10.6.10 Support for Result Tables
Result tables (also known as Subject-Property-Matrix auxiliary tables) can be used to speed up SPARQL query execution. It is recommended you first refer to Speeding up Query Execution with Result Tables, for a detailed description of result tables. These auxiliary tables are associated with individual RDF graphs. Once they are created, they are automatically used during execution of SPARQL queries, unless specific options (see SPARQL Query Options for Result Tables) are passed in to indicate otherwise (note that the query cache may need to be cleared if the same SPARQL query is to be executed right after creating a result table).
There are three types of result tables based on the type of the query pattern used for producing the results to be stored:
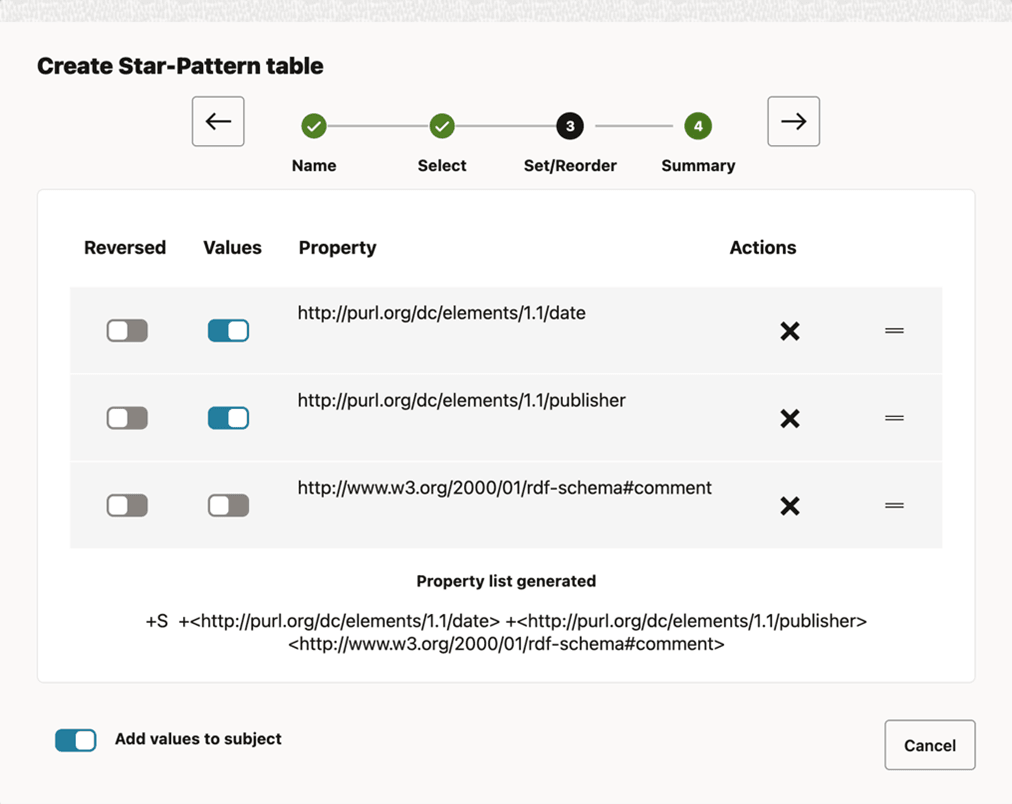
- Star-Pattern tables (also known as Single-Valued Property or SVP tables) hold values
for single-valued RDF properties. A property
pis single-valued in an RDF model if each resource in the model has at most one value forp. - Triple-Pattern tables (also known as Multi-Valued Property (MVP) tables) hold values
for individual RDF properties.The property used for a triple-pattern table may be
single-valued or multi-valued. (A property p is multi-valued in an RDF graph if it
contains two triples
(s p o1)and(s p o2)witho1not equal too2.) - Chain-Pattern tables (also known as Property Chain (PCN) tables) hold paths in the
RDF graph. A sequence of triples form a path if for each consecutive pair of
triples,
TiandTj, the object value ofTiis equal to the subject value ofTj.
Star-pattern and chain-pattern tables can be used to reduce joins during SPARQL query execution, while triple-pattern tables allow for more compact representation for triples involving individual properties. Additionally, if lexical values are included in the result tables, then joins needed for looking up lexical values can be avoided as well.
