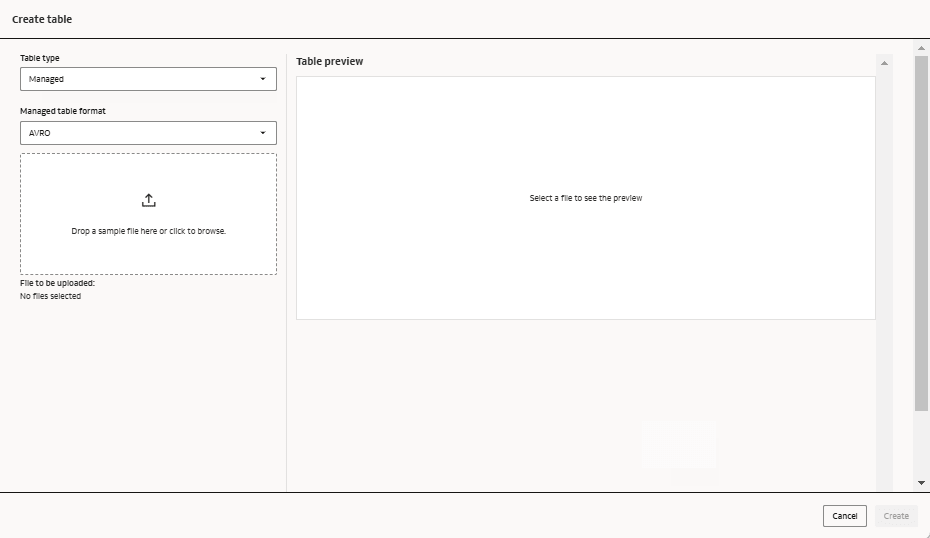
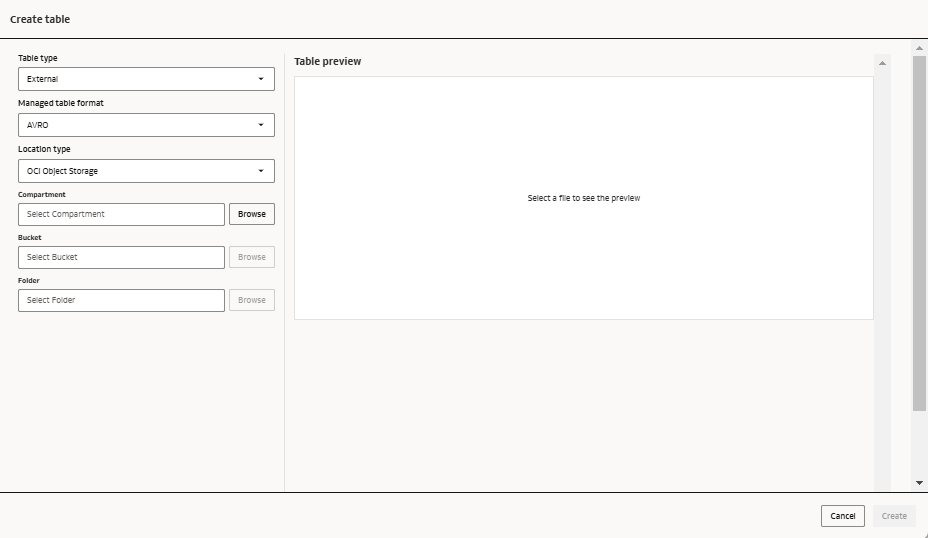
Tables
Tables define the structure for your data.
You can load new data into your tables or reference data in an existing location. You can define fine-grained access control permissions on tables by creating table permissions.
Tables can either be external or managed.
External tables
An external table defines a structure for data that's stored in a location not managed by Oracle AI Data Platform Workbench. When you create an external table in the AI Data Platform Workbench, the metadata life cycle is managed by AI Data Platform Workbench. When you delete an external table, only the table definition is deleted. The data referenced by the external table isn't deleted.
Additional IAM policies are required for external tables. For more information, see IAM Policies for Oracle AI Data Platform Workbench.
Managed Tables
A managed table defines a structure for data that's stored within the AI Data Platform and can only be accessed by AI Data Platform Workbench users.
When you delete a managed table, the table definition and the table data is deleted.
Supported Table Formats
| Format | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| Comma-separated-values (CSV) | Data is stored as a text file with a specified row based file format to structure the data. Typically, the first row in the file is a header row that contains columns names for the data. | Used to exchange tabular data between systems. Each row in the file is a row in a table. |
| JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) | Data is stored in a standard text-based format for representing structured data based on JavaScript object syntax. JSON supports lists of objects or hierarchical structures. | Used in stream applications. JSON simplifies the storage of related data with complex relationships in a single document and avoids chaotic list conversion to a relational data model. Note that JSON isn't splittable. |
| Avro | Data is stored in a row based binary format while the schema is stored in JSON format to minimize file size and maximize efficiency. Avro has reliable support for schema evolution by managing added, missing, and changed fields. This lets old software to read new data, and new software to read old data. Also known as the data serialization system. | Used for data storage as avro files are splittable and compressible. The serialized row-based storage is ideal for heavy write transaction, such as inserting data into AI Data Platform. Avro is also a good choice when schema evolution is critical during high speed writes. |
| Parquet | Data is stored in a columnar data format and is highly compressible and splittable. Parquet is optimized for the paradigm Write Once Read Many (WORM). It writes slowly but reads incredibly quickly, especially when you only access a subset of columns. | Used for solving Big Data problems as compression algorithms work better with columnar data format. You can store Big Data in various formats, such as images, videos, documents, and structured data tables. Parquet is a good choice for heavy workloads when reading portions of data. For example, when the dataset has many columns, but you only want to access a subset of columns. Ideal when you're dependent on Spark or when you want several services to access the same data stored in Object Storage. |
| Optimized Row Columnar (ORC) | Data is stored in collections of rows in a single file in columnar format. | Used for parallel processing of row collections across a cluster. Ideal when read transactions are more than write transactions or when compression is priority. |
| Delta | Data is stored in a columnar format that extends Parquet data files with a JSON file-based transaction log for ACID transactions and scalable metadata handling. | Used for transaction support. |
Limitations
The following limitations apply to tables in Oracle AI Data Platform:
- You cannot define an external table on any data files or directories within/on a volume.
- You cannot define an external table on a bucket and/or its directory that is already used for another external table or external volume
- Views cannot be viewed/listed in the Master Catalog.
Edit a Table
You can modify details of tables you manage.
- Navigate to your schema.
- Select the Tables tab.
- Next to the table you want to edit click
 Actions.
Actions.- Click Rename to change your table's name. Enter a new name and press Enter.
- Click Edit Description to change your table's description. Provide the new description and click Save.