Protect Exadata Database
Learn about various data protection methods available for Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
Data in Transit Encryption
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure is protected with encryption of data in transit by default. This ensures that data moving between application and the database is secured from unauthorized interception or tampering. Oracle Net Services supports multiple industry-standard encryption algorithms including AES, DES, 3DES, and RC4 for securing data in transit. It also offers MD5, SHA-1, and SHA-2 hashing algorithms to verify data integrity.
- TCPS (Secure TCP) Connections
- Uses TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3.
- Requires a downloadable connection wallet.
- Ensures symmetric encryption via secure handshake using the wallet.
- TLS 1.3 support is available starting with Oracle Database 26ai.
- TCP Connections with Native Network Encryption
- Uses Oracle’s built-in encryption protocol.
- Negotiates encryption during connection (AES-256, AES-192, AES-128).
- No wallet is required but connection details such as
tnsnames.oramust be known.
By default, database deployments on Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure is configured to enable native Oracle Net Services encryption and integrity. Additionally, Oracle Net Services clients are configured to enable native encryption and integrity when connecting to an appropriately configured server. If your Oracle Net Services client is explicitly configured to reject the use of native encryption and integrity, connection attempts will fail.
sqlnet.ora parameters are set by default in Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
- ENCRYPTION_TYPES_SERVER = (AES256, AES192, AES128)
- ENCRYPTION_SERVER = requested
- CRYPTO_CHECKSUM_SERVER = accepted
- CRYPTO_CHECKSUM_TYPES_SERVER = (SHA256, SHA384, SHA512)
/var/opt/oracle/dbaas_acfs/grid/tcps_wallets. The following sqlnet.ora parameters are set by default in Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
- SSL_CIPHER_SUITES = (SSL_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
- SSL_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,
- SSL_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,
- SSL_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384)

Data at Rest Encryption
Oracle Database@AWS supports encryption at rest to safeguard sensitive data residing in database files, backups, and configuration files. This protection is enabled by Transparent Data Encryption (TDE), which ensures that data is encrypted whenever it is written to persistent storage and transparently decrypted when accessed by authorized Oracle processes with no customer configuration is required. The master key encrypts tablespace keys, which in turn encrypt the data.
Transparent Data Encryption (TDE)
Encryption at rest is provided through TDE, a feature included in Oracle Advanced Security. TDE automatically encrypts tablespaces, redo logs, and undo logs, ensuring that all database data is written to disk in encrypted form and transparently decrypted for authorized users and applications. Database backups created using Oracle Recovery Manager (RMAN) or managed backup solutions adopt these encryption settings, protecting all database copies stored on persistent media.
Key Management
- Oracle-managed keys: The master encryption key is automatically generated and stored in an Oracle Wallet, which is secured within the database environment. Oracle handles all key lifecycle tasks, including backups and restores.
- Customer-managed keys: You can integrate with OCI Vault to generate and store the master encryption key outside the database, enabling centralized key control, lifecycle management, rotation, and auditing of key usage events. With customer-managed keys, you control the encryption keys used to protect your data. You can enable customer-managed keys when creating databases, switch from Oracle-managed to customer-managed keys, and rotate keys to meet security and compliance requirements.
- Oracle-managed Key (OMK)
- Oracle Wallet
- Customer-managed Key (CMK)
- OCI Vault
- Oracle Key Vault (OKV)
- AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS)
() is the default method for securing data encryption in Oracle Database@AWS. In Oracle Database, data encryption at rest is powered by TDE. When you choose , the database system automatically handles all key management, including key generation, secure storage, and rotation required by TDE. There are no prerequisites or additional configuration steps required to use on Oracle Database@AWS.
View Encryption Details- From Oracle Database@AWS dashboard, select Oracle Exadata VM clusters, and then select your Exadata VM Cluster that you are using.
- Select the Manage in OCI button, which redirects you to the OCI console.
- In the OCI console, select the Databases tab, and then select the database that you want to check the key management.
- From the Database information tab, navigate to the Encryption section to view the Encryption key details. By default, the Encryption key is set to Oracle-managed key.

