Plan Considering Operational Yields and Calculated Batch Quantities in Process Manufacturing
Oracle Fusion Cloud Supply Chain Execution now supports the ability to define a work definition where the batch quantity is dynamic. This enables you to specify the starting inputs and the batch quantities are dynamically calculated based on the intermediate batch quantities that consider operation yield. Oracle Supply Planning honors these definitions and calculates the right quantities of the inputs and outputs to meet demand over time.
This feature allows you to:
- Classify process work definition batch types as user-defined or calculated.
- Collect process work definitions and work orders of user-defined and calculated work definition batch types with the operation yield from Oracle Fusion Cloud SCM and external source systems.
- Plan make supplies considering the preceding definitions and accounting for operation yield.
- Release the planned make supplies to Oracle Cloud SCM and external source systems.
Process work definition and work order batch types:
- User-defined
- Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing supports a work definition where batch quantity isn’t a function of quantities of input ingredients or components in the work definition operation. Even though the quantities defined for the components are scaled in relation to the work definition primary product quantity, they don’t essentially contribute to the batch quantity.
- Calculated
- This is a new variation of process manufacturing work definitions and work orders, where the batch quantity is related to operation components.
The following image shows the Work Definition Batch Type column on an Operations page, which displays a value of either User-defined or Calculated.
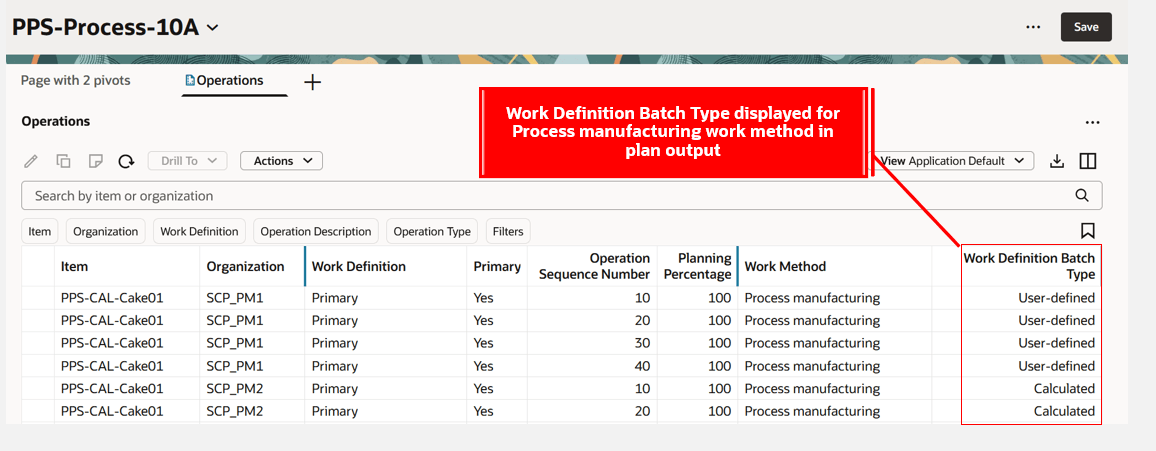
Work Definition Batch Type Displayed on Operations Page
The following table provides details of the supported item structure types for this feature.
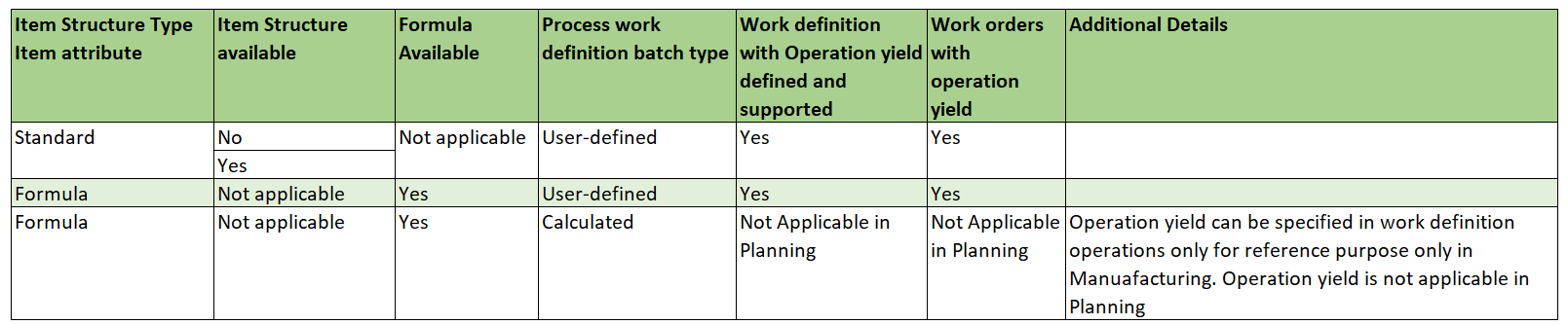
Item Structure Type and Process Work Definition Type Supported Configurations with Operation Yield
This planning feature isn’t applicable to the following scenarios:
- Configure-to-order, assemble-to-order, or pick-to-order flows
- Project-Driven Supply Chain
This feature is applicable only for constrained supply plans and constrained demand and supply plans.
