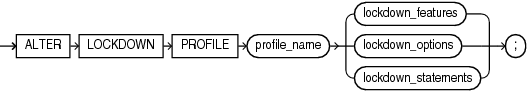
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE
Purpose
Use the ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE statement to alter a PDB lockdown profile. You can use PDB lockdown profiles in a multitenant environment to restrict user operations in pluggable databases (PDBs).
Immediately after you create a lockdown profile with the CREATE LOCKDOWN PROFILE statement, all user operations are enabled for the profile. You can then use the ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE statement to disable certain user operations for the profile. When a lockdown profile is applied to a CDB, application container, or PDB, users cannot perform the operations that are the disabled for the profile. If you later would like to reenable some of the disabled user operations, you can use the ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE statement to do so.
The ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE statement allows you to disable or enable:
-
User operations associated with certain database features (using the
lockdown_featuresclause) -
User operations associated with certain database options (using the
lockdown_optionsclause) -
The issuance of certain SQL statements (using the
lockdown_statementsclause)
See Also:
-
Oracle Database Security Guide for more information on PDB lockdown profiles
Prerequisites
-
You must issue the
ALTERLOCKDOWNPROFILEstatement from the CDB Root or Application Root. -
You must have the
ALTERLOCKDOWNPROFILEsystem privilege in the container in which you issue the statement.
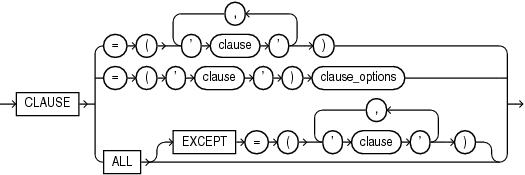
Syntax
alter_lockdown_profile::=
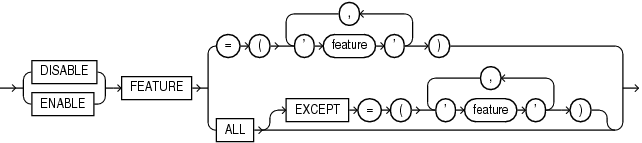
lockdown_features::=
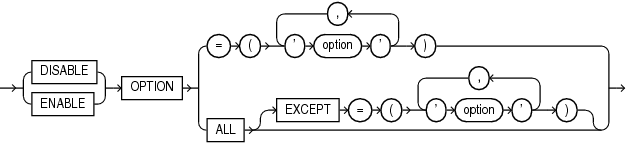
lockdown_options::=
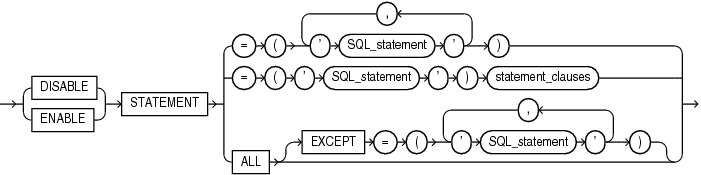
lockdown_statements::=
statement_clauses::=
clause_options::=
option_values::=
Semantics
profile_name
Specify the name of the PDB lockdown profile to be altered.
You can find the names of existing PDB lockdown profiles by querying the DBA_LOCKDOWN_PROFILES data dictionary view.
lockdown_features
This clause lets you disable or enable user operations associated with certain database features.
-
Specify
DISABLEto add a restriction for the specified features. Users will be restricted from performing these operations in any PDB to which the profile applies. -
Specify
ENABLEto remove a restriction for the specified features. Users will be allowed to perform these operations in any PDB to which the profile applies. -
Use
featureto specify the features whose operations you want to disable or enable. Table 11-1 lists the features you can specify and describes the operations associated with each feature. The table also indicates a feature bundle for each feature. Forfeature, you can specify a feature bundle name to disable or enable user operations for all features in that bundle, or you can specify an individual feature name. You can specify feature bundle names and feature names in any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters. -
Use
ALLto specify all features listed in the table. -
Use
ALLEXCEPTto specify all features listed in the table except the specified features.
If you omit this clause, then the default is ENABLE ALL.
Note:
-
The Oracle Text type
FILE_DATASTOREis deprecated. Oracle recommends that you replaceFILE_DATASTOREindexes with theDIRECTORY_DATASTOREindex type for greater security as it enables file access to be based on directory objects. -
The Oracle Text type
URL_DATASTOREis deprecated. Oracle recommeds that you replaceURL_DATASTOREwithNETWORK_DATASTORE, which uses ACLs to control access to specific servers.
