10 Managing Listeners
This chapter describes how to create, view, modify, and delete listeners. It contains the following topics:
Creating a Listener
You can create listeners by using either the administration console or the CLI.
Note:
-
When you create a listener, you are, in effect, modifying a configuration. So for the new listener settings to take effect in the Oracle Traffic Director instances, you should redeploy the configuration as described in Deploying a Configuration.
-
The CLI examples in this section are shown in shell mode (
tadm>). For information about invoking the CLI shell, see Accessing the Command-Line Interface.
Before You Begin
Before you begin creating an listener, decide the following:
-
A unique name for the listener. Choose the name carefully; after creating a listener, you cannot change its name.
-
A unique IP address (or host name) and port number combinations for the listener.
You can define multiple listeners with the same IP address combined with different port numbers, or with a single port number combined with different IP addresses. So each of the following IP address and port number combinations would be considered a unique listener:
10.10.10.1:80 10.10.10.1:81 10.10.10.2:80 10.10.10.2:81
-
For HTTP listeners: The default virtual server for the listener.
Oracle Traffic Director routes requests to the default virtual server if it cannot match the
Hostvalue in the request header with the host patterns specified for any of the virtual servers bound to the listener.For information about specifying the host patterns for virtual servers, see Creating a Virtual Server.
-
For HTTP listeners: The server name to be included in any URLs that are generated automatically by the server and sent to the client. This server name should be the virtual host name, or the alias name if your server uses an alias. If a colon and port number are appended to the server name then that port number is used in the autogenerated URLs.
-
For TCP listeners: TCP proxy for the listener.
A TCP proxy handles TCP requests through TCP listeners for traffic tunnelling. A TCP proxy can have several TCP listeners associated with it. You can associate TCP listeners and configure TCP proxy settings from this page.
For more information about creating TCP proxies, see Creating a TCP Proxy.
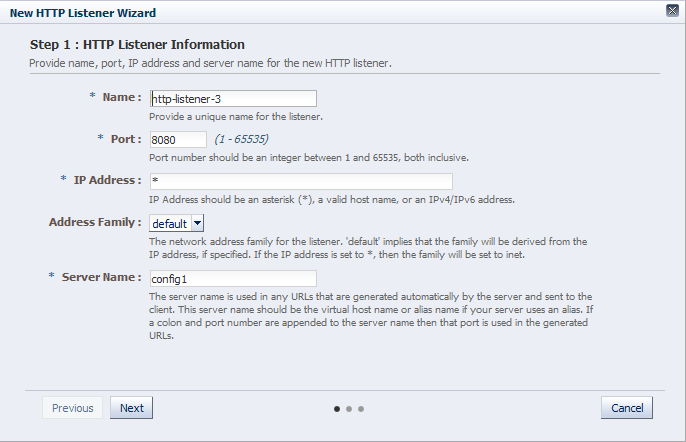
Creating an HTTP Listener Using the Administration Console
To create an HTTP listener by using the administration console, do the following:
-
Log in to the administration console, as described in Accessing the Administration Console.
-
Click the Configurations button that is situated at the upper left corner of the page.
A list of the available configurations is displayed.
-
Select the configuration for which you want to create an HTTP listener.
-
In the Common Tasks pane, click New HTTP Listener.
The New HTTP Listener wizard starts.
-
Follow the on-screen prompts to complete creation of the HTTP listener by using the details—listener name, IP address, port, and so on—that you decided earlier.
Note:
If certificates are available in the configuration, in the second screen of the wizard, an SSL/TLS check box will be available. If you want the new listener to receive HTTPS requests, click the check box to enable SSL/TLS and then select the appropriate certificate from the drop-down list.
After the HTTP listener is created, the Results screen of the New HTTP Listener wizard displays a message confirming successful creation of the listener.
-
Click Close on the Results screen.
-
The details of the listener that you just created are displayed on the Listeners page.
-
In addition, the Deployment Pending message is displayed at the top of the main pane. You can either deploy the updated configuration immediately by clicking Deploy Changes, or you can do so later after making further changes, as described in Deploying a Configuration.
-
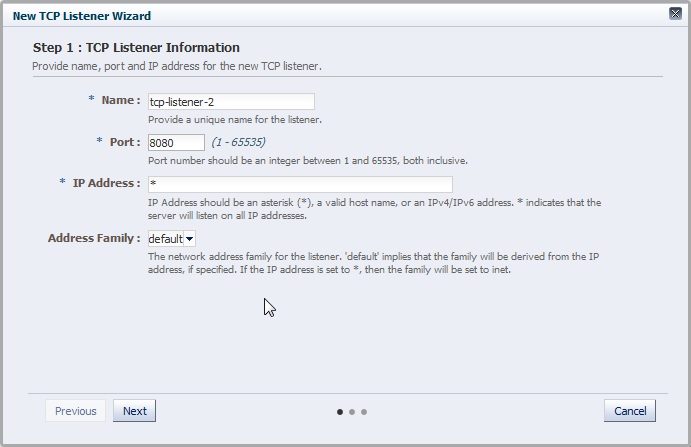
Creating a TCP Listener Using the Administration Console
To create a TCP listener by using the administration console, do the following:
Creating a Listener Using the CLI
-
To create an HTTP listener, run the
create-http-listenercommand.For example, the following command creates an HTTP listener named
listener_soafor the configurationsoa.example.comwith the port as1910and the default virtual server assoa.tadm> create-http-listener --config=soa.example.com --listener-port=1910 --server-name=soa.example.com --default-virtual-server-name=soa listener_soa OTD-70201 Command 'create-http-listener' ran successfully. -
To create a TCP listener, run the
create-tcp-listenercommand.For example, the following command creates a TCP listener named
tcp_listener_soafor the configurationsoa.example.comwith the port as1920and the TCP Proxy astcp_proxy1.tadm> create-tcp-listener --config=soa.example.com --listener-port=1920 --server-name=soa.example.com --tcp-proxy=tcp_proxy1 listener_soa OTD-70201 Command 'create-tcp-listener' ran successfully.
