DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Describes the format of the source file URIs in
operations with DBMS_CLOUD.
The format depends on the object storage service you are using.
DBMS_CLOUD guarantees
secure communication and any URI that you specify must use HTTPS, with
https:// as the prefix for the URI.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Native URI Format
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Swift URI Format
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage URI Format Using Pre-Authenticated Request URL
- URI Format Using Public URL
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Classic URI Format
- Substitution Variables in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) URLs
You can provide predefined substitution variables in your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) URLs when providing URI for theobject_uriparameter for theDBMS_CLOUDprocedures and functions. - Amazon S3 URI Format
- Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage URI Format
- Amazon S3 Compatible URI Format
- GitHub Raw URL Format
DBMS_CLOUDsupports GitHub Raw URLs to access data from a GitHub Repository. - Additional Customer-Managed URI Formats
In addition to the pre-configured, recognizedURIswith their fully-qualified domain names (FQDNs),DBMS_CLOUDcannot determine the proper authentication scheme for customer-managed endpointsURIs. In those cases,DBMS_CLOUDrelies on the properURIscheme to identify the authentication scheme for the customer-managed endpoint.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD Package
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Native URI Format
If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage in the commercial realm (OC1), it is recommended that you use the following URI format which uses Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints. See Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints, for further information.
https://namespace-string.objectstorage.region.oci.customer-oci.com/n/namespace-string/b/bucketname/o/filenameNote:
OCI Object Store dedicated endpoint URLs are only supported in commercial realms (OC1).If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage and are not in the commercial realm (OC1), you must use the following format:
https://objectstorage.region.oraclecloud.com/n/namespace-string/b/bucket/o/filenameFor example, in the commercial realm (OC1) the Native URI for the file
channels.txt in the bucketname bucket in the Phoenix data
center is:
https://namespace.objectstorage.region.oci.customer-oci.com/n/namespace/b/bucketname/o/channels.txtIn this example, namespace-string is the Oracle
Cloud Infrastructure object storage namespace and
bucketname is the bucket
name. See Understanding
Object Storage Namespaces for more
information.
DBMS_CLOUD package subroutines:
-
my$home_region: Specifies the Home region of your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy.Themy$home_regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$region: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Region of your Autonomous AI Database.Themy$regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$cloud_domain: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) domain name for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).Themy$cloud_domainsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$namespace: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage namespace.Themy$namespacesubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$compartment: Specifies the OCID of your compartment.Themy$compartmentsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$tenancy: Specifies the OCID of your tenancy.Themy$tenancysubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
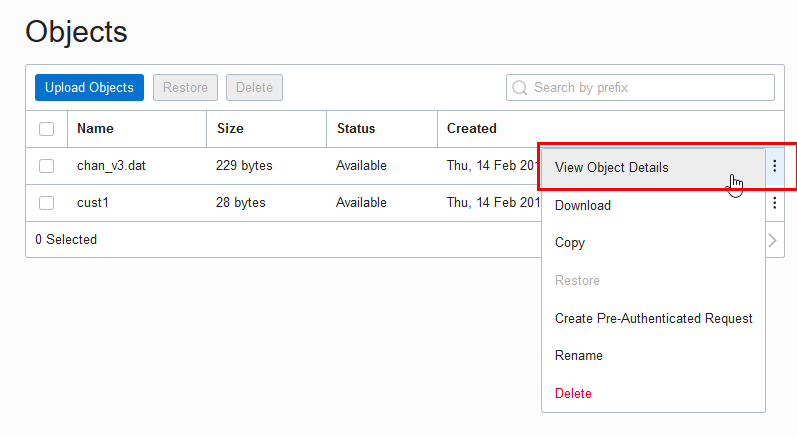
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.my$region.my$cloud_domain/n/my$namespace/b/bucket_name/o/file_name'You can find the URI from the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage "Object Details" in the right hand side ellipsis menu in the Object Store:
- Open the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Console by clicking the
 next to Oracle Cloud.
next to Oracle Cloud.
- From the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure left navigation menu click Core Infrastructure. Under Object Storage, click Object Storage.
- Under List Scope, select a Compartment.
- From the Name column, select a bucket.
- In the Objects area, click View Object Details.
- On the Object Details page, the URL Path (URI) field shows the URI to access the object.