- Manage Encryption Key
- From Oracle Database@AWS dashboard, select Oracle Exadata VM clusters, and then select your Exadata VM Cluster that you are using.
- Select the Manage in OCI button, which redirects you to the OCI console.
- From the OCI console, select the Databases tab, and then select the database that you want to change the key management or rotate the encryption key.
- Select the More Actions button, and then select the Manage encryption key option.
- From the Manage encryption key page, select the Encryption type as Change Key Management Type.
- From the Choose a key type section, you can select either OCI Vault service or Oracle Key Vault.
- If you choose the OCI Vault service as a key type, complete the following substeps.
Note
You must have a valid encryption key available in the OCI Vault service.- The Compartment is selected by default. If you want to change your compartments, select the compartment that contains your vault.
- The Compartment is selected by default. If you want to change your compartments, select the compartment that contains your vault.
- From the Vault dropdown list, select the vault that contains your key.
- The Compartment is selected by default.
- From the Master encryption key dropdown list, select the key that you want to use.
- Enable the Choose the key version option, if you want to use a specific version of the key.
- Enter the OCID of the key version.
Note
If you do not specify a version, the latest version of the key will be used.
View Encryption Details- After making the change, from the database details page, navigate to Encryption section, and then review the following encryption details.
- The name of encryption key
- Its associated OCID
There is currently no content for this page. The Oracle Database@AWS team intends to add content here, and this placeholder text is provided until that text is added.
The Oracle Database@AWS team is excited about future new features, enhancements, and fixes to this product and this accompanying documentation. We strongly recommend you watch this page for those updates.
Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure on Oracle Database@AWS supports integration with AWS Key Management Service (KMS). This capability allows users to manage Transparent Data Encryption (TDE) master encryption keys (MEKs) using AWS customer managed keys.
For Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure on Oracle Database@AWS, TDE MEKs can be stored in a file-based Oracle Wallet, Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Vault, Oracle Key Vault (OKV), or AWS KMS, providing options to align with organization-specific security policies. Integration with AWS KMS enables applications, AWS services, and databases on Exadata VM Cluster (s) to leverage a single centralized key management solution.
To configure AWS KMS to encrypt your database, complete the following steps:- Create or Verify OCI Identity Domain
- Enable Security Token Service and AWS KMS in ODB Network
- Configure Identity Provider
- Associate an IAM Role to an Exadata VM Cluster
- Create a Customer Managed Key
- Register AWS KMS Key
- Enable AWS KMS Management
-
- Use AWS KMS as the Key Management Solution During Database Creation
- Use AWS KMS as the Key Management Solution During Database Modification
- Create or Verify OCI Identity DomainOCI identity domain is a prerequisite before using AWS KMS as the key management solution for your databases. OCI identity domain acts as the identity provider, authenticating the database to allow access to AWS KMS.Note
AWS KMS integration is generally available (GA) to Oracle Database@AWS customers starting November 18, 2025. If you completed the onboarding steps after AWS KMS integration became GA, the OCI identity domain has already been created for you. Follow the Verify OCI Identity Domain steps to confirm its existence. Otherwise, follow the Configure OCI Identity Domain steps to complete this prerequisite.- Verify OCI Identity Domain
- From the AWS console, select Oracle Database@AWS, and then select Settings.
- Ensure that OCI identity domain Status is Available.
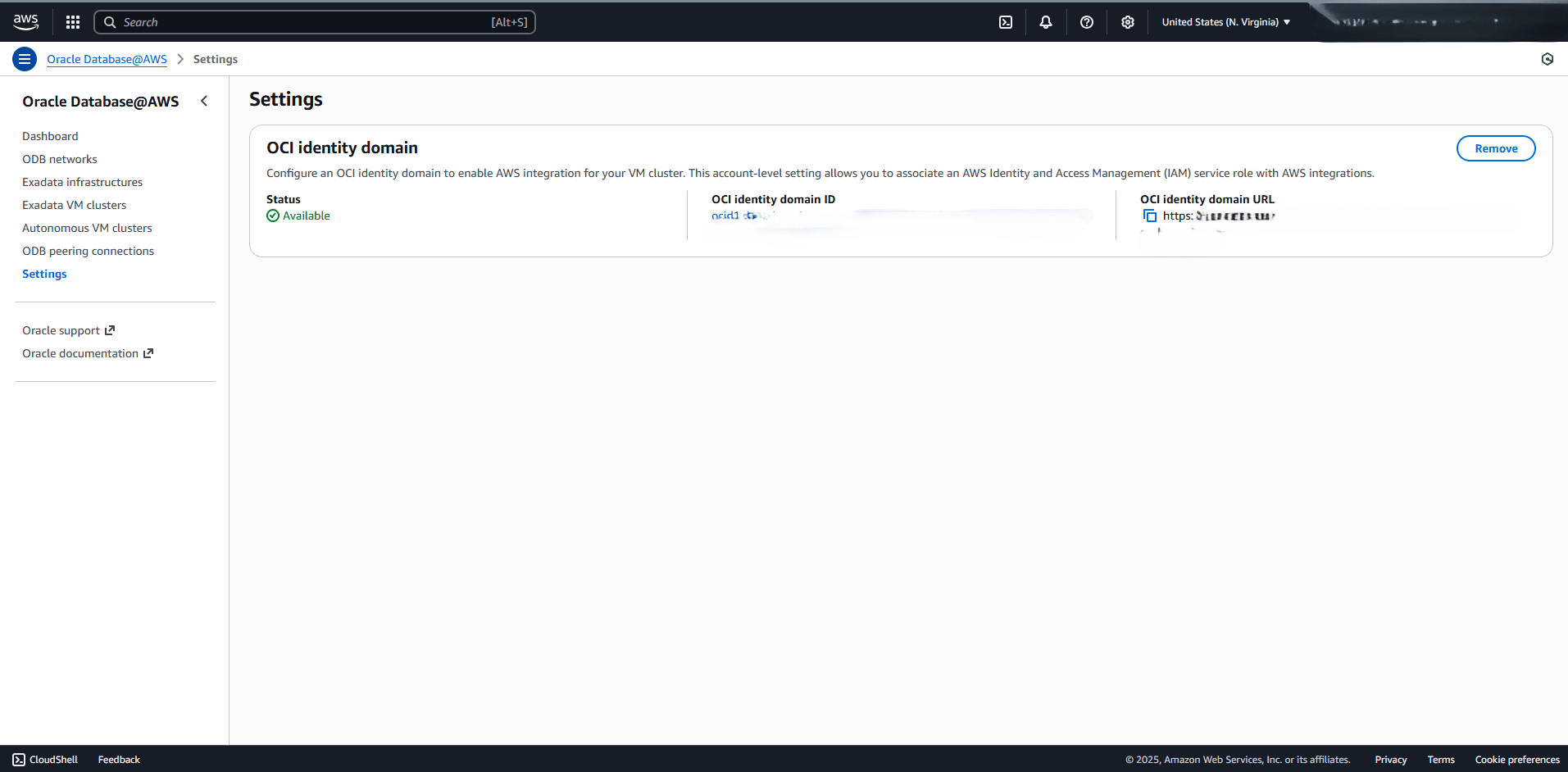
- Configure OCI Identity Domain
- From the AWS console, select Oracle Database@AWS, and then select Settings.

