Creating a Topic
On the Topics tab in Listen & Analyze, you can create and manage topics, which are search queries that collect mentions of a brand, product, industry, etc. from the social space. In this article, we'll take you step by step through creating a topic.
You can work with the Topics tab if you are an Oracle Social Engagement and Monitoring customer.
In this article:
Creating Topics Without Search Terms
Advanced Options
· Boolean Conditions
· Keywords
· Topic Scope
Targeting
· Location
· Content Type
· Indicators
· Source URLs
· Authors
Saving a Topic
· Previewing a Topic
· Themes
· Media Types
Click a link above to get directly to that section, or scroll down and start reading.
What is a Topic?
As we said before, topics are search queries that collect mentions of a brand, product, industry, or any topic of interest from the social space. You can use topics to analyze conversations to determine how a particular product is doing, to understand the opinions around your competitors' brands, to surface customer service issues through routing topics through Engage and more.
Creating Topics
To create a new topic, you must first select a specific bundle to create it in. You cannot create topics in your top level bundle.
To do this, select a bundle using the bundle picker. When the bundle loads, you'll be on the Topics page for that specific bundle, and will see only the topics that have been assigned to that particular bundle. The New Topic button will now be active - click it to begin creating your new topic.
TO CREATE A TOPIC:
First, select the bundle you want your topic to be created in. Click NEW TOPIC. You will be taken to the Create a New Topic page.
Fill out the following fields:
- Topic Name - Give your topic a name. We suggest something that will help you remember what the topic is covering.
- Language - Choose a language you want the topic to search. This will only provide results in the chosen language – the user language you have selected in Workflow & Automation is chosen by default unless that language is not yet available for topic creation. In this case, English is the default.
- The languages you can search are:
- Arabic
- Bahasa
- Bulgarian
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Finnish
- French
- German
- Greek
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Hungarian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Korean
- Latvian
- Norwegian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Romanian
- Russian
- Simplified Chinese
- Spanish
- Swedish
- Tamil
- Thai
- Traditional Chinese
- Turkish
- Vietnamese
- Search Term - Type a term or phrase and press Enter or click Add button to add them to your topic to be searched. All the terms you add to the topic will show on the right hand side in the Topic Properties section. You can enter multiple terms, phrases, or a combination of both.
For example, enter oracle to retrieve all conversations containing the term oracle. Click x on the term or phrase under Included Search Terms to remove it.By default, Listen looks for search terms on the subject and body of web pages, but not in URLs. This helps minimize spam content being collected for your topic. However, if you would like the term to be searched in URLs of the subject and body, check the Find search terms/keywords in URL box beneath the search term field.
Note: You can add up to 1,000 search terms/keywords. There's a counter in the Topic Properties box that shows you how many search terms/keywords you have added so you can easily keep track.
After you enter your search terms, you can preview a representative sample of social conversations to help you evaluate and refine your topic. This is fully covered in the Preview section below.
To learn how to create topics without search terms, see the Creating Topics Without Search Terms topic.
How Do Search Terms Work?
Our search terms are optimized to give you the most results. Just by entering simple terms, you'll get results covering multiple versions of that term.
The topic will search using the OR operator by default with the terms and phrases. For example, if you enter the terms oracle and ORCL, then your results will contain the term oracle OR the term ORCL.
(To add AND terms to your search, add keywords under the Advanced Options section.)
Punctuation & Symbols
With many search tools, you have to enter every permutation of a term to capture results that use all those variations. In topic search terms, we've simplified that. Let's look at an example:
When you enter oracle as a search term, not only will you get back mentions containing the string oracle, but also:
oracle
oracle.
oracle?
oracle!
oracle,
oracle;
oracle:
oracle-
(oracle)
[oracle]
{oracle}
oracle’
“oracle”
oracle…
#oracle
@oracle
oracle_
oracle/
By simply entering the term without capitalization or symbols, Listen will automatically return those results for you.