Note:
The source files need to be stored in an Object Storage tier bucket. Autonomous AI Database does not support buckets in the Archive Storage tier. See Overview of Object Storage for more information.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Swift URI Format
If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage in the commercial realm (OC1), it is recommended that you use the following URI format which uses Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints. See Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints, for further information.
https://namespace-string.swiftobjectstorage.region.oci.customer-oci.com/v1/namespace-string/bucket/filenameNote:
OCI Object Store dedicated endpoint URLs are only supported in the commercial realms (OC1).If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage and are not in the commercial realm (OC1), you must use the following format:
https://swiftobjectstorage.region.oraclecloud.com/v1/namespace-string/bucket/filenameFor example, in the commercial realm (OC1) the Swift URI for the file
channels.txt in the bucketname bucket in the Phoenix data
center is:
https://namespace-string.swiftobjectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oci.customer-oci.com/v1/namespace-string/bucketname/channels.txtIn this example, namespace-string is the Oracle
Cloud Infrastructure object storage namespace and
bucketname is the bucket
name. See Understanding
Object Storage Namespaces for more
information.
Note:
The source files need to be stored in an Object Storage tier bucket. Autonomous AI Database does not support buckets in the Archive Storage tier. See Overview of Object Storage for more information.
-
my$home_region: Specifies the Home region of your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy.Themy$home_regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$region: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Region of your Autonomous AI Database.Themy$regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$cloud_domain: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) domain name for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).Themy$cloud_domainsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$namespace: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage namespace.Themy$namespacesubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$compartment: Specifies the OCID of your compartment.Themy$compartmentsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$tenancy: Specifies the OCID of your tenancy.Themy$tenancysubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage URI Format Using Pre-Authenticated Request URL
If your source files reside on the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage you can use Oracle Cloud Infrastructure pre-authenticated URIs. When you create a pre-authenticated request, a unique URL is generated. You can then provide the unique URL to users in your organization, partners, or third parties to access the Object Storage resource target identified in the pre-authenticated request.
Note:
Carefully assess the business requirement for and the security ramifications of pre‑authenticated access. When you create the pre-authenticated request URL, note the Expiration and the Access type to make sure they are appropriate for your use.A pre-authenticated request URL gives anyone who has the URL access to the targets identified in the request for as long as the request is active. In addition to considering the operational needs of pre-authenticated access, it is equally important to manage its distribution.
If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage in the commercial realm (OC1), it is recommended that you use the following URI format which uses Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints. See Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints, for further information.
https://namespace-string.objectstorage.region.oci.customer-oci.com/p/encrypted_string/n/namespace-string/b/bucket/o/filename
Note:
OCI Object Store dedicated endpoint URLs are only supported in the commercial realms (OC1).If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage and are not in the commercial realm (OC1), you must use the following format:
https://objectstorage.region.oraclecloud.com.com/p/encrypted_string/n/namespace-string/b/bucket/o/filename
For example, in the commercial realm (OC1) a sample pre-authenticated URI for
the file channels.txt in the bucketname bucket in the Phoenix data center
is:
https://namespace-string.objectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oci.customer-oci.com/p/2xN-uDtWJNsiD910UCYGue/n/namespace-string/b/bucketname/o/channels.txt
In this example, namespace-string is the Oracle
Cloud Infrastructure object storage namespace and
bucketname is the bucket
name. See Understanding
Object Storage Namespaces for more
information.
You can use a pre-authenticated URL in any DBMS_CLOUD
procedure that takes a URL to access files in Oracle Cloud
Infrastructure object store, without the need to create a credential. You need to either specify the
credential_name parameter as NULL or not supply a
credential_name parameter.
For example:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.COPY_DATA(
table_name =>'CHANNELS',
file_uri_list =>'https://objectstorage.us-phoenix-1.oraclecloud.com/p/unique-pre-authenticated-string/n/namespace-string/b/bucketname/o/channels.txt',
format => json_object('delimiter' value ',') );
END;
/Note:
A list of mixed URLs is valid. If the URL list contains both pre-authenticated URLs and URLs that require authentication,DBMS_CLOUD uses the specified credential_name to
access the URLs that require authentication and for the pre-authenticated URLs the
specified credential_name is ignored.
See Using Pre-Authenticated Requests for more information.