If your source instance is Oracle Cloud SCM, you can set up operation yield to consider operation loss in the Oracle Manufacturing work definition setup. Operations must be count-point enabled. Operations may have different operation yields across different date effectivities.
For external source instances, you can prepare Routing Operation CSV files that include operation yield.
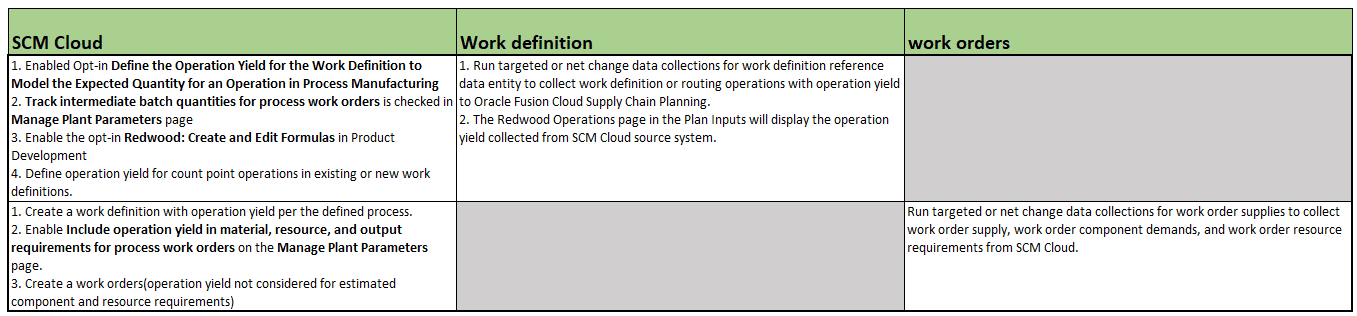
Key Steps to Enable and Collect Work Definitions and Work Orders with Operation Yield for User-Defined Batch Type
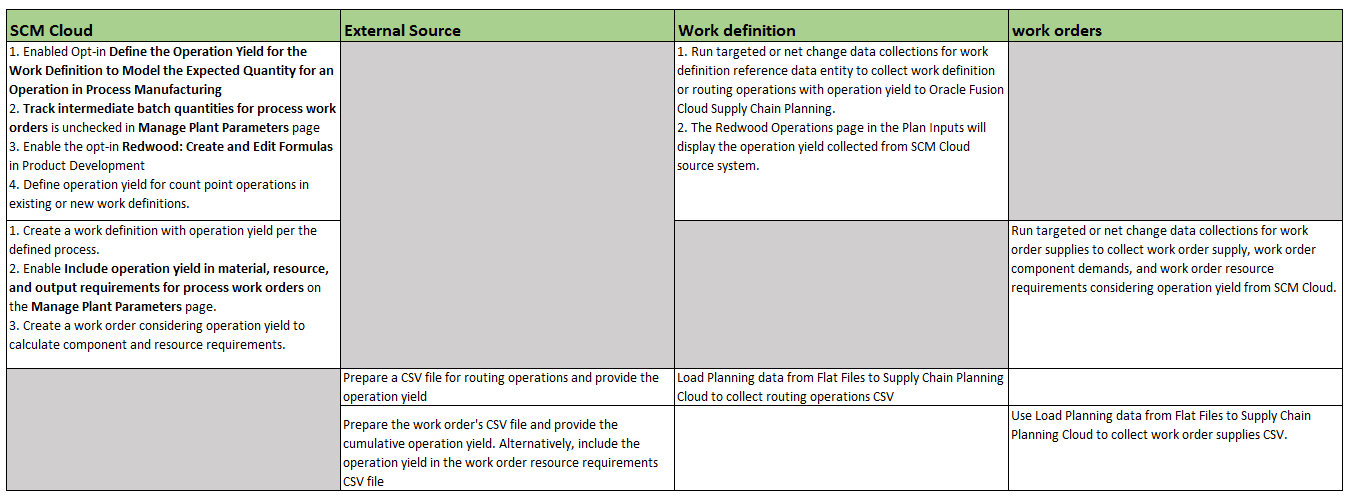
Setup Steps to Collect Work Definition and Work Orders with Operation Yield for a User-Defined Batch Type
Collection of User-Defined Batch Work Orders
The data collection process does the following for user-defined batch work orders from Oracle Cloud SCM:
- Derives cumulative operation yield for a work order from Oracle Manufacturing
- Derives the quantities for primary product, co-products, and by-products work orders
- Collects work order component demands and resource requirements considering operation yield from Oracle Cloud SCM
- Offsets completed quantity, scrapped quantity, and batch variance for computing work order component demands and resource requirements from estimated details from Oracle Manufacturing for in-progress work orders
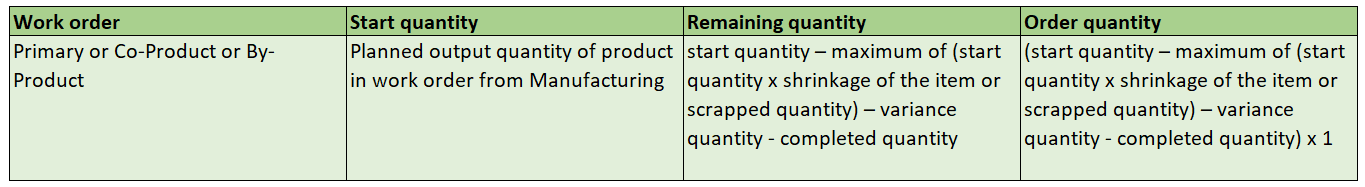
The following table provides the details of the derivation for work order quantities.
