2 Oracle GDS Architecture and Concepts
Learn about how you can use Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) to manage databases according to service properties that you specify when you create the services.
- Overview of Oracle Global Data Services Configuration
Learn how Global Data Services manages global and local database services, centralizes service configuration, and coordinates service availability across Oracle databases to database clients. - Global Data Services Architecture
Use these figures to better understand Global Data Serviceds (GDS) componenta and configuration. - Oracle GDS Concepts for Deployment Planning
To plan for deployment in your environment, review these concepts, security guideines and best practices for Oracle Global Data Services (GDS).
Overview of Oracle Global Data Services Configuration
Learn how Global Data Services manages global and local database services, centralizes service configuration, and coordinates service availability across Oracle databases to database clients.
A Global Data Services configuration consists of a set of global services for database clients. A global service is a database service managed and made available across multiple physical databases (which may be in different locations, data centers, or clusters) that are part of a GDS configuration. These global services enable users and applications to connect using a single logical service name. The GDS framework manages routing, load balancing, and failover across all databases that offer the global service. A global service manager serving a Global Data Services configuration is aware of all global services the configuration provides and acts as a mediator for database clients and databases in the configuration. A client program connects to a regional global service manager and requests a connection to a global service. The client does not need to specify a particular database or instance. The global service manager forwards the client's request to the optimal instance in the configuration that offers the global service. Ensure all your database clients that use the same global service share service-level requirements.
The functionality of local services, defined as traditional database services provided by a single database, does not change when you use global services. Oracle Database can provide local and global services simultaneously. A client application can also use both global and local services simultaneously.
The configuration and runtime status of global services are stored in the Global Data Services catalog. Each database offering global services also maintains information about those services in a local repository, such as a system dictionary or Oracle Cluster Registry, and data on local services. Global services stored in a local repository include a flag to distinguish them from traditional local services.
If you are locally connected to a particular database, you can query data on global services provided by that database. You can configure, modify, start, or stop a global service using the Global Data Services Control utility (GDSCTL) when you are connected to the Global Data Services catalog, so you can ensure centralized, coordinated management of global services. You cannot configure, modify, start, or stop a global service using the Server Control utility (SRVCTL) or the Oracle Clusterware Control utility (CRSCTL).
Note:
Under certain circumstances (such as patching a database or clusterware
software), you can stop or start global services using SRVCTL with the
-force option with the appropriate command. You must have the
appropriate system privileges.
After you configure global services for a Global Data Services configuration, the global service manager manages global services on GDS configuration databases according to the properties you specify when you create the services.
When a database joins the configuration, or if a database restarts after a shutdown, the database registers with all global service managers in the configuration. After receiving the registration request, one of the global service managers queries the GDS catalog and checks whether all global services that the database is supposed to provide are created there and have the correct attributes. If a discrepancy exists between the information in the catalog and the database, then the global service manager may create, delete, or modify global services in the database or change their attributes to synchronize them with the catalog. The global service manager then determines which global services need to run on the database and starts them as needed.
The global service manager can start or stop a global service in a database. However, if the database is an Oracle RAC database, then the global service manager does not control which particular instances within the database offer the service. Service management is controlled by the clusterware and the administrator of the Oracle RAC database.
When a database instance in a Global Data Services configuration fails, all global service managers in the configuration are notified about the failure and stop forwarding requests to the instance. If the instance belongs to a noncluster database or is the last instance available in an Oracle RAC database, then, depending on the configuration, a global service manager can automatically start the service on another database in the Global Data Services pool where the service is enabled. If you decide to manually move a global service from one database to another using the appropriate GDSCTL command, then the global service manager stops and starts the service on the corresponding databases.
Parent topic: Oracle GDS Architecture and Concepts
Global Data Services Architecture
Use these figures to better understand Global Data Serviceds (GDS) componenta and configuration.
This figure shows an example of a Global Data Services (GDS) configuration and common GDS components.