DBMS_CLOUD package subroutines:
-
my$home_region: Specifies the Home region of your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy.Themy$home_regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$region: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Region of your Autonomous AI Database.Themy$regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$cloud_domain: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) domain name for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).Themy$cloud_domainsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$namespace: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage namespace.Themy$namespacesubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$compartment: Specifies the OCID of your compartment.Themy$compartmentsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$tenancy: Specifies the OCID of your tenancy.Themy$tenancysubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.my$region.my$cloud_domain/n/my$namespace/b/bucket_name/o/file_name'Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
URI Format Using Public URL
If your source files reside on an Object Store that provides public URLs,
you can use public URLs with DBMS_CLOUD procedures. Public means the
Object Storage service supports anonymous, unauthenticated access to the Object Store
files. See your Cloud Object Storage service for details on how to make an object public
in a supported Object Store.
Note:
Carefully assess the business requirement for and the security ramifications of using public URLs. When you use public URLs, due to the file content not being authenticated, make sure this is appropriate for your use.You can use a public URL in any DBMS_CLOUD procedure that
takes a URL to access files in your object store, without the need to create a
credential. You need to either specify the credential_name parameter as
NULL or not supply a credential_name
parameter.
For example the following uses DBMS_CLOUD.COPY_DATA without a
credential_name:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.COPY_DATA(
table_name =>'CHANNELS',
file_uri_list =>'https://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com/n/namespace-string/b/bucketname/o/chan_v3.dat',
format => json_object('delimiter' value ',') );
END;
/In this example, namespace-string is the Oracle
Cloud Infrastructure object storage namespace and
bucketname is the bucket
name. See Understanding
Object Storage Namespaces for more
information.
Note:
A list of mixed URLs is valid. If the URL list contains both public URLs and URLs that require authentication,DBMS_CLOUD uses the specified credential_name to
access the URLs that require authentication and for the public URLs the specified
credential_name is ignored.
See Public Buckets for information on using Oracle Cloud Infrastructure public buckets.
DBMS_CLOUD package subroutines:
-
my$home_region: Specifies the Home region of your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy.Themy$home_regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$region: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Region of your Autonomous AI Database.Themy$regionsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$cloud_domain: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) domain name for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).Themy$cloud_domainsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$namespace: Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage namespace.Themy$namespacesubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
-
my$compartment: Specifies the OCID of your compartment.Themy$compartmentsubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
-
my$tenancy: Specifies the OCID of your tenancy.Themy$tenancysubstitution variable is only supported with the following credential types:-
OCI API Signing Key
-
OCI Resource principal
-
Auth Token/Swift credential
-
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.my$region.my$cloud_domain/n/my$namespace/b/bucket_name/o/file_name'Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Classic URI Format
If your source files reside in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Classic, see the REST page for a description of the URI format for accessing your files: About REST URLs for Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage Classic Resources.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Substitution Variables in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) URLs
You can provide predefined substitution variables in your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) URLs when providing URI for the object_uri parameter for the DBMS_CLOUD procedures and functions.
These substitution variables are pre-defined placeholders such as my$home_region and my$tenancy, which are resolved and substituted with the corresponding actual values based on the runtime context of your Autonomous AI Database. The environment-specific values such as tenancy OCID or namespace, are not hard coded, making your SQL code dynamic and portable to be deployed in multiple regions (for OCI REST APIs).
Following are the advantages of using substitution variables in OCI URLs:
-
SQL code is less prone to errors because substitution variables eliminate the need to provide hard coded values. This is particularly useful when using long identifiers.
-
SQL code is portable and not region or environment specific. The same SQL code can be reused and deployed across multiple regions for OCI REST APIs without needing to identify the current region.
-
Cross region failover for Autonomous AI Database using OCI REST APIs is convenient and less error prone.
The following table lists each substitution variable, along with its corresponding supported credential type and an example value:
| Parameter Name | Description | Supported credential types | Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Specifies the Home region of your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) tenancy. |
|
|
|
|
Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Region of your Autonomous AI Database. |
|
|
|
|
Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) domain name for your Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI). |
|
|
|
|
Specifies the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI) Object Storage namespace. |
|
|
|
|
Specifies the OCID of your compartment. |
|
|
|
|
Specifies the OCID of your tenancy. |
|
|
Example to use pre-defined substitution variables to access an Object Storage file:
SELECT TO_CLOB(DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT (
credential_name => credential_name,
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.my$region.my$cloud_domain/n/my$namespace/b/bucket_name/o/file_name'))
FROM DUAL;Example to use pre-defined substitution variables to access OCI cost report file:
SELECT TO_CLOB(DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT (
credential_name => credential_name,
object_uri => 'https://objectstorage.my$home_region.my$cloud_domain/n/namespace-string/b/my$tenancy/o/reports/cost-csv/file_name.csv.gz',
compression => DBMS_CLOUD.COMPRESS_GZIP))
FROM DUAL;Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Amazon S3 URI Format
If your source files reside in Amazon S3, see the following for a description of the URI format for accessing your files: Accessing a bucket.