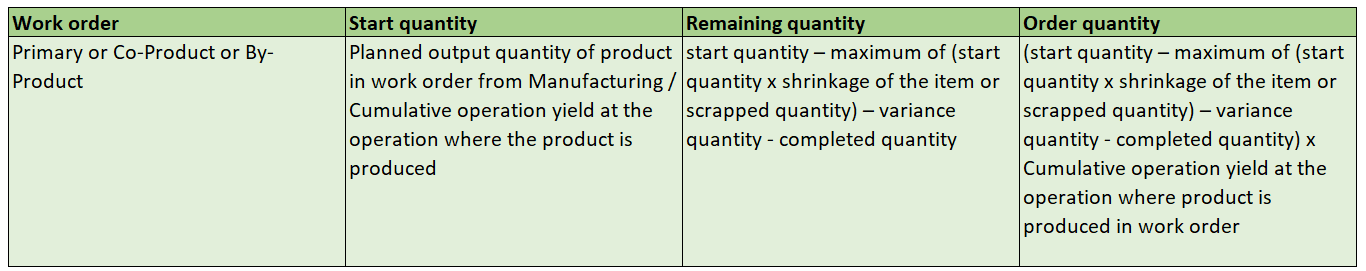
Quantity Computation for User-Defined Batch Work Definition Process Work Orders
External source data collection performs the following validations to derive cumulative operation yield and order quantity for work orders:
- Utilizes the cumulative operation yield specified in the work order supplies CSV file. If this isn’t specified, it calculates the cumulative operation yield by multiplying the operation yield specified for resource requirements across distinct operations.
- Applies the derived cumulative operation yield to the calculated remaining quantity of the work order for primary product, co-product, or by-product to obtain the order quantity.
Key Steps to Enable and Collect Calculated Batch Work Definitions and Work Orders
Setup Steps to Collect Work Definition and Work Orders for a Calculated Batch
The operation yield collected is only for reference. Planning will consider the operation yield as 1 for calculated batch process work definitions.
The work order will be collected with a cumulative operation yield of 1 for calculated batch process work orders
Collection of Calculated Batch Work Orders
The data collection process does the following for calculated batch work orders from Oracle Cloud SCM:
- Derives the work order quantities for primary product, co-products, and by-products
- Collects work order component demands and resource requirements from Oracle Cloud SCM
- Offsets completed quantity, scrapped quantity, and batch variance for computing work order component demands and resource requirements from estimated details from Oracle Manufacturing for in-progress work orders
The following table provides the details of the derivation for work order quantities.
Quantity Computation for Calculated Batch Work Definition Process Work Orders
The following image shows a Plan Inputs Operations page that displays Operation Yield and Work Definition Batch Type for process definitions.
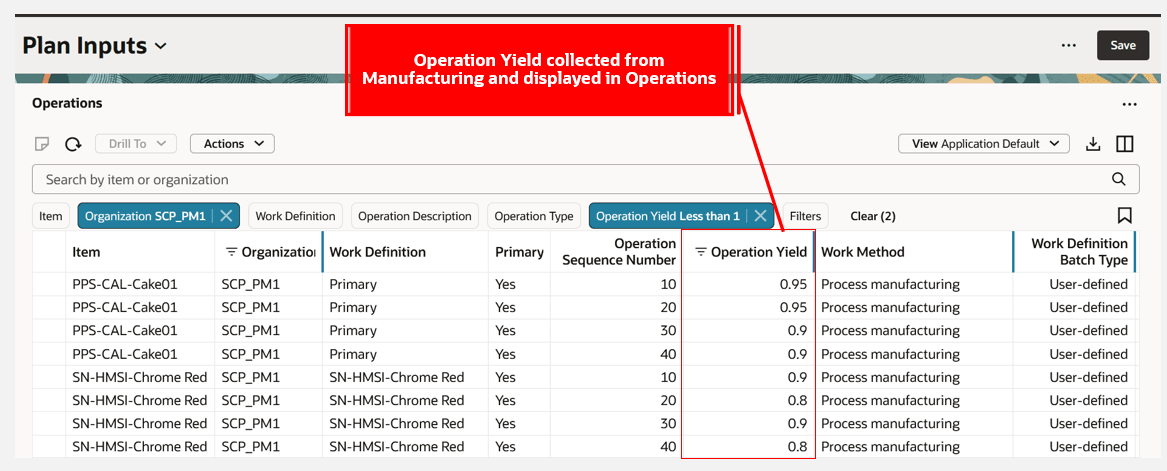
Operation Yield and Work Definition Batch Type Columns
In-Progress Process Work Order with Operation Yield Collected from Oracle Manufacturing
The Redwood Supplies and Demands page displays the cumulative operation yield for plan inputs and outputs. Also, the Redwood Resource Requirements page has been enhanced to display the resource requirement's operation yield.