- Select the Configure button. A confirmation message will appear as Successfully initiated the configuration of OCI identity domain.

- Verify that the OCI identity domain Status is updated to Available. You can also view additional information including OCI identity domain ID and OCI identity domain URL.

- From the AWS console, select Oracle Database@AWS, and then select Settings.
- Verify OCI Identity Domain
- Enable Security Token Service and AWS KMS in ODB Network
To use AWS KMS for data-at-rest encryption, the ODB network must have both Security Token Service (STS) and AWS KMS integrations enabled. For more information, follow the Create ODB Network or Modify ODB Network steps.
- Configure Identity ProviderTo complete the identity provider configuration, complete the following steps.
- From the Oracle Database@AWS dashboard, select Exadata VM clusters, and then select your Exadata VM Cluster corresponding to Exadata Database that you want to enable AWS KMS for.
- On the VM Cluster details page, select the IAM service roles tab, and then select the CloudFormation link. This will open the AWS Quick create stack page in a new tab, pre-populated with the required setup information.

- From the Quick create stack page, the pre-populated information such as Stack name, OCI Identity Domain URL, OIDCProviderArn, ResourceOcid and RoleName. Accept the I acknowledge that AWS CloudFormation might create IAM resources with customer names checkbox, and then select the Create stack button.
Note
The CloudFormation stack creates an OIDC ((OpenID Connect)) Provider and an associated IAM role. OIDC Provider is unique per account.- If you are executing the stack for the first time, do not need to provide a value for the OIDCProviderArn field.
- For any additional execution time, you must provide the ARN of the existing OIDC Provider and specify it in the OIDCProviderArn field. To obtain your existing OIDC Provider ARN in your AWS account, complete the following steps.
- From the AWS console, navigate to IAM, and then select Identity providers.
- From the Identity providers list, you can filter your provider selecting Type as OpenID Connect.
- Select the Provider link that was created when the CloudFormation stack was initially created.
- From the Summary page, copy the ARN information.
- Paste the ARN information into the OIDCProviderArn field.
- The OIDC Provider and IAM role will be used by Oracle Database to access AWS KMS keys for encryption and decryption. The role provides OCI resource level isolation.
- If the isolation for database resources is not required, ResourceOcid and RoleName values should be left blank.

