10.6.11 Advanced Graph View
The RDF Graph Query UI supports an advanced graph view feature that allows users to interact directly with the graph visualization. This is unlike the graph displayed on the RDF model editor or public component where the graph view is just an output of the SPARQL results on the paging table.
This section describes the advanced graph view component, starting from the
execution of a SPARQL CONSTRUCT or SPARQL DESCRIBE
query to advanced interaction with the graph visualization.
The main user interface (UI) elements of the advanced graph view component are as shown:
Figure 10-63 Advanced Graph View Components

Description of "Figure 10-63 Advanced Graph View Components"
The following describes the UI components seen in the preceding figure:
- SPARQL Query selector contains a text area with
the SPARQL query (must be SPARQL
CONSTRUCTor SPARQLDESCRIBE). - A Graphviz area that displays the graph with the RDF vertices and edges.
To access the advanced graph view feature, right-click on the RDF model and select Visualize as shown:
Parent topic: RDF Data Page
10.6.11.1 Query Selector Panel
To start using the advanced graph view feature, you must first execute a
SPARQL CONSTRUCT or SPARQL DESCRIBE query. The
resulting query output is displayed as an interactive graph in the Graphviz
component.
The system may automatically run additional queries to build the graph before it is displayed. A SPARQL query is executed for each resource in the initial query result set to retrieve values for its datatype properties. These additional queries ensure that each vertex in the graph is fully populated with its attributes. The maximum number of resources that can be expanded in a result set is 2,000. The application will raise an error if this limit is exceeded. In which case, you can reduce the result set size by using a more selective SPARQL query or using a LIMIT clause.
The following figure shows an example SPARQL CONSTRUCT query that
describes the person named George in a PEOPLE dataset. The Query
Selector Panel can be collapsed to provide more space for interacting with the
graph.
Parent topic: Advanced Graph View
10.6.11.2 Graphviz
The graph is displayed in the Graphviz panel and the visualization is based on the Graph Visualization Library. See Graph Visualization Library Reference in Property Graph Visualization Developer's Guide and Reference for more information.
The displayed graph is constructed from an RDF graph as follows.
- URI and blank node resources are shown as vertices and hold their
rdf:typeclass membership information in a labels array, which is used for the graph legend. Each vertex has ashortNameproperty that is used to label the vertex in the display graph. TheshortNameproperty is populated in the following priority:rdfs:labelvalue of the resource-
skos:prefLabelvalue of the resource - Local name portion of the resource’s URI or its blank node label
If multiple
rdfs:labelorskos:prefLabelvalues exist for the same resource, plain literal values are selected first, followed by en-tagged literals, followed by any other value. Data type properties for these URIs and blank nodes are shown as vertex properties. - Object properties are shown as edges connecting two vertices. These edges use the local name portion of the RDF predicate URI as the edge label for both the graph legend and the edge display label. Edges hold properties for full predicate URI, source (subject) RDF term and target (object) RDF term.
The Graphviz panel consists of the following components:
- A toolbar with the following options (described in order from left to right):
- Move/Zoom: This mode allows you to zoom in and out, as well as to move to another part of the visualization.
- Fit to Screen: This mode fits the resulting graph in the graph visualization view.
- Toggles Sticky Mode: This mode allows you to cancel the action of moving the nodes around.
- Graph Manipulation: This mode allows you
to interact with your graph visualization.
The following actions are supported:
- Expand: To expand selected vertices from the visualization.
- Drop: To remove selected vertices from the visualization. Alternatively, you can also execute this from the tooltip.
- Group: To group selected multiple vertices and collapse them into a single one.
- Ungroup: To select a group of collapsed vertices and ungroup them.
- Undo: To undo the last action.
- Redo: To redo the last action.
- Reset: To reset the visualization to the original state after the query.
- A drawing area with the RDF nodes and edges.
- A graph legend on the right side of the panel that displays vertex and edge types and their associated styles in the graph.
- A layout selector at the bottom of the display panel that provides various layout options for positioning vertices and edges on the display.
You can interact with the edges and vertices of the graph displayed in the graph view area.
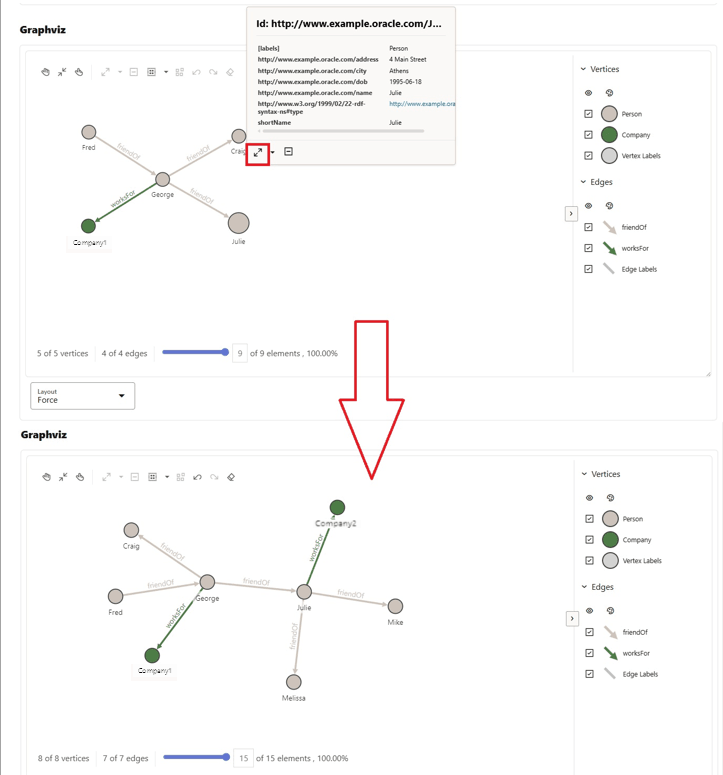
worksFor edge:
To expand a vertex in the graph, right-click on the vertex and then click the expand icon. New vertices and edges directly connected to the expanded vertex will be added to the graph. For example, in the following figure, vertex Julie is shown expanded:
Parent topic: Advanced Graph View