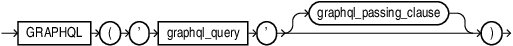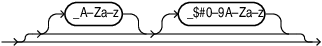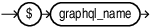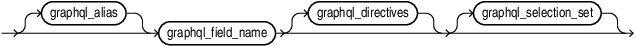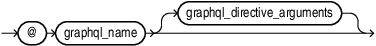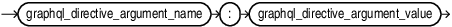GRAPHQL Table Function
graphql_string_value::=
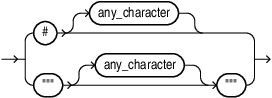
graphql_comment::=
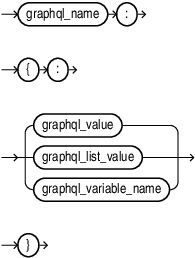
graphql_name::=
graphql_query::=
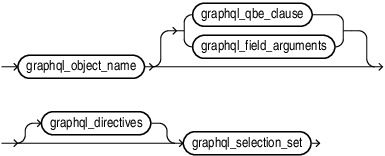
graphql_object_name::=
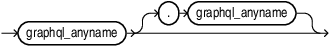
graphql_anyname::=
graphql_quoted_name::=
graphql_qbe_clause::=
graphql_qbe_argument_list::=
graphql_qbe_argument_list_continue::=
graphql_qbe_equality_argument::=
graphql_qbe_relational_argument::=
graphql_qbe_logical_argument::=
graphql_qbe_logical_argument_list::=
graphql_qbe_logical_argument_list_continue
graphql_qbe_item_operator_argument::=
graphql_qbe_item_operator_list::=
graphql_qbe_item_operator_list_continue::=
graphql_qbe_operator_name::=
graphql_field_arguments::=
graphql_field_argument_list::=
graphql_field_argument_list_continue::=
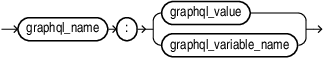
graphql_field_argument::=
graphql_variable_name::=
graphql_selection_set::=
graphql_selection::=
graphql_field::=
graphql_field_name::=
graphql_alias::=
graphql_directives::=
graphql_directive::=
graphql_directive_arguments::=
graphql_directive_argument_list::=
graphql_directive_argument_list_continue::=
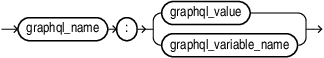
graphql_directive_argument::=
graphql_directive_argument_name::=
graphql_directive_argument_value::=
graphql_any_value::=
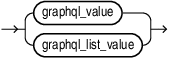
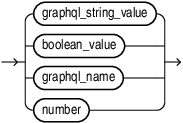
graphql_value::=
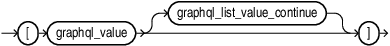
graphql_list_value::=
graphql_list_value_continue::=
graphql_passing_clause::=
graphql_variable_list::=
graphql_variable_list_continue::=
graphql_variable_identifier::=
Purpose
The GRAPHQL table function is a SQL table function that you can use to query database tables and get the result in the form of JSON documents.
The GRAPHQL table function evaluates the embedded GraphQL query that is passed in as a string literal. The function returns rows derived from the GraphQL selection set, consistent with the JSON-relational duality mapping of the referenced object.
You can use the function only in the FROM clause of the SELECT statement.
Note:
Whitespaces and comments can appear anywhere in the graphql_query clause.
Semantics
graphql_query
The input to the function, graphql_query, is a structured and hierarchical representation of the objects and fields to be queried .
The output of the function is a single column of type JSON consisting of the set of JSON documents corresponding to graphql_query.
graphql_passing_clause
If present, graphql_passing_clause provides variable bindings used by graphql_field_arguments or QBE. It starts with the keyword PASSING, and is followed by mappings of GraphQL variables to SQL expressions, literal, or bind variables.
-
graphql_object_namerefers to fully qualified names, for example,schema_name.table_nameortable_name.column_name. -
graphql_field_argumentsrefers to a set of predicates that restricts the result set. These predicates compare field values to provided literals (or even variables in the GraphQL table function). If multiple arguments are present, they are combined conjunctively (logicalAND). Each graphql field argument is a name: value pair or a name: variable pair.You must enclose the list of arguments in parentheses.
A variable in the GraphQL table is identified by the
'$'sign as the first character.
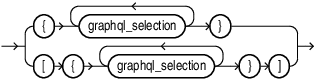
graphql_selection_set
graphql_selection_set declares the the fields that you want to project from the current object.
graphql_field maps the underlying relational object (column or table) to the JSON field.
The optional argument graphql_alias changes the output key name.
The optional argument graphql_directives alters how the field is resolved or how it affects the metadata of the duality view.
Optional nested graphql_selection_set declares the fields to be projected in the nested object.
graphql_field_name can be the name of a table or a column or even a numeric literal.
graphql_alias renames the output key of the selected field. The underlying field lookup uses graphql_field_name. The output uses graphql_alias.
graphql_qbe_clause
Use graphql_qbe_clause to filter the JSON documents, by having predicates on the fields in the GraphQL query. It can express equality, relational, logical, and item-level operators.
graphql_qbe_clause is enclosed within parentheses and starts with the CHECK keyword, followed by the colon and the list of QBE arguments within curly braces.
qbe_equality_argument is a field-level equality predicate. It evaluates to true when the field equals the provided literal or bound variable.
qbe_relational_argument is a field-level relational predicate. The QBE operator refers to a comparison, which is applied to the specified field and the provided operand.
qbe_logical_argument refers to logical composition (for example, AND, or OR). The operator combines the enclosed argument list according to its truth table, evaluated against the current scope. Nested logical clauses are also allowed.
qbe_item_operator_argument refers to QBE item operators that can be used to first perform some transformations on the field before comparing it to the value.
graphql_directives
Directives are metadata-driven modifiers applied to fields or selection sets, written as @directive_name(directive_arguments) where each graphql_directive_argument is written as graphql_directive_argument_name: graphql_directive_argument_value. They control behavior like conditional inclusion, shape in the response, computed transformations, access and mutability. The arguments for a directive are name: value pairs. The value can be a name, a string, a number or even a list of values.
Comments in a GraphQL Expression
You can specify comments in a single line in a GraphQL expression. A single line comment is preceded by a hash (# )sign, in accordance with the GraphQL standard.
You can also specify SQL comments in the query containing the GraphQL expression. A single line SQL comment is preceded by a double dash (--). A SQL comment spanning multiple lines is enclosed within "/*" and "*/".
Rules
-
The SQL comments can be placed anywhere in the query, but the GraphQL comments are valid only within the GraphQL expression.
-
These comments will be preserved in the DDL, that is when you fetch the create view DDL using
DBMS_METADATA.GET_DDL, these comments will be present in the output. -
Only single line GraphQL style comments (comments starting with # ) are allowed in the GraphQL expression provided in the GraphQL table function.
Example: Valid Comments
CREATE OR REPLACE JSON RELATIONAL DUALITY VIEW student_ov AS
student { # this is a valid single line GraphQL comment
_id: stuid
Name: name
-- SQL comments can be placed within GraphQL expression as well
};Example
Querying the DB using GraphQL query
SELECT * FROM GRAPHQL
('
employees {
_id: employee_id
Name: first_name
}
');
The output is:
{
"_id" : 174,
"Name" : "Ellen"
}
{
"_id" : 166,
"Name" : "Sundar"
}
{
"_id" : 130,
"Name" : "Mozhe"
}
{
"_id" : 105,
"Name" : "David"
}
See Declarative GraphQL Developer's Guide for more information on GraphQL.