Understanding Applications and Sharing Data
Typically you use Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Data Management to govern enterprise data for multiple external applications. For example, an organization could use Cloud EDM to manage entity nodes used in general ledger, consolidation, and Planning external applications.
Videos
| Your Goal | Watch This Video |
|---|---|
|
Learn about sharing data across applications. |
To build applications, users can manage external applications' data using these steps:
- For each external application, register a Cloud EDM application.
- Create a new view.
- In the view, create one viewpoint for each application dimension containing data to be shared. Each viewpoint must use the node set bound to the application's entity dimension.
Users then use the viewpoints to manage the enterprise data. For example, a user could compare two applications' viewpoints and then copy nodes between the viewpoints. Changes can then be exported into the external applications.
Note:
Node type converters are needed to drag and drop, compare, and locate common nodes between viewpoints that use different node types, see Working with Node Type Converters.Two Applications that Share Data
Let's say you need to rationalize nodes for entity dimensions contained by consolidation and Planning external applications. You register two external applications, defining an entity dimension for each. The registration process creates a default view, a bound viewpoint, and related bound data objects.
As shown in the following diagram, to enable sharing between applications, you create a view with two viewpoints; in this example the new view is named Entity View. Each viewpoint uses its entity dimension's bound node set.
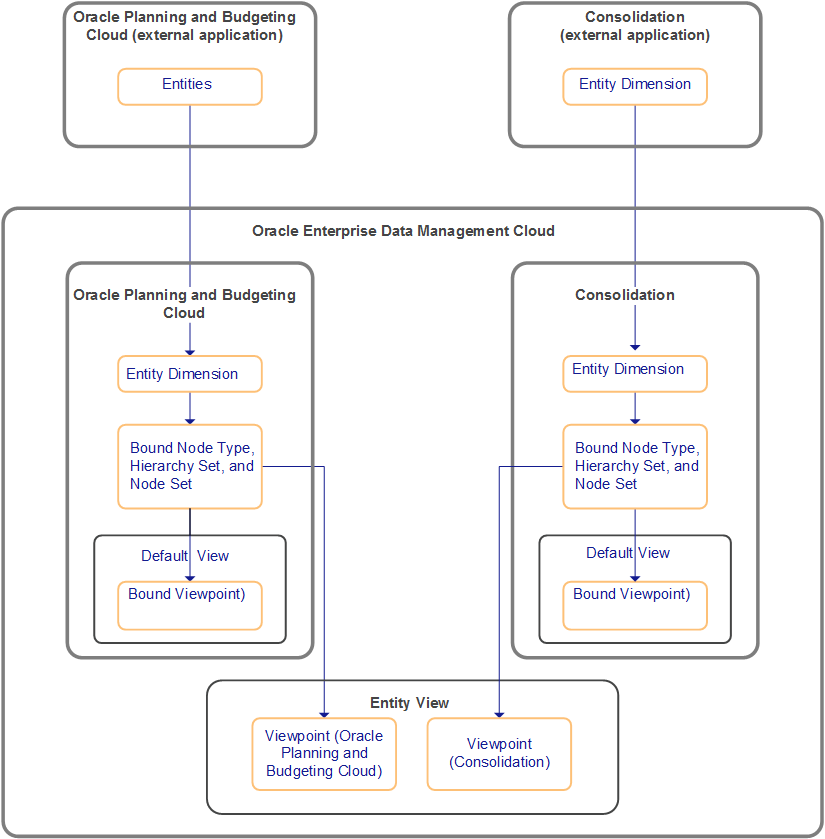
Users can use the Entity View to manage the dimensions' data; for example, users can copy nodes between the viewpoints. Since the Entity View's viewpoints use the bound node sets, any changes made in the new viewpoints are reflected in the bound viewpoints and thus can be exported.
For an example, see Comparing Enterprise Data Across Applications.