Code Editor Features
This topic provides an overview of common Code editor features.
When you open a file for editing from the DB Browser pane, it opens in the main editor window as an active tab with the file name. You can open multiple files for editing, each in its own tab. You can hide, close or detach the editor tabs. The maximum number of tabs that you can open simultaneously in the Code Editor pane is configurable.
Some commonly available Code Editor features (accessible through the context-menu of the editor pane) are listed below:
| Editor Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Split screen | The context menu available by right-clicking the editor tab lets you split the tab in multiple ways. You can also unsplit, move, close, pin and associate the tab with a specific file type. |
| Highlighting | The SQL syntax highlighting feature marks the association of the SQL script to its database connection by highlighting column names, aliases, table names and schema names. For example, if a selection list item is missing in the FROM clause, the error is highlighted.
|
| Folding | The navigation gutter of the SQL/Program editor displays markers that enable folding/unfolding the SQL statements/code within the SQL script or program code. |
| Auto Close | Automatically closes, single quote, double quotes or a bracket when you type the first one in the statement. |
| Error Indication | The editor indicates errors in the SQL statements/code lines by displaying problem markers (colored stripes corresponding to the code line having problems), on the right-hand side scroll bar. Hovering the cursor over the problem markers shows error information such as failed queries or invalid/incomplete SQL statements. |
