About Nodes
Master or reference data records used to describe, qualify, or summarize enterprise data are managed in Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Data Management as nodes. Nodes can be grouped into lists or hierarchies. For example, within a hierarchy that represents an organizational structure, a node might represent a department or a cost center.
Every node is assigned to a node type. The node type defines the properties that are available for nodes. For more information, see Working with Node Types.
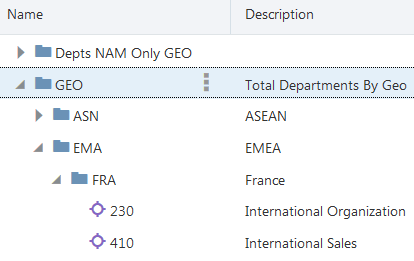
The following terms define the position and behavior of a node within a hierarchy. The examples refer to the hierarchy below.
| Node | Definition and Example |
|---|---|
|
Parent |
The node that contains other nodes. |
|
Child |
A node that is contained by another node. 230 and 410 are child nodes of |
|
Sibling |
All nodes that have the same parent node in a hierarchy. |
|
Leaf |
A bottom-level node with no children. 230 and 410 are leaf nodes. |
|
Limb |
A node that has children. |
|
Top Node |
The starting node for a hierarchy. A viewpoint can have multiple top nodes. |
|
Root Node |
The highest node in a hierarchy set for a node type. Root nodes do not have parents. For example, the highest node in a hierarchy set is the root node. |