The work order component and resource requirements are collected from Oracle Cloud SCM or an external source system. Supply planning won’t perform any additional computations to derive these requirements.
This example shows a collected in-progress work order for a user-defined process work definition batch:
- Start quantity 10
- Scrapped quantity 2
- Completed quantity 0
- Remaining quantity = start quantity – maximum of (start quantity x shrinkage of the item or scrapped quantity) – variance quantity - completed quantity = 10 – 2 – 0 – 0 = 8
- Cumulative operation yield for work order from Oracle Manufacturing 0.73103
- Order quantity = (start quantity – maximum of (start quantity x shrinkage of the item or scrapped quantity) – variance quantity - completed quantity) x cumulative operation yield = 8 x 0.73103 = 5.8482
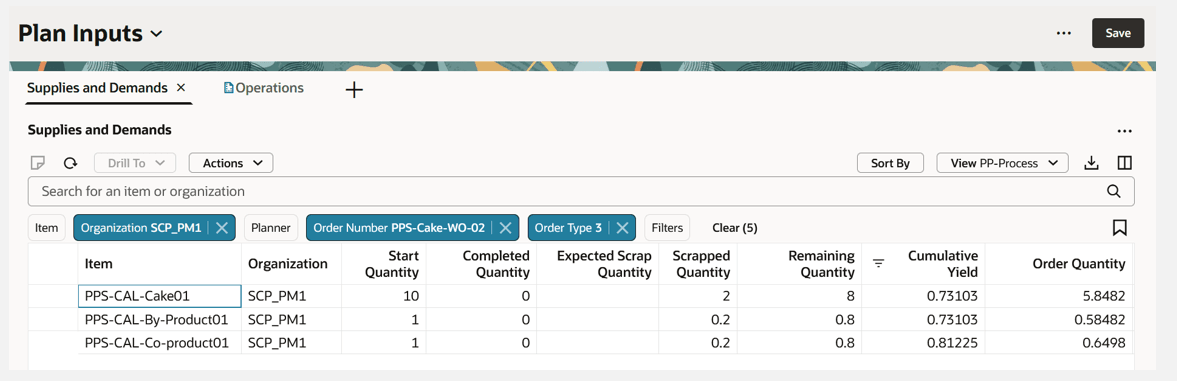
User-Defined Batch Type Process Definition In-Progress Work Order Collected Applying Operation Yield
Editing Operation Yield in a Simulation Set
You can edit the operation yield for an operation for a user-defined batch process work definition in a simulation set. You can also edit a copied work definition operation in a simulation set to update or edit the operation yield. Simulation sets with updated operation yields can be assigned to plan options to consider the updated operation yields in the planning computation.
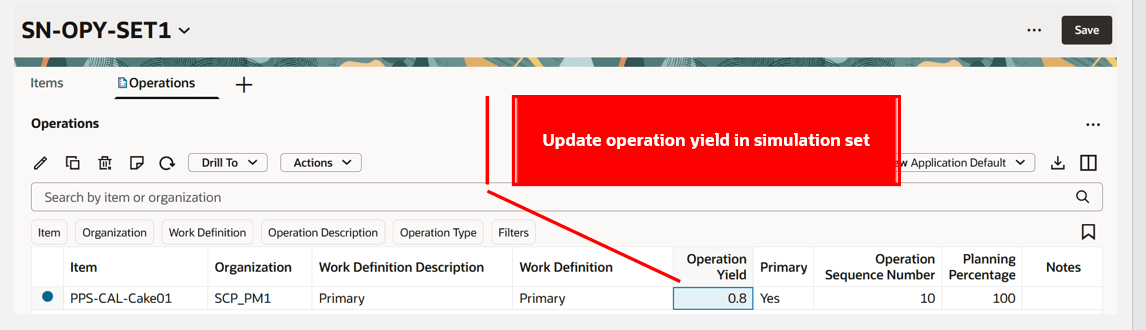
Operation Yield Updated in Simulation Set
Plan Supplies Considering Operation Yield for User-Defined Batch Process Work Definitions
Supply planning does the following while recommending planned orders considering operation yield for user-defined batch type process work definitions:
- Selects the operation yield effective on the supply start date from the operations associated with the selected work definition.
