Using a Parameter File to Pass Values for Command Execution
Most EPM Automate commands require runtime parameters. You can provide these values directly in the Command Prompt or store them in a parameter file for the command to use.
All parameter values, including credentials (Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Performance Management user name and encrypted or plain-text password), required to run a command can be stored in a parameter file instead of being entered at the Command Prompt. Using a parameter file improves reusability and security while running commands.
About the Parameter File
Each command requires its own parameter file because the parameters vary by command. For example, different parameters are used by the copyFromObjectStorage command and the copyFromSFTP command.
Command parameters are positional, meaning they must be provided in a specific order. The parameter file for each command must follow the usage pattern and sequence of that command’s mandatory parameters. Optional parameters are specified after the mandatory ones and can be listed in any order.
For example, the usage pattern of mandatory parameters for running the login command using encrypted password: is as follows:
epmautomate login USERNAME PASSWORD_FILE URLThe parameter file that you use to run the login command, for example,
login_encrypted.txt, must list the parameter values in the exact order
specified by the preceding usage pattern.
serviceAdmin
C:\mySecuredir\password.epw
https://test-cloud-pln.pbcs.us1.oraclecloud.com
A parameter file does not need to include all required parameters. For example, the
new_login_encrypted.txt file does not contain the value of the
username parameter.
C:\mySecuredir\password.epw
https://test-cloud-pln.pbcs.us1.oraclecloud.com
Because the value of username (serviceAdmin) is omitted
from the parameter file, you must supply it at the Command Prompt.
See Using the Parameter File with Commands for examples illustrating the use of
these files to run the logincommand.
Creating a Parameter File
The contents of the parameter file must match the usage pattern of the command with which the file is used. Because the required parameters are positional, ensure that they appear in the exact sequence indicated in the usage pattern.To create a parameter file:
- Using a text editor, create a new file and save it in a folder.
- Copy the usage pattern of the command for which you want to create the parameter
file and paste it into the text file you created in the preceding step. For
example, if you are creating a parameter file for the cloneEnvironment command, the usage pattern is as
follows:
epmAutomate cloneEnvironment TARGET_USERNAME TARGET_PASSWORD TARGET_URL [SnapshotName=NAME] [UsersAndPreDefinedRoles=true|false] [DataManagement=true|false] [appAudit=true|false] [jobConsole=true|false] [storedSnapshotsAndFiles=true|false] [DailyMaintenanceStartTime=true|false] [ApplicationProperties=true|false] - Edit the file:
- Delete the text preceding the first mandatory parameter; in this
example, delete
epmAutomate cloneEnvironment - Replace each mandatory parameter with the value you want to use.
- Replace each optional parameter with the value you want to use.
- Delete the optional parameters you do not want to use. EPM Automate will use their default values.
- Insert a line break after each mandatory and optional parameter value.
For example. your file's content may be similar to the following:
serviceAdmin Password.epw https://epm-test-ociarcs.epm.us.region.ocs.oc-test.com UsersAndPreDefinedRoles=true ApplicationProperties=false storedSnapshotsAndFiles=true DailyMaintenanceStartTime=false
- Delete the text preceding the first mandatory parameter; in this
example, delete
- Save the parameter file.
Using the Parameter File with Commands
Use the -p FILE_NAME option to pass the parameter file to the
command.
The position of the -p FILE_NAME option in the command
determines how the files contents are used. EPM Automate inserts the contents of the
parameter file where the -p FILE_NAME option appears.
Using the login_encrypted.txt parameter file, which contains all the mandatory values (see the preceding section), you will run the following command to start a session:
epmautomate login -p login_encrypted.txtUsing the new_login_encrypted.txt parameter file, which omits the username mandatory value, referenced in the preceding section, you will run the following command to start a session:
epmautomate login serviceAdmin -p new_login_encrypted.txtEntering Parameters in Multiple Lines
Use the -p - option to enable multi-line input, which allows you to
pass command parameters in multiple lines. After specifying all the command
parameters, enter + (the Plus character) in a new line to start the
command execution. Here's an example: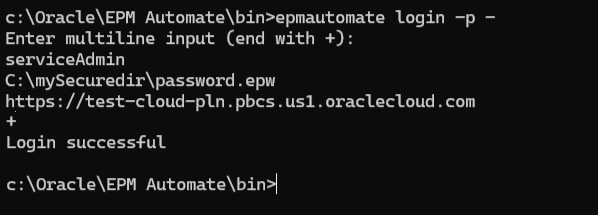
Note:
- You cannot use a parameter file in multi-line input mode; you must manually enter parameters in the console.
- Each parameter must be entered into a separate line. You will get the EPMAT-7:Invalid or missing parameter error if you enter multiple parameters into one line after invoking multi-line input mode.