Column Manipulation
Column manipulation involves applying operations, such as renaming and transformations, to the values of one or more columns to prepare or modify data during processing.
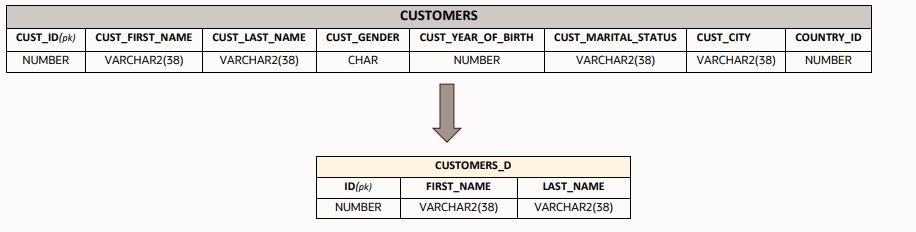
Rename Columns
IMPORT SOURCE CUSTOMERS
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS;
//column renaming
THIS[ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME] = CUSTOMERS[CUST_ID,CUST_FIRST_NAME,CUST_LAST_NAME];
END
In this example, you create the columns ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME in the target table CUSTOMERS_D with the same values and column properties as CUST_ID, CUST_FIRST_NAME,CUST_LAST_NAME from the source table CUSTOMERS.
Transform Column Data
Assign Static Column Values
You can directly assign fixed literal values to one or more columns. The values must be from these following types: NUMBER, VARCHAR2, DATE, Timestamp.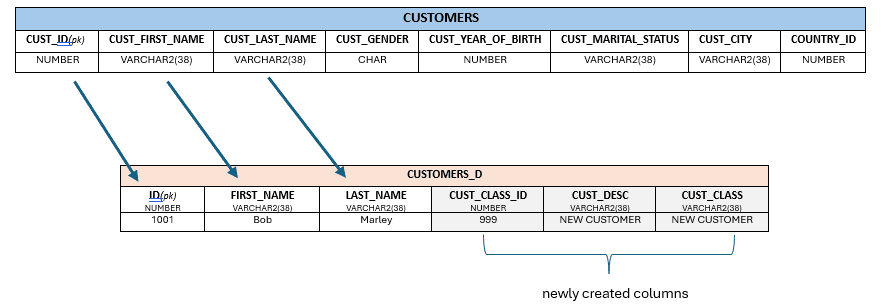
Description of the illustration dasrg-column-staticvalues.png