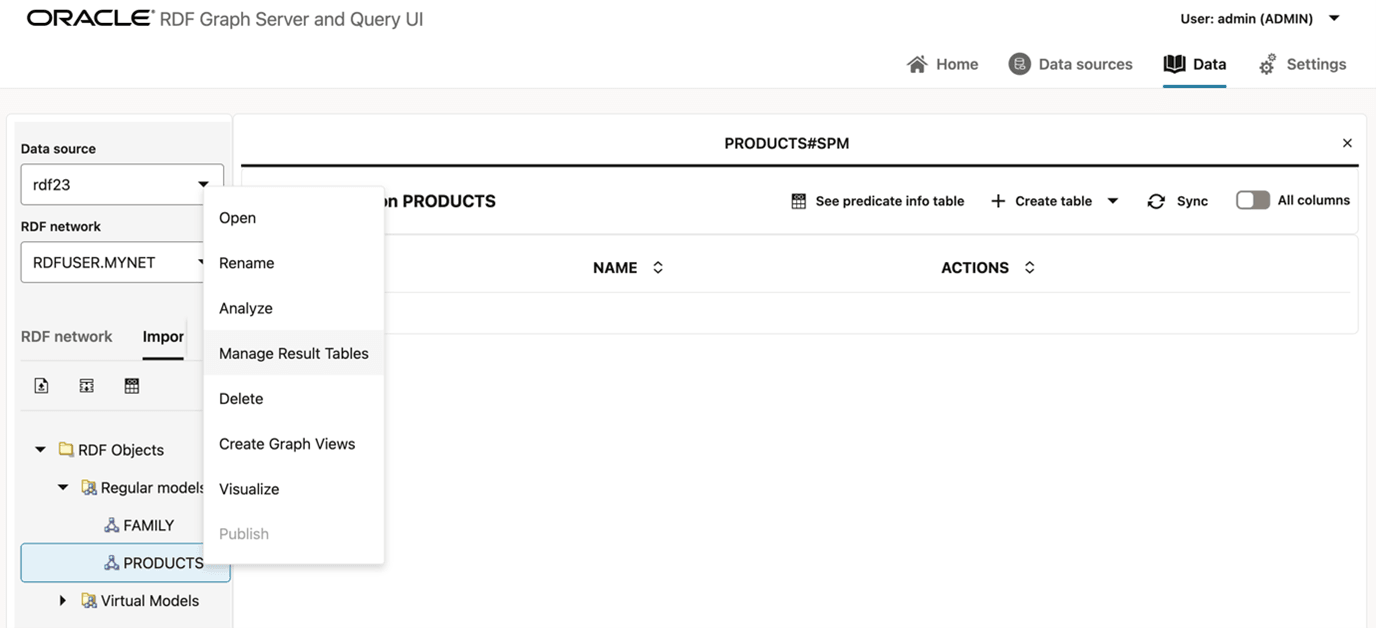
The RDF Server and Query UI web application provides support for creation and management of result tables. You can manage these auxiliary tables by right clicking the RDF graph and selecting the Manage Result Tables menu item as shown:
The Result Tables page displays a table which lists the result tables
present in the RDF graph. If you are a first time user, then this table list will be
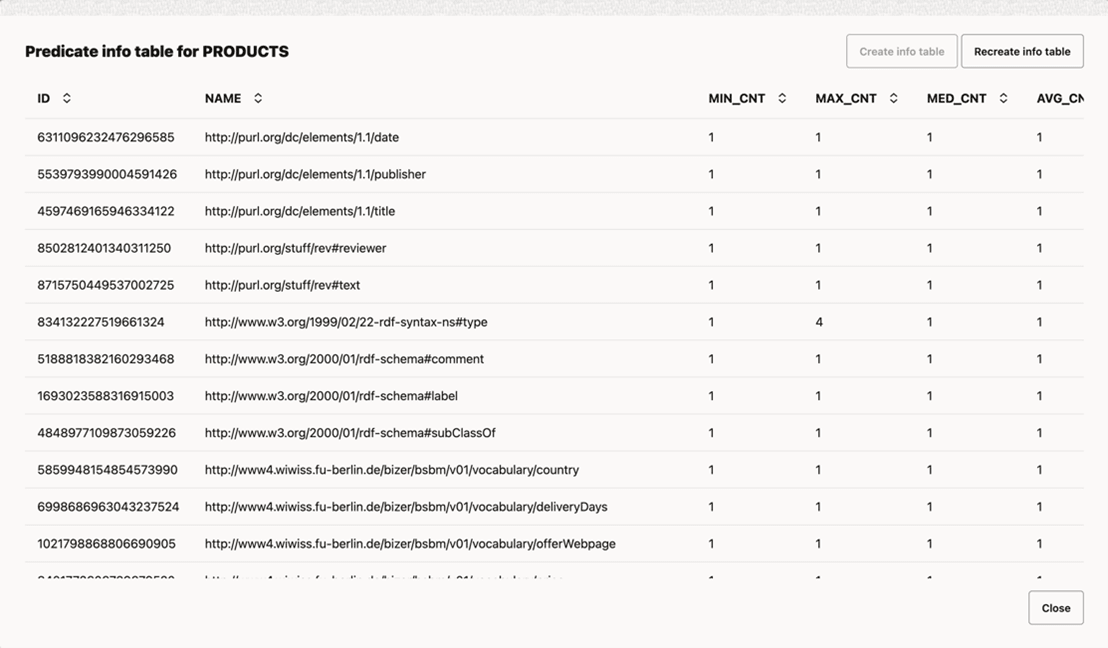
empty. In such a case, you need to create the Predicate Info Table that is
required for creating and managing the result tables. The predicate info table stores
information about each property used as predicate in the RDF graph. For each property
(or its inverse), the stored information includes its id (or negative