Note: Listen's search can handle nonspace languages like Chinese and Japanese. For example, if you search for "oracle", and in Japanese the mention says "oraclecloudisgood", the Listen categorizer knows to separate that out into "oracle" "cloud" "is" "good", so this mention will be returned.
Specific Searches
If you do enter a search term that uses punctuation or symbols, Listen will only return results for exactly what you entered. SO, If you enter #oracle, you will only see mentions that have #oracle. It will NOT include oracle as a result. This is handy if you have a very specific result you want returned.
Note: This includes case sensitivity. If you want a general result, use lower case with your search term.
Punctuation and Symbol Rules
If you use the following punctuation or symbols with your search term, it will return specific results for that mark/search term combo:
period
question mark
exclamation point
comma
semicolon
colon
dash/hyphen
parentheses
brackets
braces
apostrophe
quotation mark
ellipses
hashtags
@symbol
underscore
slash
case sensitivity
Note: Topics containing only punctuation marks in the Search Term field are not supported. Punctuation marks are any one of the following symbols:
- .
- @
- \
- '
- :
- !
- -
- &
- ?
- ;
- #
Oddities
There are certain types of search terms that can complicate the results you get, Camel Cases and Numbers.
- Camel Cases - Camel cases are compound words or phrases where both words are capitalized. For example, PowerPoint. The search will recognize this as one word, "powerpoint" and will only find mentions that contain "powerpoint" as one word.
- Numbers - Numbers are treated the same as letters in search. So searching for oracle will not return oracle123. But since they are treated the same as letters, all the punctuation and symbol rules apply (see the examples above).
Our search recognizes these terms as one word, so searching for power will not return PowerPoint. Keep that in mind when you are entering these as search terms.
Creating Topics Without Search Terms
Using search terms allows you to pinpoint relevant social posts and conversations, but sometimes you want to see the whole conversation. Most Listen topics require a search term to be entered. However, the following types of content can be retrieved without specifying a search term:
- Twitter Posts from a Twitter Account
- All Facebook Posts and Comments Made on a Particular Public Facebook Page
- Public Facebook Posts and Comments from a Specific Facebook Account
- Facebook Comments Made in Response to a Facebook Post
- Reviews of a Product
- Replies to a Message Board Post
- Comments on a Blog Post
- YouTube Posts
- Custom Data Source Analyzer API
Twitter Posts from a Twitter Account
To collect Twitter posts from a Twitter account:
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Select Microblogs as your Content Type.
- Specify the Twitter handles into the Authors section.
All Facebook Posts and Comments Made on a Particular Public Facebook Page
To collect all Facebook posts and comments made on a particular public Facebook page:
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the URL of the Facebook page in the Source/Post URL section.
For example, if you set up your topic using the Source/Post URL of facebook.com/OracleSocial, all posts and comments made on the Oracle Social Facebook page will be returned, regardless of who posted it, whether it be Oracle Social or an individual user.
Note: Replies to Facebook comments are not currently collected.
Public Facebook Posts and Comments from a Specific Facebook Account
To collect public Facebook posts and comments from a specific Facebook account:
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Select Social Sites as your Content Type.
- Then type facebook.com in the Source/Post URL section.
- Specify the name of the Facebook page, as it appears on Facebook, into the Authors section.
For example, if you set up your topic using the Source/Post URL of Facebook.com and the Author "Oracle Social", all posts and comments made on the Oracle Social Facebook page by Oracle Social will be returned. Also, comments that Oracle Social makes on other public pages will be returned. Comments or posts by anyone other than Oracle Social will not be returned.
Note: Replies to Facebook comments are not currently collected.
Facebook Comments Made in Response to a Facebook Post
To collect Facebook comments made in response to a Facebook post:
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the URL of the Facebook post in the Source/Post URL section.
Note: Replies to Facebook comments are not currently collected.
To determine the URL that you should specify in the Source/Post URL section:- Navigate to the Facebook post.
- Click the post timestamp.
Note: The post timestamp is located to the right of the profile picture and below the profile name within post.
- Copy the URL.