For example the following refers to the file
channels.txt in the adb bucket in
the us-west-2 region.
https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/adb/channels.txt You can use a presigned URL in any DBMS_CLOUD procedure that
takes a URL to access files in Amazon S3 object
store, without the need to create a credential. To use a presigned URL in
any DBMS_CLOUD procedure, either specify the
credential_name parameter as NULL,
or do not supply a credential_name parameter.
See Share an Object with Others for more information.
Note:
DBMS_CLOUD supports the standard Amazon S3 endpoint syntax to access your buckets.
DBMS_CLOUD does not support Amazon S3 legacy endpoints. See Legacy Endpoints for more
information.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage URI Format
If your source files reside in Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake Storage, see the following for a description of the URI format for accessing your files: Resource URI Syntax.
For example the following refers to the file
channels.txt in the adb container in the storage account adb_user:
https://adb_user.blob.core.windows.net/adb/channels.txtNote:
You can use Shared Access Signatures (SAS) URL in anyDBMS_CLOUD procedure that takes
a URL to access files in Azure Blob Storage or Azure Data Lake
Storage,
without the need to create a credential. To use a Shared Access Signature
(SAS) URL, either specify the credential_name parameter as
NULL, or do not supply a
credential_name parameter.
See Grant Limited Access to Azure Storage Resources Using Shared Access Signatures (SAS) for more information.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Amazon S3 Compatible URI Format
DBMS_CLOUD supports object storage service implementations that support Amazon S3 compatible URLs, including the following services:
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage with Amazon S3 compatible URL
- Google Cloud Storage with Amazon S3 compatible URL
- Wasabi Hot Cloud Storage with Amazon S3 compatible URL
Note:
To useDBMS_CLOUD with an Amazon S3 compatible object store you need to provide valid credentials. See CREATE_CREDENTIAL Procedure for more information.
If your source files reside on a service that supports Amazon S3 compatible URIs, use the following URI format to access your files:
-
Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage S3 Compatible URL
If your source files reside on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Object Storage in the commercial realm (OC1), it is recommended that you use the object URL and bucket URL formats listed below for commercial realm (OC1). See Object Storage Dedicated Endpoints, for further information.
Note:
OCI Object Store dedicated endpoint URLs are only supported in the commercial realms (OC1).Object URL Formats
-
Supported only in the commercial realm (OC1):
https://mynamespace.compat.objectstorage.region.oci.customer-oci.com/bucket_name/object_name -
Supported in all zones:
https://mynamespace.compat.objectstorage.region.oraclecloud.com/bucket_name/object_name
Bucket URL Formats:
-
Supported only in the commercial realm (OC1):
https://mynamespace.compat.objectstorage.region.oci.customer-oci.com/bucket_name -
Supported in all zones:
https://mynamespace.compat.objectstorage.region.oraclecloud.com/bucket_name
See Amazon S3 Compatibility and Object Storage Service API for more information.
-
-
Google Cloud Storage S3 Compatible URL
Object URL Format:
https://bucketname.storage.googleapis.com/object_nameBucket URL Format:
https://bucketname.storage.googleapis.com/See Migrating from Amazon S3 to Cloud Storage and Request Endpoints for more information.
-
Wasabi S3 Compatible URL
Object URL Format:
https://bucketname.s3.region.wasabisys.com/object_nameBucket URL Format:
https://bucketname.s3.region.wasabisys.com/See Wasabi S3 API Reference and Service URLs for Wasabi's Storage Regions for more information.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
GitHub Raw URL Format
DBMS_CLOUD supports GitHub Raw URLs
to access data from a GitHub Repository.
Note:
ForDBMS_CLOUD access with GitHub Raw URLs, repository access
is limited to read-only functionality. The DBMS_CLOUD APIs such as DBMS_CLOUD.PUT_OBJECT that write data are not supported
with DBMS_CLOUD APIs on a GitHub Repository.
As an alternative, use DBMS_CLOUD_REPO.PUT_FILE to upload
data to a GitHub Repository.