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS WHERE CUSTOMERS.CUST_JOINING_DATE = ‘2025/02/24’;
THIS[ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME]= CUSTOMERS[CUST_ID,CUST_FIRST_NAME,CUST_LAST_NAME];
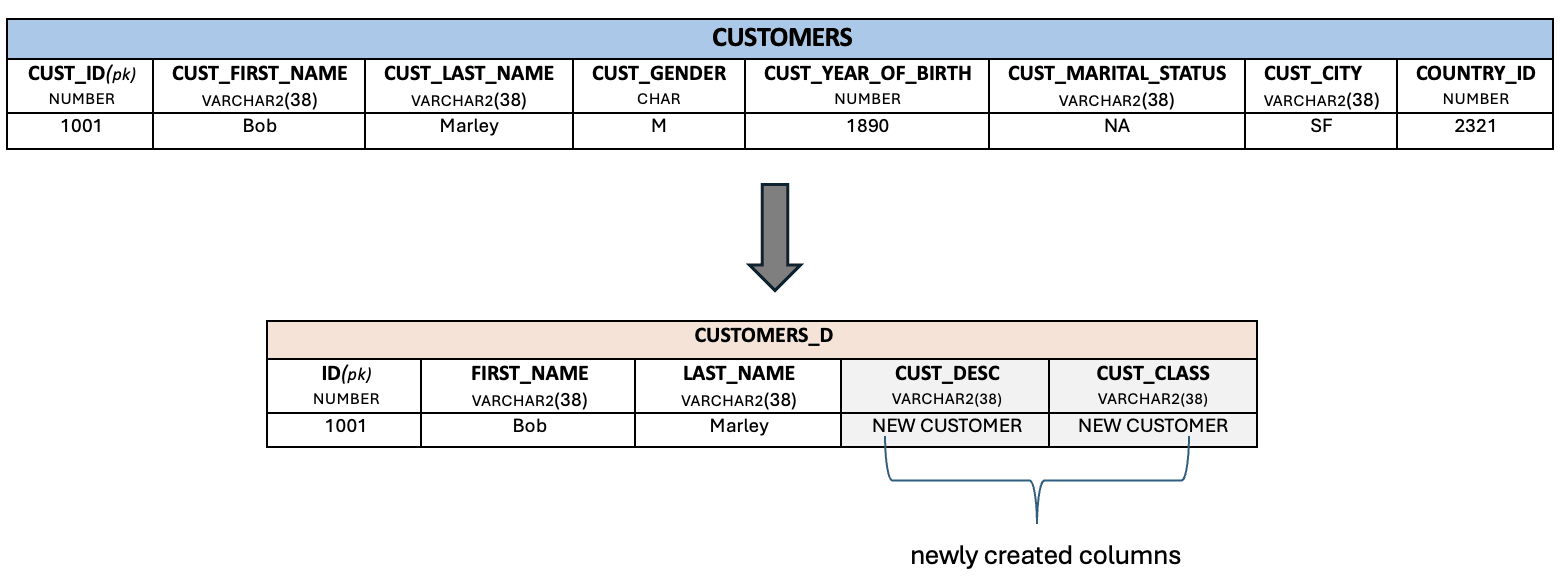
THIS[CUST_CLASS_ID] = 999; //NUMBER
THIS[CUST_DESC,CUST_CLASS] = 'NEW CUSTOMER'; //VARCHAR2(38)
ENDIn this example, you've assigned the column CUST_CLASS_ID to hold the static numeric value 999 and columns CUST_DESC,CUST_CLASS to hold the varchar2 value NEW CUSTOMER.
Apply Functions
DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D
ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS;
THIS[ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME] = CUSTOMERS[CUST_ID,CUST_FIRST_NAME,CUST_LAST_NAME];
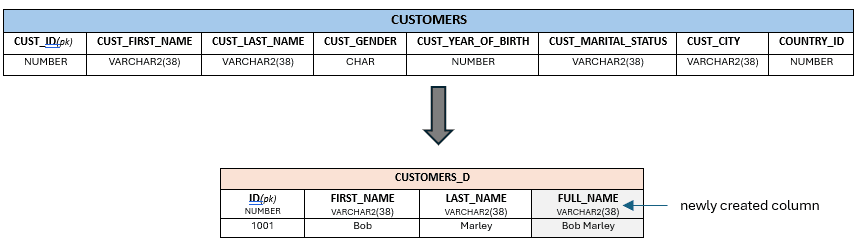
THIS[FULL_NAME] = CONCAT_WS(' ', CUSTOMERS.CUST_FIRST_NAME,CUSTOMERS.CUST_LAST_NAME);
END
In this example, you apply the CONCAT_WS function on the columns CUST_FIRST_NAME and CUST_LAST_NAME to create the column FULL_NAME.
