PREDICTION_PROBABILITY
Syntax
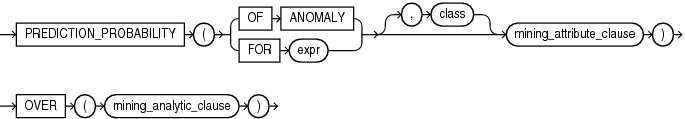
prediction_probability::=
Analytic Syntax
prediction_prob_analytic::=
mining_attribute_clause::=
mining_analytic_clause::=
See Also:
"Analytic Functions" for information on the syntax, semantics, and restrictions of mining_analytic_clause
Purpose
PREDICTION_PROBABILITY returns a probability for each row in the selection. The probability refers to the highest probability class or to the specified class. The data type of the returned probability is BINARY_DOUBLE.
PREDICTION_PROBABILITY can perform classification or anomaly detection. For classification, the returned probability refers to a predicted target class. For anomaly detection, the returned probability refers to a classification of 1 (for typical rows) or 0 (for anomalous rows).
You can use PREDICTION_PROBABILITY in conjunction with the PREDICTION function to obtain the prediction and the probability of the prediction.
Syntax Choice
PREDICTION_PROBABILITY can score the data in one of two ways: It can apply a mining model object to the data, or it can dynamically mine the data by executing an analytic clause that builds and applies one or more transient mining models. Choose Syntax or Analytic Syntax:
-
Syntax — Use the first syntax to score the data with a pre-defined model. Supply the name of a model that performs classification or anomaly detection.
-
Analytic Syntax — Use the analytic syntax to score the data without a pre-defined model. The analytic syntax uses
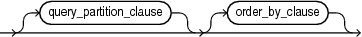
mining_analytic_clause, which specifies if the data should be partitioned for multiple model builds. Themining_analytic_clausesupports aquery_partition_clauseand anorder_by_clause. (See "analytic_clause::=".)-
For classification, specify
FORexpr, whereexpris an expression that identifies a target column that has a character data type. -
For anomaly detection, specify the keywords
OF ANOMALY.
-
The syntax of the PREDICTION_PROBABILITY function can use an optional GROUPING hint when scoring a partitioned model. See GROUPING Hint.
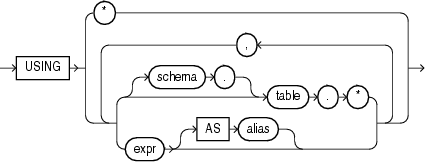
mining_attribute_clause
mining_attribute_clause identifies the column attributes to use as predictors for scoring. When the function is invoked with the analytic syntax, these predictors are also used for building the transient models. The mining_attribute_clause behaves as described for the PREDICTION function. (See "mining_attribute_clause::=".)
See Also:
-
Oracle Data Mining User's Guide for information about scoring.
-
Oracle Data Mining Concepts for information about predictive data mining.
Note:
The following examples are excerpted from the Data Mining sample programs. For information about the sample programs, see Appendix A in Oracle Data Mining User's Guide.
Example
The following example returns the 10 customers living in Italy who are most likely to use an affinity card.
SELECT cust_id FROM (
SELECT cust_id
FROM mining_data_apply_v
WHERE country_name = 'Italy'
ORDER BY PREDICTION_PROBABILITY(DT_SH_Clas_sample, 1 USING *)
DESC, cust_id)
WHERE rownum < 11;
CUST_ID
----------
100081
100179
100185
100324
100344
100554
100662
100733
101250
101306Analytic Example
This example identifies rows that are most atypical in the data in mining_data_one_class_v. Each type of marital status is considered separately so that the most anomalous rows per marital status group are returned.
The query returns three attributes that have the most influence on the determination of anomalous rows. The PARTITION BY clause causes separate models to be built and applied for each marital status. Because there is only one record with status Mabsent, no model is created for that partition (and no details are provided).
SELECT cust_id, cust_marital_status, rank_anom, anom_det FROM
(SELECT cust_id, cust_marital_status, anom_det,
rank() OVER (PARTITION BY CUST_MARITAL_STATUS
ORDER BY ANOM_PROB DESC,cust_id) rank_anom FROM
(SELECT cust_id, cust_marital_status,
PREDICTION_PROBABILITY(OF ANOMALY, 0 USING *)
OVER (PARTITION BY CUST_MARITAL_STATUS) anom_prob,
PREDICTION_DETAILS(OF ANOMALY, 0, 3 USING *)
OVER (PARTITION BY CUST_MARITAL_STATUS) anom_det
FROM mining_data_one_class_v
))
WHERE rank_anom < 3 order by 2, 3;
CUST_ID CUST_MARITAL_STATUS RANK_ANOM ANOM_DET
------- ------------------- ---------- -----------------------------------------------------------
102366 Divorc. 1 <Details algorithm="Support Vector Machines" class="0">
<Attribute name="COUNTRY_NAME" actualValue="United Kingdom"
weight=".069" rank="1"/>
<Attribute name="AGE" actualValue="28" weight=".013"
rank="2"/>
<Attribute name="YRS_RESIDENCE" actualValue="4"
weight=".006" rank="3"/>
</Details>
101817 Divorc. 2 <Details algorithm="Support Vector Machines" class="0">
<Attribute name="YRS_RESIDENCE" actualValue="8"
weight=".018" rank="1"/>
<Attribute name="EDUCATION" actualValue="PhD" weight=".007"
rank="2"/>
<Attribute name="CUST_INCOME_LEVEL" actualValue="K:
250\,000 - 299\,999" weight=".006" rank="3"/>
</Details>
101713 Mabsent 1
101790 Married 1 <Details algorithm="Support Vector Machines" class="0">
<Attribute name="COUNTRY_NAME" actualValue="Canada"
weight=".063" rank="1"/>
<Attribute name="EDUCATION" actualValue="7th-8th"
weight=".011" rank="2"/>
<Attribute name="HOUSEHOLD_SIZE" actualValue="4-5"
weight=".011" rank="3"/>
</Details>
. . .