- Determine the Facebook Page ID and the Post ID:
- Photo Posts - The URL will look similar to the following:
https://www.facebook.com/FoxNews/photos/a.184044921335.134777.15704546335/10154447630211336/?type=3&theater
In this example URL:
- 15704546335 is the Page ID
- 10154447630211336 is the Post ID
- Video Posts - The URL will look similar to the following:
https://www.facebook.com/FoxNews/videos/10154447903311336
In this example URL, 10154447903311336 is the Post ID.
- Other Posts - The URL will look similar to the following:
https://www.facebook.com/FoxNews/posts/10154447814161336
In this example URL, 10154447630211336 is the Post ID.
- Photo Posts - The URL will look similar to the following:
- (Optional) To determine the Facebook Page ID for URLs in which the Page ID does not appear, use Facebook's Graph API Explorer:
- Formulate the URL for Listen using this format: facebook.com/<Page ID>/posts/<Post ID>
Based on the example URLs in Step 4, the Listen source URL: facebook.com/15704546335/posts/10154447630211336
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the iTunes review page URL in the Source/Post URL section.
- Using a browser, navigate to the item for which you want to collect reviews.
- Copy the URL.
- Determine the ID of the item. The item ID is at the end of the URL, and is preceded by "id". For example, in the following URL:
https://itunes.apple.com/us/app/pokemon-go/id1094591345
id1094591345 is the item ID.
- Formulate the URL for Listen using this format: itunes.apple.com/customer-reviews/<Item ID>
Based on the example URLs in Step 3, the Listen source URL is: itunes.apple.com/customer-reviews/id1094591345
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the Google Play review page URL in the Source/Post URL section.
- Using a browser, navigate to the item for which you want to collect reviews.
- Copy the URL.
- Determine the ID of the item. The item ID is at the end of the URL, and is preceded by "id=". For example, in the following URL:
https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.nianticlabs.pokemongo
id=com.nianticlabs.pokemongo is the item ID.
- Formulate the URL for Listen using this format: play.google.com/store/apps/details?<Item ID>
Based on the example URLs in Step 3, the Listen source URL is: play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.nianticlabs.pokemongo
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the Amazon review page URL in the Source/Post URL section.
- Using a browser, navigate to the Amazon product page for which you want to collect reviews.
- Click the <number> customer reviews link.
- Click the See all <number> customer reviews link.
- Copy the URL.
- Determine the product name of the item. The name in the URL after amazon.com, and is between slashes (/). For example, in the following URL:
https://www.amazon.com/Amazon-Kindle-Voyage-6-Inch-4GB-eReader/product-reviews/B00IOY8XWQ
Amazon-Kindle-Voyage-6-Inch-4GB-eReader is the product name.
- Determine the product ID of the item. The product ID is at the end of the URL, after the last slash (/). For example, in the following URL:
https://www.amazon.com/Amazon-Kindle-Voyage-6-Inch-4GB-eReader/product-reviews/B00IOY8XWQ
B00IOY8XWQ is the product ID.
- Formulate the URL for Listen using this format: amazon.com/<Product Name>/product-reviews/<Product ID>
Based on the example URLs in Steps 5 and 6, the Listen source URL is: amazon.com/Amazon-Kindle-Voyage-6-Inch-4GB-eReader/product-reviews/B00IOY8XWQ
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the URL of the message board post in the Source/Post URL section. The following are example URLs:
- forum.slowtwitch.com/forum/Slowtwitch_Forums_C1/Triathlon_Forum_F1/Best_cadence_for_Ironman_P6030705
- iwindsurf.com/forums/viewtopic.php?t=31573&sid=fd55914c583318521300f0fd88551294
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Specify the URL of the blog post in the Source/Post URL section. The following are example URLs:
- insideevs.com/tesla-service-centers-get-new-fast-lane-address-minor-car-issues-quickly
- insideevs.com/elon-musk-commends-tesla-owners-rebuttal-consumer-reports-call-disable-autopilot
- Navigate to the Listen topic creation page.
- Select Videos as your Content Type.
- Specify the name of the YouTube page in the Authors section.
