Full Backups to a Third-Party Deduplicating Appliance
As an alternative to RMAN incremental backups and tape drives, some customers use third-party deduplicating appliances to process backup streams. Figure 1-3 depicts three databases writing to a centralized third-party appliance.
Figure 1-3 Third-Party Deduplicating Appliance
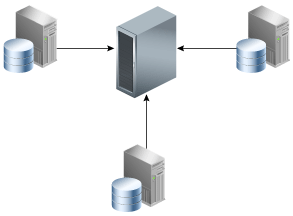
Description of "Figure 1-3 Third-Party Deduplicating Appliance"
This technique has the following advantages:
-
A central backup location serves all databases in the environment.
-
The third-party software searches for patterns at the byte and sub-byte level to eliminate redundant data from backup to backup. For example, if a full database backup is almost identical to the backup taken a week before, then the software can attempt to prune the redundant bits from the incoming backup stream.
-
To reduce network load, one optional technique utilizes source-side deduplication so that backup streams are deduplicated on the database host instead of the third-party appliance. Typically, this technique relies on an RMAN SBT plug-in.
Some disadvantages are as follows:
-
These third-party appliances do not recognize or validate Oracle Database blocks. From the perspective of the appliance, a database backup is the same as a file system backup: a stream of bytes.
-
Deduplication is only effective for full database backups that have a high degree of redundancy. Strategies that use incremental backups often do not achieve good deduplication ratios.
-
The third-party appliance dictates which Oracle Database features to use rather than the other way around. Often, adapting to the requirements of the appliance means rewriting existing backup scripts.