Table 11-1 PDB Lockdown Profile Features
| Feature Bundle | Feature | Operations |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
The PDB taking manual and automatic Automatic Workload Repository (AWR) snapshots |
|
|
|
A common user invoking an invoker’s rights code unit or accessing a |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Creation of certain security policies by a local user on a common object, including:
|
|
|
|
A common user connecting to the PDB directly. If this feature is disabled, then in order to connect to the PDB, a common user must first connect to the CDB root and then switch to the desired PDB using the |
|
|
|
A local user with the |
|
|
|
Use logging in Oracle Text PL/SQL procedures such as |
|
|
|
Java as a whole. If this feature is disabled, then all options and features of the database that depend on Java will be disabled. |
|
|
|
Operations through Java that require |
|
|
AQ_PROTOCOLS |
Using HTTP, SMTP, and OCI notification features. |
|
|
CTX_PROTOCOLS |
|
|
|
DBMS_DEBUG_JDWP |
Using the |
|
|
UTL_HTTP |
Using the |
|
|
UTL_INADDR |
Using the |
|
|
UTL_SMTP |
Using the |
|
|
UTL_TCP |
Using the |
|
|
XDB_PROTOCOLS |
Using HTTP, FTP, and other network protocols through XDB |
|
|
|
Dropping a tablespace in the PDB without specifying the |
|
|
|
Using external files or directory objects in the PDB when |
|
|
|
Using external procedure agent |
|
|
|
Using the |
|
|
|
Using |
|
|
|
Using |
|
|
|
Using the following trace views:
|
|
|
|
Using |
lockdown_options
This clause lets you disable or enable user operations associate with certain database options.
-
Specify
DISABLEto disable user operations for the specified options. Users will be restricted from performing these operations in any PDB to which the profile applies. -
Specify
ENABLEto enable user operations for the specified options. Users will be allowed to perform these operations in any PDB to which the profile applies. -
For
option, you can specify the following database options in any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters:-
DATABASEQUEUING– Represents user operations associated with the Oracle Database Advanced Queuing option -
PARTITIONING– Represents user operations associated with the Oracle Partitioning option
-
-
Use
ALLto specify all options in the preceding list. -
Use
ALLEXCEPTto specify all options in the preceding list except the specified options.
If you omit this clause, then the default is ENABLE OPTION ALL.
lockdown_statements
This clause lets you disable or enable the issuance of certain SQL statements.
-
Specify
DISABLEto disable the issuance of the specified SQL statements. Users will be restricted from issuing these statements in any PDB to which the profile applies. -
Specify
ENABLEto enable the issuance of the specified SQL statements. Users will be allowed to issue these statements in any PDB to which the profile applies. -
For
SQL_statement, you can specify the following statements in any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters:-
ADMINISTERKEY MANAGEMENT -
ALTERDATABASE -
ALTERPLUGGABLEDATABASE -
ALTERSESSION -
ALTERSYSTEM -
ALTERTABLE -
ALTERINDEX -
ALTERTABLESPACE -
ALTERPROFILE -
CREATETABLE -
CREATEINDEX -
CREATETABLESPACE -
CREATEPROFILE -
CREATEDATABASE LINK -
DROPTABLE -
DROPINDEX -
DROPTABLESPACE -
DROPPROFILE
-
-
Use
ALLto specify all statements in the preceding list. -
Use
ALLEXCEPTto specify all statements in the preceding list except the specified statements.
If you omit this clause, then the default is ENABLE STATEMENT ALL.
statement_clauses
This clause lets you disable or enable specific clauses of the specified SQL statement.
-
Use
clauseto specify the SQL keywords that form the clause you want to disable or enable. You can specify a clause in any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters. -
Use
ALLto specify all clauses for the SQL statement. -
Use
ALLEXCEPTto specify all clauses for the SQL statement except the specified clauses.
For clause, you must specify at least enough keywords to unambiguously identify a single clause for the SQL statement. The following are some examples of how to specify clause for the ALTER SYSTEM statement:
-
To specify the archive_log_clause::=, specify
ARCHIVE. This is sufficient because no otherALTERSYSTEMclause begins with the keywordARCHIVE. Alternatively, you can specifyARCHIVELOGfor semantic clarity, but theLOGkeyword is unnecessary. -
To specify either of the rolling_migration_clauses::=, you must specify
STARTROLLINGMIGRATIONorSTOPROLLINGMIGRATIONin order to distinguish these clauses from the similarly named rolling_patch_clauses::=STARTROLLINGPATCHandSTOPROLLINGPATCH. -
You cannot specify the single keyword
FLUSH, because severalALTERSYSTEMclauses begin with this keyword. You must instead specify each clause separately, such asFLUSHSHARED_POOLorFLUSHGLOBALCONTEXT.