Figure 2-1 Global Data Services Components
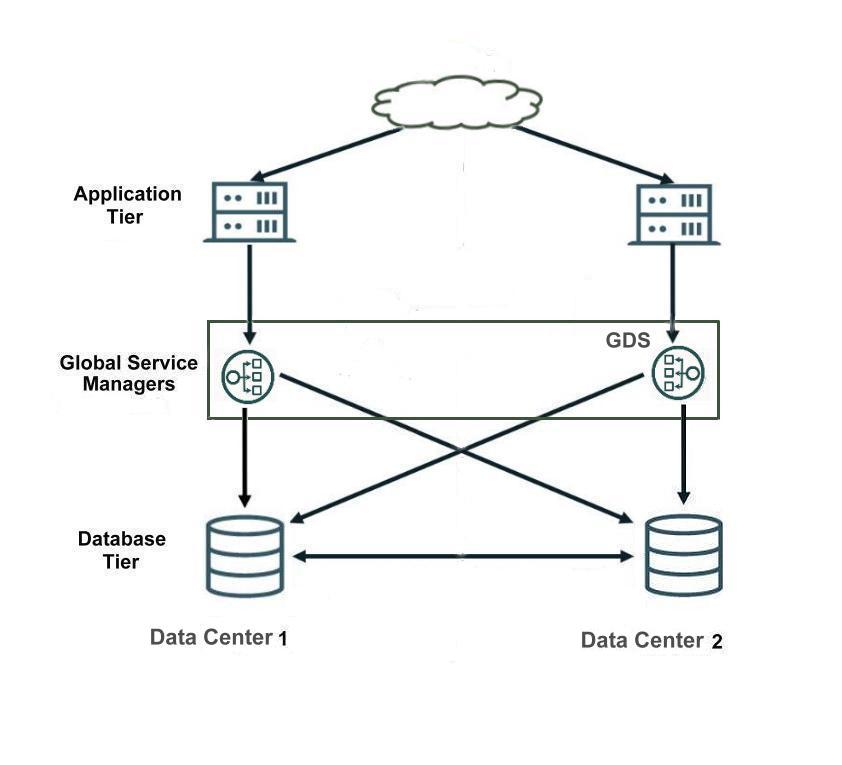
Description of "Figure 2-1 Global Data Services Components"
The illustration below shows a basic Global Data Services implementation architecture and a summary of basic requirements.
Figure 2-2 GDS Basic Reference Architecture - Summary
Parent topic: Oracle GDS Architecture and Concepts
Oracle GDS Concepts for Deployment Planning
To plan for deployment in your environment, review these concepts, security guideines and best practices for Oracle Global Data Services (GDS).
- Understanding Oracle Global Data Services Workload Management
Learn how Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) enhances your ability to manage and balance workloads across distributed, replicated Oracle databases. - Global Data Services Components
Learn how to manage key Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) components to organize, administer, and optimize global services.
Parent topic: Oracle GDS Architecture and Concepts
Understanding Oracle Global Data Services Workload Management
Learn how Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) enhances your ability to manage and balance workloads across distributed, replicated Oracle databases.
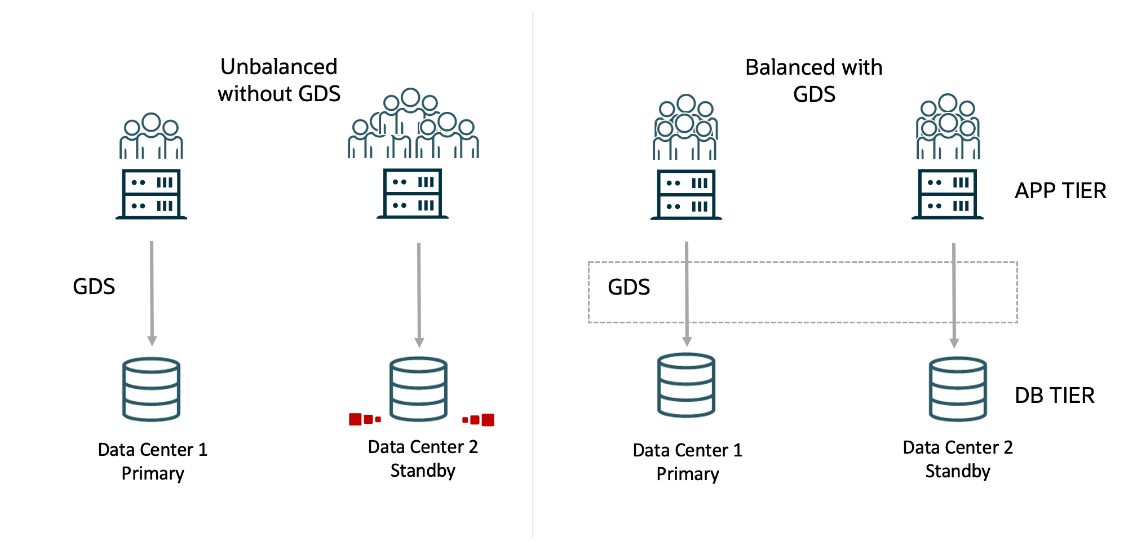
Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) global services enables you to efficiently define, manage, and balance workloads across replicated databases. Global services enable workload grouping, placement, and efficient routing in complex, distributed environments, based on replication lag and regional proximity, and overall workload administration.