- After the CloudFormation stack deployment is complete, navigate to the Resources section of the stack and Verify that the IdP and IAM Role resources were created. Copy IAM Role ARN for the next steps.
- Associate an IAM Role to an Exadata VM Cluster
Complete the following steps to associate the IAM role to an Exadata VM Cluster. This step will create an identity connector that allows access to the AWS resources.
- From the AWS console, select Oracle Database@AWS.
- From the left menu, select Exadata VM clusters, and then select your Exadata VM Cluster from the list.
- Select the IAM roles tab, and then select the Associate button.
- The AWS integration field is read-only.
- Enter the Amazon Resource Name (ARN) of the IAM role you want to associate with Exadata VM Cluster in the Role ARN field. You can obtain the ARN information from the Summary section of the role that you previously created.
- Select the Associate button to attach the role.

- After the associate process is complete, the Service role ARN Status will change to Associated.
 Note
Note
Once you associate an IAM role to your Exadata VM Cluster, an identity connector gets attached to it.
- Create a Customer Managed Key
- From the AWS console, select Key Management Service (KMS).
- From the left menu, select Customer managed keys, and then select the Create key button.
- In the Configure key section, enter the following information.
- Choose the Symmetric option as the Key type.
- Choose the Encrypt and decrypt option as the Key usage.
- Expand the Advanced options section. Both AWS KMS and AWS CloudHSM are supported.
- If you want to use KMS, choose the KMS - recommended option as Key material origin, and then choose either the Single-Region key or the Multi-Region key option from the Regionality section.
Note
Cross-region Data Guard and restoring databases to a different region are currently not supported for databases that use AWS customer managed keys for key management. - If you want to use AWS CloudHSM , choose the AWS CloudHSM key store option as Key material origin.
- If you want to use KMS, choose the KMS - recommended option as Key material origin, and then choose either the Single-Region key or the Multi-Region key option from the Regionality section.
- Select the Next button to continue the creation process.

- In the Add labels section, enter the following information.
- Enter a descriptive display name in the Alias field. Maximum 256 characters. Use alphanumeric and '_-/' characters.
Note
- The alias name cannot begin with
aws/. Theaws/prefix is reserved by AWS to represent AWS managed keys in your account. - An alias is a display name that you can use to identify the KMS key. We recommend that you choose an alias that indicates the type of data you plan to protect or the application you plan to use with the KMSkey
- Aliases are required when you create a KMS key in the AWS console.
- The alias name cannot begin with
- The Description field is optional. You can enter a brief description of the key.
- The Tags section is optional. You can use tags to categorize and identify your KMS keys and help you track your AWS costs.
- Select the Next button to continue the creation process.

- Enter a descriptive display name in the Alias field. Maximum 256 characters. Use alphanumeric and '_-/' characters.
- In the Define key administrative permissions section, complete the following substeps.
- Search the role that you previously created, and then select the checkbox. Select the IAM users and roles that can administer the KMS key.
Note
This key policy gives the AWS account full control of this KMS key. It allows account administrators to use IAM policies to give other principals permission to manage the KMS key. - From the Key deletion section, the Allow key administrators to delete this key checkbox is selected by default. To prevent the selected IAM users and roles from deleting the KMS key, you can deselect the checkbox.
- Select the Next button to continue the creation process.

- Search the role that you previously created, and then select the checkbox. Select the IAM users and roles that can administer the KMS key.
- In the Define key usage permissions section, complete the following substeps.
- Search the role that you previously created, and then select the checkbox.
- Select the Next button to continue the creation process.

- In the Edit key policy section, complete the following substeps.
- From the Preview section, you can review the key policy. If you want to make a change, select the Edit tab.
{ "Version": "2012-10-17", "Statement": [ { "Sid": "KMSKeyMetadata", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "<arn>" }, "Action": [ "kms:DescribeKey" ], "Resource": "*" }, { "Sid": "KeyUsage", "Effect": "Allow", "Principal": { "AWS": "<arn>" }, "Action": [ "kms:Encrypt", "kms:Decrypt" ], "Resource": "*" } ] } - Select the Next button to continue the creation process.

