Editing data objects
Learn more by watching the video!
- Partition strategy
- Bucketing strategy
- Incoming records flag
After publishing changes the first time for a custom data object, you can't change these configurations. After running the first publish job in your tenant, you can't change these configurations for all default data objects.
To edit a data object:
-
Click the Oracle icon
 in the bottom-right corner to open the navigation menu.
in the bottom-right corner to open the navigation menu.
- Select Data model.
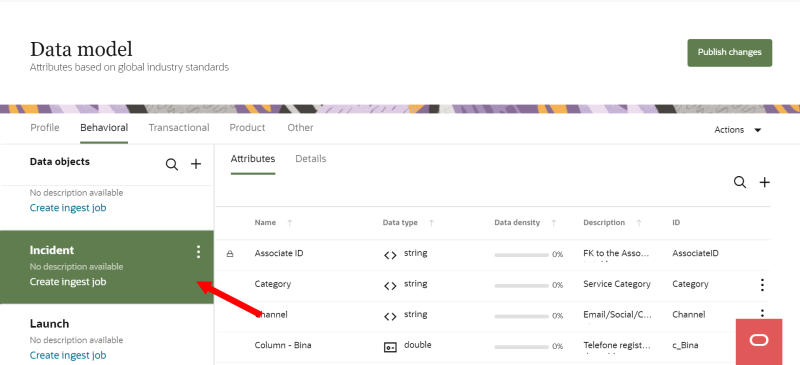
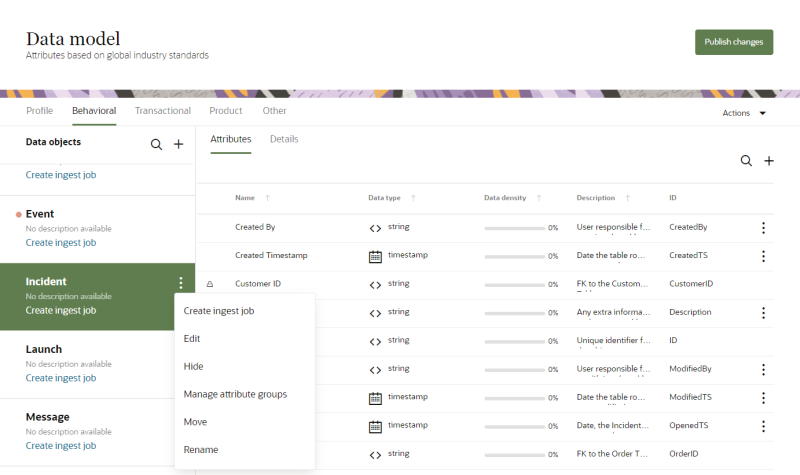
- Find the data object you want to edit in the list of Data objects.
- Move your mouse cursor over the data object and click the Action menu (
 ).
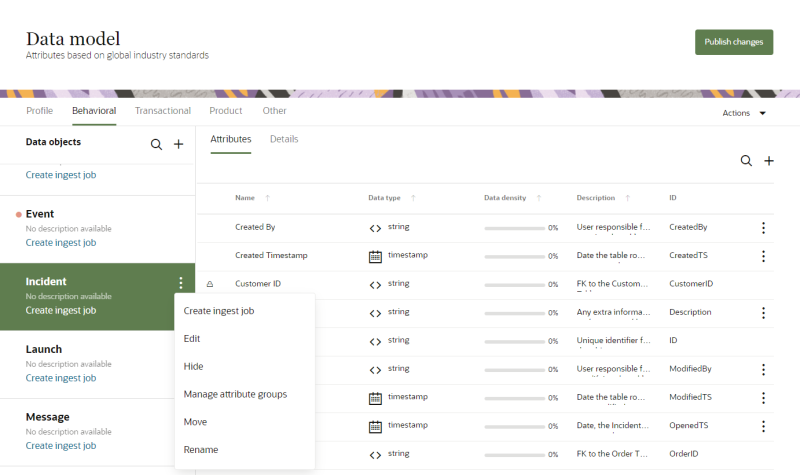
). - Select Edit. The Edit data object dialog opens.
