Monitor Flow Schedules for a Production Line Using the Production Supervisor Workbench
Flow production lines run at a steady rate to meet customer demand, so any interruption poses a risk to the product quality and on-time delivery, resulting in waste and variability. Real-time production visibility is critical to quickly resolving problems and making decisions that optimize operational performance. You can now monitor production line performance in real time and manage the flow schedules for the production line workstations.
As a production supervisor, you can perform various actions for the production line:
- Track the Key performance indicators (KPIs) for the production line against predefined benchmark values for a day's performance. The KPIs include:
- Line Capacity
- Completed Quantity
- OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness)
- Availability
- Performance
- Quality
- Downtime
- Scrapped Quantity
- Open Exceptions
- Manage open exceptions for the production line.
- View and manage flow schedules for the production line workstations. The actions include:
- Resequence flow schedules
- Reschedule flow schedules
- Cancel flow schedules
- Print labels for flow schedules
- Assign operators to workstations for the production line to execute a flow schedule.
Production Line Monitoring Tab:
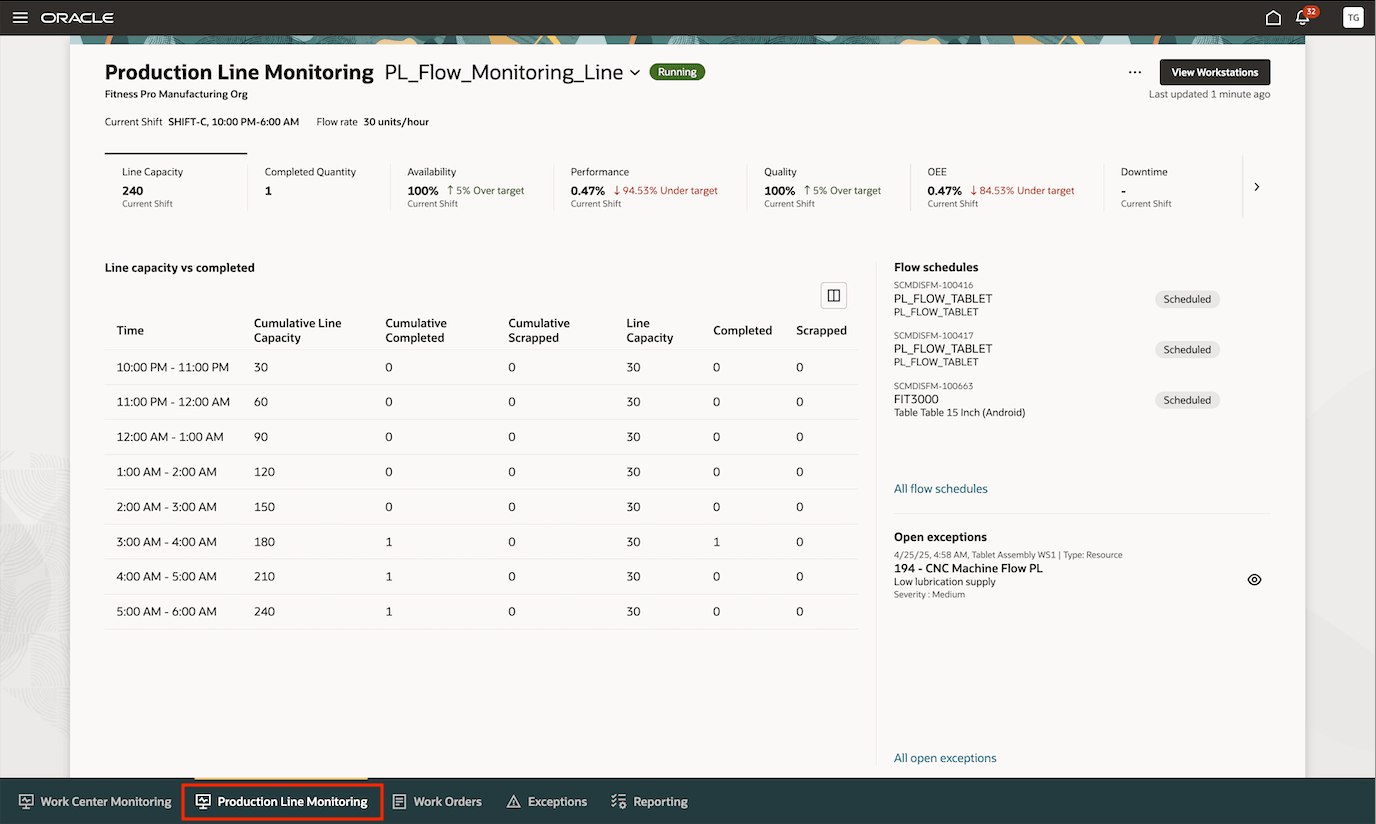
The Production Line Monitoring tab in the production supervisor workbench provides real-time insights into workstation performance, including line capacity, completed quantity, OEE, availability, performance, quality, downtime, and open exceptions. It helps supervisors track deviations, monitor exceptions, and ensure production continuity with scorecards and workstation-specific data, enabling proactive decisions to maintain efficiency and productivity on the shop floor. The workbench focuses on end-of-line reporting and does not capture intermediate operation completions within the flow schedule.
