Create AI Profile
Autonomous AI Database uses AI profiles to facilitate and configure access to an LLM and to setup for generating, running, and explaining SQL based on natural language prompts using Data Studio.
- Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Settings: RAG Settings configure Retrieval-Augmented Generation pipelines in Oracle Autonomous Database Serverless, enabling AI profiles to load and query unstructured data from knowledge bases alongside structured tables. These settings define how documents are processed into vectors for semantic search, improving
SELECT AIaccuracy for natural language queries.Note:
You cannot access RAG features like creating and using Vector Indexes in Oracle AI Database 19c. These features are supported in Oracle AI Database 26ai. - Vector Index: Vector indexes must be specified to store embeddings generated from RAG pipelines or table data, allowing efficient similarity searches during AI inference. In AI profile creation via
DBMS_CLOUD_AI.CREATE_PROFILE, the Vector Indexes link the profile to Oracle's vector search capabilities, ensuring the AI model retrieves relevant context from vectorized data. You can create Vector Indexes from Data Studio Settings. - Table Metadata:
Table metadata, provided as an
object_listin the profile's attributes (e.g., [{"owner": "SH", "name": "customers"}]), scopes the AI's access to specific database tables and enforces security policies. This prevents the AI from querying unintended data, aligns with IAM controls, and optimizes natural language to SQL generation for defined schemas.
For more details, see Select AI with Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG).
- RAG Mode: It utilizes Vector Index for semantic search over unstructured data.
- Natural Language to SQL (NL2SQL) Mode: It does not require Vector Index to enable table-focused options like object list mode.
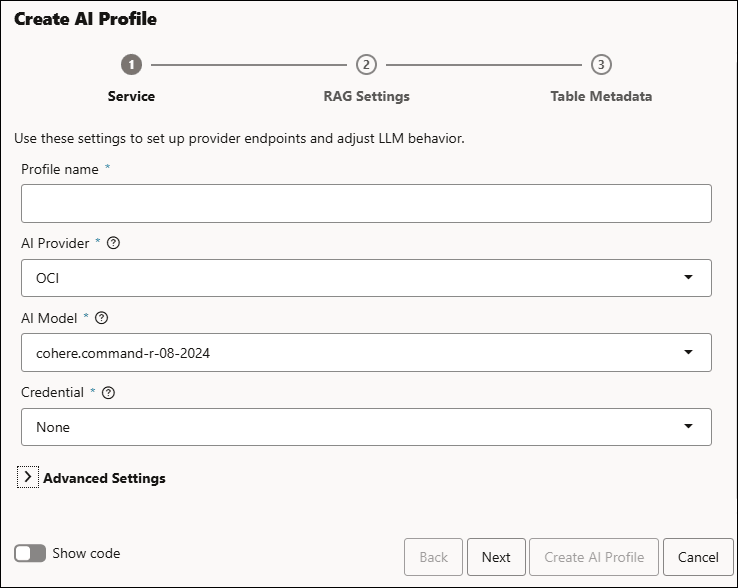
- On the Service tab of the Create AI Profile wizard, specify the following field values:
- Profile Name: Enter the name of the AI profile. For example, OCI AI.
- AI Provider: Select any of the following providers from the drop-down field:
- OCI
- Open AI
- Azure OpenAI Service
- Cohere
- Anthropic
- Hugging Face
-
AI Model: Select the available AI models from the drop-down that your AI profile will point to so that the database answers natural language questions over your data and generate or explain SQL, including retrieval‑augmented results using embeddings and vector indexes.
- Credential: These are the stored credentials that the database uses to securely connect to the external AI provider your profile is configured to use.
Under Advanced Settings, you will view Generation Settings and Service Settings:- Generation Settings: Generation Settings help you configure the behavior and limits of the AI model accessed through the profile in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure's AI services, allowing customization for different use cases like chat, SQL generation, or natural language queries from Autonomous Database.
- Service Settings: Service Settings refer to the configuration fields that dynamically appear based on the selected AI Provider, allowing users to input provider-specific credentials and parameters like endpoints, regions, or deployment names.
Note:
For AI Providers such as OpenAI, Cohere, Google, Anthropic, or Hugging Face, the Service Settings section is not displayed.
The Service Settings field values varies based on the AI Provider you select.
When you select OCI from AI Provider, you will view the following fields:- OCI API Format: This specifies what request and response schema the Generative AI endpoint expects, for example COHERE, Generic, or an OCI-native format for Oracle models.
- OCI Region: This is the OCI region identifier where the endpoint is running. It ensures calls from your database are routed to the correct regional AI models. Each Autonomous AI Database OCI region supports different LLMs—some regions like
us-chicago-1,uk-london-1, andap-osaka-1offer many, while others have fewer. We only show models available in your selected region. If the OCI AI model does not appear, you can switch regions to refresh the model list. For more information, refer to Regions with Generative AI and Pretrained Foundational Models in Generative AI. - OCI Compartment ID: This is the OCID of the OCI compartment that owns the endpoints you want to use. It scopes access and billing to the correct logical container in your tenancy, aligning with your IAM policies.
- OCI Endpoint ID: This is the OCID of a specific AI endpoint on a dedicated AI cluster, for example ocid1.generativeaiendpoint.oc1.us-chicago-1, Specifying this field tells Select AI to use that dedicated endpoint instead of a shared on‑demand model.
When you select Azure OpenAI Service from the AI Provider field, you will view the following fields:-
Azure Resource Name: Specify the unique name of your Azure OpenAI Service resource instance, which forms part of the endpoint URL (e.g., https://your-resource-name.openai.azure.com/) for accessing the service.
-
Azure Deployment Name: Specify the custom name you assign when deploying a specific language model within that Azure OpenAI resource.