- Content contains one or more keywords: Retrieves social media content that contains one or more of the keywords you enter in advanced options. For example, if your main topic search terms are Oracle and ORCL, selecting this option and entering Sun and server as advanced keywords, your topic will retrieve social content that contains the following terms:
Oracle and sun OR Oracle and server
OR
ORCL and sun OR ORCL and server
- Content contains all keywords: Retrieves social media content that contains all the keywords you enter in advanced options. Using the previous example, if you select this option, your topic will retrieve social content that contains the following terms:
Oracle and sun and server
OR
ORCL and sun and server
- Content does not contain keywords: Excludes social media content containing the keywords you enter in advanced options. Using the previous example, if you select this option, the system would exclude social content that contains the following terms:
Oracle and sun OR Oracle and server
OR
ORCL and sun OR ORCL and server.
- Case Sensitive - Only results matching the included symbols, numbers, and/or punctuation entered in the Keyword field should be returned. If you enter multiple keywords, Case Sensitive will apply separately to each keyword entered.
For example, Oracle would not return mentions of oracle or OrAcLe.
- Message Boards - Thousands of sites, including Reddit, Yahoo Answers, freeforum.net, proboards.com, etc
- Blogs - Millions of sites, including Wordpress, Quora, Yelp blogs, etc
- News - Thousands of sites, including mainstream news sites like CNN.com, Wikipedia, etc
- Microblogs - Twitter, TenCent Weibo (Add On Data Source)
- Social Sites - Facebook, Google+
- Consumer Reviews - Hundreds of sites, including Amazon, GooglePlay, Indeed, Glassdoor, iTunes, Consumer Affairs, etc
- Videos - YouTube
- Custom - CDSA API data (Add On Data Source)
- facebook.com/disney -> Include
- facebook.com/disney/pixar -> Exclude
- facebook.com/disneyland -> Exclude
- More Like This: Click this button to include a theme that has messages you definitely want in your topic.
- Less Like This: Click this button to exclude a theme that has messages that you definitely don't want in your topic.
Reviews of a Product
iTunes Reviews
To collect iTunes reviews:
To determine the iTunes review URL to specify in the Source/Post URL section:
Google Play
To collect Google Play reviews:
To determine the Google Play review URL to specify in the Source/Post URL section:
Amazon
To collect Amazon reviews:
To determine the Amazon review URL to specify in the Source/Post URL section:
Note: Listen provides review content for some of the most popular Amazon products. If after several days you still do not get reviews that you are searching for, please log an SR or contact your Oracle Social Representative.
Replies to a Message Board Post
To collect replies for a message board post:
Comments on a Blog Post
To collect all comments to a blog post:
Note: Listen can collect blog comments from blogs that host their own comments. Listen does not collect blog comments from blogs that use a third party comment system.
YouTube Posts
To collect YouTube posts from a specific YouTube account:
Note: Comments on YouTube posts are not currently collected.
Custom Data Source Analyzer API
You do not need to use a Search Term for a topic you have created for a Custom Data Source. For more information on CDSA, refer to Custom Data Source Analyzer API.
Working With Advanced Options
Advanced options are optional and help you further filter your search by adding a keyword/phrase or content type to look for specific conversations. For example, you could track a campaign by searching for the campaign hashtag, or target the conversation around specific products by searching for mentions of an advertisement or gift certificate for that product.
To add advanced options, click Advanced Options on the Create A Topic page. There you'll see three sections, Boolean Conditions, Keywords, and Topic Scope.
Boolean Conditions
Boolean Conditions refine your searchs by comparing two values to each other. Here, we use options with additional keywords so you get exactly the results you want. There are three options for you to use:
Keywords
Use keywords with a boolean condition to help refine the content coming in from your main search terms.
To add a keyword, type a term or phrase and hit Enter or click Add to add them to your topic. You'll see them displayed in the Topic Properties section on the right side of the screen. You can add multiple keywords. To remove a keyword, click X on the keyword in the Topic Properties section.
Users have the option to conduct Case Sensitive searches in Advanced Options by selecting the appropriate checkbox under the keyword field.