You can determine the status of a production line by viewing the badge displayed next to the production line name in the page header. The production line status badge reflects the real-time state of all workstations linked to the line. The status is considered running when all associated workstations are in-use. The badge shows idle if at least one workstation is idle, and it switches to down if even a single workstation tied to the line reports a down status.
Production Line Monitoring Tab
The following key metrics can be monitored for a production line:
Line Capacity: Line Capacity represents the total number of units a production line can produce within the current shift. It reflects the planned throughput under ideal circumstances without interruptions or slowdowns. Line capacity is determined by the flow rate specified during the production line configuration. The calculation uses the plant-level calendar, which defines working and non-working days, including holidays and shutdowns, for all production lines within the plant. This ensures consistency in how capacity is planned and reported across shifts.
Completed Quantity: Completed quantity refers to the number of units successfully produced and completed on a production line or workstation for the current shift. This metric helps track actual output against planned quantities and is essential for evaluating efficiency, order fulfilment progress, and production goal attainment in real time.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): OEE measures how effectively a workstation or production line is utilized, combining Availability, Performance, and Quality into a single metric. It reflects the percentage of scheduled production time that is truly productive, helping identify loss areas and drive manufacturing efficiency improvements, for the current shift.
Availability: Availability indicates the proportion of scheduled time a production line is actually running in the current shift. It accounts for unplanned and planned downtime events and reflects equipment readiness. High availability ensures minimal interruptions and supports consistent flow in production schedules.
Performance: Performance measures how fast a production line operates compared to its maximum potential speed in the current shift. It considers minor stops and reduced operating speeds. Monitoring performance helps identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies that prevent equipment from running at optimal throughput levels.
Quality: Quality reflects the percentage of good units produced without defects on a production line for the current shift. It excludes any units that fail inspection. Maintaining high quality ensures product consistency, reduces waste, and supports customer satisfaction and compliance.
Downtime: Downtime refers to periods when a workstation is not operational, including both scheduled maintenance and unplanned interruptions. Downtime directly affects Availability and OEE and must be tracked using reason codes to identify root causes and reduce productivity losses.
Scrapped Quantity: Scrapped Quantity refers to the number of units discarded during production at a workstation or production line due to defects or non-conformance for the current shift. Tracking scrap helps identify quality issues, reduce material waste, and improve overall production efficiency and cost control.
Open Exceptions: Open Exceptions are unresolved issues or deviations detected during production at the workstation or line level, such as quality failures, resource conflicts, or schedule variances. Monitoring open exceptions enables faster corrective actions and prevents disruptions from impacting throughput or delivery timelines.
