使用 Groovy 脚本执行 Financial Consolidation and Close 植入规则
按需规则 (On-Demand Rule, ODR) 允许在合并或转换过程之外执行计算。这对于业务要求不需要合计合并的情况很有用。按需规则还非常高效,对于满足快速计算需求非常有用。以下示例说明如何使用按需规则编写 Groovy 脚本规则。
方法 1 - 使用基于 EPM 云的命名连接
-
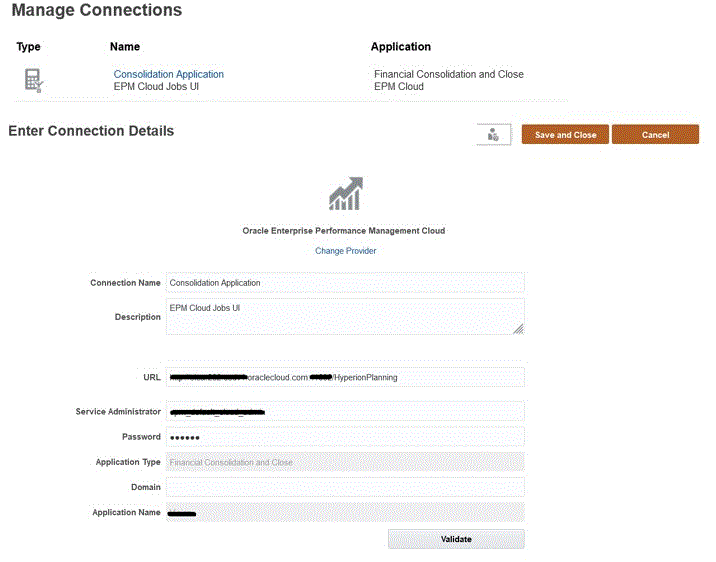
新建基于 EPM 云的连接。
-
提供以
/HyperionPlanning结尾的 URL。 -
提供服务管理员凭据。
-
提供域名。
-
单击验证以对连接进行验证。
-
单击保存并关闭。
Groovy 脚本示例 1
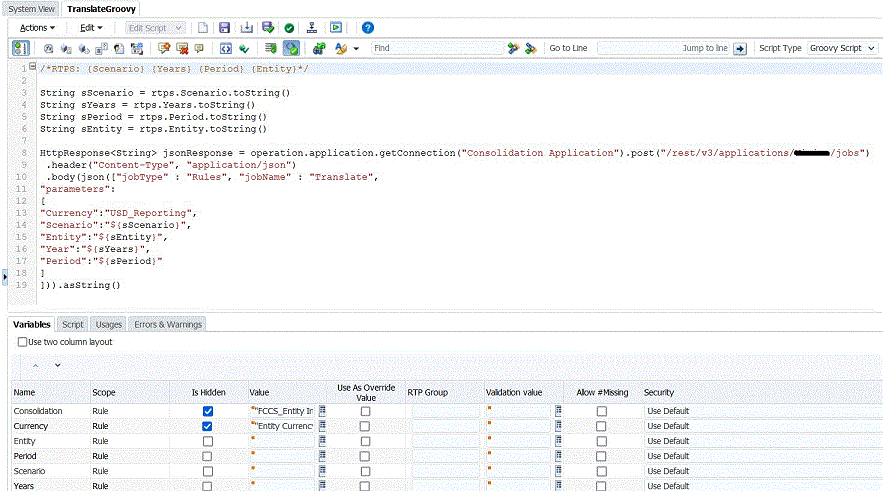
/*RTPS: {Scenario} {Years} {Period} {Entity}*/
String sScenario = rtps.Scenario.toString()
String sYears = rtps.Years.toString()
String sPeriod = rtps.Period.toString()
String sEntity = rtps.Entity.toString()
HttpResponse<String> jsonResponse = operation.application.getConnection("Consolidation Application").post("/rest/v3/applications/<AppName>/jobs")
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.body(json(["jobType" : "Rules", "jobName" : "Translate",
"parameters":
[
"Currency":"USD_Reporting",
"Scenario":"${sScenario}",
"Entity":"${sEntity}",