For more information about create-http-listener and create-tcp-listener, see the Oracle Traffic Director Command-Line Reference or run the command with the --help option.
For the updated configuration to take effect, you should deploy it to the Oracle Traffic Director instances by using the deploy-config command.
Viewing a List of Listeners
You can view a list of HTTP or TCP listeners by using either the administration console or the CLI.
Note:
The CLI examples in this section are shown in shell mode (tadm>). For information about invoking the CLI shell, see Accessing the Command-Line Interface.
Viewing a List of Listeners Using the Administration Console
To view a list of HTTP or TCP listeners by using the administration console, do the following:
You can view the properties of a listener in detail by clicking on its name.
Viewing a List of Listeners Using the CLI
-
To view a list of HTTP listeners, run the
list-http-listenerscommand, as shown in the following example:tadm> list-http-listeners --config=soa --verbose --all name ip port ssl-enabled default-virtual-server ----------------------------------------------------------------------- listener-1 * 1904 false vs1 listener-2 * 80 false vs1You can view the properties of an HTTP listener in detail by running the
get-http-listener-propcommand.For more information about the
list-http-listenersandget-http-listener-propcommands, see the Oracle Traffic Director Command-Line Reference or run the commands with the--helpoption.
-
To view a list of TCP listeners, run the
list-tcp-listenerscommand, as shown in the following example:tadm> list-tcp-listeners --config=soa --verbose --all name ip port ssl-enabled tcp-proxy-name ------------------------------------------------------------------------ listener-1 * 9090 false tcp_proxy1 listener-2 * 9092 false tcp_proxy1You can view the properties of an TCP listener in detail by running the
get-tcp-listener-propcommand.For more information about the
list-tcp-listenersandget-tcp-listener-propcommands, see the Oracle Traffic Director Command-Line Reference or run the commands with the--helpoption.
Modifying a Listener
You can modify listeners by using either the administration console or the CLI.
Note:
-
When you modify a listener, you are, in effect, modifying a configuration. So for the new settings of a listener to take effect in the Oracle Traffic Director instances, you should redeploy the configuration as described in Deploying a Configuration.
-
The CLI examples in this section are shown in shell mode (
tadm>). For information about invoking the CLI shell, see Accessing the Command-Line Interface.
Modifying a Listener Using the Administration Console
To modify an HTTP or TCP listener by using the administration console, do the following:
Modifying a Listener Using the CLI
-
To change the properties of an HTTP listener, run the
set-http-listener-propcommand. For example, the following command changes the port number of the listenerls1in the configurationsoato1911.tadm> set-http-listener-prop --config=soa --http-listener=ls1 port=1911 OTD-70201 Command 'set-http-listener-prop' ran successfully.
To change the SSL/TLS settings of an HTTP listener, run the
set-ssl-propcommand. For example, the following command enables SSL 3.0 support for the listenerls1in the configurationsoa. -
tadm> set-ssl-prop --config=soa --http-listener=ls1 ssl3=true OTD-70201 Command 'set-ssl-prop' ran successfully.
To change the properties of a TCP listener, run the
set-tcp-listener-propcommand. For example, the following command changes the port number of the listenertcp_ls1in the configurationsoato1911.
-
tadm> set-tcp-listener-prop --config=soa --tcp-listener=tcp_ls1 listen-queue-size=238 OTD-70201 Command 'set-tcp-listener-prop' ran successfully.
To change the SSL/TLS settings of an TCP listener, run the
set-ssl-propcommand. For example, the following command enables SSL 3.0 support for the listenertcp_ls1in the configurationsoa. -
tadm> set-ssl-prop --config=soa --tcp-listener=ls1 ssl3=true OTD-70201 Command 'set-ssl-prop' ran successfully.
For the updated configuration to take effect, you should deploy it to the Oracle Traffic Director instances by using the deploy-config command.
For a list of the properties that you can set or change by using the set-tcp-listener-prop and set-ssl-prop commands, see the Oracle Traffic Director Command-Line Reference or run the commands with the --help option.
Deleting a Listener
You can delete HTTP or TCP listeners by using either the administration console or the CLI.
Note:
-
When you delete a listener, you are, in effect, modifying a configuration. So for the updated configuration to take effect in the Oracle Traffic Director instances, you should redeploy the configuration as described in Deploying a Configuration.
-
The CLI examples in this section are shown in shell mode (
tadm>). For information about invoking the CLI shell, see Accessing the Command-Line Interface.
Deleting a Listener Using the Administration Console
To delete an HTTP or TCP listener by using the administration console, do the following:
Deleting a Listener Using the CLI
-
To delete an HTTP listener, run the
delete-http-listenercommand, as shown in the following example:tadm> delete-http-listener --config=soa http-listener-1 OTD-70201 Command 'delete-http-listener' ran successfully.To delete an TCP listener, run the
delete-tcp-listenercommand, as shown in the following example:tadm> delete-tcp-listener --config=soa tcp-listener-1 OTD-70201 Command 'delete-tcp-listener' ran successfully.
For the updated configuration to take effect, you should deploy it to the Oracle Traffic Director instances by using the deploy-config command.
For more information about delete-http-listener and delete-tcp-listener, see the Oracle Traffic Director Command-Line Reference or run the command with the --help option.