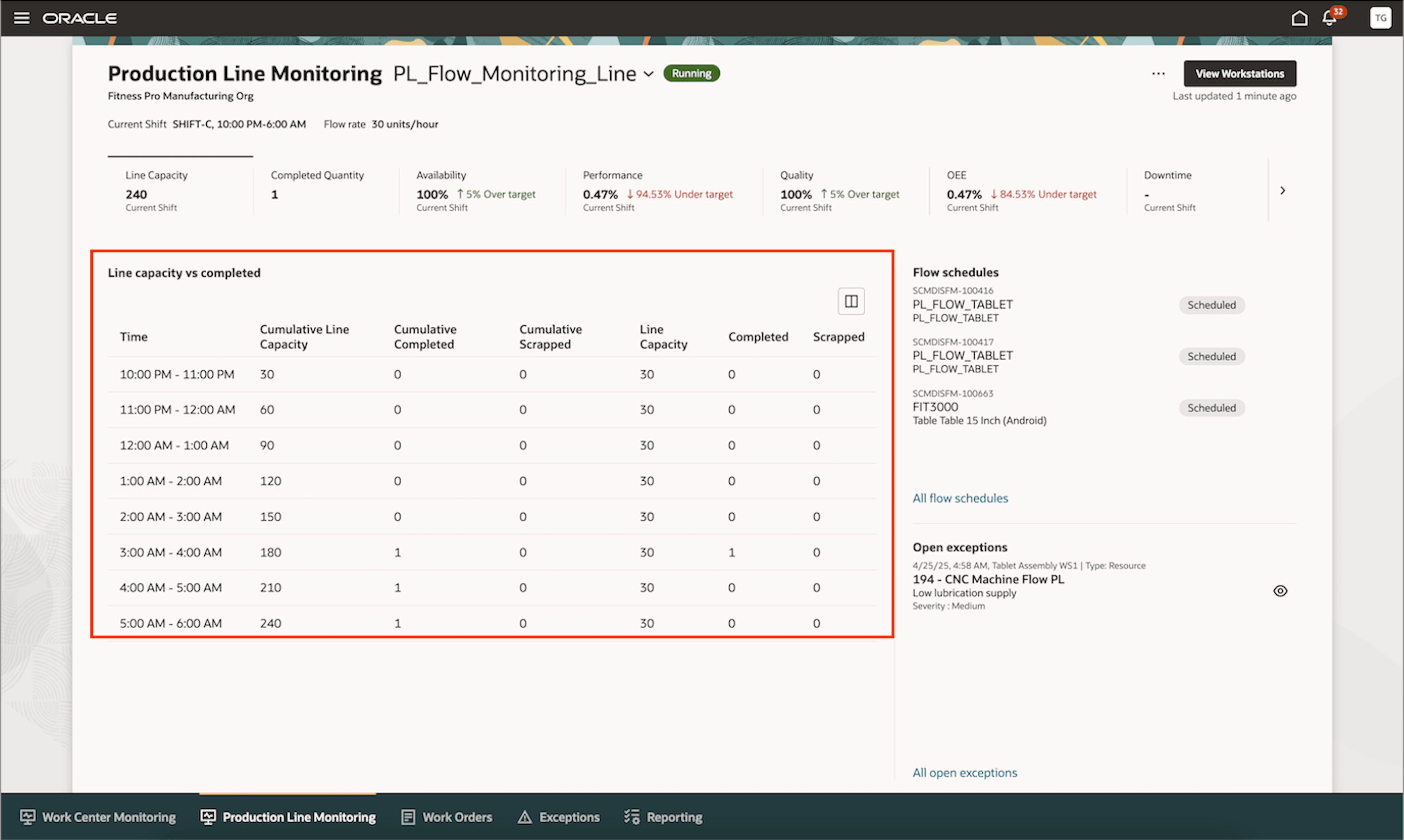
Line Capacity versus Completed Quantity Table: The Line Capacity vs Completed Quantity table provides a detailed, time-based view of how a production line is performing throughout a shift. By comparing planned capacity to actual output at regular intervals, supervisors can monitor progress, identify issues early, and take corrective actions to ensure production goals are met. This table helps track not only the quantity produced but also defective output, offering a complete picture of operational performance on the line.
Line Capacity vs Completed Table
Time: Represents a one-hour interval within the shift, dividing the shift into manageable periods for tracking production metrics and performance.
Line Capacity: The maximum number of units that can be produced in an hourly time interval (for example, hourly), based on shift hours and the flow rate of the production line.
Completed: The actual number of units produced within a specific time interval, tracked based on operation completions recorded in the system.
Scrapped: The number of defective or unusable units identified at the workstation level during production, which cannot proceed further.
Cumulative Line Capacity: The total available production capacity from the start of the shift up to the current time. It is calculated as the sum of line capacity values for each completed time interval within the shift.
Cumulative Completed: The total number of units successfully produced so far, starting from the beginning of the shift. This helps in tracking overall production progress, as compared to the expected capacity.
Cumulative Scrapped: The total number of scrapped units recorded from the start of the shift.
The Line Capacity vs Completed table rounds off quantity values to display whole number values for each hourly interval.