- Derives the cumulative operation yield based on the operation yield of the selected operations of the primary product planned order supply.
- In case the demand is for co-product, in the absence of its work definition, primary product work definition is referenced by planning and cumulative operation yield is derived based on the operation where co-product is produced.
- Applies the cumulative operation yield to derive the start quantity of the primary product.
- If shrinkage is available, the same is applied with operation yield for derivation of start quantity.
- Computes order quantity, expected scrap, and remaining quantity of the primary product planned orders.
- Derives start quantity and order quantity for both co-product planned orders and by-product planned orders based on the usage rate with reference to primary product from work definition and operation yield.
- Computes processing quantity for each operation based on the operation yield and primary product start quantity.
- Computes planned order component requirements and resource requirement based on the usage rate with reference to primary product from work definition and operation yield.
- Computes batch quantity for the planned order supply based on the proportional scaling with reference to work definition and primary product.
The following table provides the details of quantity and resource requirement computation for user-defined batch type work definitions.
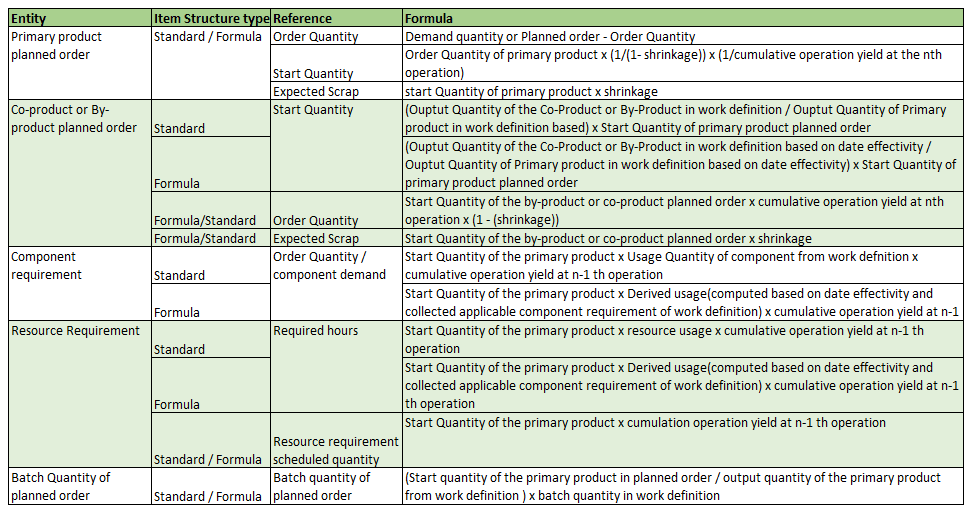
Planned Order Computation Formula for User-Defined Batch Type Work Definition with Operation Yield
Supply planning doesn’t apply operation yield for outside processing operations. Suppose a work definition contains both in-house operations with operation yield and outside processing operations. In that case, the predecessor in-house operation's end quantity serves as the reference for the outside processing operations. For in-house operations following an outside processing operation, the start quantity remains the same as the preceding outside processing operation.
Additionally, supply planning supports time-phased yield by selecting operation yield based on the operation's date effectivity and the start date of the supply.
Example 1. Planning Supplies with a User-Defined Batch Work Definition
To understand the computations done by the planning process to recommend planned orders that consider operation yield, let's look at an example where the work definition batch type is User-defined and the item structure type is Standard.
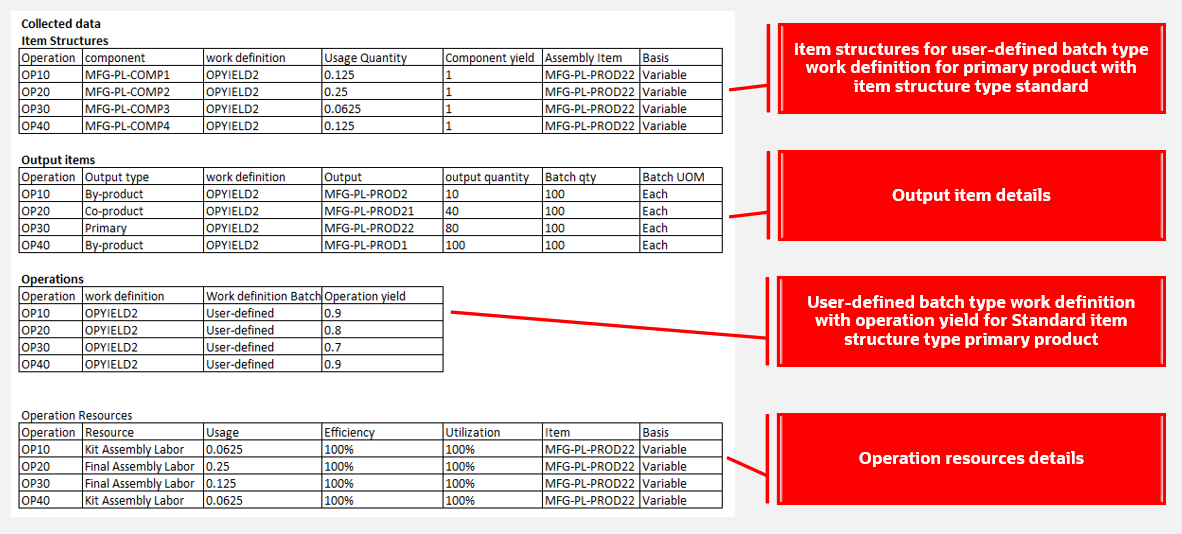
Collected Data
Using the collected data shown in the preceding image for item structures, output items, operations, and operation resources, the calculations and plan output would be as follows.
