2.4 Schema View
The Graph Visualization library allows you to visualize a graph's schema in the form of a property graph.
In order to enable schema view, you must configure the properties described in Schema View Configuration Parameters.
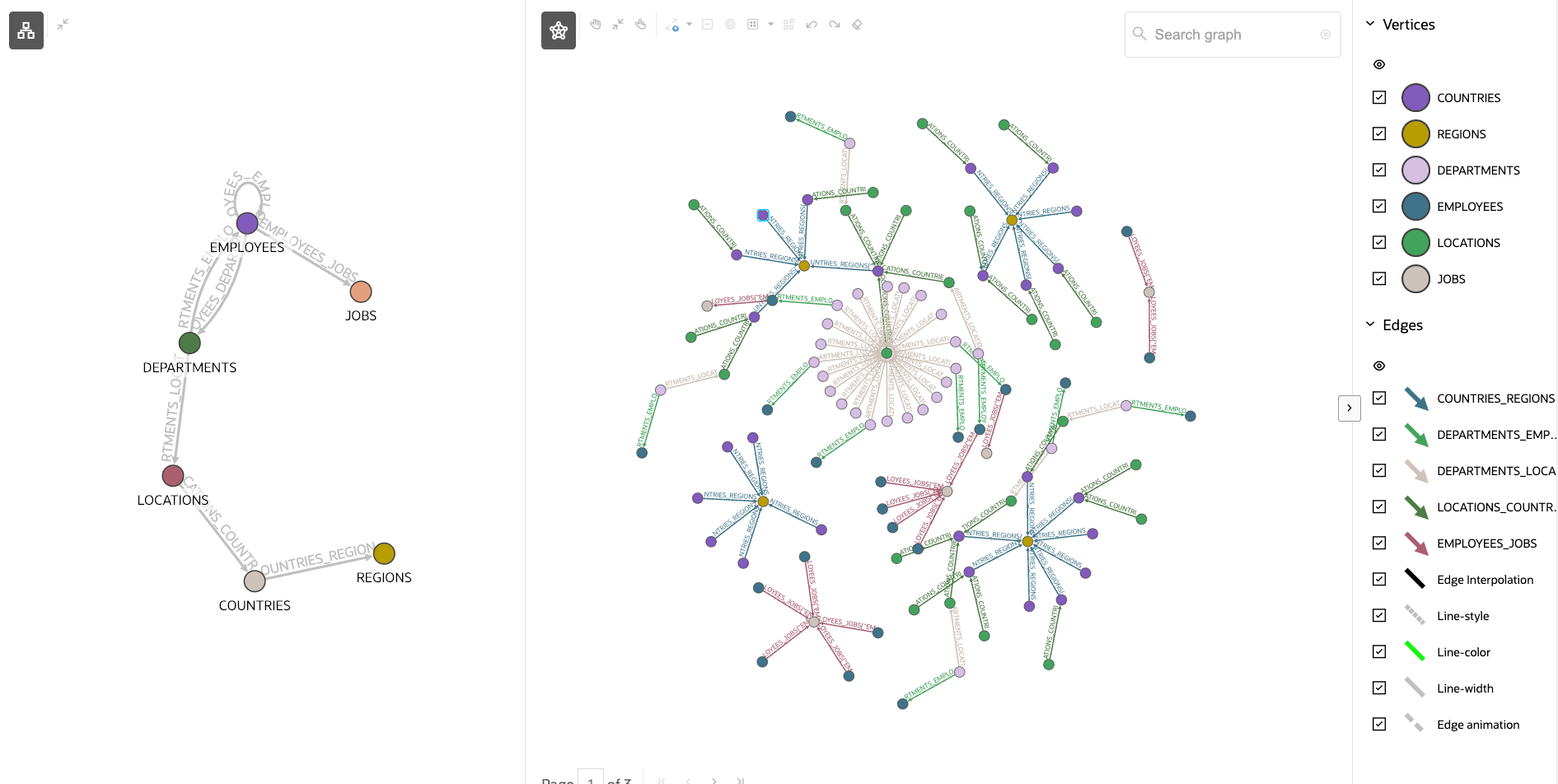
Once the schema view is enabled, it will appear along side the graph in the graph visualization panel as shown:
Figure 2-17 Visualizing Schema and Graph Views
- Schema View Modes
You can switch between Schema view, Graph view, or use both in the graph visualization panel using the toggle buttons in the toolbar. - Schema Validation
In addition to rendering the schema of a graph, the Graph Visualization library automatically validates the provided graphdataagainst theschemaif one is available. - Schema View Configuration Parameters
In order to enable Schema View in your visualization, you must configure a few related properties. - Validation Rules
The graphdatamust conform to theschemabased on the certain validation rules.
