About Apps
Apps (also known as data delivery platforms) enable you to deliver data via pre-configured integrations to partners. Partners can use this data for media targeting, dynamic creative optimization. and many other purposes,
You install each app separately using the same basic workflow. Because each app is unique, there can be minor variations to installation and configuration procedures. These variations are described in the app's documentation. After you have installed an app, you can select it to deliver data for one or more audiences.
You can deliver audience data to partners without using an app. See Embedded apps, Shared audiences, and Pixel URL delivery.
In this topic:
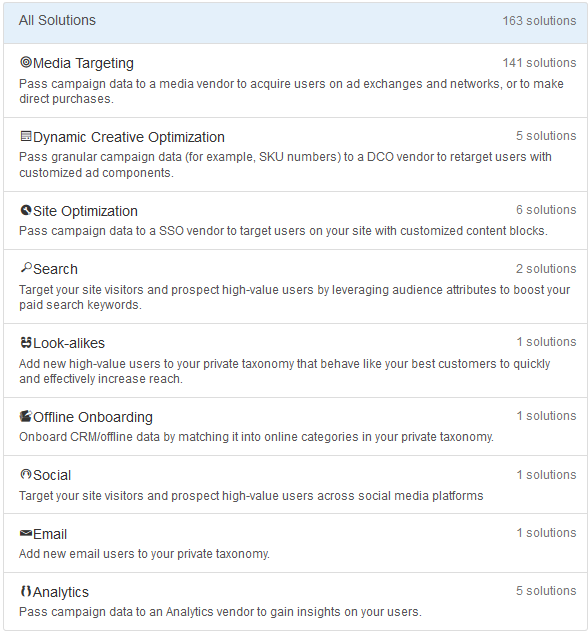
Solution type
Apps are categorized into solution types depending on their purpose. When you install an app, you can search by solution type to find what you need. The figure below displays the most common solution types. The selection of solution types you see depends on your partner seat.
App characteristics
Apps have several important characteristics you need to consider when selecting apps. Make sure that the app you are install supports the your audience data.
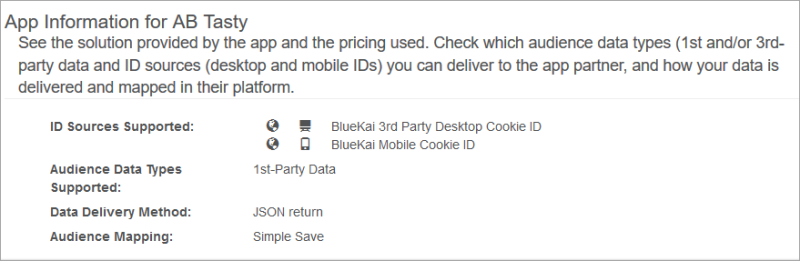
- Supported ID sources. Apps can support IDs derived from desktop and mobile cookies, MAIDs (IDFA and ADID), OTT IDs ( Amazon Fire TV, Apple TV, Android TV, Playstation, Roku TV, and Chromecast), and private IDs.
- Audience data types. Apps can support first-party data, third-party data, or both. In some cases, a partner provides separate apps for each data type.
- Regions. Some apps support data from only one country or group of countries (whitelisting). Other apps restrict delivery from certain countries (blacklisting).
- Data transfer method. An app can use one of several data transfer types:
- Server Data Transfer (SDT): Oracle Data Cloud directly sends audience data directly to a media partner server.
JSON return: Oracle Data Cloud transfers audience data in a JSON object to a JSON return tag on a web page.
Note: JSON return by an app is different from JSON return that you can specify separately when you deliver audience data. The same technology is used in both cases, but is pre-configured in an app.
Pixel: Oracle Data Cloud delivers data to an image pixel endpoint.
Note: Pixel delivery is now deprecated, but may still be used in older apps. Note that pixel delivery by an app is different from "paste-a-pixel" data delivery that you can specify to deliver an audience without an app.
- Server Data Transfer (SDT): Oracle Data Cloud directly sends audience data directly to a media partner server.
- Audience mapping method.Audience data that you deliver to partners needs to be mapped to their audiences and segments. Each app can use one of these three mapping methods.
- Audience injection. The Oracle Data Cloud platform authenticates into the media partner's system and uses their APIs to create audience objects. The partner APIs return external audience IDs for the injected audiences to the Oracle Data Cloud platform, which includes them in subsequent data deliveries.
- Managed mapping. When an audience is delivered, the platform sends an email mapping request to the partner that includes all the information needed to map their data into their segments. After the partner completes the mapping request, data delivery begins.
- Manual mapping. The partner manually shares mapping information with their clients.
You can see information about these characteristics when you select and install an app in the App Catalog.
The information panel in the app catalog may display Simple Save for both managed mapping and manual mapping apps. Managed mapping is more common.