Creating Product Definitional Elements
To create product definitional elements, use the Product Installation (PROD_INSTALLATION), Automatic Numbering (AUTO_NUM_PNL), Product Group (PROD_GROUP_TBL), Product Category (PROD_CATEGORY), Product Brand (PROD_BRAND), Competitors (COMPETITOR_CD), Region (RB_REGION), Attribute Definition (RB_ATTRIBUTE), and Auto Numbering (AUTO_NUM_PNL) components.
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Usage |
|---|---|---|
|
PROD_INSTALLATION |
Select options for managing products. |
|
|
RF_INSTPRD_DFLT |
Specify rules that determine how system transactions create and update installed products. |
|
|
AUTO_NUM_PNL |
Define automatic numbering options for product IDs. |
|
|
PROD_GROUP_TBL |
Define product group codes. |
|
|
PROD_GRP_OVERVIEW |
View products that belong to a product group. |
|
|
PROD_CATEGORY |
Define product category codes. |
|
|
PROD_BRAND |
Define product brand codes. |
|
|
COMPETITOR_CD |
Define competitor codes. |
|
|
RC_BS_MAIN |
Define a branch script for support and sales personnel. |
|
|
Region Page |
RB_REGION |
Set up regions. |
|
Competencies Page |
COMPETENCY_TABLE |
Establish competency codes. |
|
RB_RELATIONS |
Set up the codes that describe relationships between products. |
|
|
RB_ATTRIBUTE_MAIN |
Define a product attribute. |
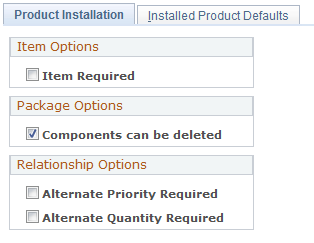
Use the Product Installation page (PROD_INSTALLATION) to select options for managing products.
Navigation
Image: Product Installation page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Product Installation page.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Item Required |
Select if you have installed PeopleSoft Supply Chain Management (PeopleSoft SCM) or PeopleSoft Integrated FieldService. You can deselect this check box if the order fulfillment system does not require items or if products are not inventoried. If you select this check box, you must use the Item Definition component to define product IDs, descriptions, and standard units of measure. You then complete the product definition in the Product Definition component. |
| Components can be deleted |
Select to enable deletion of components in a product package. |
| Alternate Priority Required and Alternate Quantity Required |
Select to enter a priority and quantity on the Product Relationships page for an alternate relationship type. Select these check boxes when the PeopleSoft CRM system is integrated with PeopleSoft SCM. |
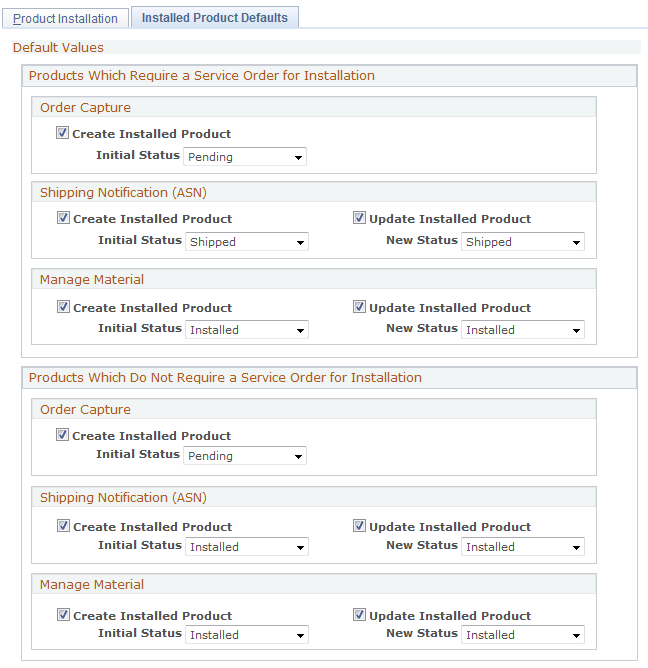
Use the Installed Product Defaults page (RF_INSTPRD_DFLT) to specify rules that determine how system transactions create and update installed products.
Navigation
Image: Installed Product Defaults page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Installed Product Defaults page.
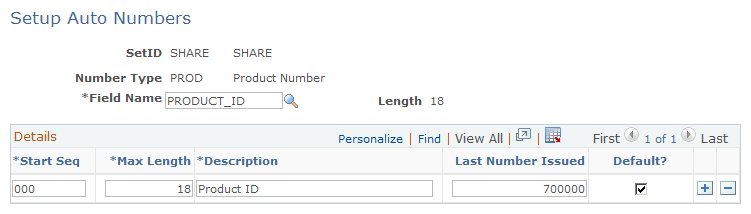
Use the Setup Auto Numbers page (AUTO_NUM_PNL) to Define automatic numbering options for product IDs.