Parent topic: Interactive Graph Visualization Features
2.4.1 Schema View Modes
You can switch between Schema view, Graph view, or use both in the graph visualization panel using the toggle buttons in the toolbar.
Depending on which toggle button is active the corresponding view will be displayed. The following describes more about the supported modes:
- Schema: In this mode, the schema view is displayed spanning the entire visualization.
- Graph (default): In this mode, the graph is displayed spanning the entire visualization.
- Schema and Graph: In this mode, when both the toggle buttons are active, the schema and graph regions will appear side-by-side with a separator in between, as shown in Figure 2-17. The separator can be dragged to resize the regions.
It is important to note that depending on your data and settings configurations, either the Schema or Graph view will be always enabled in the toolbar. If both the toggle buttons are manually turned off, then it automatically defaults to Graph view.
Parent topic: Schema View
2.4.2 Schema Validation
In addition to rendering the schema of a graph, the Graph
Visualization library automatically validates the provided graph
data against the schema if one is
available.
If the graph data conforms to the
schema based on the defined validation rules (see
Validation Rules), then the Graph Visualization library initializes
without any problems. Also, in the absence of a schema, the
Schema view will not be displayed, and the
schema validations will not be executed.
If the schema validation fails, then the errors will be displayed in the following JSON format:
[{
errorType : string // Used by consuming application to summarize or detail the error
entityType: 'vertex' | 'edge' // Can be used to format the error message to specify the context
entityId?: string // Used to identify the entity in the message
entityDescriptor?: string[] // Used to represent name or labels of the entity in the message
property?: string // Name of the property that failed validation
expectedType?: string // Expected type of the property
actualType?: string // Actual type of the property
message?: string // Ready to use message if no further customization is needed at the consuming side
}]The consuming applications can then use the message property to
obtain the complete message for display on its interface. They can also
derive their own custom message, summarize errors, or categorize errors
using errorType and other properties provided in the error
message.
Parent topic: Schema View
2.4.3 Schema View Configuration Parameters
In order to enable Schema View in your visualization, you must configure a few related properties.
The following properties control the behavior of Schema View:
schema(optional): This provides the data that is shown in a Schema View. This property takes data in theGraphSchemaformat that is described in settings. Schema View will not be supported if this property is not confgured.schemaSettings(optional): This defines various settings (for example, styling) to control the rendering of Schema View. This property follows theSettingsformat that is described in settings.schemaSettings.baseStylesandschemaSettings.ruleBasedStylesallow custom styling of the Schema View. This is similar tosettings.baseStylesandsettings.ruleBasedStylesthat customize styling for the existing graph view.If styling is not specified through
schemaSettings, then the Graph Visualization library will use a default styling to render vertices and edges in Schema View. Also, certain features like pagination, legends, and so on will not apply to Schema View. Therefore, such attributes will not have any effect even if configured inSettings.- The
Settingsinterface supports the following additional properties to customize Schema and Graph views display in the graph visualization panel. See settings for more information on each of the following properties.viewMode(optional): This controls the Schema View and Graph View display. It can also be used to switch between views at runtime. Supported values areexpandedandcollapsed. Schema View mode will be determined byschemaSettings.viewModeand Graph View mode will be determined bysettings.viewMode.viewLabel(optional): This specifies a label that is displayed in Schema View or Graph View. If configured, the value will appear as a label on the top center of the corresponding view. It will also be used in the tooltip for the Schema View and Graph View toggle buttons.legendState(optional): This specifies whether the legend region in the Graph View is in expanded or collapsed state. Supported values areexpandedandcollapsed. This property will not have any effect when specified inschemaSettingsfor Schema View as there is no legend region for this view.