Database services are logical abstractions for managing workloads in an Oracle database. Each service represents a workload with common attributes, service-level thresholds, and priorities. The grouping can be based on work characteristics, including the application function. For example, the Oracle E-Business Suite defines a service for each application module, such as general ledger, accounts receivable, and order entry. Services are built into Oracle Database, providing a single system image for workloads. Services enable administrators to configure a workload, administer it, enable and disable it, and measure the workload as a single entity. Clients connect using a database service name.
For replicated environments, GDS introduces the concept of a "global service". Global services are provided across a set of databases containing replicated data that belongs to a particular administrative domain known as a GDS pool. Examples of a GDS pool are a SALES pool or an HR pool. A set of databases in a GDS configuration and the database clients are said to be in the same GDS region if they share the network proximity. Examples of GDS regions are the Asian region, European region, and so on.
All of the characteristics of traditional database services are supported by global services. Global services extends traditional database services with additional attributes such as global service placement, replication lag (Oracle Active Data Guard and Oracle GoldenGate from 19c onwards), and region affinity.
Global service placement: When a global service is created, GDS allows the preferred and available databases for that service to be specified. The available databases support a global service if the preferred database fails. In addition, GDS allows you to configure a service to run on all the replicas of a given GDS pool.
Replication lag: Clients can be routed to the Oracle Active Data Guard standbys that are not lagging by the tolerance limit established with the lag attribute of a global service.
Region affinity: A global service allows you to set preferences to which region (for example Asia or Europe) your given applications should connect.
Figure 2-3 Workload Balancing with Global Data Services
Parent topic: Oracle GDS Concepts for Deployment Planning
Global Data Services Components
Learn how to manage key Oracle Global Data Services (GDS) components to organize, administer, and optimize global services.
- GDS Networks
Global Data Services (GDS) networking supports high availability, workload management, and scalable sharding by orchestrating network communication between distributed Oracle Database environments. - Global Data Services Pool
Use Global Data Services pools to group databases for simplified service management and increased security in GDS configurations. - Global Data Services Region
Use Global Data Services regions to group databases and clients with low-latency communication and ensure high availability in distributed environments. - Global Service Manager
Learn what a global service manager is, how it functions in Global Data Services, and why it is essential for service management. - Global Data Services Catalog
Understand the purpose of the Global Data Services catalog and how to plan for its location and availability. - Oracle Notification Service Servers
Understand how Oracle Notification Service servers deliver load balancing and high availability event notifications in a Global Data Services environment.
Parent topic: Oracle GDS Concepts for Deployment Planning
GDS Networks
Global Data Services (GDS) networking supports high availability, workload management, and scalable sharding by orchestrating network communication between distributed Oracle Database environments.
GDS networking components include GDS management, registration, event notifications, connection forwarding, workload routing, and cross-sharding connections. Cross-sharding connections are communications that occur between different database shards within a sharded Oracle database environment.
Networking Components
-
GDS: Global Data Services
Enables workload balancing and high availability across distributed, replicated database environments..
-
GSM: Global Service Manager
The GDS component that manages services, provides load balancing, routes client connections, and monitors database/service health.
-
ONS: Oracle Notification Service
Mechanism for broadcasting Fast Application Notification (FAN) and load balancing events to clients and services across the GDS environment.