A production line is considered to have started only after an operator marks at least one flow schedule as complete.
Monitoring Production Lines Using Workstations
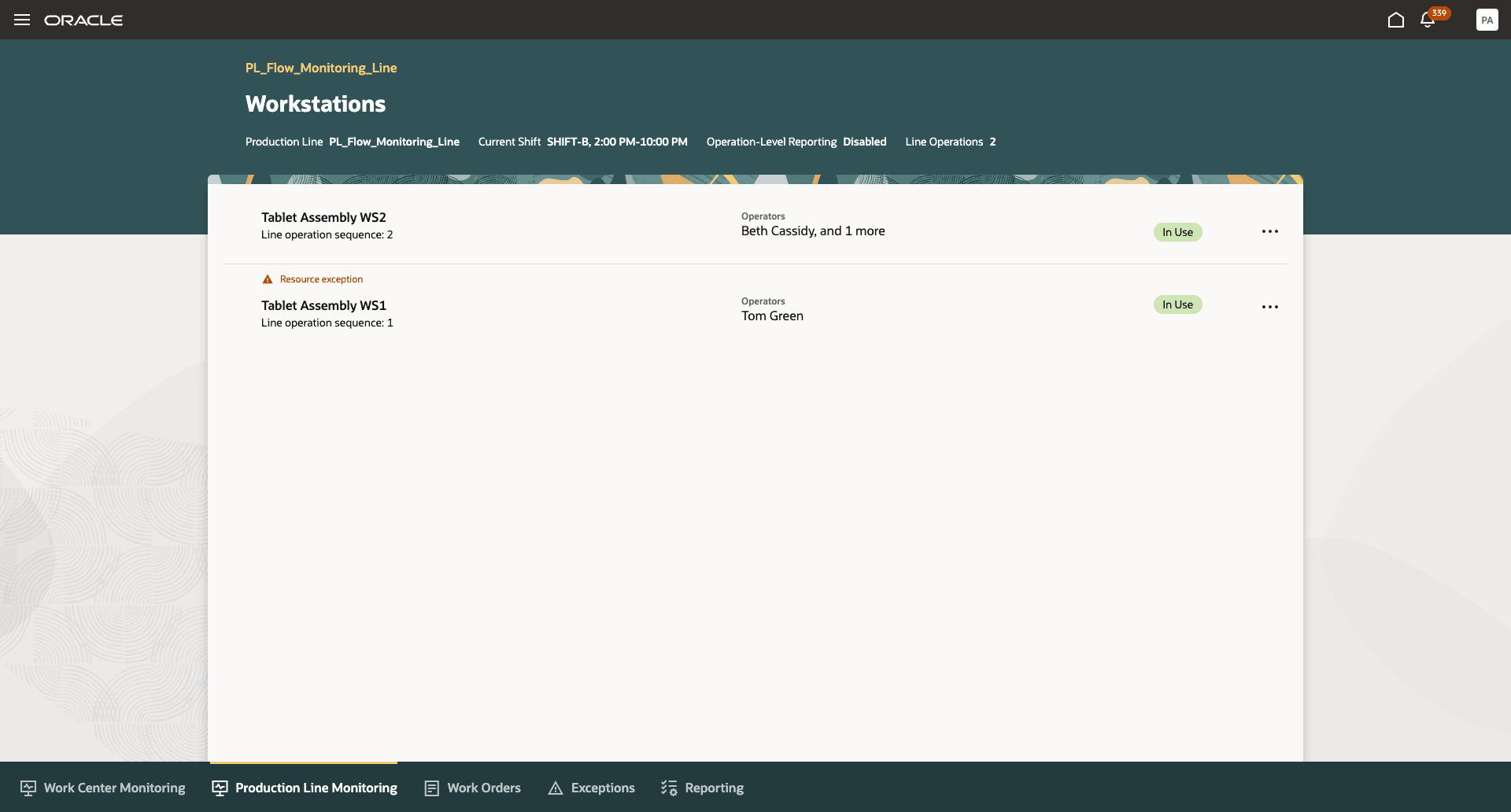
Each production line is designed to support flow manufacturing by running at a steady pace aligned with customer demand. To manage this, production lines can be configured with multiple line sequences, each representing a specific step in the overall process. Workstations are linked to these line sequences, enabling manufacturers to assign operations, track progress, and ensure smooth production flows from one stage to the next. Any disruptions at a workstation whether due to downtime, material shortages, or operator issues can introduce variability and compromise quality or delivery targets. This makes real-time tracking of workstation performance essential for maintaining Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and identifying areas where performance, availability, or quality losses occur.