| Code Completion | If the Database Navigator plug-in recognizes some identifier as a table/view name, it helps complete the names of tables/columns/views, classes, methods, fields, and keywords within the scope of the database schema by providing them as suggestion in a list form that you can double-click and select. |
| Code Analysis | The editor provides options to conduct semantic analysis, resolve aliases, inspect the code and conduct code cleanup, analyze nullity scope in the file or project, and view dependencies. |
| Context-aware Intention Actions | The Show Context Actions icon (represented by a light bulb) to the left of the query text displays a list of intention actions you can take on the SQL script, based on the cursor placement. |
| Code Navigation | The editor lets you navigate to respective type declarations, code declaration or usages, implementations, super classes (if the selected method is overridden) and even reserved SQL keywords/characters. You can also move between opened files and tabs or jump to the navigation bar. |
| Code Generation | When editing Java code, the code editor allows you to generate standard code constructs such as method overrides and implementations, constructor for a Java class, delegation methods, getters and setters to name a few. |
| Code Refactoring | The code refactoring feature helps you improve your source code and provides multiple options to refactor a method, fields or a Java class. |
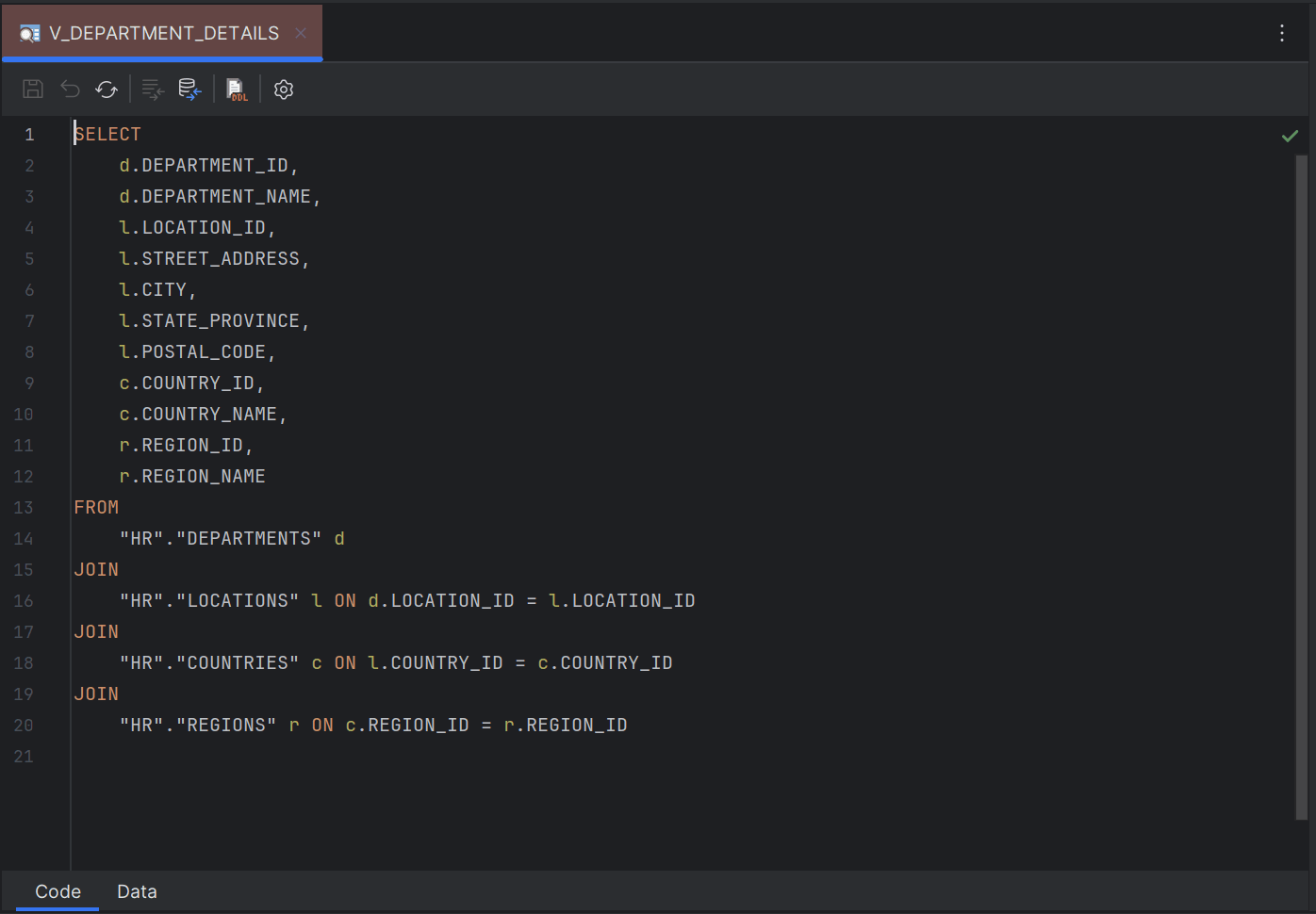
Sample Code Editor for Database Views
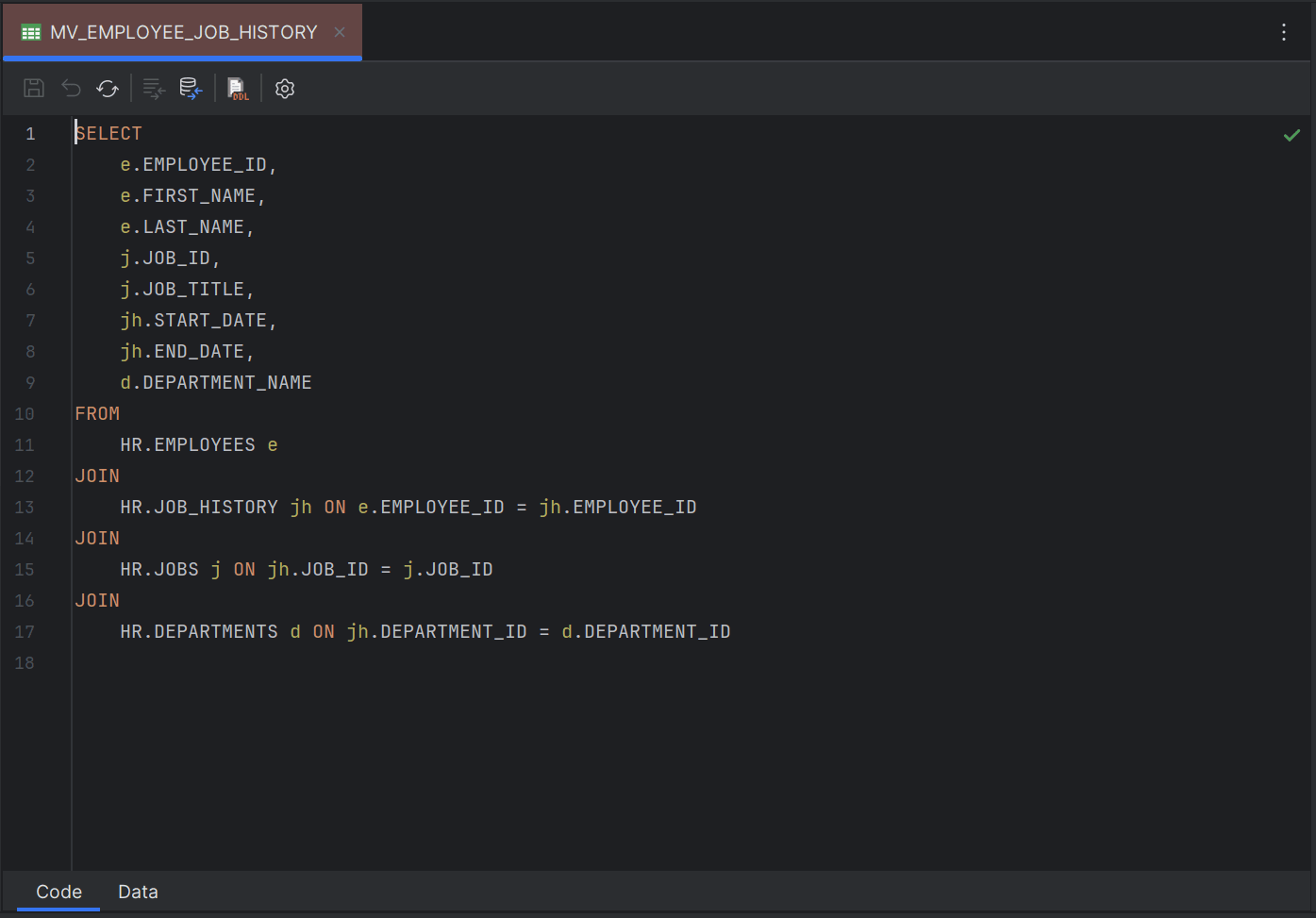
Sample Code Editor for Database Materialized View
Parent topic: Configuration of Code Editors