Navigation
Image: Setup Auto Numbers page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Setup Auto Numbers page.
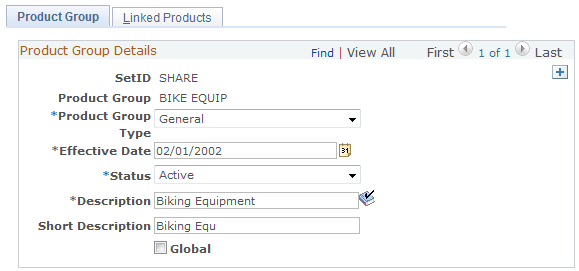
Use the Product Group page (PROD_GROUP_TBL) to define product group codes.
Navigation
Image: Product Group page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Product Group page.
Note: You cannot delete a product group from this page. If you integrate your PeopleSoft CRM applications with your PeopleSoft SCM applications, the system would also delete the product from your SCM database. This happens because SCM subscribes to a message that the CRM database publishes. If the system allowed you to delete the product group from this page, it could cause problems in your SCM operating environment. As such, this design is intentional.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Product Group Type |
Select the product group type from these values:
|
| Global |
Select to include all products in the product group. Note: This selection is not used for product groupings in the catalog. |
Use the Linked Products page (PROD_GRP_OVERVIEW) to view products that belong to a product group.
Navigation
Image: Linked Products page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Linked Products page.
This page displays the active products that are included in the product group.
Use the Product Category page (PROD_CATEGORY) to define product category codes.
Navigation
Image: Product Category page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Product Category page.
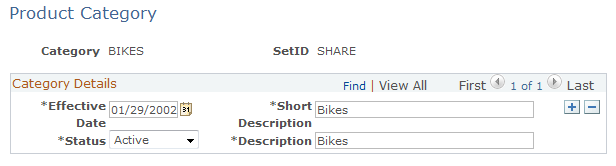
Use this page to define product category codes. Enter the date the product category will be effective, short and long descriptions, as well as the status; either Active or Inactive.
Use the Product Brand page (PROD_BRAND) to define product brand codes.
Navigation
Image: Product Brand page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Product Brand page.
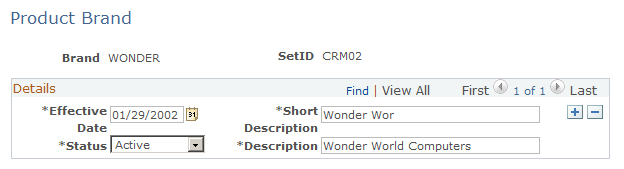
Use this page to define product brands. Enter the date the product brand will be effective, short and long descriptions, as well as the status; either Active or Inactive.
Use the Competitors page (COMPETITOR_CD) to define competitor codes.
Navigation
Image: Competitors page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Competitors page.
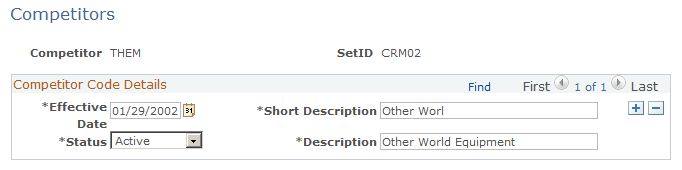
Enter competitor information on this page. Enter the date the competitor will be effective, short and long descriptions, as well as the status; either Active or Inactive..
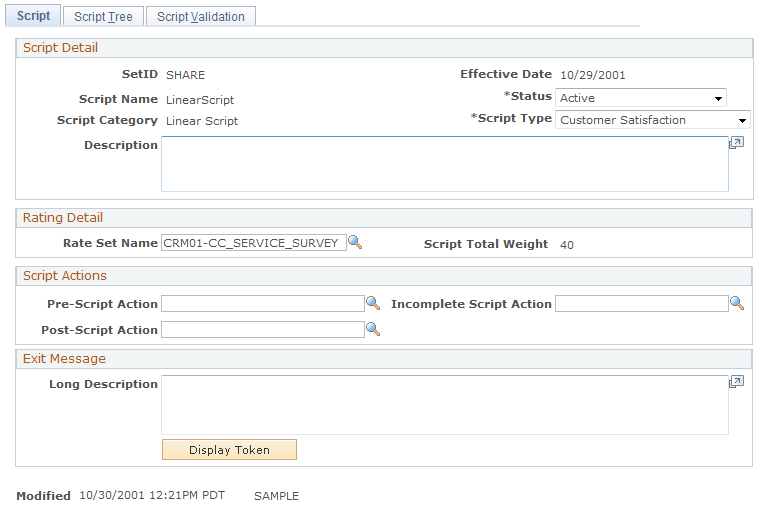
Use the Script page (RC_BS_MAIN) to define a branch script for support and sales personnel.