Topic Scope
Note: You will only see this option if you have Custom Data enabled for your account. For more info on Custom Data, please see the Custom Data Source Analyzer help article.
The Topic Scope section is where you choose what kind of topic you are creating. If you are creating a topic for a Custom Data Source, then you choose Custom For a normal topic, choose Semantic API. You must choose a topic scope before you can create your topic.
Working With Targeting Options
Targeting Options are also optional, and allow you to target a specific segment of conversation by filtering your search by demographic information. For example, you could create topics searching for campaign results in different countries to compare them against one another or only search for conversations in a specific region to limit message volume.
To add targeting options, click Targeting Options on the Create A Topic page. There you'll see five sections, the Location filter, Content Types, Indicators, Source/Post URLs, and Author.
You can add up to 1,000 targeting options. There's a counter in the Topic Properties box that shows you how many targeting options you have added so you can easily keep track.
Location Filter
Click on countries and/or regions to include or exclude from your topic search. All countries are included by default. Once you’ve started including locations, you will not be able to exclude specific locations unless you clear your selection(s) and vice versa. You can clear your selection(s) by clicking the Reset to include all locations link or by clicking x next to each location in your Topic Properties.
Note: No Location is for messages that have no location attributed to them. You can include or exclude messages like this by selecting this option.
Content Types
You can also include or exclude certain content types from your search:
Indicators
In this section, you can include or exclude custom or standard indicators in your topic search. Adding an indicator allows you to take advantage of all the Dashboard charts when combining topics and indicators.
Source/Post URLs
Enter in any URLs that you want to include or exclude from your topic search. This will pull in messages that contain this exact URL in them.
Source URL also supports using both include and exclude options at the same time. This is helpful when filtering URLs that have substrings that you might or might not want. For example, if you include "facebook.com/disney”, the following URLs are also returned: "facebook.com/disneyland" and "facebook.com/disney/pixar".
If you do not want "facebook.com/disneyland" and "facebook.com/disney/pixar”, enter:
Using the above example, Disney Facebook pages are returned, but the Pixar and Disneyland ones are not.
Bulk Include/Exclude
You can also include or exclude multiple URLs at one time. Clicking either button will open a modal, allowing you to upload a CSV file with all the source/post URLs you want to include or exclude in your topic.
Note: Do not include the http:// from the URL.
Author
Enter in any names of authors you want to include or exclude from your topic search. For Twitter, enter their Twitter handle; for Facebook, enter their Facebook username; for YouTube and blogs, enter the name on their channel or blog name.
For Twitter and Facebook authors, a search term is not required. This allows for the collection of all public posts from a Twitter or Facebook account without specifying any words to match.
For example, the following topic definition will collect all public posts by Le Monde.fr on any Facebook page that has been added to the SRM collection list using the Manage Facebook Pages link on the main Topic page of the SRM account:
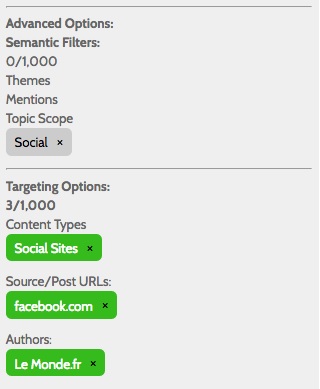
The following topic definition example collects all posts made by @oraclesocial on Twitter:
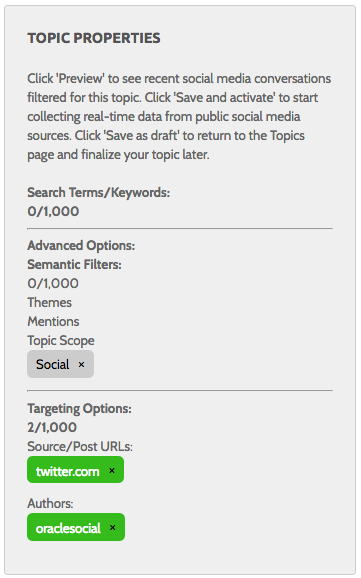
Bulk Include/Exclude
You can also include or exclude multiple Authors at one time. Clicking either button will open a modal, allowing you to upload a CSV file with all the Authors you want to include or exclude in your topic. You can also select whether you want to do a Contains or Exact Match search from this modal.
