4 Post-Discovery Configuration and Verification
-
Verify SNMP Subscription of the Oracle Management Agent to Exadata Storage Server
-
Configure the Compute Node ILOM SNMP for Enterprise Manager Monitoring
-
Accessing Oracle Support Workbench for Exadata Storage Server
Note:
You must remove the SNMP notification on the cell, InfiniBand switch, ILOM, Cisco switch, and PDU manually if you remove these targets from Enterprise Manager.
Starting with Exadata plug-in Release 12.1.0.3.0, when the Exadata Database Machine target is deleted through Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, there is an option to remove the SNMP notification from the cells and InfiniBand switches.
Verify SNMP Subscription of the Oracle Management Agent to Exadata Storage Server
Exadata Storage Server SNMP configuration is performed using the cellcli command and can be run in batch using dcli from a compute node.
Note:
-
During the discovery process, you can optionally provide the necessary
rootcredentials to subscribe for SNMP traps from Exadata Storage Servers. If you have done so, then you can skip the remaining steps of this section and proceed with Configure and Verify SNMP for InfiniBand Switch Targets. -
While the
publicstring is used for the SNMP examples in the following sections, it is supported to use any valid SNMP community string. -
Use SNMP V3 subscriptions for IPv6-based Exadata Storage Server targets because of limitations in the SNMP V1 protocol.
Using the ALTER CELL Command
While using the ALTER CELL command, all existing subscribers should be specified along with the new subscriber being added. Similarly, you can also modify the notificationPolicy or notificationMethod attributes.
While using the ALTER CELL command, the host= and community= attribute values should be quoted, and type= is NOT quoted.
If you are using the DCLI utility to set up SNMP alerting, then any command containing punctuation, which will be interpreted by the local shell, must be enclosed with double quotation marks. If the command includes the following characters, then outer quotation marks and escape characters are required:
- $ (dollar sign)
- ' (quotation mark)
- < (less than)
- > (greater than)
- ( ) (parentheses)
The backslash (\) is the escape character that allows the characters to be passed to the CellCLI utility without being interpreted by the remote shell.
Check Current SNMP Configuration
Check the current SNMP configuration using the following cellcli commands:
Verify SSH Connectivity
Open a new terminal and verify whether the SSH connectivity was successfully established:
$ ssh -l cellmonitor <cell_ipaddress> cellcli -e 'list cell detail'
-
If you are not prompted for any password, then you can assume that the connectivity is established.
-
If you are asked to confirm whether you want to continue connecting, specify Yes.
Remove a Subscription
To remove the subscription, use the ALTER CELL command again by excluding the host name that you want to remove from the snmpsubscriber list.
Note:
The SNMP receivelet listens on a single address and port for all monitored targets. The port is the UDP port with the same number as the TCP port used in the EMD_URL.
By default, the SNMP receivelet listens on all addresses; if the property SnmpRecvletListenNIC is set in the emd.properties file, the receivelet will attempt to resolve the value as either a name or IP address, and listen on only that address.
This parameter is independent of AgentListenOnAllNICs and EMD_URL because in some installations, the Agent may need to communicate with the OMS and with managed targets on different networks.
Configure and Verify SNMP for InfiniBand Switch Targets
The SNMP configuration for Enterprise Manager monitoring of InfiniBand Switches is done automatically as part of the Enterprise Manager guided discovery process. It is good practice, however, to verify that SNMP configuration has been successful.
Note:
-
During the discovery process, you can optionally provide the necessary
rootcredentials to set up SNMP trap for the InfiniBand Switch. If you have done so, then you can skip the remaining steps of this section and proceed with Configure the Compute Node ILOM SNMP for Enterprise Manager Monitoring. -
ilom-adminis the preferred user when discovering an InfiniBand Switch target for full monitoring. If the switch is discovered using root orilom-adminuser, the community string provided during discovery is added to the switch, if it doesnt exist already. -
During SNMP V3 discovery, the V3 user added by the (discovery) user during discovery is added to the switch if the discovery is perfomred using root or the
ilom-adminuser.