-
OCI: Oracle Call Interface
A low-level API for interacting with database services, used by applications and middleware to access databases.
-
AQ: Advanced Queuing
Oracle Message queuing service, sometimes used internally for database notifications and inter-process communication.
-
NSGR: Namespace Global Registration (Listener Registration)
Internal Oracle protocol for registering service information with listeners (such as GSM listeners), supporting dynamic service discovery.
-
IPC: Inter-Process Communication
Mechanism for communication between processes on the same server, used for internal component operations.
-
JDBC: Java Database Connectivity
Standard Java API for database connections, used by Java applications to connect to Oracle databases (including for administration).
-
RPC: Remote Procedure Call
Protocol enabling a program on one server to execute code on another server, used for some inter-component operations.
GDS and Oracle Processes
- gsmoci: GSM Oracle Call Interface process
- lreg: Database (instance) registration process
- tnslsnr: Oracle TNS listener process
- gsmopxy: GSM proxy process
- gsmonsc: GSM ONS client process
- gsmmon: GSM monitor process
- pinger: Network performance measurement process within GSM
The following table explains how GDS networking components are used within the Global Data Services environment.
Table 2-1 Network Communication Configuration
| Purpose | Client | Server | Protocol | Default Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GDS Management |
GSM ( |
Database (foregrounds) |
OCI/AQ |
1521 |
|
Catalog and global services registration |
Database ( |
GSM (tnslsnr)
|
NSGR |
1521 |
|
Service/database/sharding events |
GSM ( |
Clients |
ONS Notifications |
6234 |
|
Connection forwarding |
Clients |
GSM ( |
SQL*Net |
1522 |
|
Workload |
Clients |
GSM Pool (databases) |
driver |
1521 |
|
Cross-sharded |
Clients |
GSM Pool (databases) |
driver |
1521 |
|
Status/start/stop |
GDS |
GSM ( |
IPC (same server) |
No default (private ports) |
|
GDS Management |
GDS |
GSM Catalog |
JDBC/OCI |
1521 |
|
Status/validate |
GDS |
GSM pool (databases) |
JDBC/OCI |
1521 |
|
Network performance measure |
GSM (pinger) |
GSM (pinger) |
RPC |
No default (private ports) |
|
ONS subscription |
GSM ( |
GSM Pool (databases) |
ONS notifications |
6234 |
Parent topic: Global Data Services Components
Global Data Services Pool
Use Global Data Services pools to group databases for simplified service management and increased security in GDS configurations.
A Global Data Services pool (GDS pool) is a named subset of databases within a GDS configuration. Each GDS pool provides a unique set of global services and belongs to a single administrative domain. Partitioning GDS configuration databases into pools simplifies service management and increases security, because each pool can be administered by a different administrator.
A database can belong to only one Global Data Services pool. Not all databases in a pool must provide the same set of global services. However, every database that provides a specific global service must belong to the same pool.
Parent topic: Global Data Services Components
Global Data Services Region
Use Global Data Services regions to group databases and clients with low-latency communication and ensure high availability in distributed environments.
A Global Data Services region (GDS region) is a named subset of databases in a GDS configuration and database clients that share network proximity with that configuraiton. Network latency between members of a region is typically lower than between members of different regions.
A region usually corresponds to a local area network (LAN) or metropolitan area network (MAN). For example, a data center hosting one or more GDS configuration databases and database clients in geographical proximity can be considered a single region.
A region can contain multiple Global Data Services pools, and a pool can also span multiple regions.
For high availability, each region in a GDS configuration should have a designated buddy region. A buddy region is a region that contains Global Service Managers (GSMs) to provide continued access to the GDS configuration if the Global Service Managers in the local region become unavailable.
Parent topic: Global Data Services Components
Global Service Manager
Learn what a global service manager is, how it functions in Global Data Services, and why it is essential for service management.
A global service manager (GSM) is the central software component of Global Data Services (GDS). The GSM provides service-level load balancing, failover, and centralized management of services within a GDS configuration. Global Data Services clients use a GSM to perform all GDS configuration operations.