Plan Output
- Primary product MFG-PL-PROD22 – Planned order computation
- Demand for primary product MFG-PL-PROD22 is 100 units.
- Primary product planned order: Order quantity will be 100 units.
- Primary product is produced at operation 30. Hence, cumulative operation yield at operation 30 is 0.9 x 0.8 x 0.9 = 0.504.
- There’s no shrinkage defined for the item. Start quantity of primary product = 100/0.504 = 198.4 units.
- Co-product MFG-PL-PROD21 – Planned order computation
- Co-product is produced at operation 20. Hence, cumulative operation yield at operation 20 is 0.9 x 0.8 = 0.72.
- Start quantity of co-product is (Output Quantity of the co-product or by-product in work definition / Output Quantity of primary product in work definition based) x Start Quantity of primary product planned order = 40/80 x 198.4 = 99.2 units.
- Order quantity of planned order co-product = 99.2 x 0.72 = 71.4 units.
- Component requirement for MFG-PL-COMP4
- MFG-PL-COMP4 is a component at operation 40.
- Cumulative operation yield at the (n-1) operation, that is, operation 30 is 0.504.
- Usage quantity of the component = 198.4 (start quantity of primary product) x 0.125(usage quantity of component) x 0.504(cumulative operation yield at (n-1) operation) = 12.5 units.
- Batch quantity
- Work definition batch quantity is 100.
- Primary product output quantity in the work definition is 80.
- Batch quantity of planned order = 100/80 x 198.4 = 248.1 units.
- Resource Final Assembly Labor – resource requirement computation
- Resource is in operation 30.
- Cumulative operation yield at the (n-1) operation, that is, operation 20 is 0.72.
- Resource usage is 0.125.
- Resource required hours = 198.4 (start quantity of primary product) x 0.125 (resource usage) x 0.72 (cumulative operation yield at (n-1) operation) = 17.9 hours.
- Scheduled quantity at operation 30 = 198.4127 (start quantity of primary product) x 0.72 (cumulative operation yield at (n-1) operation) = 142.9.
Supply planning does the following when planning user-defined batch type work definition work orders with operation yield:
- Identifies the work order as user-defined batch type based on the work definition associated with the work order.
- Honors the collected cumulative operation yield for work order supplies and operation yield for resource requirements of the work order.
- Computes the expected scrap quantity of the work order based on the shrinkage of the item. Supply planning honors the shrinkage defined in the simulation set associated with the plan definition. Computes the expected scrap as a product of start quantity of the work order and shrinkage of the item.
- Recomputes order quantity of the work order as: (Start quantity - max(expected scrap quantity, scrapped quantity) - completed quantity - variance) x cumulative operation yield at the nth operation.
- Remaining quantity of the work order is computed as: Start quantity - scrapped quantity - completed quantity - variance.
Plan for Calculated Batch Process Work Definitions
Supply planning does the following while recommending planned orders for calculated batch process work definitions:
- Selects the operations effective on the supply start date from the operations associated with the selected work definition.
- If shrinkage is available, the same is applied with operation yield for derivation of start quantity.
- Computes order quantity, expected scrap, and the remaining quantity of the primary product planned orders.
- Derives start quantity, order quantity for co-product, and by-product planned orders based on the usage rate with reference to the primary product from the work definition.
- Computes processing quantity for each operation based on the operation yield and primary product start quantity.
- Computes planned order component requirements and resource requirement based on the usage rate with reference to the primary product from the work definition.
- Computes batch quantity for the planned order supply based on the sum of the component requirements across all operations for components for which Contribute to Yield is set to Yes and Supply Type is Push.
The following table provides the details of quantity and resource requirement computations for a user-defined batch type work definition.
