Obtaining geocode information from attribute values
You can create a full set of geocode attributes (country, region, subregion, etc.) based on any String attribute that has partial address information. The full set of geocode attributes allows you to display the geographic information in a Thematic Map.
For details about using the geocode attributes in a chart, see Thematic Map. For details about using geocode (geotag) functions and their data type requirements, see Enrichment functions.
To obtain geocode information from attribute values:
Example 19-1 Example
Suppose your source data has attributes named city, county, and zip_code with values that represent city names, county names, and postal codes in the state of California:
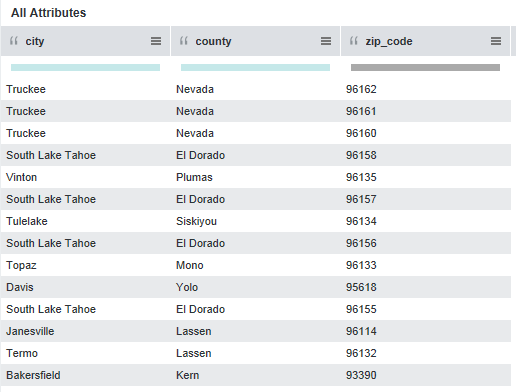
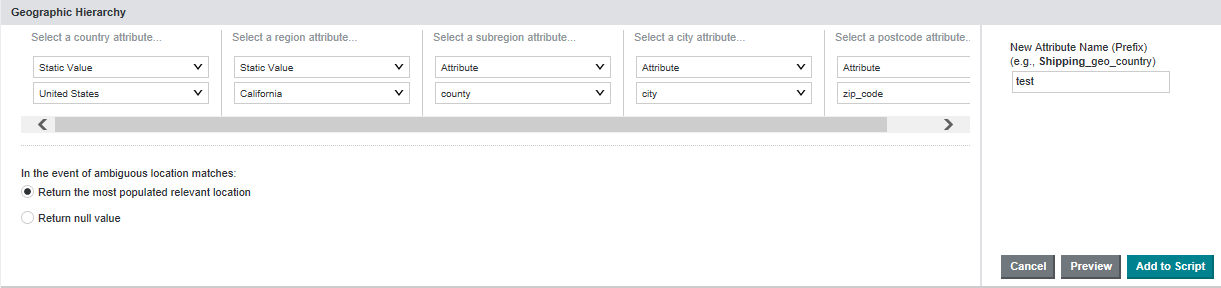
However, the source data does not have country or state information. You can create the geocode attributes by setting the Create Geographic Heirarchy as follows:
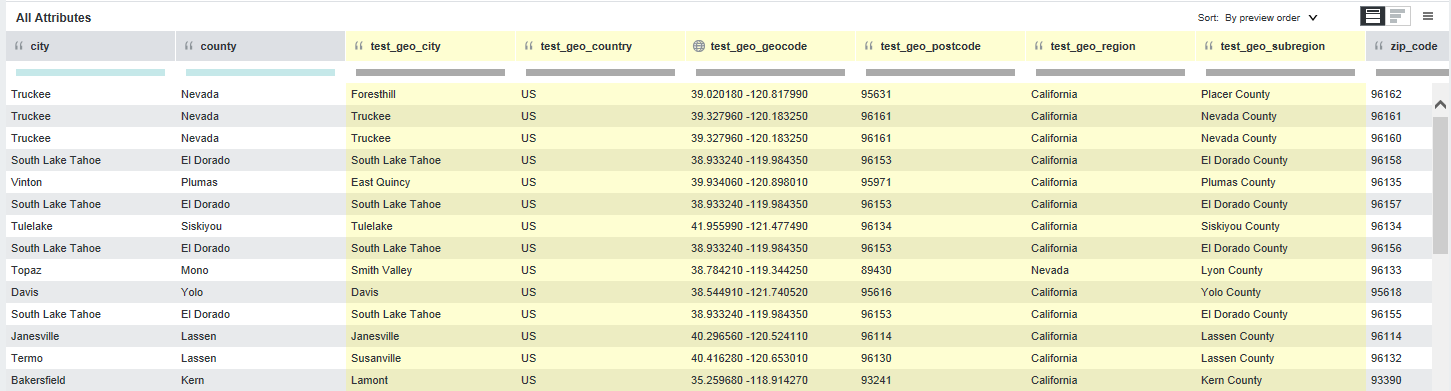
After you click Preview, you see that Studio created the following new geocode attributes highlighted in yellow:
If you are done making changes to the project data set, you can commit the changes. See Running the transformation script against a project data set.