Manage Compute
This section covers the basic functions of creating, changing, or removing compute clusters in your AI Data Platform Workbench.
About Compute Clusters
All-purpose compute clusters provide you the compute resources to process your workloads in an AI Data Platform Workbench instance.
You manage your compute clusters from the Compute page in your Oracle AI Data Platform Workbench.
Types of Compute
Two types of compute exist in your AI Data Platform Workbench: all-purpose compute clusters and Default Master Catalog Compute Cluster.
You can only create all-purpose compute clusters in your AI Data Platform Workbench. All-purpose compute clusters are suitable for a versatile range of workloads and can be attached to your notebooks and used in workflows. Unless otherwise specified, any references to 'compute cluster' or 'cluster' in documentation refer to all-purpose compute clusters.
When you create a new all purpose compute cluster, you can choose either the Quickstart or Custom configuration. The Quickstart configuration is optimized to provide fast startup, while Custom configuration allows you to fine-tune your all purpose compute cluster to suit the specific workloads you need it to process. In both Quickstart and Custom configuration options, you can view cost projections and modify idle timeout options.
Note:
Installing custom libraries to a Quickstart configured all purpose compute cluster automatically changes it to the Custom configuration. This can impact startup performance.Default Master Catalog Compute Cluster is present in all AI Data Platform Workbench instances. This cluster is responsible for essential AI Data Platform Workbench functions, like search crawls, refreshing catalog objects, creating, editing, and deleting objects, and testing connections.
Cluster Runtime
All-purpose compute clusters can be created with an Apache Spark 3.5 runtime. The runtime environment is compatible with:
- Spark 3.5.0
- Delta 3.2.0 (pre-included)
- Python 3.11
- Hadoop 3.3.4
- Java 17
Only Python and SQL-based user code is currently supported by AI Data Platform Workbench. Java and Scala support are coming soon.
Maintenance Updates for Compute Clusters
AI Data Platform Workbench compute automatically applies maintenance updates without user intervention. The maintenance updates cover any necessary security patches or bug fixes for operating system and AI Data Platform Workbench internal components.
AI Data Platform Workbench verifies there are no running clusters before applying these monthly maintenance updates.
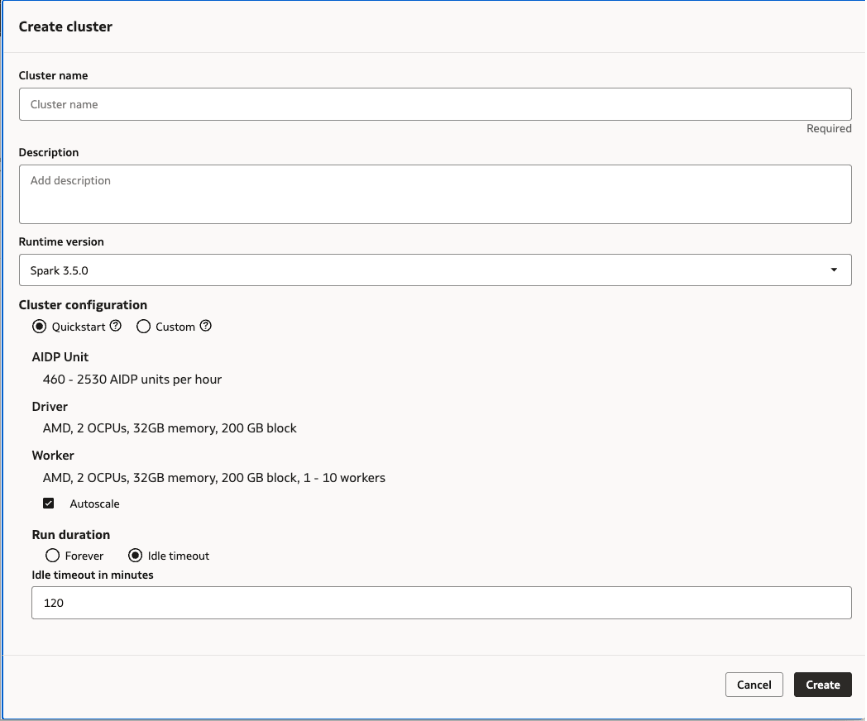
Create a Quickstart Cluster
You can choose to create an all-purpose compute cluster with preconfigured settings to process data and AI workloads in your AI Data Platform Workbench.
You can edit your cluster at any time after creation.
