About Components and Terminology
Learn about the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure components and terminology related to your setup and configuration of Oracle Essbase.
Essbase Topology within OCI
This diagram displays an example of a default, full topology of Essbase created using an Oracle Cloud Infrastructure via Marketplace deployment with Oracle Identity Cloud Service integration. Sample CIDRs are used in the diagram for illustrative purposes.
Note:
As an additional resource, see an Interactive Architecture Diagram (IAD) version of the diagram below, at Oracle Essbase 21c Technical Architecture. The diagram contains clickable links to display additional, related documentation content.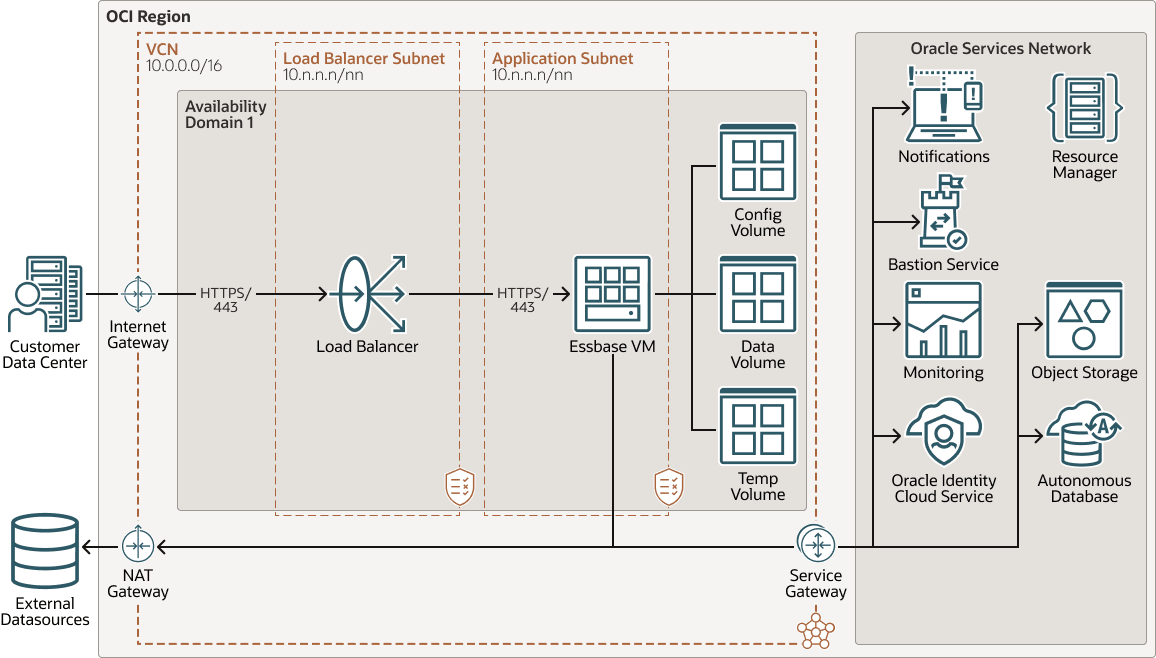
Essbase Topology Components
- Virtual Cloud Network and Subnet Components in OCI Region
-
Virtual Cloud Network and Subnets: Essbase scripts assign compute instances and load balancers to specific subnets in a virtual cloud network (VCN). A VCN in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure covers a single, contiguous Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) block of your choice. A subnet is a subdivision of a VCN that consists of a contiguous range of IP addresses that don't overlap with other subnets in the VCN. A VCN includes one or more subnets, route tables, security lists, gateways, and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) options. See Networking Components Overview
Essbase scripts can automatically create a VCN and subnets for the new stack deployment, or you can create your own. By default, subnets are public. Any compute instances assigned to a private subnet can't be directly accessed from outside of Oracle Cloud.
-
Load Balancer Subnet: Load balancer is an optional component that provides an extra layer of security, allowing the Essbase compute node to be isolated on a private subnet. Load balancer is recommended for supporting SSL, and provides an easier interface to manage the outbound SSL certificate and host name settings. Load balancer routes all requests from clients to a single Essbase instance. See Overview of Load Balancing in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
-
-
Gateways in OCI Region: These are among the optional virtual routers you can add to your VCN.
-
NAT Gateway: NAT Gateway along with associated subnets and partitions, provides cloud resources without public IP addresses access to the internet without exposing those resources to incoming internet connections. If you set up a NAT gateway, when using public and private subnets, the NAT gateway needs to be added to ingress rules in load balancer security rules for partitions to work.