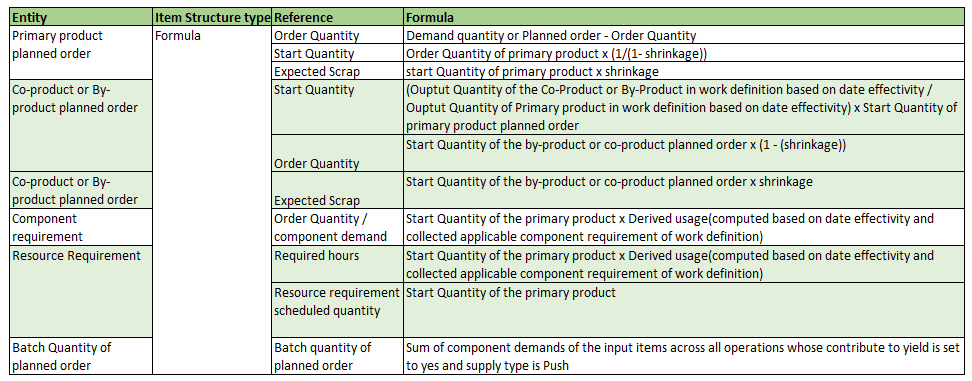
Planned Order Computation Formula for Calculated Batch Work Definitions
In a calculated batch work definition, the planning process applies unit of conversions for the component demand quantity which are eligible for batch quantity computation when the component primary unit of measure is different from the primary product unit of measure in the work definition.
Example 2. Planning Supplies with a Calculated Batch Work Definition
To understand the computations done by the planning process to recommend planned orders, let's look at an example where the work definition batch type is Calculated and the item structure type is Formula.
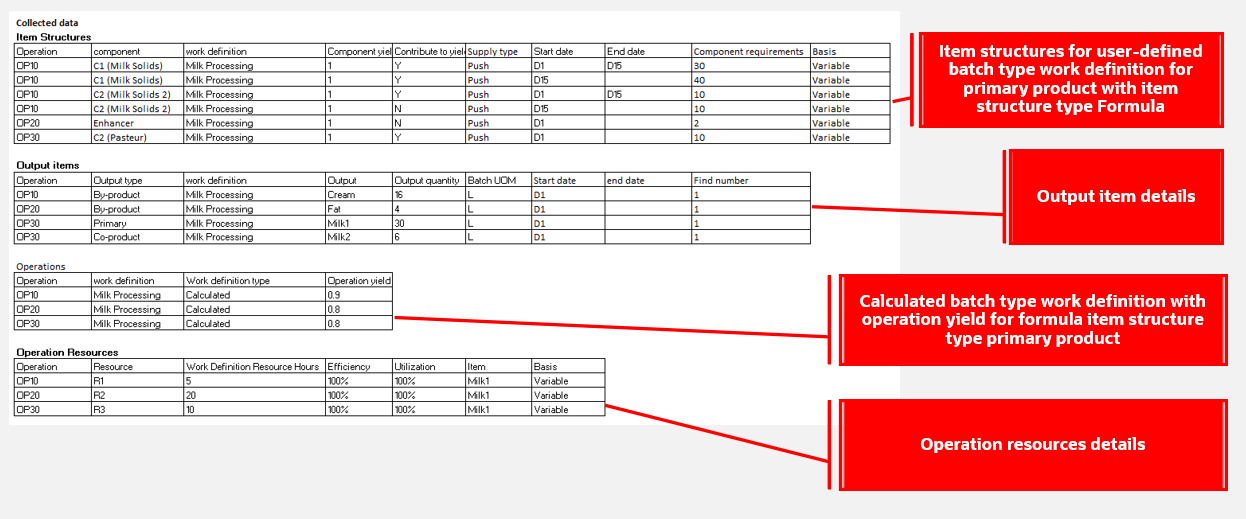
Collected Data
Using the collected data shown in the preceding image for item structures, output items, operations, and operation resources, the calculations and plan output would be as follows.
Plan Output
- Primary Product Milk1 – Planned order supply computation
- Demand for primary product Milk1 is 45 units on D40.
- Primary product planned order: Order quantity will be 45 units.
- Supply start date is after D15. Hence, primary product output quantity from the work definition is 15 units.
- There’s no shrinkage defined for the item. Output quantity of primary product is 45 units. (Cumulative operation yield is always considered as 1 for calculated batch work definition.)
- Co-product Milk2 – Planned order supply computation
- Co-product is produced at operation 30.
- Start quantity of co-product is (Output Quantity of the co-product or by-product in work definition / Output Quantity of primary product in work definition based on date effectivity) x Start Quantity of primary product planned order = 6/30 x 45 = 9 units.
- Order quantity of planned order co-product is 9 units. (Cumulative operation yield is always considered as 1 for calculated batch work definition.)
- Component requirement computation for C1 (Milk Solids)
- C1 (Milk Solids) is a component at operation 10.
- Usage quantity of the component is:
- Component effective usage = Work definition quantity / output quantity primary product based on effectivity = 40/30 = 1.33.
- Component requirement = 45 x 1.33 = 60 units.
- Batch quantity
- Sum of component requirement of all components across operations whose Contribute to Yield is set to Yes and Supply Type is Push.
- Component requirement for component in operation 10 + component requirement in operation 30 = 60 + 15 = 75 units.
- Resource R2 – Resource requirement computation
- Resource is in operation 20.