Use GitHub Raw URLs with DBMS_CLOUD APIs to access source files that reside on a
GitHub Repository. When you browse to a file on GitHub and
click the Raw link, this shows the GitHub Raw URL. The
raw.githubusercontent.com domain provides unprocessed versions of
files stored in GitHub repositories.
For example, using DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.GET_OBJECT(
credential_name => 'MY_CRED',
object_uri => 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/myaccount/myrepo/master/data-management-library/autonomous-database/adb-loading.csv',
directory_name => 'DATA_PUMP_DIR'
);
END;
/For example, using DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_EXTERNAL_TABLE:
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.CREATE_EXTERNAL_TABLE(
credential_name => 'MY_CRED',
table_name => 'EMPLOYEES_EXT',
file_uri_list => 'https://raw.githubusercontent.com/myaccount/myrepo/master/data-management-library/autonomous-database/*.csv',
column_list => 'name varchar2(30), gender varchar2(30), salary number',
format => JSON_OBJECT('type' value 'csv')
);
END;
/
SELECT * FROM employees_ext;DBMS_CLOUD procedures that take a URL to access a GitHub Repository do not require credentials with public
visibility GitHub repositories. To use a public visibility URL you can specify the
credential_name parameter as NULL or not supply a
credential_name parameter. See Setting repository visibility for
more information.
Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats
Additional Customer-Managed URI Formats
URIs with their fully-qualified domain names (FQDNs), DBMS_CLOUD cannot determine the proper authentication scheme for customer-managed endpoints URIs. In those cases, DBMS_CLOUD relies on the proper URI scheme to identify the authentication scheme for the customer-managed endpoint.
| URI Scheme | Authentication Type | Access Method Description | URI Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| basic:// | Basic authentication | Username and password stored in database credential object is used to authenticate the HTTP request | basic://api.github.com/users/myaccount |
| bearer:// | Bearer token authentication | Bearer token stored in the password field in database credential object is used to specify the Authorization header for the HTTP request | bearer://api.sendgrid.com/v3/resource |
| oci:// | OCI native | OCI signing key obtained from database credential object stored and used to sign requests using the OCI authentication protocol | oci://objectstorage.us-ashburn-1.oraclecloud.com |
| public:// | No authentication | Public URLs | public://cms.data.gov/ |
| s3:// | Amazon Web Services S3-compatible | Access key and secret key obtained from the username/password field of database credential object, and S3-compatible authentication performed for the HTTP request. | s3://bucket.myprivatesite.com/file1.csv |
Examples:
Customer-managed endpoint using S3-compatible authentication.
This example shows how for new URIs, customers can add the public or private host name pattern using DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN package. The code block, executed by user ADMIN, enables HTTPS access for user SCOTT to endpoints in domain *.myprivatesite.com. It then shows how user SCOTT accesses the newly enabled endpoint. Note that credential MY_CRED for user SCOTT must store the access key and secret key for S3-compatible authentication performed for the HTTP request indicated by the URI prefix.
BEGIN
DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.APPEND_HOST_ACE(
host => '*.myprivatesite.com',
ace => xs$ace_type(privilege_list => xs$name_list('http'),
principal_name => 'SCOTT',
principal_type => xs_acl.ptype_db),
private_target => TRUE );
END;
/
BEGIN
DBMS_CLOUD.get_object(
credential_name => 'MY_CRED',
object_uri => 's3://bucket.myprivatesite.com/file1.csv',
directory_name => 'MY_DIR' );
END;
/
Customer-managed endpoint with public access
This example shows how to register the SCOTT user to access public REST APIs. The ADMIN user creates a network ACL for the host to provide access to SCOTT user.
BEGIN
DBMS_NETWORK_ACL_ADMIN.APPEND_HOST_ACE(
host => 'data.cms.gov',
ace => xs$ace_type(privilege_list => xs$name_list('http'),
principal_name => 'SCOTT',
principal_type => xs_acl.ptype_db)
);
END;
/
SELECT DBMS_CLOUD.get_response_text(
DBMS_CLOUD.send_request(
uri => 'public://data.cms.gov/provider-data/api/1/datastore/imports/a',
method => DBMS_CLOUD.METHOD_GET,
headers => JSON_OBJECT('Accept' VALUE 'application/json')
)
)
FROM DUAL;
/Parent topic: DBMS_CLOUD URI Formats