To gain an overview of how workstations relate to the production line, production supervisors can click View Workstations from the Production Line Monitoring page. This displays all workstations mapped to each line sequence, along with the operator checked in at each workstation, any open exceptions, and the current workstation status.
View Workstation Details
Manage Operator Assignments
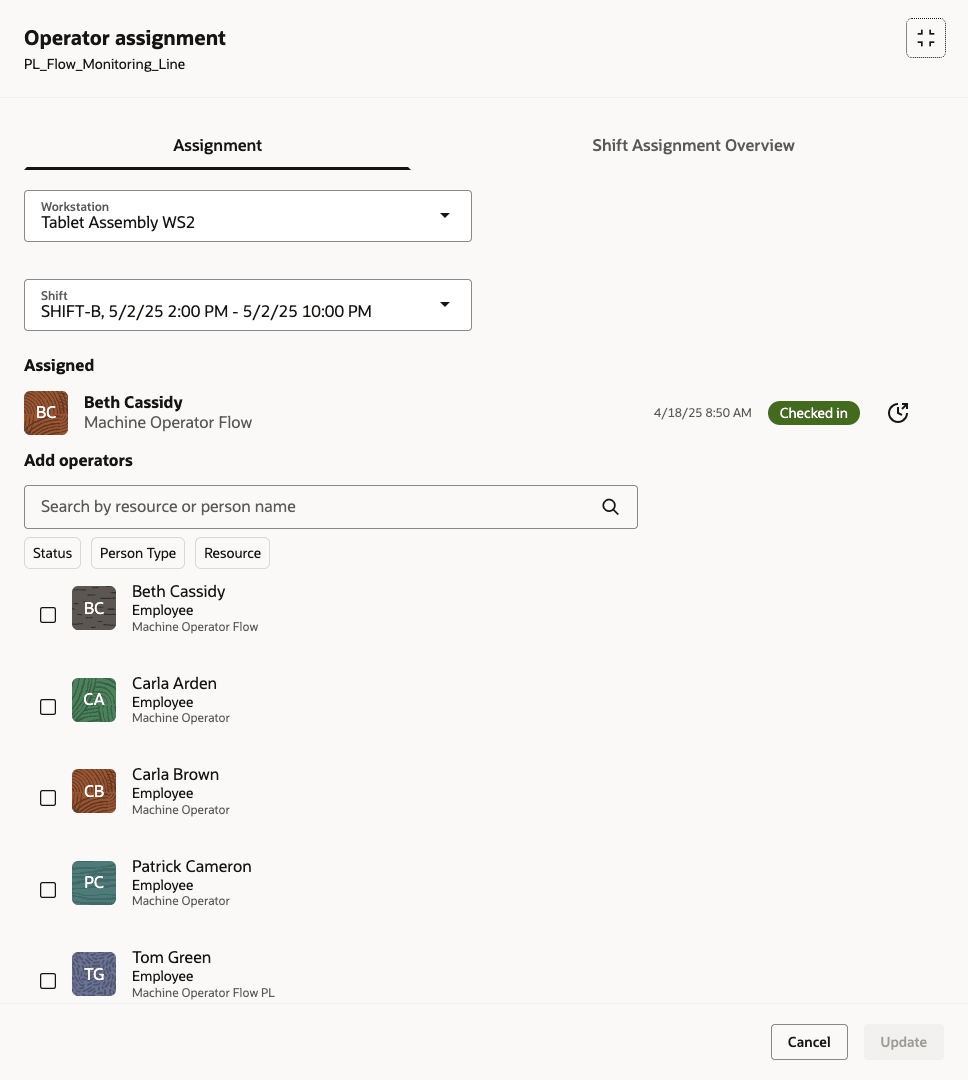
Managing operator assignments is key to ensuring that the right personnel are executing operations at the appropriate workstations. Supervisors can assign one or more operators to a workstation. In production line environments where lines run at a steady pace to meet customer demand, proper operator alignment is essential to prevent interruptions that could impact quality or on-time delivery.