-
Service Gateway: This gateway provides a path for private network traffic between your VCN and supported services in the Oracle Services Network
-
Internet Gateway: This gateway provides direct internet access
-
- Oracle Services Network Components in OCI Region
-
Notifications Service: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Notifications service broadcasts messages to distributed components for applications hosted on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure and externally. See Notifications Overview in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
-
Bastion Service: (optional) An OCI Bastion service instance is needed when an Essbase node is created on a private network, without a public IP. Previously, in 19.3.0.4.5, a Bastion host and compute node was created in the Essbase stack. Now, OCI Bastion service is employed. You may access a stack with private IP by making use of OCI Bastion service. Additionally, you must enable Oracle Cloud Agent (OCA) Bastion plugin on the compute node that you want to access. In order to do that, open the Essbase compute instance in OCI console, go to Oracle Cloud Agent tab and enable the Bastion toggle switch. You then need to create the Bastion provided under Identity & Security. For more information on OCA plugin, see Manage Plugins with Oracle Cloud Agent.
Bastion provides administrative access to a domain on a private subnet. Oracle recommends Bastion as a way to control external access (for example, SSH) to VCN hosts. Usually, a Bastion in a VCN public subnet controls access to VCN private subnet hosts. You can put the load balancer and Essbase on existing private subnets.
-
Monitoring Service: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Monitoring service enables you to actively and passively monitor your cloud resources using the Metrics and Alarms features. See Monitoring Overview in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
-
Oracle Identity Cloud Service: Oracle Identity Cloud Service provides identity management, single sign-on (SSO), and identity governance for applications on premise, in the cloud, or on mobile devices. Employees and business partners can access applications at any time, from anywhere, and on any device in a secure manner. See About Oracle Identity Cloud Service in Administering Oracle Identity Cloud Service documentation.
-
Resource Manager: Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resource Manager provisions resources on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure for Essbase setup and configuration. See Overview of Resource Manager in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
-
Additional Terminology Used with Essbase Deployment
-
Marketplace: Essbase is deployed in Oracle Cloud Marketplace, an online store available in the Oracle Cloud Infrastructure console. When you select Essbase from Marketplace, it prompts you for some basic information, directs you to Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resource Manager to provision resources on Oracle Cloud Infrastructure, and then configures Essbase. See Overview of Marketplace in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
-
Stack: A stack is a collection of related cloud resources provisioned by Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Resource Manager. The stack includes an Oracle Autonomous Database instance, a compute instance, block storage volumes, object storage bucket, load balancer, and additional network components. It can include but isn't limited to the following Oracle Cloud Infrastructure components:
- Compute instance, running the administration server and the managed server. The compute shape is the resources allocated to a compute instance. See Compute Shapes and Supported Compute Shapes.
- Virtual cloud network (VCN), described above, which you can provide, or specify in Resource Manager to provision one for you.
- Load balancer, described above.
- Bastion, described above. You can use the Bastion service to gain administrative access to a domain on a private subnet.
- Database for Essbase metadata. You have the following options for deploying the Essbase stack:
- Oracle Autonomous Database using either the Autonomous Transaction Processing or Data Warehouse workload types. See Overview of Autonomous Database in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation.
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Database System. You must deploy Oracle Cloud Infrastructure before starting the Essbase listing. You can deploy a Virtual Machine database system. See Overview for Database System documentation.
-
Vault:
Note:
Prior to 19.3.0.3.4, this was referred to as Key Management, and metadata names were listed as KMS.Oracle Cloud Infrastructure Vault enables you to manage sensitive information when creating a server domain. A vault is a container for encryption keys or secrets. Previously, in 19.3.0.4.5, you may have encrypted required passwords for a new domain using a key, and then Resource Manager used the same key to decrypt the passwords when creating the domain. We use secrets, created with the Vault UI. In your vault, you enter the password, and the latest version of it is stored as part of your key, in the vault. You refer to it using the OCID of the secret. See Overview of Vault in Oracle Cloud Infrastructure documentation, and see Create a Vault and Secrets, and Encrypt Values.
-
Node Manager: This Java utility runs as a separate process from Oracle WebLogic Server and allows you to perform common operations for a Managed Server, regardless of its location with respect to its Administration Server.
-
Administration Server: This server operates as the central control entity for the configuration of the entire domain. It maintains the domain's configuration documents and distributes changes in the configuration documents to Managed Servers. The Administration Server serves as a central location from which to monitor all resources in a domain. Each domain must have one server instance that acts as the Administration Server.
-
Managed Server: This includes host business applications, application components, Web services, and their associated resources.