16 Discovering, Promoting, and Adding System Infrastructure Targets
Discovering and Promoting Oracle MiniCluster
Prerequisites
Enterprise Manager Agents have to be installed on Oracle Solaris global zones of both MiniCluster compute nodes. You can install EM Agents into Oracle Solaris Global and Non-Global Zones using Add Host Targets wizard.
Credentials Required for Oracle MiniCluster Discovery
The following are the credentials required for the discovery of Oracle MiniCluster.
| Target Type | Credentials | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Systems Infrastructure Server |
ILOM Monitoring Credentials, SNMP Credentials |
Required to monitor MiniCluster compute nodes through their ILOMs |
Oracle MiniCluster Discovery
To discover the Oracle MiniCluster system, perform the following steps:
Prerequisites
Note:
To enable monitoring of Oracle VM for SPARC the non-privileged user used to install and run the Enterprise Manager agent must be granted the solaris.ldoms.read and solaris.ldoms.ldmpower authorizations and be assigned the LDoms Power Mgmt Observability rights profile.
For example:
/usr/sbin/usermod -A solaris.ldoms.read,solaris.ldoms.ldmpower oracle
/usr/sbin/usermod -P 'LDoms Power Mgmt Observability' oracle
Configuring Snmp traps for Supercluster and Minicluster monitored hosts
-
Find the EM agent numeric IP address and port number.
Login to the host where the EM agent is deployed. From the agent directory
<AGENT_HOME>/binrun the following command to obtain the port number of the agent:$ emctl status agent | grep 'Agent URL' Agent URL: https://hostname.domain:3863/emd/main/The port number can be seen after the fully qualified domain name of the agent, it is 3863 in the example above.
To get the numeric IP address, use ping or
nslookupcommand. -
Configure the snmpd.
Add the
trap2sinkentry information into thesnmpd.confconfiguration file.The configuration file
snmpd.confis in different location for Solaris 10 and Solaris 11.For Solaris 11 the location isvi /etc/net-snmp/snmp/snmpd.confFor Solaris 10 the location isvi /etc/snmp/snmpd.confAdd the following line:
where,trap2sink <numericip> public <transport>-
The <transport> is the port number obtained in step (1). It is the port number of the EM agent.
-
The <numericip> is the IP address of the EM agent host, obtained in step (1).
trap2sink 10.133.249.68 public 3863 -
-
Restart the SNMP services.
For Solaris11:svcadm restart net-snmp svcadm restart snmp-notifyFor Solaris10:svcadm restart smaIf the SNMP service was not enabled before, ensure that the services are enabled.
For Solaris11:svcadm enable net-snmp svcadm enable snmp-notifyFor Solaris10:svcadm enable sma -
Optionally, verify the snmpd configuration by making sure the status for Telemetry Status is ON in the host target, in the Telemetry Alert Config metric.
After the configuration of the snmp through steps (1) – (3), navigate to Host home page and perform the following steps:-
Select Host and click Configuration.
-
Click Last collected.
-
Select Telemetry Alert Config metric.
-
Click Refresh, wait for few minutes until the metrics get refreshed.
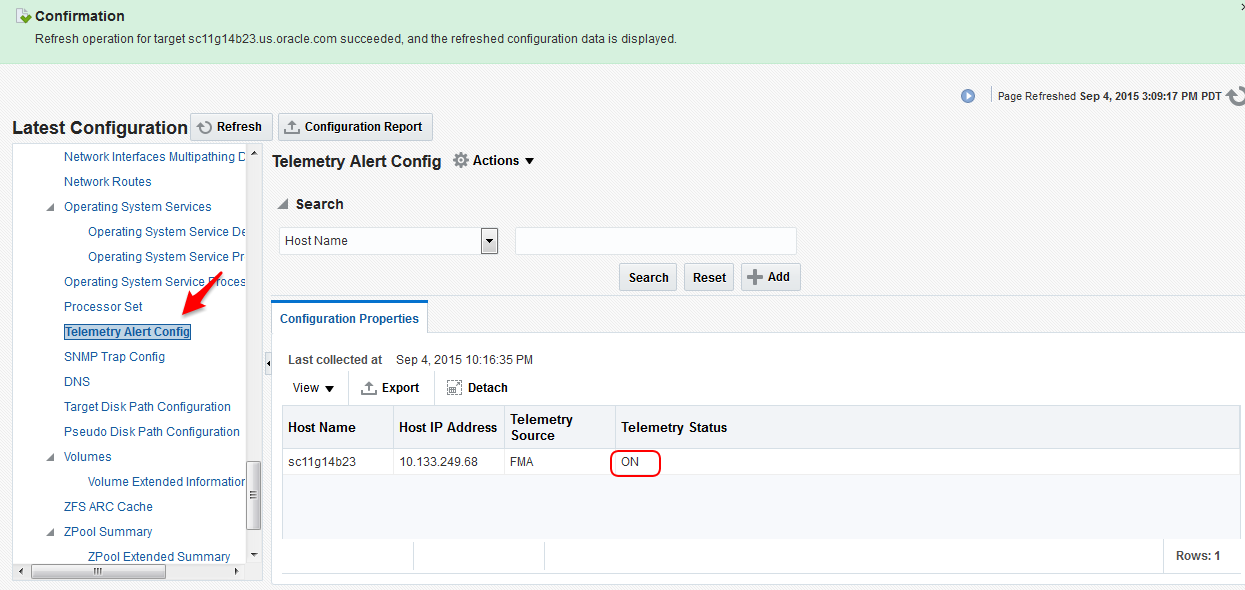
If the Telemetry Status is ON in Telemetry Alert Config metric, it indicates the the configuration of FMA SNMP traps is done correctly.
-