id, for the inverse), name, and statistics on
cardinality (that is, the number of triples that use this property) per distinct subject
(or, object, for the inverse). A value of one in the MAX_CNT column
indicates that the property was single-valued when the statistics were last
computed.
To create the predicate info table, click See predicate info table in the table menu bar and then select Create info table. Note that you also have the option to recreate the table at a later time as shown in the following image:
Once the predicate info table is created, you can then create and manage the result tables.
Parent topic: RDF Data Page
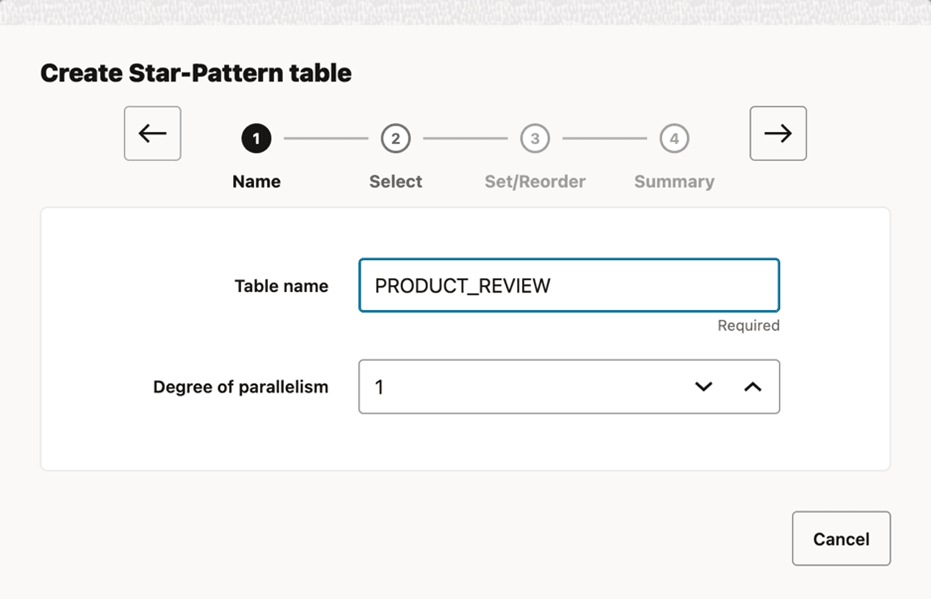
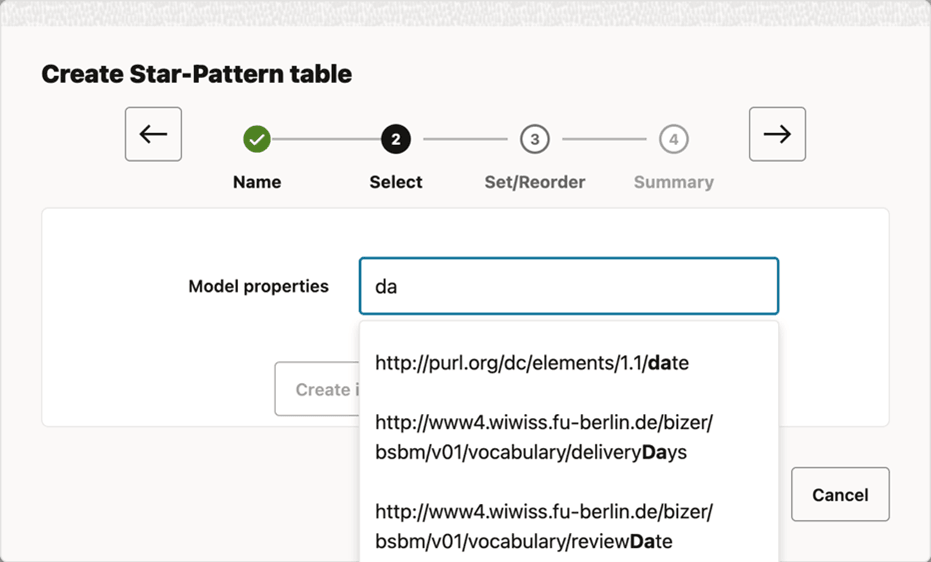