"Year":"${sYears}",
"Period":"${sPeriod}"
]
])).asString()
方法 2 - 使用其他 Web 服务提供商命名连接
-
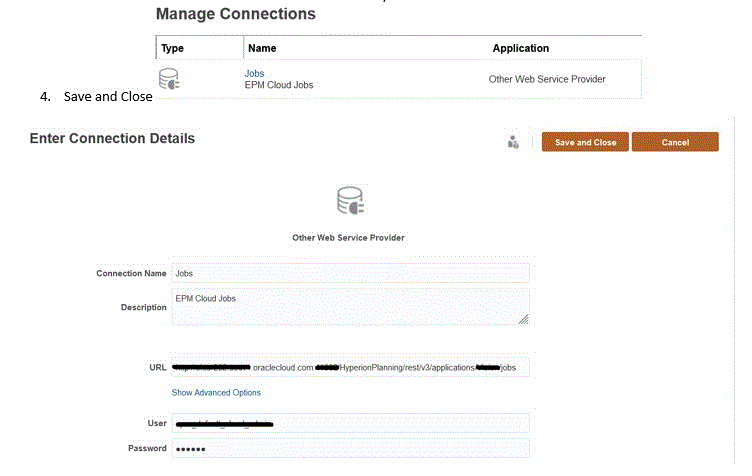
创建新的基于其他 Web 服务提供商的连接。
-
提供带有
/HyperionPlanning/rest/v3/applications/<AppName>/jobs的完整 URL。 -
提供要用于执行 Groovy 规则的用户凭据。
-
单击保存并关闭。
Groovy 脚本示例 2
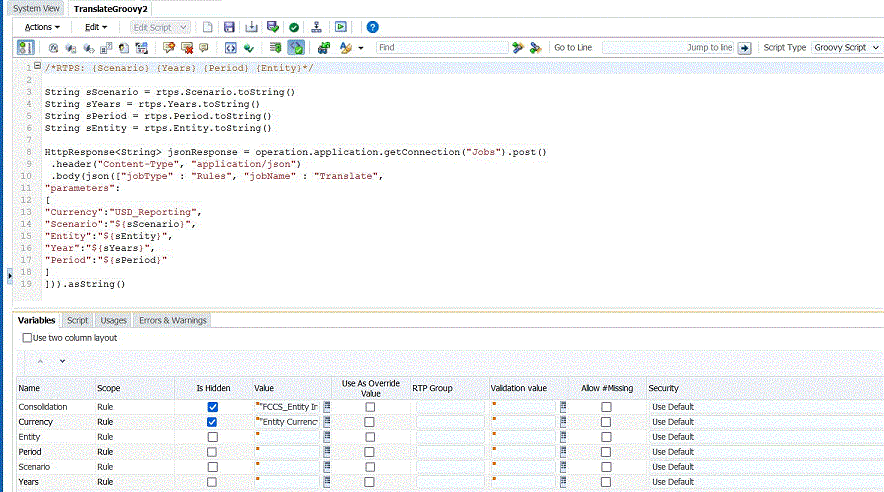
/*RTPS: {Scenario} {Years} {Period} {Entity}*/
String sScenario = rtps.Scenario.toString()
String sYears = rtps.Years.toString()
String sPeriod = rtps.Period.toString()
String sEntity = rtps.Entity.toString()
HttpResponse<String> jsonResponse = operation.application.getConnection("Jobs").post()
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.body(json(["jobType" : "Rules", "jobName" : "Translate",
"parameters":
[
"Currency":"USD_Reporting",
"Scenario":"${sScenario}",
"Entity":"${sEntity}",
"Year":"${sYears}",
"Period":"${sPeriod}"
]
])).asString()
使用上述方法之一创建连接之后,可以从规则卡或作业或使用 EPM Automate 执行基于 Groovy 的规则。