The following shows an example
schemaSettingsfor Schema View.{"viewMode": "expanded", "viewLabel": "Schema View", "baseStyles": { "vertex": { "label": "${properties.labelName}", "color": "blue" }}}The following shows an example
settingsfor Graph View.{"viewMode": "collapsed", "viewLabel": "Graph View", "legendState": "collapsed", "baseStyles": { "vertex": { "label": "${properties.labelName}", "color": "red"}}}
Parent topic: Schema View
2.4.4 Validation Rules
The graph data must conform to the
schema based on the certain validation rules.
The graph data is validated against the schema
by verifying the following rules:
- MANDATORY_PROPS_IN_SCHEMA_MISSING_IN_GRAPH: This rule verifies
that all the properties that are marked as mandatory in the
schemahave values in the graphdata.The following shows a sample error if this validation fails:
{ errorType: "MANDATORY_PROPS_IN_SCHEMA_MISSING_IN_GRAPH", entityType: "vertex", entityId: "0", entityDescriptor: ["Hermione"], property: "id", message: "Vertex 'Hermione' with id '0' doesn't have a property 'id' while it is marked as mandatory in the schema" } - ENTITY_IN_SCHEMA_MISSING_IN_GRAPH: This rule verifies that when
entities (vertices or edges) are defined in the
schema, the provided graphdataalso has those entities in it.The following shows a sample error if this validation fails:
{ errorType: "ENTITY_IN_SCHEMA_MISSING_IN_GRAPH", entityType: "edge", message: "The graph's data doesn't have Edges in it, but is specified in the schema" } - ITEMS_IN_GRAPH_NOT_DEFINED_IN_SCHEMA: This rule verifies that
entities (vertices or edges, labels, or properties) that are present
in the graph, have definitions in the
schema.The following shows a sample error if this validation fails due to edges being present in the graph
datawithout having edges defined in the schema:``` { errorType: "ITEMS_IN_GRAPH_NOT_DEFINED_IN_SCHEMA", entityType: "edge", message: "Edge that is present in the graph is not defined in the schema." } ```The following shows a sample error if this validation fails due to a label being present in the graph
datawithout having that label defined in the schema:``` { errorType: "ITEMS_IN_GRAPH_NOT_DEFINED_IN_SCHEMA", entityType: "vertex", entityDescriptor: ["misc"], message: "Vertex with label 'misc' that is present in the graph is not defined in the schema." } ```The following shows a sample error if this validation fails due to a property being present in the graph
datawithout having that property defined in the schema:``` { errorType: "ITEMS_IN_GRAPH_NOT_DEFINED_IN_SCHEMA", entityType: "vertex", entityId: "0", entityDescriptor: ["Tom Jones"], property: "date", message: "Property 'date' of vertex 'Tom Jones' with id '0' that is present in the graph is not defined in the schema." } ``` - TYPE_MISMATCH_BETWEEN_SCHEMA_AND_GRAPH: This rule verifies that
the data type of properties in the graph
dataconforms with its definition in theschema.The following shows a sample error if this validation fails:
{ errorType: "TYPE_MISMATCH_BETWEEN_SCHEMA_AND_GRAPH", entityType: "vertex", entityDescriptor: ["Mary"], property: "id", expectedType: "string", actualType: "number", message: "Vertex 'Mary' has an attribute 'id' of type 'number' while it is specified to be of type 'string' in the schema" } - MISMATCH_BETWEEN_LABELS_IN_SCHEMA: This rule verifies that all
properties defined in the
schemaacross multiple labels do not contradict, when those labels are used in a vertex or edge of the graphdata.The following shows a sample error if this validation fails:
{ errorType: "MISMATCH_BETWEEN_LABELS_IN_SCHEMA", entityType: "edge", entityId: "0", entityDescriptor: ["default", "Label 1", "Label 2", "Label 3"], property: "id", message: "Edge 'default' with id '0' has mismatch in the schema definition of 'id' property among its labels 'Label 1', 'Label 2', and 'Label 3'" }
Parent topic: Schema View