- Using File Server in Oracle Integration Generation 2
- Administer File Server
- Configure File Server Settings
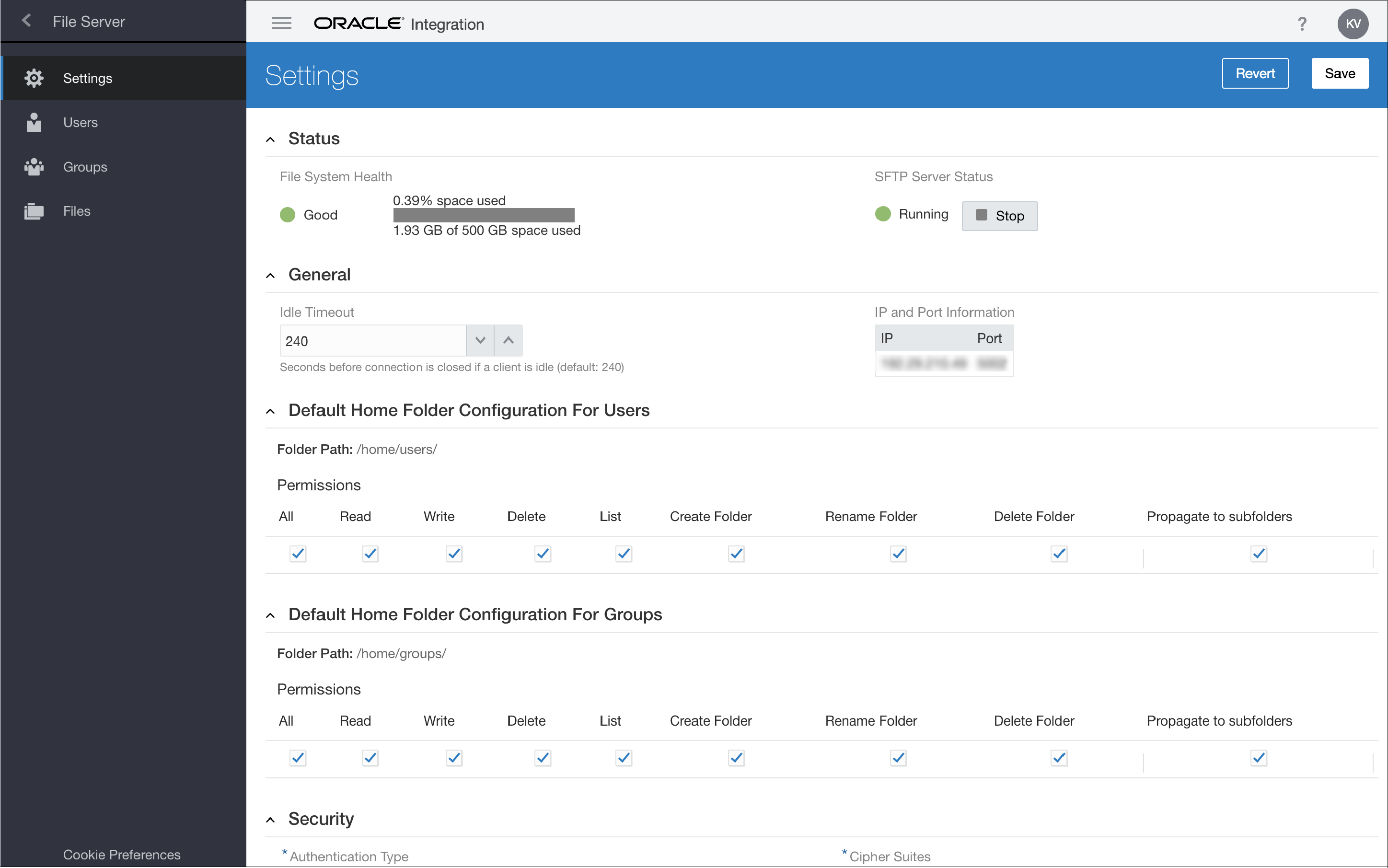
Configure File Server Settings
Use the Settings page to monitor the overall health of File Server and to change its main settings.
- From the side pane of the Oracle Integration Home page,
choose Settings, then File Server,
then Settings. The Settings page is displayed.
- Under Status settings, monitor the server's status, and
stop or restart as needed.
Field Description File System Health
View the total space and percent in use. Each File Server service instance provides 500GB of storage.
- If the available space falls below 10%, a warning is displayed.
- If no space is available, a red indicator is displayed and uploading stops, although operations that do not use additional space still function.
SFTP Server Status
View the SFTP server’s state: Running or Stopped.