- Resource usage = Work definition resource hours / output quantity primary product based on effectivity = 20/30 = 0.67.
- Resource required hours = 45(start quantity of primary product) x 0.67(resource usage) = 30.00 hours.
- Scheduled quantity at operation 20 = 45(start quantity of primary product).
Supply planning does the following when planning calculated batch type work definition work orders:
- Identifies the work order as calculated batch type based on the work definition associated with the work order.
- Honors the collected supplies, component demands, and resource requirements of the work order.
- Computes the expected scrap quantity of the work order based on the shrinkage of the item. Supply planning honors the shrinkage defined in the simulation set associated with the plan definition. Computes the expected scrap as a product of start quantity of the work order and shrinkage of the item.
- Recomputes order quantity of the work order as: (Start quantity – max (expected scrap quantity, scrapped quantity) - completed quantity - variance).
- Remaining quantity of the work order is computed as: Start quantity - scrapped quantity - completed quantity – variance.
REST Services
- The Plan Inputs, Supply Planning, and Demand and Supply Planning REST services now retrieve the cumulative operation yield for user-defined batch process work order supplies using the GET operation.
- The Plan Inputs, Supply Planning, and Demand and Supply Planning REST services now retrieve the Work Definition Batch Type for a work definition using the GET operation.
Production Scheduling
- In Oracle Production Scheduling, you can schedule planned orders that have operation yield enabled. This scheduling ensures that resource and material requirements affected by operation yield are properly considered.
- In Oracle Supply Planning, you can now incorporate operation yield-enabled planned orders scheduled in Production Scheduling within a user-specific firm window.
Release from Planning
- You can now release the make planned orders of user-defined batch type work definitions recommended by a plan considering operation yield to Oracle Cloud SCM or to external source systems. The process releases start quantities of the planned orders to the source system to create work orders. Oracle Manufacturing applies operation yield to compute estimated component and resource requirements when creating work orders.
- You can now also release the make planned orders of calculated batch type work definitions recommendation by a plan to Oracle Cloud SCM. The process releases start quantities of the planned orders to the source system to create work orders. Oracle Manufacturing creates work orders for calculated batch type work definition with estimated component and resource requirements.
- You can also reschedule or cancel recommendations for user-defined batch or calculated batch process work orders to Oracle Manufacturing.
Steps to enable and configure
You don't need to do anything to enable this feature.
Tips and considerations
- Supply planning doesn’t refer to either of the following Oracle Manufacturing plant parameters:
- Include operation yield in material, resource, and output requirements for process work orders
- Track intermediate batch quantities for process work orders
- Instead of using shrinkage, it's suggested to set up operation yield to model operation loss.
- If a work order's cumulative operation yield value is null, greater than 1, or less than zero in a CSV file, it's set to 1 by default during data collection.
- Operation yield values that are null, greater than 1, or less than zero in work order resource requirement CSV files are defaulted to 1 during data collection.
- Operation yield values in work definition or routing operations CSV files that are null, greater than 1, or less than zero are defaulted to 1 during data collection.
- The component yield of the component is applied while computing component demand for user-defined and calculated batch work definition planned order demands.
- Existing process manufacturing without operation yield is supported as user-defined batch type process work definition with operation yield as 1.
- Planning always represents a batch unit of measure for a primary product planned order in the primary product’s unit of measure.
Key resources
- Refer to the 26A feature Honor the Validity Dates of Process Manufacturing Outputs Specified on a Formula in the Oracle Fusion Cloud Supply Planning 26A What’s New for additional details related to planning formula-based item structures and work definitions.
- Refer to the 25D feature Define the Operation Yield for the Work Definition to Model the Expected Quantity for an Operation in Process Manufacturing in the Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing 25D What’s New for additional details on configuring operation yield for user-defined process work definition batch types and work orders with operation yield in Oracle Manufacturing.
- Refer to the 25D feature Redwood: Create and Edit Formulas in the Oracle Fusion Cloud Product Lifecycle Management 25D What’s New for additional details on configuring formula and associated changes of using formula in process manufacturing work definitions.
- Refer to the 26A feature Track Intermediate Inputs and Outputs for Calculated Batch Quantities in Process Manufacturing in the Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing 26A What’s New for additional details on configuring calculated process work definition batch types and its work orders in Oracle Manufacturing.
- Refer to the 26A feature Define Operation Yield for Calculated Batch Quantities in Process Manufacturing in the Oracle Fusion Cloud Manufacturing 26A What’s New for defining and tracking actual execution operation yield for calculated process work definition batch types and work orders in Oracle Manufacturing.
Access requirements
Users who are assigned a configured job role that contains these privileges can access this feature:
- Monitor Supply Planning Work Area (MSC_MONITOR_SUPPLY_PLANNING_WORK_AREA_PRIV)
- Monitor Demand and Supply Planning Work Area (MSC_MONITOR_DEMAND_AND_SUPPLY_PLANNING_WORK_AREA_PRIV)
These privileges were available prior to this update.