- From the Edit data object dialog, edit the following fields:
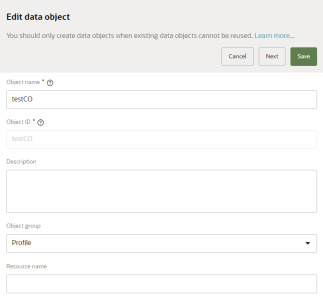
- Object name: Enter a name for the data object. This is the name used to identify the object throughout the application. The name must be 1 or more characters, up to a maximum of 40. Other than underscores (_) and hyphens (-), special characters are not allowed. The first character cannot be a space. You can use characters from all languages supported in the language settings.
- Object ID: You can't change this field after creating the data object.
- Description: This field is optional, but it is highly recommended to add descriptions for any entity created. This helps all other users get additional context when using and navigating the platform. The description can have a maximum of 512 characters with no restrictions on characters used. You can use characters from all languages supported in the language settings.
- Object Group: The object group the data object should belong to. You can change the current selection to any other object group: Profile, Behavioral, Transactional, Product, or Other.
- Resource name: The name that the Oracle Audience Segmentation API will use to access the data object. You should enter a resource name only if you want the data object to be accessible through an API. The resource name can have a maximum of 50 characters. Use only letters (a–z and A–Z), numbers (0–9), and underscores (_).
- Do one of the following depending on if the data object has been published.
- If the data object hasn't been published, you can also manage additional configurations. Click Next.
- If the data object has been published, review the changes and click Save.
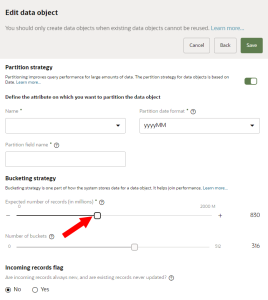
Partition strategy
You can enable and update partition strategies in default and custom data objects.
-
You can enable and update partition strategies in default data objects before running the first publish job in your tenant.
-
You can enable and manage custom data objects before publishing changes for the data object the first time.
-
You can enable a partition strategy for a data object and then edit it to select a different attribute that will be used to create partitions. This only applies if you haven't run the first publish job in your tenant (default data objects) or published changes for the custom data object the first time.
-
When editing a data object, the field names in the Partition strategy section will depend on if a partition strategy was previously enabled or not.
Partition strategy improves query performance for large amounts of data. The partition strategy for data objects is based on Date. Learn more about Partitioning.
To update the partition strategy:
- Turn the toggle on. The options for partition strategy will display.
- Configure the details for the partition strategy.
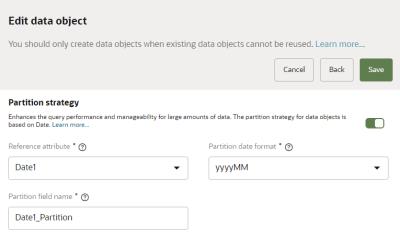
- Reference attribute or Name: The name of this field depends on if a partition strategy was previously enabled.
- Name: If no partition strategy was previously enabled, enter the name of the attribute you want to use to create partitions. For example, you may want to partition from the EventTS attribute. The name must be 1 or more characters, up to a maximum of 50. Other than underscores (_) and hyphens (-), special characters are not allowed. The first character cannot be a space. You can use characters from all languages supported in the language settings.
- Reference attribute: If a partition strategy was previously enabled and you want to update the attribute used to create partitions, use the drop-down list to select a different attribute with a Date data type.
- Partition date format: Select the date format of partitions. The format controls the size of the partition. Selecting yyyyMM creates monthly partitions and yyyy creates yearly partitions. Ingested records are stored in the corresponding partition based on the format.
- Partition field name: This field name is used to retrieve the data stored in the corresponding partition based on the date format. Oracle Audience Segmentation uses the value from the attribute entered in the Name field to generate the values in the partition field name.
- This field is auto-populated from the attribute ID you enter but can be changed. For example, if you partition the EventTS attribute, this field will auto-populate with the EventTS_Partition field name.
- The partition field name must be 1 or more characters, up to a maximum of 50. Use only letters (a–z and A–Z), numbers (0–9), and underscores (_). The first character must be a letter.
Bucketing strategy
Bucketing strategy is one part of how the system stores data for a data object. It helps join performance. Learn more about Bucketing strategy.
To update the bucketing strategy:
- For Expected number of records (in millions), use the slider to estimate the number of records the data object will have. The Number of buckets value will automatically adjust based on the number of records you select. After publishing the data object, you can't change these values.