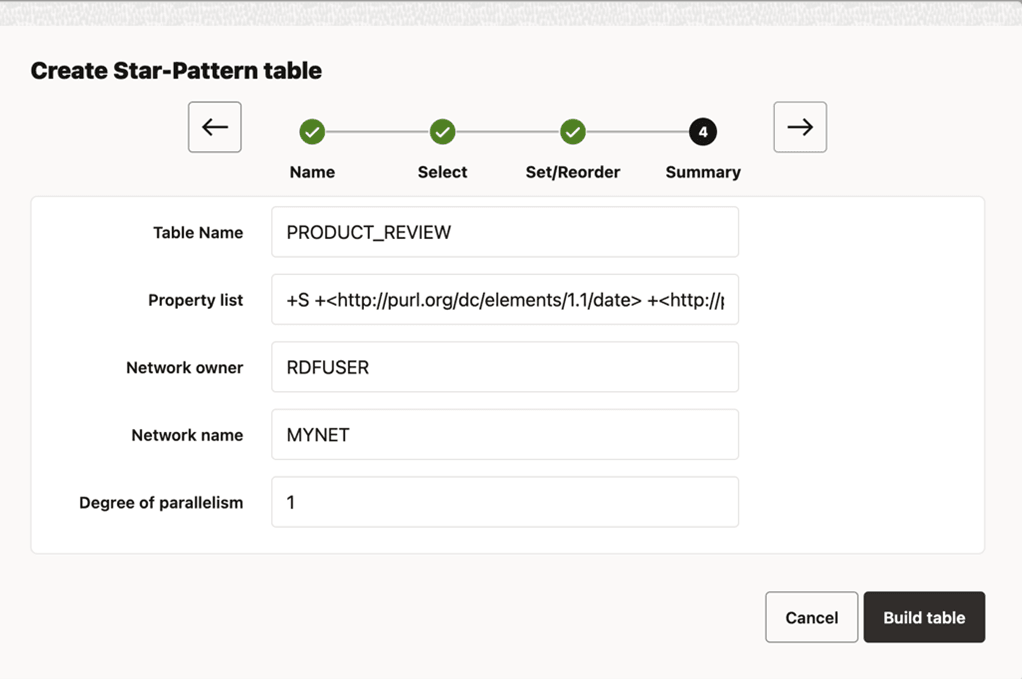
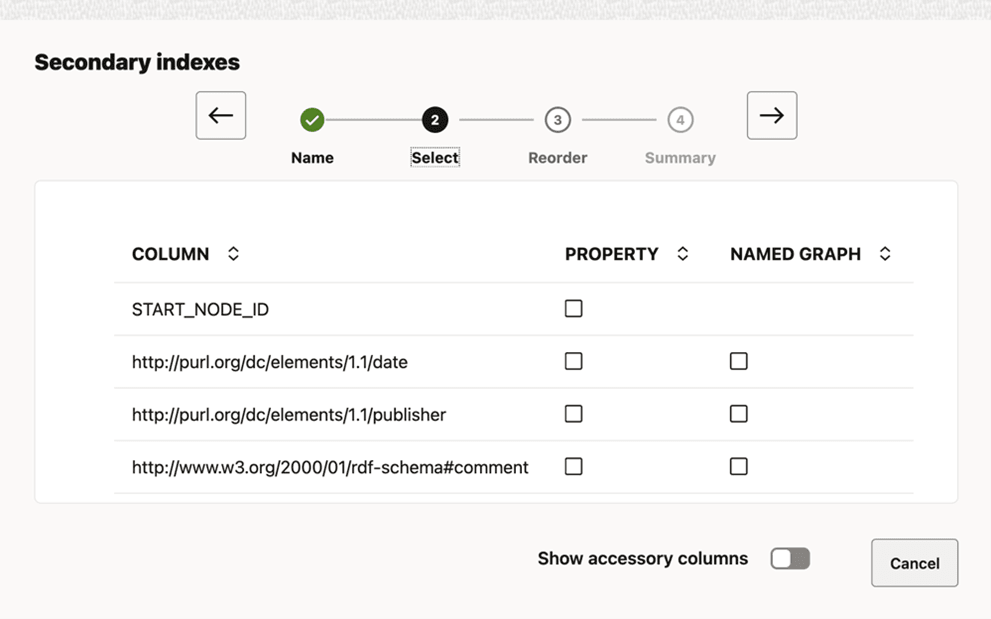
10.6.10.1 Creating Result Tables
The preceding workflow steps are common when creating any type of result table. However, the following 26ai features are available only for certain types of tables:
- Inverse Property Path: This feature is only available for chain-pattern
or star-pattern tables. It can be enabled individually for each property,
directly from the Set/Reorder properties step. In the following example,
the property
http://purl.org/dc/elements/1.1/dateis shown Reversed. This implies that the subject and object of the triple switch places. See the W3C documentation for more information on inverse property path.Figure 10-52 Configuring Inverse property path
- Multi-Occurrence : This new feature in which the same property can be
replicated multiple times is only available for chain-pattern tables. To
duplicate a property, click the Duplicate property button under the
Actions column on the Set/Reorder step. Note that once the
table is created, for ease of differentiation, each replicated property is
appended an identifier consisting of a “#” followed by a cardinal number.
Parent topic: Support for Result Tables
10.6.10.2 Managing Result Tables

Description of the illustration manage_actions_result_table.png
You can then choose to perform any of the following actions:
Parent topic: Support for Result Tables
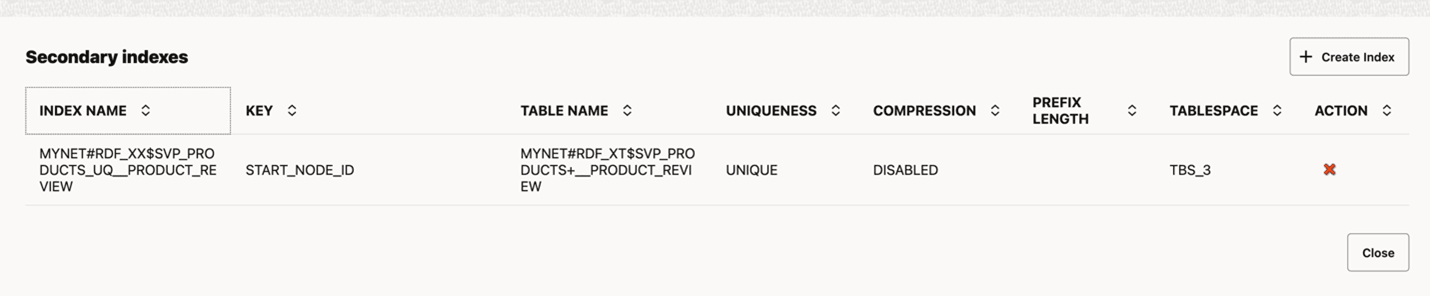
10.6.10.2.1 Creating an Index on a Result Table
Parent topic: Managing Result Tables