To configure (if necessary) and verify the SNMP configuration for an InfiniBand Switch:
Configure the Compute Node ILOM SNMP for Enterprise Manager Monitoring
Note:
These instructions apply only for the Exadata Database Machine and are not applicable to the Oracle SuperCluster.
The compute node ILOM targets are responsible for displaying a number of disk failure alerts for their respective compute node that are received as SNMP traps. For Enterprise Manager to receive those traps, the /opt/oracle.cellos/compmon/exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl script must be run to configure SNMP subscriptions for the agents (both primary and backup agents) that have been configured to monitor the compute node ILOM targets. This step is applicable to Exadata plug-in Release 12.1.0.2.0 and later.
Note:
- While configuring the SNMP traps for the ILOM telemetry source, if discovery is done using the root user, the entry is automatically added to the SNMP subscription table, provided there are free slots available. IF discovery is performed using a non-root user, the user will need to manually update this table from ILOM console.
- During SNMP V3 discovery, the SNMP V3 user added by the user during discovery is added to the ILOM, if the discovery is done using root user. For discovery using a non-root user, the administrator will need to manually create the SNMP V3 user in the ILOM console.
The exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl script is run as the root user with the -set_snmp_subscribers parameter to add SNMP subscribers. For example:
# /opt/oracle.cellos/compmon/exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl -set_snmp_subscribers "(host=hostname1.mycompany.com,port=3872,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444),(host=hostname2.mycompany.com,port=3872,community=public,type=asr,fromip=12.345.67.890)" Try to add ASR destination Host - hostname1.mycompany.com IP - 11.222.33.44 Port - 3872 Community - public From IP - 22.333.44.555 Try to add ASR destination Host - hostname2.com IP - 11.111.11.111 Port - 3872 Community - public From IP - 22.333.44.555
The script needs to be run on each compute node:
-
The
hostvalues should be the hostnames of the agents configured to monitor the compute node ILOM target associated with the compute node. -
The
fromipvalues should be the IP address of the compute node that the compute node ILOM target is associated with.
For example, if you have an X2-2 machine with compute node targets edbm01db01 through edbm01db08 and associated compute node ILOM targets edbm01db01-c through edbm01db08-c, then you would need to run the script once on each compute node - therefore, the script would be run eight times in total.
-
On compute node
edbm01db01, thehostandportvalues would be the hostnames and ports of the agents monitoring compute node ILOM targetedbm01db01-cand thefromipvalue would be the IP address of the compute node itself,edbm01db01. -
On compute node
edbm01db02, thehostandportvalues would be the hostnames and ports of the agents monitoring compute node ILOM targetedbm01db02-cand the 'fromip' value would be the IP address of the compute node itself, edbm01db02, ... and so on.
This is a good example of where Manual selection of Management Agents for targets is useful. If the first two compute nodes are always the Monitoring Agent and Backup Monitoring Agent, then it is easy to work out the values needed for -set_snmp_subscribers parameters, the host and port values would be the same for all compute nodes.
Note:
The exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl script, overwrites any existing SNMP subscriptions. While setting the SNMP subscribers, make sure that current subscribers are included in the new list of subscribers.
It is possible to use the exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl script to get the current set of subscribers using the -get_snmp_subscribers parameter.
