Setting up Pay Types for 1099 Processing
You set up pay types for 1099 processing to accurately allocate earnings, other than wages, for contract or pension employees.
You must set up these pay types before you can enter the employee's pay in time entry and process it through a payroll cycle.
Setting up pay types for 1099 processing includes the following tasks:
Setting up pay types for contract employees
Setting up pay types for pension employees
Setting up Pay Types for Contract Employees
You set up pay types for 1099 processing to accurately allocate earnings, other than wages, for contract employees. You use special handling tables to attach pay types to the year-end workfile build.
The Payroll system supports the following IRS-approved pay types for 1099-MISC forms:
Rents
Royalty payments
Prizes and awards
Other income
Medical and health care services
Substitute payments
Excess golden parachute payments
The Payroll system supports the following IRS-approved pay types for 1099-NEC forms:
Nonemployee Compensation
Contract employee information generally falls under the category of nonemployee compensation. To transfer contract employee information to the workfile build process, the system requires the following information for the pay type:
Pay type code
Paystub text
Tax exempt status
After you set up this pay type, you enter the employee's pay in time entry and process it through the payroll cycle. The system prints checks and loads the pay amounts to history. To correctly process 1099 forms, we strongly recommend that you use this process to load history amounts.
You then run integrity reports to verify that dollar amounts are correct and that any necessary tax calculations exist. Make corrections, if needed, to the history tables before running the workfile build.
To set up pay types for contract employees
Navigation
From Pay/Deductions/Benefits Setup (G0742), choose Pay Type Setup
On Pay Type Setup, complete the following fields:
Pay Type
Paystub Text
Source of Pay
Auto Pay Methods
Pay Type Multiplier
Method of Printing
Effect on GL

Choose Tax Exempt Authorities Window (F8).
On Tax Exempt Window, enter *in the following field and click Enter:
Tax Type
On Pay Type Setup, click Add.
Field |
Explanation |
|---|---|
Source of Pay |
A user defined code (07/PB) that defines the value upon which the system bases the employee's pay. H, hours worked, is the default value. Other valid values exist for tip and piecework processing. Use E, estimated pay, for an advance pay interim check. The Interim Check program (Format 2) automatically deletes this type of timecard so that you can enter the actual time when it is known. |
Auto Pay Methods |
A code that specifies how the system treats this pay type when computing automatically generated pay (typically for salaried employees). It also identifies supplemental pay. Valid values are: Y – The dollars with this pay type are part of the employee's base pay, for example, regular, holiday, sick, and vacation pay. N – The dollars with this pay type are in addition to the employee's base pay, for example, overtime pay and time off without pay. S – The hours with this pay type are subtracted from the employee's base pay at standard rate and added back at the entered pay rate. B – The dollars with this pay type are in addition to the employee's base pay and are treated as supplemental pay for taxation purposes, for example, bonuses, commissions and payoffs. C – The hours/dollars entered using this pay type override all autopay instructions. If multiple jobs are used, a Y in this field might cause the pay type to be paid in addition to the regular pay. If you have overridden the job code/job step, home business unit, or position at time entry; multiple active jobs exist for this employee; and the overridden information does not match an existing active job record, the system processes this as additional pay. JD Edwards World recommends that you always use a pay type with N in this field when paying someone for work in addition to their regular pay. This ensures that the system processes the pay type the same in multiple-job or single-job situations. If your company docks employees' pay when they take leave in excess of what has been earned, you should have pay type 997 set up as the pay type to dock pay. Enter N as the autopay method for this pay type. If your company attaches contract calendars to employees to accumulate wages, you should have pay type 996 set up as the pay type to accumulate wages. Enter C as the autopay method for this pay type. |
Multiplier - Pay Type Multiplier |
A factor by which the base hourly rate is multiplied to obtain the actual payment hourly rate. For example, you could use 1.5 to designate time-and-one-half for overtime pay. 0 (zero) is not a valid multiplier. |
Method of Printing |