A GSM is similar to the remote listener in an Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) database, but it serves multiple databases instead of one. The GSM is associated with one and only one GDS configuration. Each region in the GDS configuration must have at least one GSM. Configure multiple GSMs in each region to improve availability and performance. Every GSM in a GDS configuration manages all global services supported by the configuration.
A global service manager performs the following functions:
- Acts as a regional listener that clients use to connect to global services.
- Provides connect-time load balancing for clients.
- Manages global services across the regions of a GDS configuration.
- Collects performance metrics from databases in the GDS configuration and measures network latency between configuration regions.
- Creates a run-time load balancing advisory and publishes it to client connection pools.
- Monitors availability of database instances and global services, and notifies clients if they fail.
Note:
A master GSM makes metadata changes in the catalog database, for instance when adding a new global data service or adding a new shard. If the master GSM goes down, then another GSM will become the new master. Any other GSMs associated to a region is a region GSM.Parent topic: Global Data Services Components
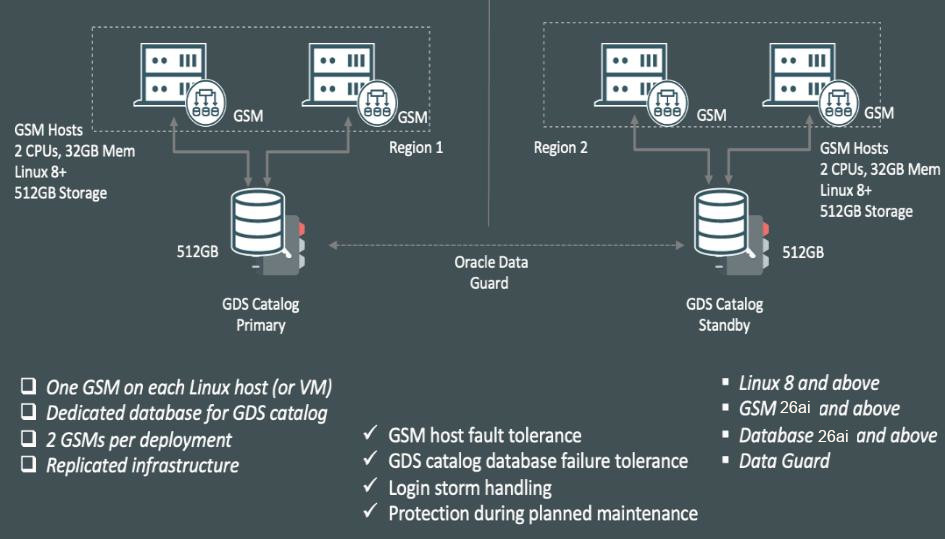
Global Data Services Catalog
Understand the purpose of the Global Data Services catalog and how to plan for its location and availability.
A Global Data Services catalog (GDS catalog) is a repository that stores configuration data for a Global Data Services configuration and all global services provided by that configuration.
A GDS catalog is associated with one and only one GDS configuration. A catalog must reside in an Oracle database, and that database can be either inside or outside the associated GDS configuration. For large-scale GDS configurations, Oracle recommends that the GDS catalog is hosted outside the databases in the GDS configuration. The GDS catalog can be co-hosted along with catalogs of RMAN or Oracle Enterprise Manager.
To enhance the availability of the Global Data Services catalog database, Oracle recommends that you configure the GDS catalog database on high availability technologies such as Oracle RAC, Oracle Data Guard, and Oracle Clusterware.
Parent topic: Global Data Services Components
Oracle Notification Service Servers
Understand how Oracle Notification Service servers deliver load balancing and high availability event notifications in a Global Data Services environment.
GDS clients use Oracle Notification Service (ONS) to receive run-time load balancing advisory and high availability events from global service managers.
An ONS server is co-located with each global service manager. All such ONS servers within a region are interconnected. Clients of global services subscribe to the ONS server network within their region and their buddy region, and receive FAN notifications from those ONS server networks.
Note:
An Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) database in a Global Data Serviced configuration can also contain ONS servers running on the cluster nodes. These ONS servers generate Fast Application Notification (FAN) events related to local services and do not connect to ONS server networks in the GDS regions.
Parent topic: Global Data Services Components