For example:
# /opt/oracle.cellos/compmon/exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl -get_snmp_subscribers -type=asr
Suppose the current list is:
(host=hostname1.mycompany.com,port=162,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444), (host=hostname2.mycompany.com,port=162,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444)
Then new subscriptions can be added using the following command:
# /opt/oracle.cellos/compmon/exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl -set_snmp_subscribers "(host=asrhostname1.mycompany.com,port=162,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444), (host=asrhostname2.mycompany.com,port=162,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444), (host=hostname1.mycompany.com,port=3872,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444), (host=hostname2.mycompany.com,port=3872,community=public,type=asr,fromip=11.222.33.444)"
After adding the new subscribers, run the command exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl script with the -get_snmp_subscribers parameter to get the list of SNMP subscribers and verify the new SNMP subscriptions were added successfully. For example:
# /opt/oracle.cellos/compmon/exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl -get_snmp_subscribers -type=asr (host=asrhostname1.mycompany.com,port=162,community=public,type=asr,fromip=10.10.10.226), (host=asrhostname2.mycompany.com,port=162,community=public,type=asr,fromip=10.10.10.226), (host=hostname1.mycompany.com,port=3872,community=public,type=asr,fromip=10.10.10.226), (host=hostname2.mycompany.com,port=3872,community=public,type=asr,fromip=10.10.10.226)
Configure the Compute Node ILOM SNMP for Compute Nodes Running Management Server
For compute nodes running Management Server, the call to the exadata_mon_hw_asr.pl script is replaced with dbmCLI commands, which are similar to cellCLI commands on the Exadata Storage Servers.
Configure SNMP Values Using dbmcli
For Virtualized Exadata, these commands need to be executed in Dom0.
Configure SNMP for Oracle SuperCluster (If root is not used for discovery)
Note:
- This section is applicable only if ILOM target discovery is performed as a non-root user. If discovery is done using a root user, the entry is automatically added to the table, provided there are free slots available.
- During SNMP V3 discovery, the SNMP V3 user added by the user during discovery is added to the switch, if the discovery is performed as a root user. For discovery using a non-root user, the administrator has to manually create the SNMP V3 user in the ILOM console.
Set Up SNMP for Cisco Ethernet Switch Targets
The Cisco Ethernet Switch must be configured to allow the Agents that monitor it to be able to both poll the switch and to receive SNMP alerts from the switch. To allow this, perform the following steps (swapping the example switch name dm01sw-ip with the name of the Cisco Ethernet Switch target being configured):
Note:
This procedure is valid for SI targets if the monitoring of the switch is performed with a non-administrator user. If Enterprise Manager monitors the switch with an administrator user, the following procedure is automatically performed as part of the discovery process.
Verify the Cisco Ethernet Switch SNMP Configuration
Run the snmpwalk command line utility or equivalent tool to verify the Cisco Switch configuration.
Run the following commands to fetch and display the data from the Cisco switch:
$ snmpget –v 1 –c <community_string> <hostname_of_cisco_switch> 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.56.0 $ snmpget –v 2c –c <community_string> <hostname_of_cisco_switch> 1.3.6.1.4.1.9.2.1.56.0
Note:
If a timeout message is displayed as an output for the above command, then it means that the Cisco Switch is not yet configured correctly.
Set Up SNMP for Power Distribution Unit (PDU) Targets
To enable Enterprise Manager to collect metric data and raise events for the PDU target, you must configure the PDU to accept SNMP queries from the Agents that monitor the PDU target. Also, appropriate threshold values for different phase values needs to be set on the PDU.
This section assumes that this is a first time configuration of the PDU. SNMP must be enabled and the trap section completed. Granting SNMP access to a different monitoring Agent IP address is an example where only the "Trap Host Setup" section needs to be changed.
For details on configuring the PDU thresholds settings, see the "Configuring Oracle Exadata Database Machine" chapter in your Exadata Database Machine Owner's Guide. This guide is pre-loaded along with other Exadata user documentation onto your Oracle Exadata Database Machine.
Verify the PDU SNMP Configuration
Use the snmpwalk command line utility or equivalent tool to verify the PDU configuration.
Run the following command to fetch and display the data from PDU:
snmpget –v 1 –c <community_string> <hostname_of_pdu> 1.3.6.1.4.1.2769.1.2.3.1.1.1.0
Note:
If a timeout message is displayed as an output for the above command, then it means that the PDU is not yet configured correctly.