Navigation
Image: Script page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Script page.
Use the Product Relations Codes page (RB_RELATIONS) to set up the codes that describe relationships between products.
Navigation
Image: Product Relations Codes page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Product Relations Codes page.
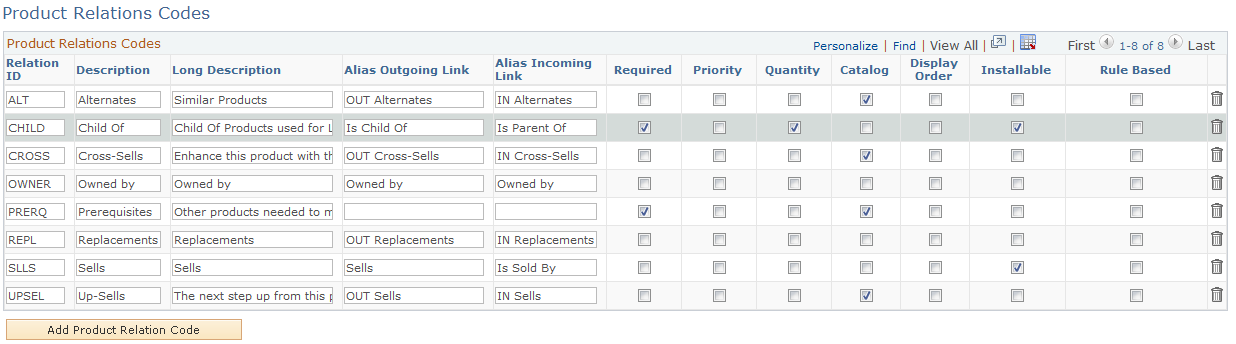
The Product Relations Codes page lists the possible relationships among products of all types that are supported in the product definition model. The options that you select for a relationship type determine the options that are available on the Product Relationships page when you define a product.
|
Field or Control |
Definition |
|---|---|
| Required |
Select to include the Required check box on the Product Relationships page. The Required check box enables you to require that the related product is present whenever the listed product appears. |
| Priority |
Select to include the Priority check box on the Product Relationships page. The Priority check box enables you to specify a priority among alternative related products. |
| Quantity |
Select to include the Quantity field on the Product Relationships page. The Quantity field enables you to specify how many times the given relationship can occur. |
| Catalog |
Select to include the Catalog check box on the Product Relationships page. The Catalog check box controls whether related products appear in the catalog along with the main product. |
Note: The product relations codes that appear in the preceding example are delivered as system data. You can add relations, but you should not remove any delivered relations.
These fields are not used in the CRM system: Alias Outgoing Link, Alias Incoming Link, Installable and Rule Based.
Use the Attribute Definition page (RB_ATTRIBUTE_MAIN) to define a product attribute.
Navigation
Image: Attribute Definition page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Attribute Definition page.
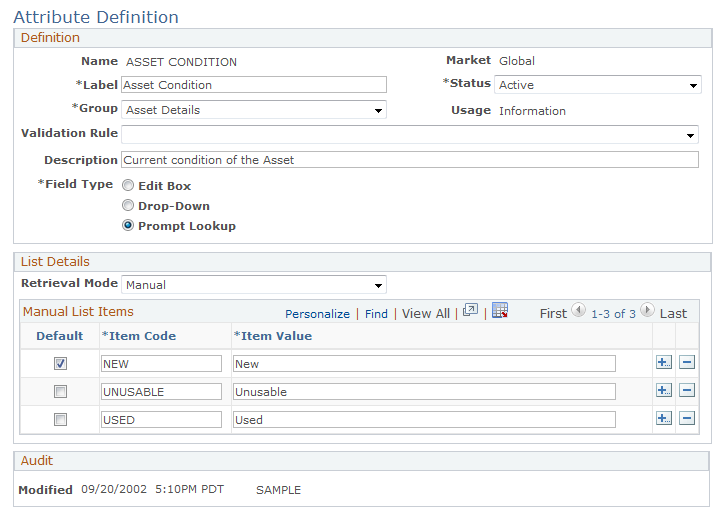
Warning! Although product attributes provide flexibility for modeling products, attributes can adversely affect runtime performance. We suggest that you not use more than a few attributes per product.