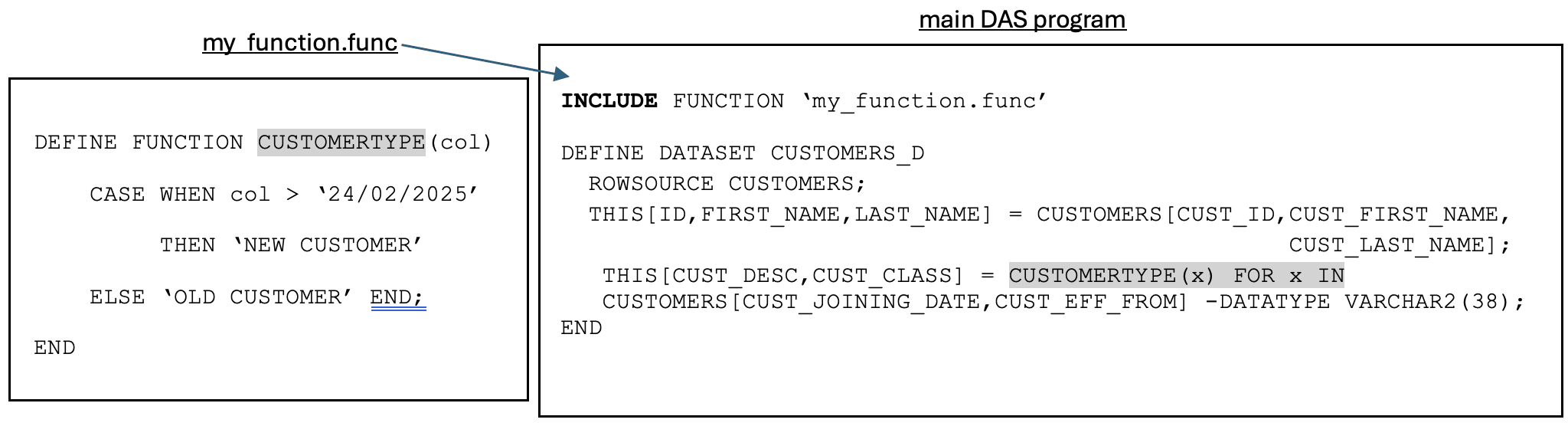
Create User-Defined Functions
- Define the function within the main Data Augmentation Scripts program.
Example:
DEFINE FUNCTION CUSTOMERTYPE(col) CASE WHEN col > ‘2025/02/24’ THEN ‘NEW CUSTOMER’ ELSE ‘OLD CUSTOMER’ END; END DEFINE DATASET CUSTOMERS_D ROWSOURCE CUSTOMERS; THIS[ID,FIRST_NAME,LAST_NAME] = CUSTOMERS[CUST_ID,CUST_FIRST_NAME,CUST_LAST_NAME]; THIS[CUST_DESC,CUST_CLASS] = CUSTOMERTYPE(x) FOR x IN CUSTOMERS[CUST_JOINING_DATE,CUST_EFF_FROM] -DATATYPE VARCHAR2; END - Define the function in a
.funcfile within the project directory, which you can then use within the main Data Augmentation Scripts program with theINCLUDEkeyword.Example:
Specify the Data Type
Data Augmentation Scripts can infer the data type. You must include a datatype specification (-DATATYPE) for the new column when the datatype can't be inferred or needs to be intentionally overridden.
- Create a new column and assign a datatype value.
DEFINE DATASET MY_SALES ROWSOURCE SALES; THIS[PROD_VERSION] = 101 -DATATYPE NUMBER; ENDThis example creates a column
PROD_VERSIONof the datatypeNUMBER. - Create a new column when the datatype can't be inferred.
DEFINE DATASET MY_SALES ROWSOURCE SALES; THIS[INFO] =CONCAT(SALES.PROD_NAME, ' - ', CAST(SALES.SALES_AMT AS VARCHAR2(28))) -DATATYPE VARCHAR2(50); ENDIn this example, you perform the
CONCATfunction on columns with two different data types:PROD_NAME(VARCHAR2(38)) andSALES_AMT(NUMBER). You explicitly define the resulting columnINFOas datatypeVARCHAR2(50). - Create a new column and override the datatype.
DEFINE DATASET MY_SALES ROWSOURCE SALES; THIS[TOTAL_SALES] = SUM(SALES.SALE_AMOUNT) -DATATYPE NUMBER(10,2); ENDIn this example, the
SALE_AMOUNTcolumn is of datatypeNUMBER(10), but you specify that theTOTAL_SALESvalue is stored with a specific precision asNUMBER(10,2).