Step 4: Clean up Prior Integrations in TDATASEG
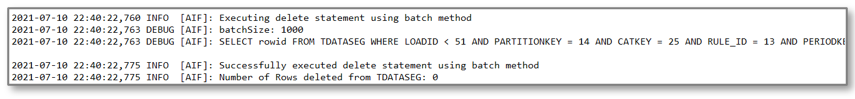
Upon the successful completion of mapping, the system deletes the prior run from the TDATASEG table. (The TDATASEG table is where the data for the workbench is stored.) If this is the first execution of the integration, this step completes quickly because there isn’t any prior period data. If there is a large amount of prior data, then this step can potentially take a long time.
As you see below, the batch size parameter is used to delete chunks of data from the TDATASEG table so that the delete process does not hit the processing limit for an individual SQL statement. It’s possible to tune this step by adjusting the batch size so that you limit the number of delete statements. For this execution, the batch size was set to 1000, and it could be set higher. On a subsequent execution, this step took 6 minutes to delete the prior load of approximately a million records.
Note:
Do not set the batch size to be very large as the data is loaded to memory for processing based on the batch size, and can use up memory. The system memory is common for the Oracle Fusion Cloud Enterprise Performance Management and can impact other areas of the instance.