Operator assignments can be reviewed and adjusted directly within the Production Supervisor Workbench, giving supervisors real-time visibility into who is operating each workstation. This enables quick reassignments in response to absence, bottlenecks, or performance issues.
Additionally, the Operator Assignment parameter in the Smart Operations Configurations page controls whether operators must check in at specific workstations. Enforced mode limits check-in to assigned workstations, while Not Enforced allows check-ins at any workstation. Operator check-in is required in both modes to execute work.
Manage Operator Assignments
Manage Flow Schedules in a Production Line
Production supervisors can effectively manage flow schedules to ensure production lines operate smoothly and stay aligned with customer demand. Flow schedules represent planned production for a specific product on a flow line, and their proper sequencing and timing are critical for maintaining continuous flow. Supervisors have the ability to resequence flow schedules, adjusting their execution order based on real-time priorities or material availability. This is particularly important in dynamic manufacturing environments where downstream constraints, resource changes, or urgent orders require fast reordering of tasks to avoid idle time at workstations.
Supervisors can also take additional actions, such as rescheduling flow schedules to adjust their planned start or completion dates, canceling schedules when demand drops or material is unavailable, and printing labels for individual flow schedules to support packaging, traceability, or downstream processes. These capabilities provide real-time control over execution and enhance operational agility.
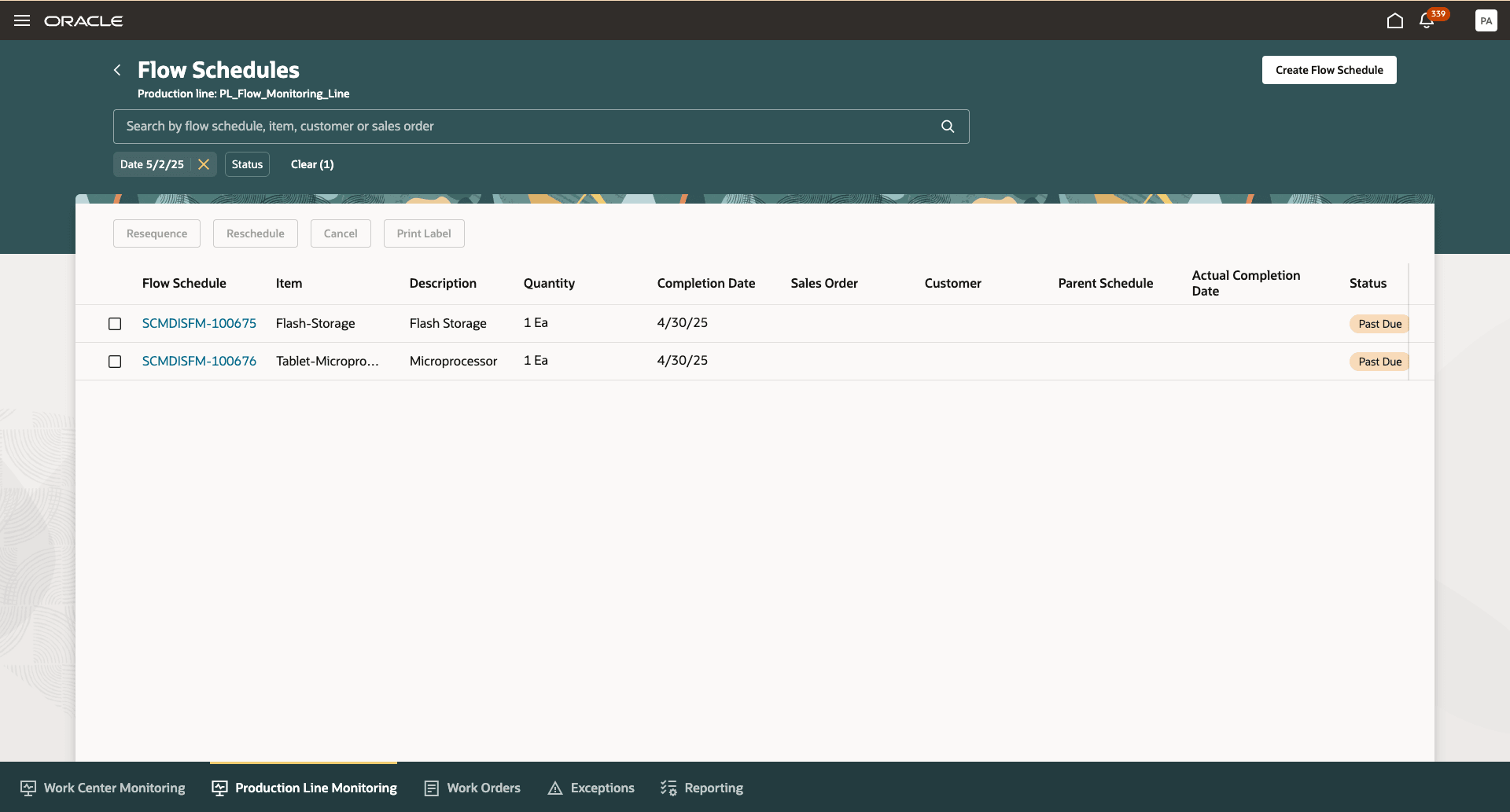
Manage Flow Schedules
Viewing Exceptions
The Exceptions tab has been enhanced to show open exceptions on production lines. Supervisors can create new exceptions, report exceptions, and close them once the exceptions are resolved.