-
Azure Embedding Deployment Name: Specify the custom name of a separate deployment for an embedding model (such as text-embedding-ada-002 or text-embedding-3-large) within the same resource, used exclusively for creating vector representations of text.
See Azure OpenAI Embedding skill - Azure AI Search | Microsoft Learn for more information on the above fields.
Under Generation Settings, you can view the fields:-
Stop Tokens: These are token sequences that instruct the AI model where to stop generating further text output. When the model generates any of these tokens, it stops. This helps in controlling the response length and preventing unwanted trailing text.
-
Max Tokens: This defines the maximum number of tokens the AI model can generate in response to a prompt. It limits the length of the generated output to avoid overly long or expensive responses.
-
Case Sensitive Values: This setting indicates whether the input values or parameters should be treated as case sensitive by the AI processing. If true, exact casing must be matched for input or parameter values.
-
Conversation: This typically indicates whether the AI profile supports conversational context, allowing the model to retain context over multiple interactions or prompt exchanges—useful for chat-style AI applications.
-
Temperature: This is a slider parameter controlling randomness in the AI's responses. A lower temperature (e.g., 0.2) makes output more focused and deterministic, while a higher temperature (e.g., 0.8) yields more creative and diverse text generation.
Click Next to proceed to the RAG Settings tab of Create AI Profile.
- RAG Settings:
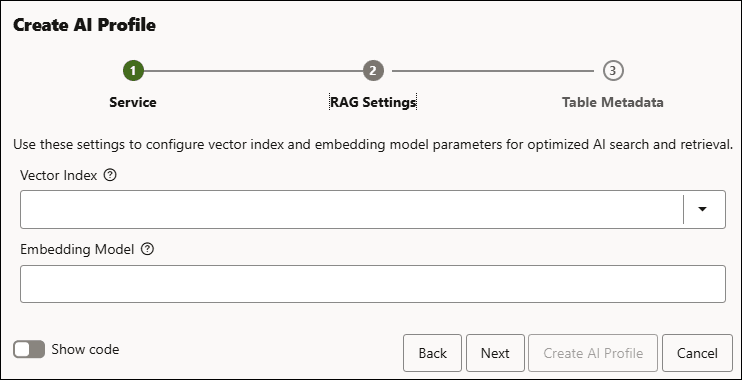
You can view the following optional fields in RAG Settings.:
- Vector Index: Select the Vector Index you create from the list of available vector indexes. It specifies which Oracle Database vector index to use for storing and searching the embeddings of your documents, so the AI profile can quickly find the most relevant content during Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
See Create Vector Index for more information.
Your AI Profile requires a Vector Index to function.
-
Embedding Model: It specifies which embedding model is used to convert your text into vector representations that are stored in that index, ensuring the semantic search behavior matches the model you configure for RAG.
The above fields are optional. You can skip them and click Create AI Profile to create AI Profile. You can alternatively proceed to the Table Metadata tab.
- Vector Index: Select the Vector Index you create from the list of available vector indexes. It specifies which Oracle Database vector index to use for storing and searching the embeddings of your documents, so the AI profile can quickly find the most relevant content during Retrieval-Augmented Generation.
-
Under Table Metadata tab, you can view the following optional fields:
Note:
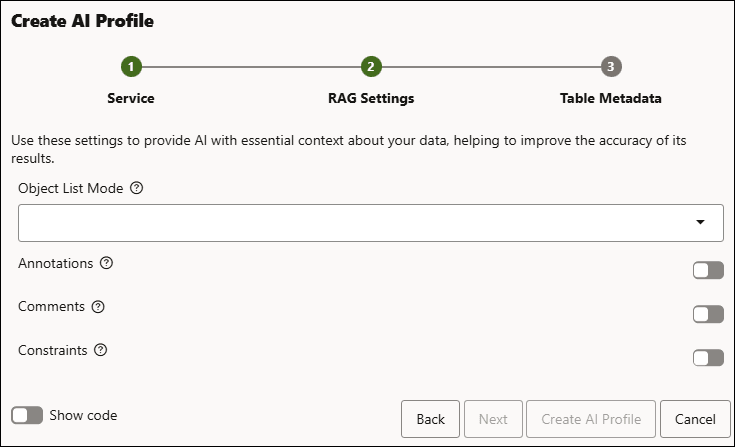
If you skipped selecting a Vector Index in the previous step, you will view a setting called Object List Mode.
-
Object List Mode: You can select any of the available field options:
-
All: This option sends metadata for all tables in the specified schemas to the LLM, so it can generate SQL against any of them.
-
Automated: This option lets Select AI automatically choose a subset of relevant tables by running vector search on schema metadata, so only the most likely tables for a given prompt are used.
-
Selected Tables: This option limits metadata to only the specific tables you list in the AI profile, so SQL generation is restricted to those tables.
You can also view Object List where you can select list of objects LLM can use.
Selecting Object List will also show another additional setting Enforce Object List switch.
- None: This option does not send any table metadata from an object list, so the AI either cannot generate SQL over tables or rely on other configuration that does not use an explicit object list.
Note:
You cannot view the Object List Mode field with Oracle AI Database 19c. -
-
Annotations: Use this toggle to enable Annotations that indicates whether the AI can use extra descriptive metadata attached to objects (like column descriptions or tags) as additional context when generating results.
- Comments: Use this toggle to controls if table and column comments from the data dictionary are exposed to the AI as context, which can help it better understand the meaning of your data.
- Constraints: Use this toggle to controls whether information about primary keys, foreign keys, and other constraints is provided to the AI, helping it reason about relationships between tables and improve query accuracy.
Click Create AI Profile.
-
You have successfully created and configured your AI profile in the Data Studio Settings wizard.
Parent topic: Data Studio Settings