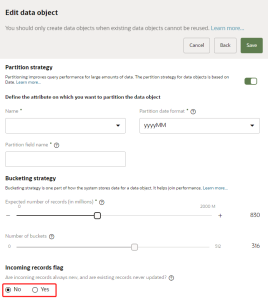
Incoming records flag
You have the option of configuring how records are updated for the data object.
To update the incoming records flag:
- For Are incoming records always new, and are existing records never updated?, choose one of the following options.
- No: The system allows you to both insert new and update existing records. This is the default value.
- Yes: The system allows you to only add new records. You can't update existing records. Use this when you don’t need to update existing records, such as when creating an Event object.
- When you are satisfied with all the updates to the data object, click Save.
When you are fully satisfied with the partition strategy, bucketing strategy, and incoming records flag configurations for the data object, you can follow the steps for Publishing changes.
Hiding and showing data objects
When you hide a data object, it is no longer visible or accessible in the data model. Learn more about Managing the visibility of data.
If you need to view which data objects have been tagged as hidden, you can do so by Viewing hidden items.
To hide a data object:
-
Click the Oracle icon
 in the bottom-right corner to open the navigation menu.
in the bottom-right corner to open the navigation menu.
- Select Data model.
- Find the data object you want to hide in the list of Data objects.
- Move your mouse cursor over the data object and click the Action menu (
 ).
). - Select Hide.
- Confirm the action and click Yes.
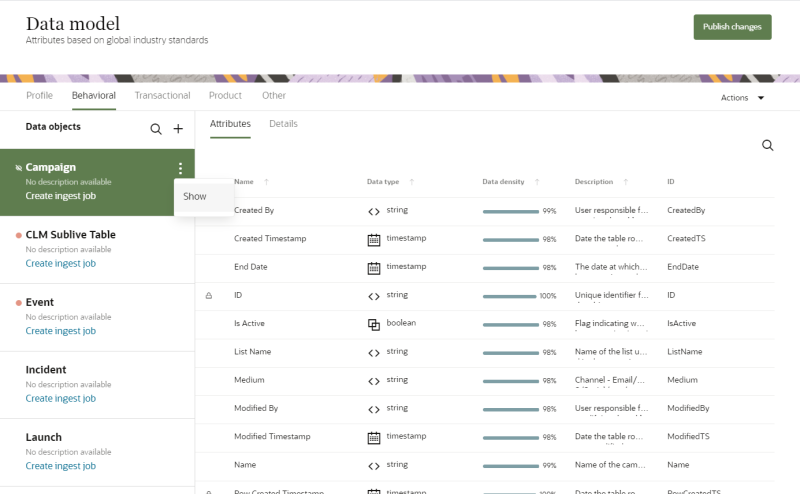
To show a hidden data object:
-
Click the Oracle icon
 in the bottom-right corner to open the navigation menu.
in the bottom-right corner to open the navigation menu.
- Select Data model.
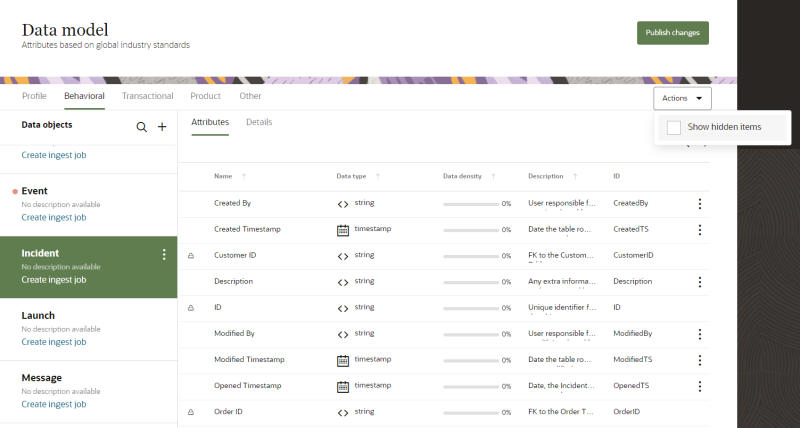
- Click Actions and click the checkbox for Show hidden items.
- Find the data object you want to show in the list of Data objects. It will have the hidden tag
 next to the name.
next to the name. - Move your mouse cursor over the data object and click the Action menu (
 ).
). - Select Show.
- Confirm the action and click Yes.
Note: If you show a data object with individual attributes that were previously hidden, those attributes will remain hidden.
Learn about the default data model
Managing the Oracle Audience Segmentation data model