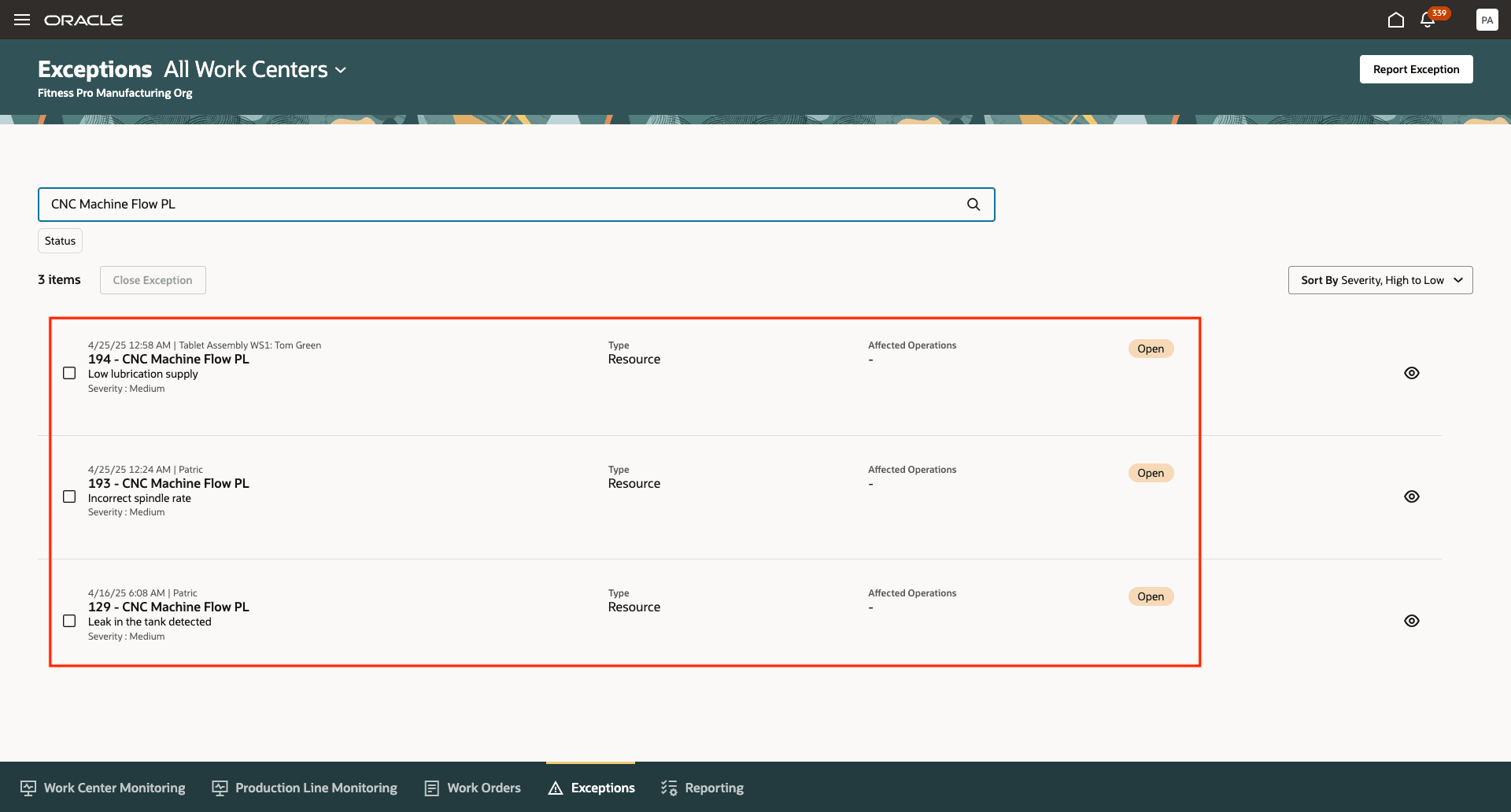
View Exceptions
Real-time insights on production line performance helps supervisors address issues on time, manage their teams efficiently, and optimize the use of people and equipment.