There is no need to specify optional keywords within a clause, because they have no effect. For example:
-
The archive_log_clause::= has an optional
INSTANCEkeyword. However, you cannot enable or disable onlyARCHIVELOGclauses that contain theINSTANCEkeyword. SpecifyingARCHIVELOGINSTANCEis equivalent to specifyingARCHIVEorARCHIVELOG.
There is no need to specify parameter values within a clause, because they have no effect. For example:
-
The shutdown_dispatcher_clause::= requires you to specify a
dispatcher_name. However, you cannot enable or disableSHUTDOWNclauses that contain a specific dispatcher name. SpecifyingSHUTDOWNdispatcher1is equivalent to specifyingSHUTDOWN.
See Also:
ALTER DATABASE, ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE, ALTER SESSION, and ALTER SYSTEM for complete information on the clauses for these statements
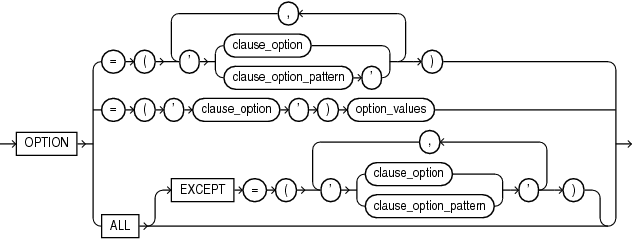
clause_options
This clause is valid only when you specify one of the following for lockdown_statements and statement_clauses:
{ DISABLE | ENABLE } STATEMENT = ('ALTER SESSION') CLAUSE = ('SET')
{ DISABLE | ENABLE } STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM') CLAUSE = ('SET')This clause lets you disable or enable the setting or modification of specific options with the ALTER SESSION SET or ALTER SYSTEM SET statements.
-
Use
clause_optionto specify the option you want to disable or enable. -
Use
clause_option_patternto specify a pattern that matches multiple options. Within the pattern, specify a percent sign (%) to match zero or more characters in an option name. For example, specifying'QUERY_REWRITE_%'is equivalent to specifying both theQUERY_REWRITE_ENABLEDandQUERY_REWRITE_INTEGRITYoptions. -
You can specify
clause_optionandclause_option_patternin any combination of uppercase and lowercase letters. -
Use
ALLto specify all options. -
Use
ALLEXCEPTto specify all options except the specified options.
See Also:
The alter_session_set_clause clause of ALTER SESSION and the alter_system_set_clause clause of ALTER SYSTEM for complete information on the options you can specify for these statements
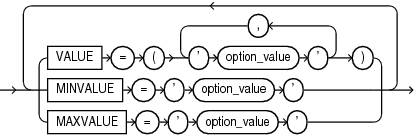
option_values
This clause is valid only when you specify one of the following for lockdown_statements, statement_clauses, and clause_options:
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SESSION') CLAUSE = ('SET') OPTION = clause_option
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM') CLAUSE = ('SET') OPTION = clause_optionThis clause lets you specify a default value for an option when disabling the setting of that option. For options that take numeric values, this clause also lets you restrict users from setting an option to certain values.
-
The
VALUEclause lets you specify a defaultoption_valueforclause_option, which will go into effect for any PDB to which the profile applies after you close and reopen the PDB. Ifclause_optionaccepts multiple default values, then you can specify more than oneoption_valuein a comma-separated list. The purpose of using this clause is to simultaneously set a default value for an option and restrict users from setting or modifying the value. -
The
MINVALUEclause lets you restricts users from setting the value ofclause_optionto a value less thanoption_value. You can specify this clause only for options that take a numeric value. -
The
MAXVALUEclause lets you restricts users from setting the value ofclause_optionto a value greater thanoption_value. You can specify this clause only for options that take a numeric value. -
You can specify both the
MINVALUEandMAXVALUEclauses together to restrict users from setting the value ofclause_optionsto any value less thanMINVALUEor greater thanMAXVALUE. -
MINVALUEandMAXVALUEsettings take effect immediately when the lockdown profile is assigned to a PDB; you need not close and reopen the PDB.
See Also:
Oracle Database Reference for complete information on the values allowed for the various options
Examples
The following statement creates PDB lockdown profile hr_prof:
CREATE LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof;The remaining examples in this section alter hr_prof.
Disabling Features for PDB Lockdown Profiles: Examples
The following statement disables all features in the feature bundle NETWORK_ACCESS:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE FEATURE = ('NETWORK_ACCESS');The following statement disables the LOB_FILE_ACCESS and TRACE_VIEW ACCESS features:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE FEATURE = ('LOB_FILE_ACCESS', 'TRACE_VIEW_ACCESS');The following statement disables all features except the COMMON_USER_LOCAL_SCHEMA_ACCESS and LOCAL_USER_COMMON_SCHEMA_ACCESS features:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE FEATURE ALL EXCEPT = ('COMMON_USER_LOCAL_SCHEMA_ACCESS', 'LOCAL_USER_COMMON_SCHEMA_ACCESS');The following statement disables all features:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE FEATURE ALL;Enabling Features for PDB Lockdown Profiles: Examples
The following statement enables the UTL_HTTP and UTL_SMTP features, as well as all features in the feature bundle OS_ACCESS:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE FEATURE = ('UTL_HTTP', 'UTL_SMTP', 'OS_ACCESS');The following statement enables all features except the AQ_PROTOCOLS and CTX_PROTOCOLS features:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE FEATURE ALL EXCEPT = ('AQ_PROTOCOLS', 'CTX_PROTOCOLS');The following statement enables all features:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE FEATURE ALL;Disabling Options for PDB Lockdown Profiles: Examples
The following statement disables user operations associated with the Oracle Database Advanced Queuing option:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE OPTION = ('DATABASE QUEUING');The following statement disables user operations associated with the Oracle Partitioning option:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE OPTION = ('PARTITIONING');Enabling Options for PDB Lockdown Profiles: Examples
The following statement enables user operations associated with the Oracle Database Advanced Queuing option:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE OPTION = ('DATABASE QUEUING');The following statement enables user operations associated both with the Oracle Database Advanced Queuing option and the Oracle Partitioning option:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE OPTION ALL;Disabling SQL Statements for PBB Lockdown Profiles: Examples
The following statement disables the ALTER DATABASE statement:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER DATABASE');The following statement disables the ALTER SYSTEM SUSPEND and ALTER SYSTEM RESUME statements:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM')
CLAUSE = ('SUSPEND', 'RESUME');The following statement disables all clauses of the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement, except DEFAULT TABLESPACE and DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE')
CLAUSE ALL EXCEPT = ('DEFAULT TABLESPACE', 'DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE');The following statement disables using the ALTER SESSION statement to set or modify COMMIT_WAIT or CURSOR_SHARING:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SESSION')
CLAUSE = ('SET')
OPTION = ('COMMIT_WAIT', 'CURSOR_SHARING');The following statement disables using the ALTER SYSTEM statement to set or modify the value of PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT. It also sets the default value for PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT to 'cdb1_pdb0', 'cdb1_pdb1'. This default value will take effect the next time the PDB is closed and reopened.
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM')
CLAUSE = ('SET')
OPTION = ('PDB_FILE_NAME_CONVERT')
VALUE = ('cdb1_pdb0', 'cdb1_pdb1');The following statement disables using the ALTER SYSTEM statement to set or modify the value of CPU_COUNT to a value less than 8:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM')
CLAUSE = ('SET')
OPTION = ('CPU_COUNT')
MINVALUE = '8';The following statement disables using the ALTER SYSTEM statement to set or modify the value of CPU_COUNT to a value greater than 2:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM')
CLAUSE = ('SET')
OPTION = ('CPU_COUNT')
MAXVALUE = '2';The following statement disables using the ALTER SYSTEM statement to set or modify the value of CPU_COUNT to a value less than 2 or greater than 6:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
DISABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SYSTEM')
CLAUSE = ('SET')
OPTION = ('CPU_COUNT')
MINVALUE = '2'
MAXVALUE = '6';Enabling SQL Statements for PBB Lockdown Profiles: Examples
The following statement enables all statements except ALTER DATABASE:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE STATEMENT ALL EXCEPT = ('ALTER DATABASE');The following statement enables the ALTER DATABASE MOUNT and ALTER DATABASE OPEN statements:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER DATABASE')
CLAUSE = ('MOUNT', 'OPEN');The following statement enables all clauses of the ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE statement, except DEFAULT TABLESPACE and DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER PLUGGABLE DATABASE')
CLAUSE ALL EXCEPT = ('DEFAULT TABLESPACE', 'DEFAULT TEMPORARY TABLESPACE');The following statement enables using the ALTER SESSION statement to set or modify COMMIT_WAIT or CURSOR_SHARING:
ALTER LOCKDOWN PROFILE hr_prof
ENABLE STATEMENT = ('ALTER SESSION')
CLAUSE = ('SET')
OPTION = ('COMMIT_WAIT', 'CURSOR_SHARING');