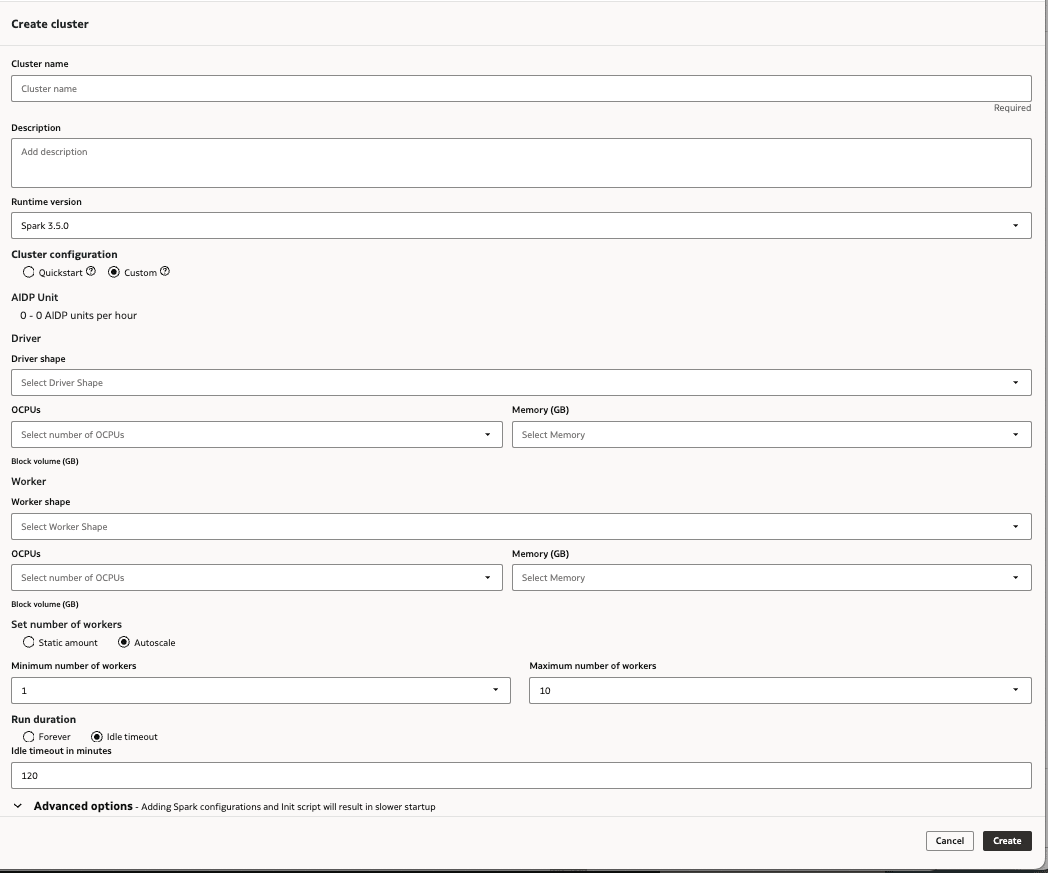
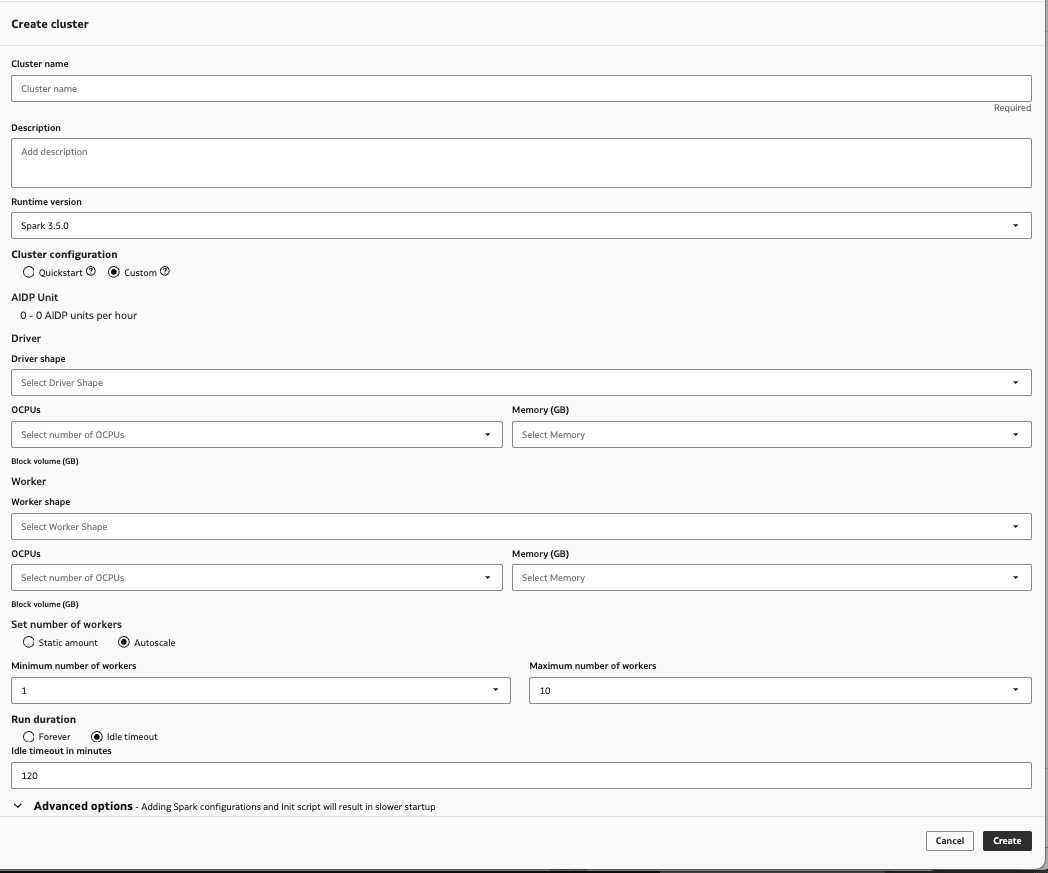
Create a Custom Cluster
You can create an all-purpose compute cluster with configuration settings of your own choosing to process data and AI workloads in your AI Data Platform Workbench.