- Click Stop to stop the server at any time. File Server stops after all current file transfers are complete.
- Once stopped, the button's name changes to Start. Click Start to restart the server.
- Under General settings, specify a timeout and note the
IP and Port settings.
Field Descripton Idle Timeout (sec)
Set the number of seconds that an SFTP client can be idle before being disconnected by File Server. The default timeout value is 240 seconds (4 minutes) and the maximum value is 300 seconds (5 minutes).
IP and Port Information
Note the read only, public IP and port values of the SFTP server for this Oracle Integration instance, which were assigned during provisioning. Use these values in configuring the Oracle Integration FTP adapter and SFTP clients.
- Under Users Default Configuration for Home Folder, view
the user home folder's base path and specify the folder's default permissions.
Field Description Folder Path
Displays the default home folder path for users. (Configure individual users on the Users page, as described in Configure Users.) You can't change the system's default home.
- For users, the default home path is
home/users/. If you leave a user configured to use the default home (choose User Default as Home Folder Type on the Users page), the full path to the user's home is/home/users/[username]. - If a user's home folder is set to Group Inherited on the Users page and the user is a member of a group, then the user will inherit the group's home folder.
Permissions
Set default permissions for the user home folder. (Configure permissions for specific folders on the Folders page, as described in Configure Folders and View List of Files.) If you don’t assign specific permissions, these settings are used.
- All: Assign all permissions to the user home folder.
- Read: Allow files to be downloaded.
- Write: Allow files to be uploaded.
- Delete: Allow files to be deleted.
- List: Allow folder contents to be listed.
- Create Folders: Allow subfolders to be created.
- Rename Folders: Allow subfolders to be renamed.
- Delete Folders: Allow subfolders to be deleted.
- Propagate to subfolders: Apply the selected permissions to all subfolders. You can block this setting using the Do not inherit setting when configuring subfolder permissions from the Folders page.
- For users, the default home path is
- Under Groups Default Configuration for Home Folder, view
the home folder's base path and specify the folder's default permissions.
Field Description Folder Path
Displays the base path for group home folders. (Configure individual groups on the Users page, as described in Configure Users.) You can't change the system's default home.
For groups, the default home path is
home/groups/. If you leave a group configured to use the default home (choose Group Default as Home Folder Type on the Users page), the full path to the group's home is/home/users/[groupname].Permissions
Set default permissions for the group home folder. (Configure permissions for specific folders on the Folders page, as described in Configure Folders and View List of Files.) If you don’t assign specific permissions, these settings are used.
- Propagate to subfolders: Apply the selected permissions to all subfolders. You can block this setting using the Do not inherit setting when configuring subfolder permissions from the Folders page.
- All: Assign all permissions to the user or group home folder.
- Read: Allow files to be downloaded.
- Write: Allow files to be uploaded.
- Delete: Allow files to be deleted.
- List: Allow folder contents to be listed.
- Create Folders: Allow subfolders to be created.
- Rename Folders: Allow subfolders to be renamed.
- Delete Folders: Allow subfolders to be deleted.
- Under Security, select an authentication type and change
security settings as needed.
Field Description Authentication Type
Specify whether authentication is by password, SSH key based, or either.
To configure SSH key based authentication:- Generate an SSH key pair. See Generate SSH Keys in PEM Format to Connect to a
Public or On-Premises sFTP Server in Using the FTP
Adapter with Oracle Integration Generation 2.
Note:
Key based authentication supports Open SSH format only. - On the Users page in File Server, select the user and upload the OpenSSH format key.
- On the Users page, enable the user.
- Use the private key to connect via the sftp client.
Security Settings
Specify values from the standard SSH/SFTP settings listed below, which are made up of a list of allowed values. To remove a value, click its x. If you remove a value, File Server no longer supports the value (until you add it back). Add new values by clicking a field and selecting from the list that appears.
- Signature Algorithms
- Key Exchange Algorithms
- Cipher Suites
- Message Authentication Algorithms
- Compression Methods
See IETF RFC 4253 - SSH Transport Layer Protocol for detailed descriptions.
Note:
The FTP client that connects to File Server must support the same configuration that is defined in this section. For example, if your FTP client doesn't support one of the Key Exchange Algorithms that File Server supports, the FTP client won't be able to connect to File Server. - Generate an SSH key pair. See Generate SSH Keys in PEM Format to Connect to a
Public or On-Premises sFTP Server in Using the FTP
Adapter with Oracle Integration Generation 2.
- If needed, revert changes made to these server settings since their last save by clicking Revert.
- Click Save.