Custom policy action handler class for sending email notifications";
end-method;
method Execute
/+ &policyInstanceObj as String, +/
/+ &policyArtifactObj as String, +/
/+ &handlerInputObj as String +/
Local string &artifactId = %Super.GetPolicyArtifactId(&policyInstanceObj, &policyArtifactObj);
Local JsonParser &jsonParser1 = CreateJsonParser();
Local boolean &ret = &jsonParser1.Parse(&policyInstanceObj);
Local JsonObject &policyInstance = &jsonParser1.GetRootObject();
Local string &policyInstanceId = &policyInstance.GetAsString("policy_instance_id");
Local string &curdatetime = DateTimeToLocalizedString(%Datetime, "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Local string &policyName = "";
/* Populate email title and body */
Local string &topic = "Topic-PTU";
Local string &title = "Policy execution notification";
SQLExec("select ecl_name from ps_ecl_policy_mon where ecl_rp_id = :1", &policyInstanceId, &policyName);
Local string &body = Char(10) | Char(10) | "Policy execution details below" | Char(10);
&body = &body | Char(10) | "Policy Name : " | &policyName | Char(10);
&body = &body | Char(10) | "Environment: " | &artifactId | Char(10);
&body = &body | Char(10) | "Performed at: " | &curdatetime | Char(10);
/* Add any custom data passed to the policy in case if needed */
If &handlerInputObj <> "" Then
Local JsonParser &jsonParser2 = CreateJsonParser();
&ret = &jsonParser2.Parse(&handlerInputObj);
Local JsonObject &handlerInput = &jsonParser2.GetRootObject();
If &handlerInput.IsExist("notes") Then
&body = &body | Char(10) | "Notes: " | &handlerInput.GetAsString("notes") | Char(10);
End-If;
End-If;
/* Send email notification */
/* Refer CM documentation on how to setup a notification topic for email notifications */
Local JavaObject ¬ificationObj = CreateJavaObject("com.peoplesoft.pa.cl.common.OCINotificationServiceImpl");
Local JavaObject &messageObj = CreateJavaObject("com.peoplesoft.pa.cl.common.Message");
&messageObj.setBody(&body);
&messageObj.setTitle(&title);
¬ificationObj.send(&topic, &messageObj);
/* Expose policy action output if needed */
Local string &actionOutput = "Successfully executed EmailNotificationHandler. Mail content: " | &body;
%Super.SavePolicyActionOutput(&policyInstanceObj, &policyArtifactObj, &actionOutput);
end-method;To add a policy with a custom action:
In Application Designer, write PeopleCode for the desired action based on the ECL_CM:Governance:CustomActionHandler class.
In Cloud Manager, define a policy and select Custom Action as the Policy Action.
Click the Parameter button for the Policy Action and supply these parameters to associate the PeopleCode application class with the policy action.
Field or Control
Description
PeopleCode Handler class
Enter the name of the PeopleCode application class to be invoked when the policy action is run.
Input (JSON)
(Optional) Enter the JSON string that is to be passed to the handler class when the policy action is run.
Environment Name
This parameter is available for policies with Repository Artifact policy object.
Click the search icon to display the Set Parameter Values page. Select a tab and use one of these methods to identify the environment:
Environment Names: Click the search icon to select a provisioned environment to associate with the custom action.
Tag: Select a Tag Namespace, and then select a tag that is associated with a provisioned environment.
Initiate the policy and follow the status on Policy Monitor.
See Using Policy Monitor.
Click the Policy Action Output icon (>) to view the output of the policy in JSON format.