Contains and Exact Match
By default, the Author field supports a Contains type match. The Contains type match looks for any Author that contains the Authors you have entered.
For example, if you use ILUVYOU as a filter, the following entries are returned: ILUVYOU and ILUVYOUMOM.
If you want an Exact Match, you can select the radio button to switch to Exact Match. The Exact Match will only look for Authors that match exactly what you have entered.
For example, if you use ILUVYOU as a filter, only the following entry is returned: ILUVYOU. ILUVYOUMOM will not be returned.
Saving a Topic
You have three options when you need to save your topic, Save and preview, Save as draft, and Save and activate. These options are all in the drop down Save button above the Topic Properties box. Each of these options does something different, so let's go through each one.
Preview
Preview is fully featured and won't cost you any messages for your account. Preview provides a 90 day sample of up to 1,000 social posts which match your topic criteria. This historical sample of social posts which match your topic will give you a good indication of what type of content will be returned for a topic. All content types are reflected in Preview. All Targeting Options selected will be used to filter Preview content.
Since Preview shows a historical sample, the social posts you see in Preview will not be included in your topic when you save and activate it. Listen topics only gather content from the point in time they are created or modified. Preview is meant to guide your topic creation efforts. Preview content does not appear in new topics.
If you want to get a preview of your topic, click Save and Preview. Your info will be saved, and a preview of the themes and social media messages the topic will collect will appear at the bottom of the page. The preview will show you info in three sections, Messages, Themes, and Media Types.
Note: The Preview feature is not a live capture of messages in real time.
Preview what has been returned in these sections to help evaluate your topic's results. If you aren't getting the right results, change the search terms, advanced options, and themes in your topic until the content you are getting matches what you want.
Your topic is in draft status and can be changed as often as you need while in Preview. Remember to click Preview again after you make any changes so those new results are displayed below.
Messages
This tab displays a sample of the social media messages the topic is retrieving, and a timeline showing you when those messages were posted. You can sort these messages by source or date. If the messages are not what you want to topic to retrieve, try modifying your topic options.
The timeline displays message volume in a particular date range. Hovering over the timeline will show you daily message volumes.
Themes
This tab shows you themes for the messages the topic is retrieving. These themes group related messages by their contextual meaning. For example, the term Java is used in the context of programming as well as coffee. So searching for Java would give you different themes for those two contexts.
Clicking a theme shows you a word cloud of the terms that are used most often used in the messages that fall into that theme. The size of the term indicates its frequency in the messages. You'll also see a selection of messages that fall in the selected theme.
To help refine your topic, you choose whether the theme is providing the kind of messages you want. You'll see two buttons at the top of the theme:
Note: There is no need to include or exclude every theme. Only include or exclude themes that are clearly desirable or undesirable. For example, if you are interested in the Java programming language, then the coffee theme is of no interest and should be excluded.
Media Types
This tab displays a pie chart of the content types where your messages are coming from. Clicking on a pie slice displays a selection of messages from that content type.
If you are not getting desirable messages from a particular content type, you can exclude it in the Advanced Options section.
Save as draft
When you save a topic as a draft, all the options you have set for the topic will be saved, but the system will not beging collecting messages for the topic. You can come back and make changes, preview the topic, and activate it once you are ready.
Save and activate
When you are satisfied with all your topic options, click Save and activate button. The system will begin monitoring the social web and retrieving messages.
Note: After a topic is activated, it takes about 15-30 minutes to begin collecting data. You will not see analytics in the Dashboard for the topic until data collection begins. Depending on the Content Types being collected, the data may take 15-30 minutes to come in, to a couple days.
Once you have activated your topic, you will see it in the Topics Grid with a green circle under the Status column, showing it is active.
Note: Your new topic will not include social posts which were shown in Preview.