Identifies whether the item is to be printed on the paystub and whether the item is to be printed on a separate check from other payroll items. Valid codes are: Pay Types/Payroll Taxes: Y – Print on paystub (default) S – Print separate check (one item per check) C – Print separate check (C types combined) N – Do not print on paystub Deduction/Benefit/Accrual Types: Y – Print as total deductions (default) S – Print separate check (one item per check) C – Print separate check (include detail) N – Do not print on paystub I – Print individual transactions T – Print by DBA Print Group The separate check feature is not available for any payroll taxes being withheld from the employee's paycheck. |
Effect on GL |
A code that specifies whether you want journal entries passed from payroll to the general ledger and the method that you want to use. Valid codes are: Y – Pass dollars only to the general ledger. N – Pass dollars and hours to the general ledger. M – Do not pass dollars or hours to the general ledger and do not calculate workers' compensation and general liability. H – Pass hours only to the general ledger. This code is valid for Generate Timecard Journals. It should not be used when journals are generated through the pay cycle. W – Do not pass dollars or hours to the general ledger, but calculate workers' compensation and general liability. Workers' compensation and general liability amounts will be passed to the general ledger. |
Tax Type |
You can specify up to 15 tax types for which the respective payroll tax is not to be computed for a pay, deduction, or benefit code. If you enter * as the first element of this list, no taxes are computed. Screen-specific information For U.S. state and local tax types, you can use two methods of coding: Single-character tax types: F (state income tax), L (county tax), M (city tax), and N (school tax) *F, *L, *M, or *N During payroll processing, both methods of coding result in the DBA being exempt from taxes of the specified type. For example, with either F or *F, the system exempts the DBA amount from income taxation in all states. W-2 processing differs depending on the presence or absence of an asterisk. If you need to add back wages to specific states at year-end, you need to enter F in this field when setting up DBA or Pay types. For single-character state and local tax types that are to be added back during W-2 processing, specify the tax areas on the State/Local W-2 additions window. |
Setting up Pay Types for Pension Employees
You set up pay types for 1099 processing to accurately allocate earnings, other than wages, for pension employees.
The Payroll system supports the following IRS-approved types of pay for 1099-R forms. The IRS-defined special handling code for each type of pay displays in parentheses. These distribution types are in box 7 of the 1099-R form. On the Pay Type Setup screen, you enter the appropriate code type in the first position of the W-2 Special Handling Description field.
Early distribution, no exception - in most cases, under age 59¾ (1)
Early distribution, exception applies - under age 59¾ (2)
Disability (3)
Death (4)
Prohibited transaction (5)
Section 1035 exchange - a tax-free exchange of life insurance, annuity, qualified long-term care insurance, or endowment contract (6)
Normal distribution (7)
Excess contributions plus earnings/excess deferrals (and /or earnings) taxable in 2024 (8)
Cost of current life insurance protection - premiums paid by a trustee or custodian for current insurance protection (9)
May be eligible for 10-year tax option (A)
Designated Roth account distribution (B)
Reportable death benefits under section 6050Y (C)
Distribution under Employee Plans Compliance Resolution System (EPCRS) (E)
Charitable gift annuity (F)
Direct rollover and rollover contribution (G)
Direct rollover of distribution from a designated Roth account to a Roth IRA (H)
Early distribution from a Roth IRA - this code may be used with Code 8 or P (J)
Loans treated as deemed distributions under section 72(p) (L)
Qualified plan loan offset (M)
Recharacterized IRA contribution made for 2017 (N)
Excess contributions plus earnings/excess deferrals taxable in 2010 (P)
Qualified distribution from a Roth IRA - distribution from a Roth IRA when the 5-year holding period has been met, and the recipient has reached 59¾, has died, or is disabled (Q)
Early distribution from a SIMPLE IRA in the first 2 years, no known exception (S)
Roth IRA distribution, exception applies because participant has reached 59¾, died or is disabled, but it is unknown if the 5-year period has been met (T)
Distribution from ESOP under Section 404(k) (U)
Charges or payments for purchasing qualified long-term care insurance contracts under combined arrangements (W)
To transfer pension employee information to the workfile build program, the system requires the following information for the pay type:
Pay type code
Special handling description
Tax exempt status
After you set up pay types for pension employees, you enter the employee's pay in time entry and process it through the payroll cycle. The system prints checks and loads the pay amounts to history. To correctly process 1099 forms, we recommend that you use this process to load history amounts.
