1.1 Introduction to Oracle Semantic Technologies Support
Oracle AI Database enables you to store RDF data and ontologies, to query RDF data and to perform ontology-assisted query of enterprise relational data, and to use supplied or user-defined inferencing to expand the power of querying on RDF data.
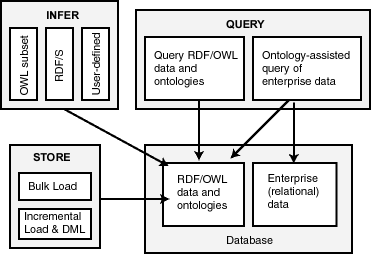
Figure 1-1 shows how these capabilities interact.
As shown in Figure 1-1, the database contains RDF data and ontologies (RDF/OWL graphs ), as well as traditional relational data. To load RDF data, bulk loading is the most efficient approach, although you can load data incrementally using transactional INSERT statements.
Note:
If you want to use existing RDF data from a release before Oracle Database 11.1, the data must be upgraded as described in Enabling RDF Semantic Graph Support.
You can query RDF data and ontologies, and you can also perform ontology-assisted queries of RDF and traditional relational data to find semantic relationships. To perform ontology-assisted queries, use the SEM_RELATED operator, which is described in Using Semantic Operators to Query Relational Data.
You can expand the power of queries on RDF data by using inferencing, which uses rules in rulebases. Inferencing enables you to make logical deductions based on the data and the rules. For information about using rules and rulebases for inferencing, see Inferencing: Rules and Rulebases.
Parent topic: RDF Graph Overview