- From the Preview section, you can review the key policy. If you want to make a change, select the Edit tab.
- In the Review section, review your information, and then select the Finish button.
- Register AWS KMS KeyTo enable AWS KMS for your Exadata VM Cluster, you must first register the AWS KMS key in the OCI console.
- From the OCI console, select Oracle AI Database and then select Database Multicloud Integrations.
- After selecting Database Multicloud Integrations, the default page opens.
- From the left menu, select the Previous button to navigate to AWS Integration, and then select AWS Keys.
- Select the Register AWS keys button, and then complete the following substeps.
- From the dropdown list, select the Compartment in which your Exadata VM Cluster resides.
- Under the AWS keys section, select your identity connector from the dropdown list.
Note
Ensure that the role associated with the connector has the DescribeKey permission on the key. This permission is required to successfully perform discovery. - The Key ARN field is optional.
- Click the Discover button.
- Once the key is discovered, select the Register button to register the key in OCI.

- Enable AWS Key Management
- From the OCI console, select Oracle AI Database and then select Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
- From the left menu, select Exadata VM Clusters, and then select your Exadata VM Cluster.
- Select the VM Cluster information tab, and select the Enable button next to AWS key management.
 Note
Note
If you do not want use AWS key management, you can disable it by selecting the Disable button. This action will disable AWS key management at the VM Cluster level. Disabling it will impact the availability of the databases using AWS key management. Ensure that no database is currently using AWS key management.
-
- Use AWS KMS as the Key Management Solution During Database CreationNote
- To see the key at Exadata VM Cluster level, you must run the following policy.
Allow any-user to read oracle-db-aws-keys in compartment id <your-compartment-OCID> where all { request.principal.type = 'cloudvmcluster'} - If AWS KMS is enabled in your Exadata VM Cluster, you can create databases only with AWS KMS encryption or Oracle Wallet encryption. Creating databases with Oracle Key Vault or OCI Vault encryption is not supported.
- Complete the following steps described in the Exadata Database documentation to create an Exadata Database.
- Navigate to the Encryption section which provides two options. These options include Oracle Wallet and AWS Customer Managed Key.
- Select the AWS Customer Managed Key as the key management. Select the Compartment and the Key from the dropdown list.

- Review your information, and then select the Create button.
- To see the key at Exadata VM Cluster level, you must run the following policy.
- Use AWS KMS as the Key Management Solution During Database ModificationNote
To see the key at Exadata VM Cluster level, you must run the following policy.Allow any-user to read oracle-db-aws-keys in compartment id <your-compartment-OCID> where all { request.principal.type = 'cloudvmcluster'}To update key management from Oracle Wallet to AWS KMS, complete the following steps:
- From your Exadata VM Clusters, navigate to Databases tab, and then select the database that you are using.
- From the Encryption section, confirm that Key management is set to Oracle Wallet, and then select the Change button.

- From the Change key management page, enter the following information.
- Select your Key management as AWS Customer Managed Key from the dropdown list.
- Select the key compartment you are using, and then select the desired key from the dropdown list.
- Select the Save changes button.

- Use AWS KMS as the Key Management Solution During Database Creation
AWS Customer Managed Key allows you to rotate the key at both Container Database (CDB) and Pluggable Database (PDB) levels to meet your security compliance requirements. Complete the following steps to rotate the key:
-
- Rotate the AWS KMS Key of a Container Database (CDB)
- From the OCI console, select Oracle AI Database and then select Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
- From the left menu, select Exadata VM Clusters, and then select your Exadata VM Cluster that you want to rotate encryption keys.
- Select the Databases tab, and then select the name of the database that you want to rotate encryption keys.
- From the Encryption section, verify that the Key Management is set to AWS key management, and then select the Rotate button.

- Select the Confirm button to save the changes.
- Rotate the AWS KMS Key of a Pluggable Database (PDB)
- From the OCI console, select Oracle AI Database, and then select Oracle Exadata Database Service on Dedicated Infrastructure.
- Select your Exadata VM Cluster, and then select Databases tab.
- Select the Name field of your database you are using, then select Pluggable Databases link under the Resources section.
- Select the Name field of the Pluggable Database you want to use.
- The Encryption section displays that the Key management is set as AWS key management. Select the Rotate button, and then select the Confirm button to save the changes.

- Rotate the AWS KMS Key of a Container Database (CDB)