You then run integrity reports to verify that dollar amounts are correct and that tax calculations, if necessary, exist. Before running the workfile build, make corrections, if necessary, to the history tables.
Government tax publications General Instructions for Forms 1099, 1098, 5498, and W-2c for more information about the Box 7 changes for the 1099-R.
To set up pay types for pension employees
Navigation
From Pay/Deductions/Benefits Setup (G0742), choose Pay Type Setup
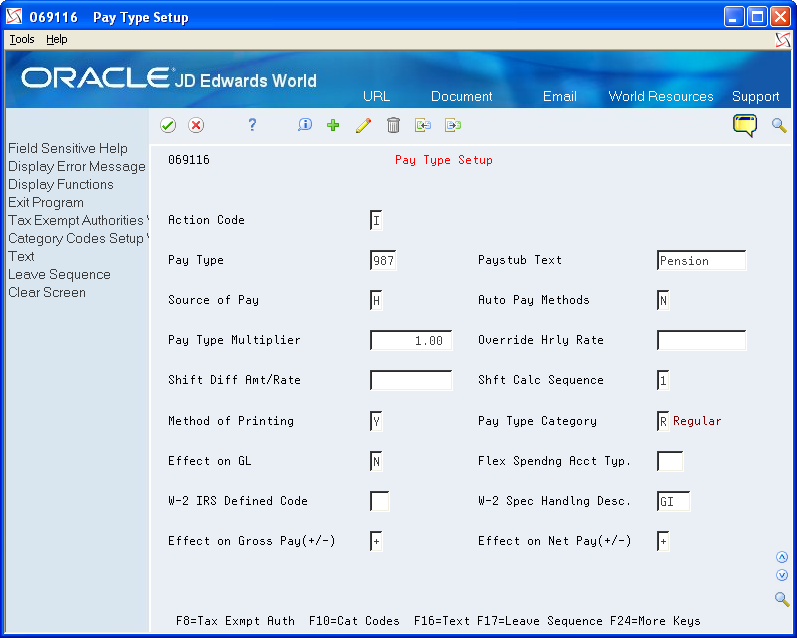
On Pay Type Setup, complete the following fields:
Pay Type
Paystub Text
Source of Pay
Auto Pay Methods
Pay Type Multiplier
Method of Printing
Effect on GL
W-2 Spec Handling Desc
Choose Tax Exempt Authorities Window (F8).
On Tax Exempt Window, complete the following field with * and click Enter:
Tax Type
On Pay Type Setup, click Add.
Field |
Explanation |
|---|---|
W-2 Spec Handling Desc |
This field has several purposes in the W-2 system. Valid values are: 1 – The system prints the first three characters of this field as the amount description for Special Handling items placed in box 14. 2 – The Payroll Tax Calculation system does not calculate all school district taxes. Some clients have created special deductions to withhold these taxes. You must add a specific description on the school district tax deduction. This description is printed with the tax amount on the W-2. For school districts, use all four characters of the description. If the school district is in Ohio, enter the four-digit code of the school district here. 3 – The first position of the W-2 Special Handling Description field represents the IRS Distribution Code that prints in box 7 on the 1099-R form. Enter Code EPP in this field to print excess golden parachute amounts on form 1099-MISC Screen-specific information If the distribution form is from an IRA or SEP, the second character of this description line must contain a I to mark the IRA/SEP box on the 1099-R. |