Here's the demo of these capabilities:
Steps to Enable
While this feature is enabled when the parent temporary opt-in feature, Execute Flow Schedules at a Workstation, is enabled, users must perform the following setup steps to use it effectively:
- Define workstations and associate them with the appropriate production line.
- Set up line operation sequences in the production line definition.
- Associate each workstation with a line operation sequence.
- Configure relevant Smart Operations Configuration parameters, including operator assignment settings.
Tips And Considerations
Using the extensibility features of VB Studio, you can edit the page to:
- Assign the Production Line Monitoring tab as your default tab.
- Modify the default ordering of tabs.
- Hide or display seeded scorecard metrics.
If your role has the Configure OTBI Reports on Landing Page privilege, you can add your own KPI metrics and visualization reports to the dashboard pages by creating them with Oracle Transactional Business Intelligence (OTBI).
Key Resources
- Watch the feature demo for Monitor Flow Schedules on a Production Line Using the Production Supervisor Workbench.
- Oracle Fusion Cloud SCM: Refer to Manage Flow Schedules for Manufacturing Execution on a Production Line on the Oracle Help Center.
- Oracle Fusion Cloud SCM: Refer to Execute Flow Schedules at a Workstation (25C).
- Oracle Fusion Cloud SCM: Refer to the Using Manufacturing guide, available on the Oracle Help Center.
- Oracle Fusion Cloud SCM: Refer to the Implementing Manufacturing and Supply Chain Materials Management guide, available on the Oracle Help Center.
Access Requirements
Users who are assigned a configured job role that contains these privileges can access this feature:
- Supervise Production (WIP_SUPERVISE_PRODUCTION_PRIV)
- Manage Assignment of Operators to Workstation (WIP_MANAGE_WORKSTATION_OPERATORS_PRIV)
- Execute Production at a Workstation (WIP_EXECUTE_WORKSTATION_PRIV)
- View Production Exceptions (WIP_VIEW_PRODUCTION_EXCEPTIONS_PRIV)
- View Production Shift Details (WIP_GET_PROD_SHIFT_DETAILS_PRIV)
- Configure OTBI Reports on Landing Page (WIS_CONFIGURE_OTBI_REPORTS_LANDING_PAGE_PRIV)
In addition to the preceding privileges, users should have item class data security configured with the View Item Basic action set to allowed.
Flow Manufacturing:
- Manage Flow Schedules by Service (WIP_MANAGE_FLOW_SCHEDULES_SERVICE_PRIV)
- Manage Flow Schedules (WIP_MANAGE_FLOW_SCHEDULES_PRIV)
- Execute Flow Schedules (WIP_EXECUTE_FLOW_SCHEDULES_PRIV)
- View Flow Schedules (WIP_VIEW_FLOW_SCHEDULES_PRIV)
- Get Flow Schedules by Service (WIP_GET_FLOW_SCHEDULES_SERVICE_PRIV)
Visualization Configurations:
- View Service Manager Dashboard (SVC_VIEW_SERVICE_MANAGER_DASHBOARD_PRIV)
- View Service Representative Dashboard (SVC_VIEW_SERVICE_REPRESENTATIVE_DASHBOARD_PRIV)
Guided Journeys: Role Codes:
- Use REST Service - Guided Journeys Read Only (Role Code ORA_PER_REST_SERVICE_ACCESS_GUIDED_JOURNEYS_RO)
- Use REST Service - Guided Journey Responses (Role Code ORA_PER_REST_SERVICE_ACCESS_GUIDED_JOURNEY_RESPONSES)