You can edit your cluster at any time after creation.
Create an NVIDIA GPU Cluster
You can choose to use an NVIDIA GPU in an All Purpose Compute Cluster to accelerate any workload in your unified AI and data pipeline.
NVIDIA GPU shapes use the following configurations:
Table 13-1 NVIDIA GPU Shapes
| GPU Count | OCPU | Block storage (GB) | GPU memory (GB) | CPU memory (GB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 1500 | 24 | 240 |
| 2 | 30 | 3000 | 48 | 480 |
Note:
When you use NVIDIA GPU shapes, both the Driver and Worker shape must be an NVIDIA GPU. Mixing CPU and GPU shapes for the same cluster is currently not supported.NVIDIA GPU Cluster Tuning
You can tune your NVIDIA GPU clusters to optimize their performance by using recommendations from the GPU provider and by installing optional libraries.
Tuning GPU clusters can help optimize the performance of those clusters when called on by jobs in your AI Data Platform Workbench.
For NVIDIA GPU-based clusters, you can follow NVIDIA's Tuning Guide for recommendations and steps you can take to optimize performance.
You also have the option of installing Spark RAPIDS libraries to assist with optimization:
- Spark RAPIDS library is a RAPIDS accelerator for Apache Spark and provides a set of plugins that leverage GPUs to accelerate processing.
- Spark RAPIDS ML library enables GPU-accelerated, distributed machine learning on Apache Spark and provides several PySpark ML compatible algorithms powered by the RAPIDS cuML library.
The Spark RAPIDS library is commonly used first for feature engineering and data cleaning, and then cross validation is performed at scale using the Spark RAPIDS ML library. You can use these libraries for use cases like fraud detection (time series), web clickstream, and A/B experimentation.
Table 13-2 Recommended Spark Configurations
| Setting | Value | Note |
|---|---|---|
| spark.executor.instances | 4 | Number of worker x GPU count per worker
If the number of workers is 4, and GPU count per worker is 1, then recommended spark.executor.instances config is 4 x 1 = 4 |
| spark.executor.cores | 16 | GPU count/ worker / CPU cores, maximum of 16 |
| spark.executor.memory | 32 GB | 2GB / core or 80% of CPU memory / GPU count per worker (whichever is less) |
| spark.task.resource.gpu.amount | 0.0625 | 1 / spark.executor.cores |
| spark.rapids.sql.concurrentGpuTasks | 3 | GPU memory / 8GB, maximum of 4 |
| spark.rapids.shuffle.multiThreaded.writer.threads | 32 | CPU cores / GPU count per worker |
| spark.rapids.shuffle.multiThreaded.reader.threads | 32 | CPU cores / GPU count per worker |
| spark.shuffle.manager | com.nvidia.spark.rapids.spark350.RapidsShuffleManager | - |
| spark.rapids.shuffle.mode | MULTITHREADED | - |
| spark.plugins | com.nvidia.spark.SQLPlugin | - |
| spark.executor.resource.gpu.amount | 1 | - |
| spark.sql.files.maxPartitionBytes | 2 GB | Optional, recommended for large datasets |
| spark.rapids.sql.batchSizeBytes | 2 GB | Optional, recommended for large datasets |
| spark.rapids.memory.host.spillStorageSize | 32 G | Optional, recommended for large datasets |
| spark.rapids.memory.pinnedPool.size | 8 G | Optional, recommended for large datasets |
| spark.sql.adaptive.coalescePartitions.minPartitionSize | 32 MB | Optional, recommended for large datasets |
| spark.sql.adaptive.advisoryPartitionSizeInBytes | 160 MB | Optional, recommended for large datasets |
| spark.rapids.filecache.enabled | True | Optional, recommended if workloads will be reusing datasets |
Modify a Cluster
You can change settings or add additional parameters for your clusters.
- Navigate to your workspace and click Compute.
- Next to the compute cluster you want to modify, click
 Actions then click Edit.
Actions then click Edit. - Modify the attributes of your compute cluster or add additional parameters as needed.
- Click Save.
Delete a Cluster
You can delete compute clusters that are unused or no longer needed.
- Navigate to your workspace and click Compute.
- Next to the cluster you want to delete, click
 Actions and click Delete.
Actions and click Delete. - Click Delete.
View Cluster Details
You can review the shape and settings of a cluster at any time.
- Navigate to your workspace and click Compute.
- Click the name of the cluster you want to view details for.
- Click the Details tab.
Maintenance Updates for Compute Clusters
Oracle AI Data Platform compute automatically applies maintenance updates without user intervention.
The maintenance updates cover any necessary security patches or bug fixes for operating system and AI Data Platform internal components. AI Data Platform verifies there are no running clusters before applying these monthly maintenance updates.