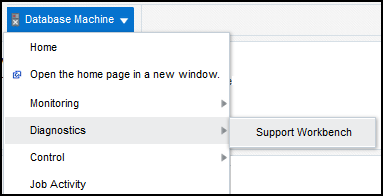
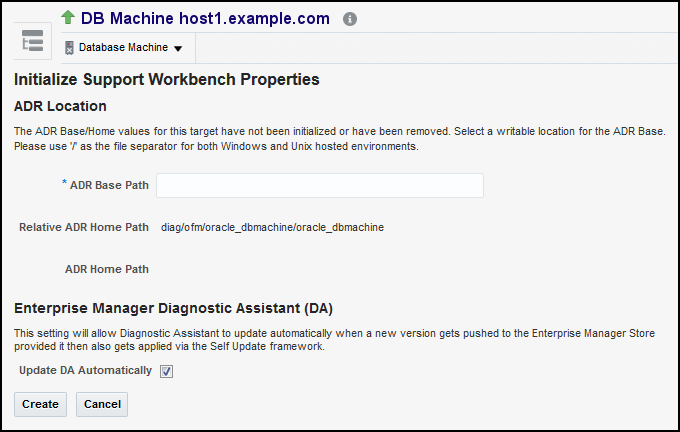
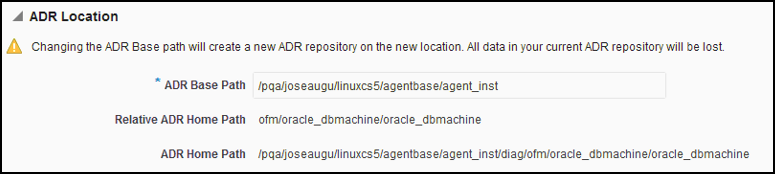
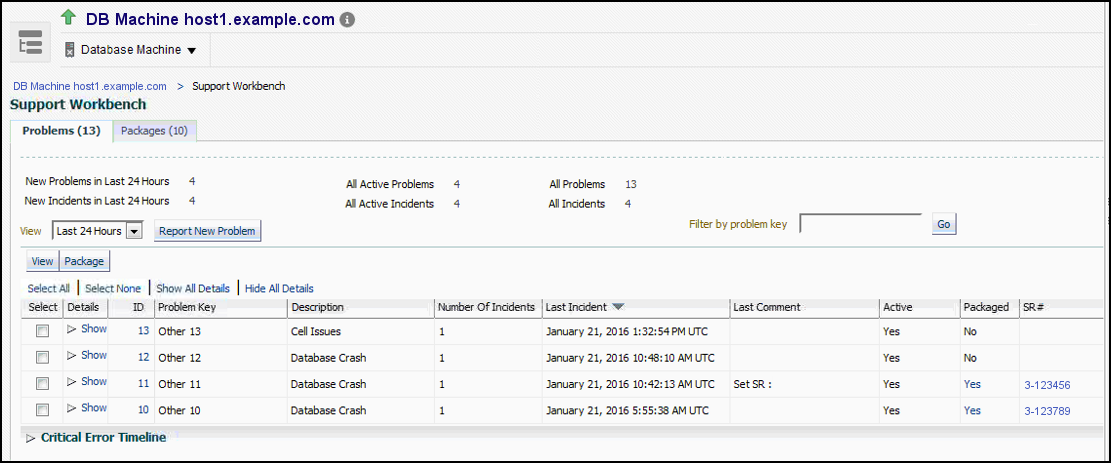
Accessing Oracle Support Workbench for Exadata Storage Server
You can access the Oracle Support Workbench for the current Exadata Storage Server to access diagnostic data for problems and incidents related to the cell.
To access the Support Workbench for a single Exadata Storage Server, follow these steps:
Oracle Exadata Database Machine Dashboard Creation
You can create a Database Machine dashboard to monitor the performance and usage metrics of the Database Machine system, its sub-components, as well as all the database system components residing on the Database Machine.
How to Make the Report "Public"
The generated report is accessible only by the Enterprise Manager user who creates it. To make the report public:
- Select the dashboard report from the list of reports shown after following the steps mentioned above.
- Click Edit.
- Select the Run report using target privileges of the report owner option under Privileges section in General tab.
- Click the Access tab.
- Select the Allow viewing without logging in to Enterprise Manager option.
- Click OK.