Understand the Cube.TypedMeasures Worksheet
In application workbooks, the Cube.TypedMeasures worksheet defines date measures and text lists, which extend the analytical capabilities of Essbase beyond numerical data to text-based content.
- Date measures are tagged as “date” in the Accounts dimension. Date measures enable cell values in the form of a formatted date. The ability to process dates in the measures dimension can be useful for types of analysis that are difficult to represent using the Time dimension.
- Text lists are used to work with text measures, which are tagged as
“text” in the Accounts dimension. They enable cell values to contain one of an
enumerated list of text labels. These labels are defined, at the outline level,
using a mapping artifact called a text list.
Storage and analysis of textual content can be useful when a cell needs to have one of a finite list of textual values; for example, a product may be sold in 5 different colors. The color is a text measure whose value must be one of the 5 colors. The colors are a set of text strings mapped to corresponding numeric IDs.
Date measures and text list mappings are contained in tables in the Cube.TypedMeasures worksheet.
The following image shows the Cube.TypedMeasures worksheet in a sample application workbook.
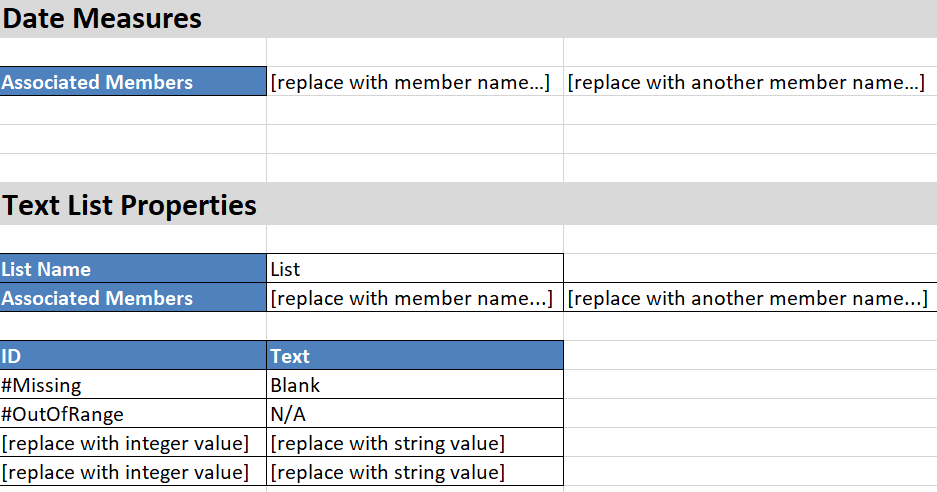
Date Measures table fields and values:
| Property or Field | Valid Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Associated Members | Members from the dimension tagged as “Accounts.” | The Associated Members row contains member names from the Accounts dimension. |
Text List Properties table fields and values:
| Property or Field | Valid Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| List Name |
Must not exceed 80 characters. |
A text list must start with a list name followed by its value in the adjacent cell. |
| Associated Members |
Existing member names. |
Member names added in adjacent cells. Multiple members can be added in adjacent cells to the right. |
| ID |
The first two values under ID are #Missing and #OutOfRange. These two values must exist in every text list table. The other IDs must be integers. |
Each ID, including the #Missing, #OUTOFRANGE and numeric values, must map to a text value. The first two IDs, #Missing and #OUTOFRANGE, are for handling cases where the textual data is invalid or empty. For example, if you try to load an unmapped value such as “Average” to a text measure, the cell value would not be updated, and would display as #Missing in a subsequent query. If you load a numeric cell value that is unmapped, the subsequent query would return N/A. |
| Text |
Up to 80 characters. |
The text column contains the text values for each text measure. Each text value must map to an integer in the ID column. Any text value that does not map to an integer in the text list is considered by Essbase to be invalid. |
See: