2 Features
Note:
The performance and capacity of the UDR system may vary based on the call model, feature or interface configuration, and underlying CNE and hardware environment, including but not limited to the size of the json payload, operation type, and traffic model.Table 2-1 Features Applicability
2.1 Traffic Segregation
This feature provides end-to-end traffic segregation to UDR based on traffic types. Within a Kubernetes cluster, traffic segregation can divide applications or workloads into distinct sections such as Operations Administration and Maintenance (OAM), Service Based Interface (SBI), Kubernetes control traffic, and so on. The Multus Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin for Kubernetes enables attaching multiple network interfaces to pods to help segregate traffic to and from UDR edge microservices like Ingress and Egress Gateway microservices.
This feature addresses the challenge of logically separating IP traffic of different profiles, which are typically handled through a single network (Kubernetes overlay). The new functionality ensures that critical networks are not cross-connected or sharing the same routes, thereby preventing network congestion.
With traffic segregation, operators can segregate traffic to external feeds and applications more effectively. Previously, all external traffic was routed through the same external network, but now, egress traffic from the UDR pods can be directed through non-default networks to third-party applications. This separation is achieved by leveraging cloud-native infrastructure and the load balancing algorithms in OCCNE.
The feature requires configuration of separate networks, Network Attachment Definitions (NADs), and the Cloud Native Load Balancer (CNLB). These configurations are required for facilitating Ingress/Egress traffic segregation, and optimizing load distribution in UDR.
Note:
The Traffic Segregation feature is only available in UDR, SLF, and EIR if OCCNE is installed with CNLB.Cloud Native Load Balancer (CNLB)
CNE provides CNLB for managing the ingress and egress network as an
alternate to the existing LBVM, lb-controller, and egress-controller solutions. You
can enable or disable this feature only during a fresh CNE installation. When this
feature is enabled, CNE automatically uses CNLB to control ingress traffic. To
manage the egress traffic, you must preconfigure the egress network details in the
cnlb.ini file before installing CNE.
For more information about enabling and configuring CNLB, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment User Guide and Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Network Attachment Definitions for CNLB
- Ingress Network Attachment Definitions: Ingress NADs are used to
handle inbound traffic only. This traffic enters the CNLB application
through an external interface service IP address and is routed internally
using interfaces within CNLB networks.
- Naming Convention:
nf-<service_network_name>-int
- Naming Convention:
- Egress Only Network Attachment Definitions: Egress Only NADs enable
outbound traffic only. An NF pod can initiate traffic and route it through a
CNLB application, translating the source IP address to an external egress IP
address. An egress NAD contains network information to create interfaces for
NF pods and routes to external subnets.
- Prerequisites:
- Ingress NADs are already created for the desired internal networks.
- Destination (egress) subnet addresses are known beforehand
and defined under the
cnlb.inifile'segress_destvariable to generate NADs. - The use of an Egress NAD on a deployment can be combined with Ingress NADs to route traffic through specific CNLB apps.
- Naming Convention:
nf-<service_network_name>-egr
- Prerequisites:
Managing Ingress and Egress Traffic Segregation
Enable:
This feature is disabled by default. To enable this feature, you must configure the network attachment annotations in the ocudr_custom_values_yaml file.
Configuration:
For more information about Traffic Segregation configuration, see "Configuring Traffic Segregation" section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Observe
There are no metrics, KPIs, or alerts available for this feature.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.2 Support for Post Operation for an Existing Subscription
When a DELETE request fails to remove the previous subscription, cnPCRF sends a POST
request to cnUDR to create a new subscription, cnUDR would respond with a 400
Bad Request (Duplicate Subscription)' error since the subscription already
existed in the database. With this feature, UDR supports the POST request from cnPCRF
for subscription creation (subs-to-notify requests) that overwrites the existing
subscription.
The feature is enabled by using the
allowSubscriptionRecreation parameter. When the parameter is
enabled the duplicate POST request sent is checked for the combination of
notificationUri and monitoredResourceUris in the
database. If the combination exists, then additional details, such as expiry time is
updated in the database. If the parameter is disabled, then cnUDR responds with a
400 Bad Request (Duplicate Subscription) error.
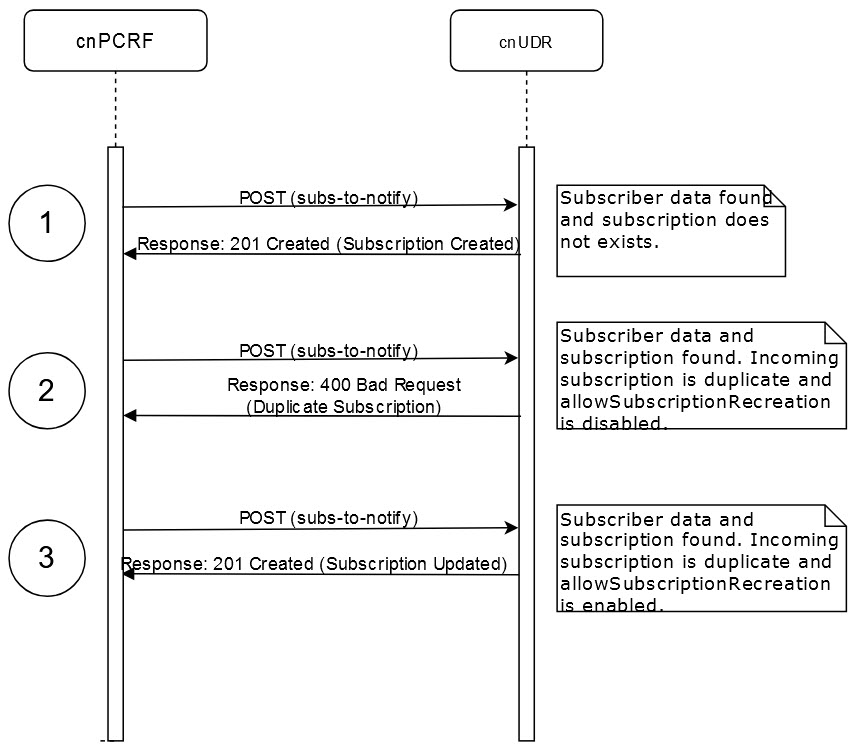
- A combination of
notificationUriandmonitoredResourceUrisparameters are used to check the duplicate POST requests. - If the combination of
notificationUriandmonitoredResourceUrisparameters are not found in the database, then a new subscription is created. - If a combination is found in the database and the POST request is received
multiple times with
allowSubscriptionRecreationenabled, then the existing subscription is updated.
notificationUri and monitoredResourceUris, if any
one of the parameters are changed, then a new subscription is
created.{
"expires": "2099-04-23T18:25:43.511Z",
"supportedFeatures": "f",
"notificationUri": "http://notify-stub-service.ats-shriats:8080/policy-data/uri1/",
"monitoredResourceUris": [
"http://ocudr-ambassador.myudr.svc.cluster.local/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/msisdn-461772271137732/ue-policy-set",
"http://ocudr-ambassador.myudr.svc.cluster.local/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/msisdn-461772271137732/sm-data/mk1",
"http://ocudr-ambassador.myudr.svc.cluster.local/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/msisdn-461772271137732/sm-data"
]
}Managing Post Operation for an Existing Subscription
Enable
You can enable or disable the feature by setting the Allow
Subscription Recreation field to true or false in the Data Repository Service in the CNC Console.
Configure
You can configure this feature using REST APIs.
/nudr-config/v1/udr.nudrservice.cfg/DR-SERVICE to enable or
disable the feature. For more information, see Oracle
Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"hikariPoolSize": 25,
"defaultSlfGroupName": "DefaultGrp",
"onDemandMigrationEnabled": true,
"tracingEnabled": true,
"defaultGroupIdEnabled": false,
"subscriptionDataSubscriptionsOnly": false,
"allowSubscriptionRecreation":true
}Upgrade and Rollback of Post Operation for an Existing Subscription
The allowSubscriptionRecreation parameter must be added
after upgrading from the previous releases and during rollback, the previous release
configurations must be restored.
Observe
Metrics
The udr_subscriptions_recreated metric is used for this
feature. For more information about the metric, see nudr-dr-service Metrics.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.3 Support for Kubernetes Resource
This section provides information about the Kubernetes resource features.
2.3.1 Network Policies
Network Policies are an application-centric construct that allows you to specify how a pod can communicate with various network entities. Network Policies create pod-level rules to control communication between the cluster's pods and services. It determines which pods and services can access one another inside the cluster.
Previously, UDR could communicate with other namespaces, and pods of one namespace could communicate with other pods other namespaces without any restriction. In this release, namespace-level isolation is provided for the UDR pods, and communications are allowed between the UDR and pods outside the cluster. The network policies enforce access restrictions for all the applicable data flows except communication from Kubernetes node to pod for invoking container probe.
Managing Support for Network Policies
Enable
createNetworkPolicy parameter to true in the global section of
the ocudr-custom values.yaml file.
# Create network policy
createNetworkPolicy: truecreateNetworkPolicy parameter to false in the global section of
the ocudr-custom values.yaml file. When the feature is disabled, and:
- If UDR is already deployed and upgrade is performed using the updated ocudr-custom values.yaml file, the network policies will not be present after the Helm upgrade.
- If it is a fresh UDR deployment and installation is performed using the updated ocudr-custom values.yaml file, the network policies will not be present after the Helm install.
The default network policy can be edited by using the ocudr_custom_values.yaml file. You must perform helm upgrade to apply the network policy rules.
Configure
You can configure this feature using Helm. For information about configuring Network Policies for UDR deployment, see Oracle Communications Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Observe
There are no specific metrics and alerts required for the Network Policy feature.
2.3.2 Kubernetes Probes
One of the key feature that Kubernetes provides is high availability. This is achieved by the smallest deployment model called Pods. The health check of these Pods are performed by Kubernetes Probes.
- Liveness Probe: Indicates if the container is operating. If the container is operating, no action is taken. If not, the kubelet kills and restarts the container.
- Readiness Probe: Indicates whether the application running in the container is ready to accept requests. If the application is ready, services matching the pod are allowed to send traffic to it. If not, the endpoints controller removes the pod from all matching Kubernetes Services.
- Startup Probe: Indicates whether the application running in the container has started. If the application is started, other probes start functioning. If not, the kubelet kills and restarts the container.
2.4 Suppress Notification
Earlier, the Cloud Native Unified Data Repository (cnUDR) was sending notifications to Cloud Native Policy and Charging Rules Function (cnPCRF) Ingress Gateway endpoint when sm-data PATCH or subs-to-notify POST request was received from cnPCRF Egress Gateway endpoint. cnUDR was unable to determine if the update operations (PUT, PATCH, or DELETE) received were from the same cnPCRF or different cnPCRF. cnUDR requires a mechanism to validate the source of the update operations to regulate the notifications.
Using the Suppress Notification feature, cnUDR can store the User-Agent header received in the POST request from cnPCRF in the subscription table. cnUDR compares the User-Agent header received during an update operation from cnPCRF with the stored User-Agent header. If the User-Agent header matches, the notification is suppressed. If the User-Agent header does not match or if there is no User-Agent header in the update request, the notification is sent to cnPCRF.
This feature enables cnUDR to identify the unique cnPCRF instance that has sent the update operations and suppress notifications to the same cnPCRF instance if the User-Agent header matches. This is achieved by using the User-Agent header in the HTTP requests received on cnUDR. The User-Agent header feature must be enabled from cnPCRF Egress Gateway. For more information about the User-Agent header, see "Support for User-Agent header" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Policy User Guide.
The User-Agent header feature sends cnPCRF NFInstanceID and NF FQDN for every request toward cnUDR. When cnUDR receives sm-data PATCH or subs-to-notify POST from cnPCRF, cnUDR stores the User-Agent header along with the corresponding subscription in the subscription table. When cnUDR receives another update request (PATCH, PUT, or DELETE), the received User-Agent header is compared with the User-Agent header stored in the subscription table. The notification is suppressed if the User-Agent matches.
The Suppress Notification feature is applicable only for signaling requests from cnPCRF, not for provisioning requests
Prerequisites
You must enable the User-Agent header feature from cnPCRF. For more information about the feature, see Support for User-Agent Header section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core Policy User Guide.
Signaling Requests
Figure 2-1 Signaling Requests

- When cnPCRF1 sends a POST (subs-to-notify) request to cnUDR, cnUDR collects the User-Agent header (Example, cnPCRF1.abc.com) from the request and saves it in the subscription table against the subscriber.
- If cnPCRF1 sends another PATCH request to cnUDR with the same User-Agent header (Example, cnPCRF1.abc.com), then notify-service validates the User-Agent header with the saved User-Agent header in the subscription table. Since the User-Agent header matches in this case the notification is suppressed.
- If cnPCRF2 sends a PATCH request to cnUDR with a different User-Agent header (Example, cnPCRF2.abc.com), notify-service validates the User-Agent header with the saved User-Agent header in the subscription table. In this case, the User-Agent header does not match and the notification is sent.
Provisioning Requests
Figure 2-2 Provisioning Requests

- When cnPCRF sends a POST (subs-to-notify) to cnUDR, cnUDR the collects the User-Agent header (Example, cnPCRF.abc.com) from the request and saves it in the subscription table against the subscriber.
- If an update request from the provisioning system with the same User-Agent header (Example, cnPCRF.abc.com) is sent from POST subs-to-notify, it is not validated and notification is triggered.
Multiple User-Agents Header
When the feature is enabled and if multiple User-Agents header are received in the request only the first occurrence is considered and saved in the subscription table.
For example, if two User-Agents header are received in the request, such as User-Agent: PCF-123 and User-Agent: NRF-123. Only User-Agent; PCF-123 is considered and saved in the subscription table.
Managing Suppress Notification
Enable
- You can enable or disable the feature by setting the
suppressNotificationEnabledparameter to true or false in the global section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. When the flag is set to true, the notification is suppressed if the User-Agent header matches. The default value is set as true. For more information on this parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Configure
- Configure using CNC Console:
You can disable or enable the feature by setting the
suppressNotificationEnabledparameter to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console. - Configure using REST API:
You can perform the PUT operation on the
http://10.75.229.45:30015/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBALto enable or disable the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.{ "dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb", "udrServices": "All", "udsfEnabled": false, "ingressHttpPort": "", "ingressHttpsPort": "", "snssai": "2-FFFFFF", "dnn": "dnn1", "autoCreate": true, "autoEnrolOnSignalling": true, "etagEnabled": true, "sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false, "consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF", "nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1, "subscriberActivityEnabled": false, "addDefaultBillingDay": true, "enableControlledShutdown" : true, "keyType": "imsi", "keyRange": "2013020001-2013020002", "nfType": "UDR", "nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com", "suppressNotificationEnabled": true, "configClientConnectTimeout": 1000, "configClientReadTimeout": 1000, "subscriberIdentifers": { "msisdn": [], "imsi": [], "nai": [], "extid": [] } }
Upgrade and Rollback of Suppress Notification Feature
Suppress notification feature works for subscriptions created on 24.2.0. release version only. Suppress notification feature does not work as expected if an upgrade or rollback is performed on the subscriptions created on a different release version.
- Rollback scenario: If the subscriptions is created on 24.2.0 release versions, then if a rollback to 24.1.x release or older release version is performed, the notifications are not generated or suppressed as expected.
- Upgrade scenario: If the subscriptions is created on 24.1.x release or older release versions, then if an upgrade to 24.2.0 release version is performed, the notifications are not generated or suppressed as expected.
It is recommended to create a new subscriptions on upgraded or rollback release versions for the suppress notification feature to work as expected.
Observe
Metrics
- suppress_user_agent_not_found
- nudr_notif_suppress_notifications
Alerts:
- UserAgentHeaderNotFoundMorethan10PercentRequest
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.5 Support for Ingress Gateway and Egress Gateway APIs in CNC Console
Earlier, the configuration for common service APIs was supported only using REST. With the implementation of this feature, UDR supports the configuration of Ingress Gateway and Egress Gateway parameters using the CNC Console.
For more information about the common service APIs, see "Configuration APIs for Common Services" section in the Oracle Communication Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Managing common service APIs in the CNC Console
Enable
This feature is enabled automatically along with the UDR instance deployment.
Configure
You can configure the common services APIs in the CNC Console. For more information, see Egress Gateway and Ingress Gateway sections.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.6 Support for Automated Certificate Lifecycle Management
UDR uses secure protocols, such as HTTPS and Secure Socket Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS), to establish and manage secure connections. This is achieved using Public and Private Keys and the presence of trusted authorities such as Certificate Authorities (CA), which create and issue certificates. These certificates have validity. You must renew these certificates before they expire. These certificates can be revoked when the CA or its keys are compromised
Starting with UDR 24.2.x, you can integrate UDR with Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Certificate Management (OCCM) to support automation of certificate lifecycle management. OCCM manages TLS certificates stored in Kubernetes secrets by integrating with Certificate Authority (CA) using the Certificate Management Protocol Version 2 (CMPv2) protocol in the Kubernetes secret. OCCM obtains and signs TLS certificates within the UDR namespace. For more information about OCCM, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Certificate Management User Guide.
Figure 2-3 Support for OCCM

The above diagram indicates that OCCM writes the keys to the certificates and UDR reads these keys to establish a TLS connection with other NFs.
- 5G Service Based Architecture (SBA) client TLS certificates
- 5G SBA server TLS certificates
- Message Feed TLS certificates
- Upgrade: When UDR is deployed with OCCM, follow the specific upgrade procedure. For information about the upgrade strategy, see "Upgrading UDR" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
- Rollback: For more information on migrating the secrets from UDR to OCCM and removal of Kubernetes secrets from the yaml file, see "Postupgrade Task" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Configure
There are no additional configuration changes required at UDR.
Observe
oc_egressgateway_connection_failure_totaloc_ingressgateway_connection_failure_total
Maintain
If you encounter any OCCM-specific alerts, see the "OCCM Alerts" section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Certificate Management User Guide.
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.7 Support for TLS
UDR use Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS) to establish secured connections with consumer NFs and producer NFs, respectively. These communication protocols are encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS).
- Handshake Protocol: Exchanges the security parameters of a connection. Handshake messages are supplied to the TLS record layer.
- Record Protocol: Receives the messages to be transmitted, fragments the data into multiple blocks, secures the records, and then transmits the result. Received data is delivered to higher-level peers.
This feature enables the support for TLS 1.3 to all consumer NFs, producer NFs, the Data Director, SBI Interfaces, and any interfaces previously supporting TLS 1.2. Support for TLS 1.2 will remain available.
TLS Handshake
This section describes the differences between TLS 1.3 and TLS 1.2 and the advantages of TLS 1.3 over TLS 1.2 and earlier versions.
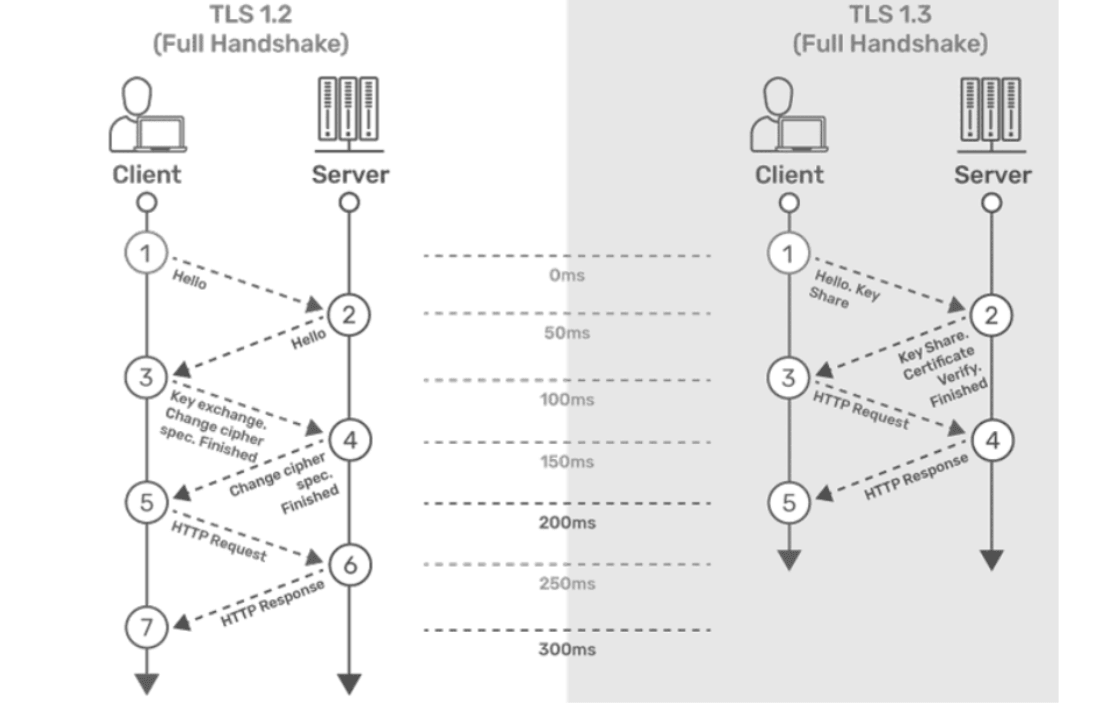
Step 1: The connection or handshake starts when the client sends a "client hello" message to the server. This message consists of cryptographic information such as supported protocols and cipher suites. It also contains a random value or random byte string.
Step 2: To respond to the "client hello" message, the server sends a "server hello" message. This message contains the CipherSuite that the server has selected from the options provided by the client. The server also sends its certificate, along with the session ID and another random value.
Step 3: The client verifies the certificate sent by the server. When the verification is complete, it sends a byte string encrypted using the public key of the server certificate.
Step 4: When the server receives the secret, both the client and server generate a master key along with session keys (ephemeral keys). These session keys are used for symmetrically encrypting the data.
Step 5: The client sends an "HTTP Request" message to the server to enable the server to transition to symmetric encryption using the session keys.
Step 6: To respond to the client’s "HTTP Request" message, the server does the same and switches its security state to symmetric encryption. The server concludes the handshake by sending an HTTP response.
Step 7: The client-server handshake is completed in two round trips.
TLS 1.3Step 1: The connection or handshake begins when the client sends a "client hello" message to the server, which includes the list of supported cipher suites. The client also sends its key share for that particular key agreement protocol.
Step 2: To respond to the "client hello" message, the server sends the key agreement protocol that it has chosen. The "Server Hello" message includes the server key share, server certificate, and the "Server Finished" message.
Step 3: The client verifies the server certificate, generates keys since it has the server's key share, and then sends the "Client Finished" message along with an HTTP request.
Step 4: The server completes the handshake by sending an HTTP response.
Table 2-2 Digital Signature Algorithms
| Algorithm | Key Size (Bits) | Elliptic Curve (EC) |
|---|---|---|
| RS256 (RSA) | 2048 | NA |
| 4096 This is the recommended value. | NA | |
| ES256 (ECDSA) | NA | SECP384r1
This is the recommended value. |
Comparison Between TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3
Table 2-3 Comparison of TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3
| Feature | TLS 1.2 | TLS 1.3 |
|---|---|---|
| TLS Handshake |
|
|
| Cipher Suites |
|
|
| Round-Trip Time (RTT) | This has a high RTT during the TLS handshake. | This has low RTT during the TLS handshake. |
| Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) | This doesn't support PFS. | TLS V1.3 supports PFS. PFS ensures that each session key is completely independent of long-term private keys, which are keys that are used for an extended period to decrypt encrypted data. |
| Privacy | This is less secure, as the ciphers used are weak. | This is more secure, as the ciphers used are strong. |
| Performance | This has high latency and a less responsive connection. | This has low latency and a more responsive connection. |
Note:
- UDR does not prioritize cipher suites on the basis of priorities. To select cipher on the basis of priorities, you must write the cipher suites in the decreasing order of priority.
- UDR does not prioritize supported groups on the basis of priorities. To select supported group on the basis of priorities, you must write the supported group values in the decreasing order of priority.
-
If you want to provide values for the signature_algorithms extension using the clientSignatureSchemes parameter, the following comma-separated values must be provided to deploy the pods:
- rsa_pkcs1_sha512
- rsa_pkcs1_sha384
- rsa_pkcs1_sha256
- The mandatory extensions as listed in RFC 8446 cannot be
disabled on the client or server side. The following is the list of the
extensions that cannot be disabled:
- supported_versions
- key_share
- supported_groups
- signature_algorithms
- pre_shared_key
Advantages of TLS 1.3
- In TLS 1.3, all handshake messages after the ServerHello are encrypted.
- TLS 1.3 improves efficiency in the handshake process by requiring fewer round trips than TLS 1.2. It also uses cryptographic algorithms that are faster.
- TLS 1.3 has better security than TLS 1.2. It addresses known vulnerabilities in the handshake process.
- TLS 1.3 got rid of data compression.
Table 2-4 TLS Combinations
| Client | Server | TLS Version Used |
|---|---|---|
| TLS1.2+1.3 | TLS1.2+1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.2+1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.2+1.3 | TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.3 |
| TLSv1.2 | TLSv1.2+1.3 | TLSv1.2 |
| TLSv1.2+1.3 | TLSv1.2 | TLSv1.2 |
| TLSv1.3 | TLSv1.2 | FATAL sent by server |
| TLSv1.2 | TLSv1.3 | FATAL sent by server |
Note:
- If Egress Gateway is deployed with both the versions of TLS (TLSv1.2 and TLSv1.3), then Egress Gateway as client sends both versions of TLS in the client hello message during the handshake and the server needs to decide which version to be used.
- If Ingress Gateway is deployed with both the version of TLS (TLSv1.2 and TLSv1.3), then Ingress Gateway as the server uses the TLS version received from the client in the server hello message during the handshake.
Managing Support for TLS v1.2 and 1.3
Enable
This feature can be enabled or disabled at the time of UDR
deployment for both Ingress and Egress traffic. For more information on enabling
initssl, enableIncomingHttps, and
outgoingHttps flags, see the "Enabling HTTPS on Ingress
Gateway" and Enabling HTTPS on Egress Gateway sections in the
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data
Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Configure
Generate HTTPS certificates for both the ingress and egress gateways. Ensure that the certificates are correctly configured for secure communication. After generating the certificates, create a Kubernetes secret for each gateway (egress and ingress). Then, configure these secrets to be used by the respective gateways.
You can configure this feature using Helm parameters. The following parameters in the Ingress Gateway and Egress Gateway microservices must be customized to support TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3.
service.ssl.tlsVersionindicates the TLS version.cipherSuitesindicates supported cipher suites.allowedCipherSuitesindicates allowed Ciphers suites.
service.ssl.tlsVersionindicates the TLS version.cipherSuitesindicates the supported cipher suites.allowedCipherSuitesindicates the allowed cipher suites.clientDisabledExtensionis used to disable the extension sent by messages originated by clients during the TLS handshake with the server.serverDisabledExtensionis used to disable the extension sent by messages originated by servers during the TLS handshake with the client.tlsNamedGroupsis used to provide a list of values sent in the supported_groups extension. These are comma-separated values.clientSignatureSchemesis used to provide a list of values sent in the signature_algorithms extension. These are comma-separated values.
For more information about configuring the values of the above-mentioned parameters, see "ocudr-ingressgateway-sig Microservice Parameters", "ocudr-ingressgateway-prov Microservice Parameters", and "ocudr-egressgateway Microservice Parameters" sections in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide
Observe
Metrics
oc_ingressgateway_incoming_tls_connectionsoc_egressgateway_outgoing_tls_connectionssecurity_cert_x509_expiration_seconds
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.8 Support for Provisioning Logs
The provisioning log feature enhances the provisioning logging functionality by enabling a logging type that is independent of the logging level. This feature helps in collecting the subscriber provisioning logs by enabling the provisioning logging mechanism. It also enables the operators to log the 5G subscriber provisioning requests for create, update, and delete operations.
{"timeStamp":"","logType":"","correlationId":"","nfInstanceId":"","method":"","request/response":""}- timeStamp: It is the request and response time provided in
Tue, 07 Jun 2021 01:11:22 GMTformat. - logType: It is the differentiator that is used to search in OpenSearch.
- correlationId: It identifies the provisioning transaction
- nfInstanceId: Identifies the site to which the logs belong.
- method: It is the HTTP method.
- request/response: It is the JSON request payload or JSON response payload.
Request:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1708691773,"nanoOfSecond":619264712},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-2","level":"INFO","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.model.UdrDataUri","message":"Request received: http://10.75.229.173:31331/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/msisdn-33123654862/sm-data/vsa {\r\n \"subscriber\": {\r\n \"IMSI\": [\"302370123456789\"],\r\n \"ACCOUNTID\": [\"178322212122\"],\r\n \"MSISDN\": [\"33123654862\"],\r\n \"BillingDay\": 6,\r\n \"Entitlement\": [\"DayPass\", \"DayPassPlus\"]\r\n },\r\n \"usage\": {\r\n \"quota\": [{\r\n \"totalVolume\": \"100\",\r\n \"Type\": \"quota\",\r\n \"name\": \"Weekend\",\r\n \"cid\": \"9223372036854775808\",\r\n \"nextResetTime\": \"2014-01-10T02:00:00Z\",\r\n \"QuotaState\": \"active\"\r\n },\r\n {\r\n \"totalVolume\": \"100\",\r\n \"Type\": \"quota\",\r\n \"name\": \"Evenings\",\r\n \"cid\": \"9223372036854775809\",\r\n \"nextResetTime\": \"2014-02-01T00:00:00Z\",\r\n \"QuotaState\": \"active\"\r\n }\r\n ],\r\n \"version\": 3\r\n },\r\n \"definition\": {\r\n \"SequenceNumber\": 1,\r\n \"version\": 1,\r\n \"DynamicQuota\": [{\r\n \"InstanceId\": \"15678\",\r\n \"Priority\": \"4\",\r\n \"InitialInputVolume\": \"15000\",\r\n \"InterimReportingInterval\": \"1000\",\r\n \"Duration\": \"100\",\r\n \"InitialOutputVolume\": \"5000\",\r\n \"Type\": \"pass\",\r\n \"activationdatetime\": \"2015-03-09T11:20:32\",\r\n \"expirationdatetime\": \"2015-04-09T11:20:32\",\r\n \"InitialTotalVolume\": \"20000\",\r\n \"name\": \"DynamicAggregateLimit\",\r\n \"InitialServiceSpecific\": \"9\",\r\n \"InitialTime\": \"135\"\r\n }]\r\n },\r\n \"state\": {\r\n \"property\": [{\r\n \"name\": \"mcc\",\r\n \"value\": \"123\"\r\n }, {\r\n \"name\": \"expire\",\r\n \"value\": \"201402-09T11:20:32\"\r\n }],\r\n \"version\": 1\r\n }\r\n}","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger","threadId":191,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2024-02-23T12:36:13.619+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"24.1.0-beta.54","mktgVersion":"23.4.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-33123654862","resourceId":"nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/sm-data/vsa","ocLogId":"1708691773617_191_ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-5b58c78644-xd6gh","requestType":"POST"}
Response:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1708691773,"nanoOfSecond":641078272},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-2","level":"INFO","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.services.VsaDbHandler","message":"creating smPolicySnssaiData using default values","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger","threadId":191,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2024-02-23T12:36:13.641+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"24.1.0-beta.54","mktgVersion":"23.4.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-33123654862","resourceId":"nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/sm-data/vsa","ocLogId":"1708691773617_191_ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-5b58c78644-xd6gh","requestType":"POST"}- POST:
- Success request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:52:05 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1708686574409-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a10", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"POST", "request":"{"subscriber":{"MSISDN":["33123654863"],"IMSI":["302370123456782"],"ACCOUNTID":["178322212123"],"BillingDay":6,"Entitlement":["DayPass","DayPassPlus"]},"usage":{"quota":[{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Weekend","nextResetTime":"2014-01-10T02:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775808","QuotaState":"active"},{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Evenings","nextResetTime":"2014-02-01T00:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775809","QuotaState":"active"}],"version":3},"definition":{"DynamicQuota":[{"InstanceId":"15678","Priority":"4","InitialInputVolume":"15000","InterimReportingInterval":"1000","Duration":"100","InitialOutputVolume":"5000","Type":"pass","activationdatetime":"2015-03-09T11:20:32","expirationdatetime":"2015-04-09T11:20:32","InitialTotalVolume":"20000","name":"DynamicAggregateLimit","InitialServiceSpecific":"9","InitialTime":"135"}],"SequenceNumber":1,"version":1},"state":{"property":[{"name":"mcc","value":"123"},{"name":"expire","value":"201402-09T11:20:32"}],"version":1}}"} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:52:05 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1708686574409-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a10", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"POST", "response":"201 CREATED"} - Failure request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:58:07 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1708686574419-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a11", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"POST", "request":"{"subscriber":{"MSISDN":["33123654863"],"IMSI":["302370123456782"],"ACCOUNTID":["178322212123"],"BillingDay":6,"Entitlement":["DayPass","DayPassPlus"]},"usage":{"quota":[{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Weekend","nextResetTime":"2014-01-10T02:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775808","QuotaState":"active"},{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Evenings","nextResetTime":"2014-02-01T00:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775809","QuotaState":"active"}],"version":3},"definition":{"DynamicQuota":[{"InstanceId":"15678","Priority":"4","InitialInputVolume":"15000","InterimReportingInterval":"1000","Duration":"100","InitialOutputVolume":"5000","Type":"pass","activationdatetime":"2015-03-09T11:20:32","expirationdatetime":"2015-04-09T11:20:32","InitialTotalVolume":"20000","name":"DynamicAggregateLimit","InitialServiceSpecific":"9","InitialTime":"135"}],"SequenceNumber":1,"version":1},"state":{"property":[{"name":"mcc","value":"123"},{"name":"expire","value":"201402-09T11:20:32"}],"version":1}}"} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:58:07 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1708686574419-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a11", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"POST", "response":"400 BAD_REQUEST"}
- Success request and
response:
- PUT:
- Success request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:53:04 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705920784991-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a12", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PUT", "request":"{"subscriber":{"MSISDN":["33123654863"],"IMSI":["302370123456782"],"ACCOUNTID":["178322212123"],"BillingDay":6,"Entitlement":["DayPass","DayPassPlus"]},"usage":{"quota":[{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Weekend","nextResetTime":"2014-01-10T02:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775808","QuotaState":"active"},{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Evenings","nextResetTime":"2014-02-01T00:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775809","QuotaState":"active"}],"version":3},"definition":{"DynamicQuota":[{"InstanceId":"15678","Priority":"4","InitialInputVolume":"15000","InterimReportingInterval":"1000","Duration":"100","InitialOutputVolume":"5000","Type":"pass","activationdatetime":"2015-03-09T11:20:32","expirationdatetime":"2015-04-09T11:20:32","InitialTotalVolume":"20000","name":"DynamicAggregateLimit","InitialServiceSpecific":"9","InitialTime":"135"}],"SequenceNumber":1,"version":1},"state":{"property":[{"name":"mcc","value":"123"},{"name":"expire","value":"201402-09T11:20:32"}],"version":1}}"} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:53:05 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705920784991-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a12", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PUT", "response":"201 CREATED"} - Failure request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 11:00:54 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705921254488-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a13", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PUT", "request":"{"subscriber":{"MSISDN":["33123654863"],"IMSI":["302370123456782"],"ACCOUNTID":["178322212123"],"BillingDay":6,"Entitlement":["DayPass","DayPassPlus"]},"usage":{"quota":[{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Weekend","nextResetTime":"2014-01-10T02:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775808","QuotaState":"active"},{"totalVolume":"100","Type":"quota","name":"Evenings","nextResetTime":"2014-02-01T00:00:00Z","cid":"9223372036854775809","QuotaState":"active"}],"version":3},"definition":{"DynamicQuota":[{"InstanceId":"15678","Priority":"4","InitialInputVolume":"15000","InterimReportingInterval":"1000","Duration":"100","InitialOutputVolume":"5000","Type":"pass","activationdatetime":"2015-03-09T11:20:32","expirationdatetime":"2015-04-09T11:20:32","InitialTotalVolume":"20000","name":"DynamicAggregateLimit","InitialServiceSpecific":"9","InitialTime":"135"}],"SequenceNumber":1,"version":1},"state":{"property":[{"name":"mcc","value":"123"},{"name":"expire","value":"201402-09T11:20:32"}],"version":1}}"} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 11:00:54 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705921254488-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a13", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PUT", "response":"400 BAD_REQUEST"}
- Success request and
response:
- PATCH:
- Success request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:54:24 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705920864822-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a14", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PATCH", "request":"[{"op":"add","patchFields":{"Entitlement":["DayPass"]},"filters":null},{"op":"replace","patchFields":{"MSISDN":["14161234567"]},"filters":null},{"op":"delete","patchFields":{"Entitlement":null},"filters":null}]"} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:54:24 UTC", "LogType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705920864822-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a14", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PATCH", "response":"204 NO_CONTENT"} - Failure request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 11:02:07 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705921327563-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a15", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PATCH", "request":"[{"op":"add","patchFields":{"Entitlement":["DayPass"]},"filters":null},{"op":"replace","patchFields":{"MSISDN":["14161234567"]},"filters":null},{"op":"delete","patchFields":{"Entitlement":null},"filters":null}]"} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 11:02:07 UTC", "LogType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705921327563-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a15", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"PATCH", "response":"400 BAD_REQUEST"}
- Success request and
response:
- DELETE:
- Success request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:55:26 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705920926635-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a16", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"DELETE", "request":""} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 10:55:26 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705920926635-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a16", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"DELETE", "response":"204 NO_CONTENT"} - Failure request and
response:
{"timeStamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 11:02:51 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705921371341-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a17", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"DELETE", "request":""} {"Timestamp":"Mon, 22 Jan 2024 11:02:51 UTC", "logType":"OCUDR-PROV-LOGS", "correlationId":"1705921371341-61110498-0699-420d-baae-770fb5623a18", "nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "method":"DELETE", "response":"404 NOT_FOUND"
- Success request and
response:
Managing Provisioning Logs
Enable
- Set the
provLogsEnabledparameter to true or false in the nudr-dr-provservice section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file to enable or disable the provisioning logs. The default value is set as false. For more information about this parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide. - Set the
provLogsApiNamesparameter to the supported provisioning APIs. The default value forprovLogsApiNamesparameter isnudr-dr-prov. The supported provisioning APIs are as follows:nudr-dr-provnudr-group-id-map-provslf-group-provn5g-eir-prov
Note:
When you enable the provisioning logs feature, the log storage value fornudr-dr-provmust be set to 4000 to accommodate provisioning logs.
# nudr-dr-provservice microservice configurations
nudr-dr-provservice:
# nameOverride: "nudr-dr-provservice"
# Image Details
enabled: *drProvisioningEnabled
onDemandMigrationProvEnabled : false
provLogsEnabled : false
provLogsApiNames : "nudr-dr-prov"
image:
name: nudr_datarepository_service
tag: ${nudr drservice tag}- Set the
provLogsEnabledparameter to true or false in the Provisioning Data Repository Service in CNC Console. - Set the
provLogsApiNamesparameter to the supported provisioning APIs in the Provisioning Data Repository Service in CNC Console.
Configure using REST API:
http://10.75.229.173:31252/nudr-config/v1/udr.nudrprovservice.cfg/DR-PROV-SERVICE
to enable or disable the provisioning logs feature and set the
provLogsApiNames parameter to the supported provisioning APIs.
For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native
Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"provLogsEnabled": true,
"hikariPoolSize": 25,
"onDemandMigrationEnabled": false,
"tracingEnabled": false,
"provLogsApiNames": [
"nudr-dr-prov"
]
}Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
Accessing Provisioning Logging
You can access the provisioning logging by using OpenSearch or by copying logs from the running pod.
Accessing Provisioning Logging Using OpenSearch
- On OpenSearch Dashboards GUI, click the Hamburger icon on the top left corner to open the sidebar menu.
- Expand the Management section and select Stack Management.
- Select Index Patterns and click Create index pattern.
- Enter the name of index pattern in the Index pattern name field.
- Verify that you get a "Your index pattern matches <n> sources" message
and index patterns in the logstash-YYYY.MM.DD format as seen in the
following image:
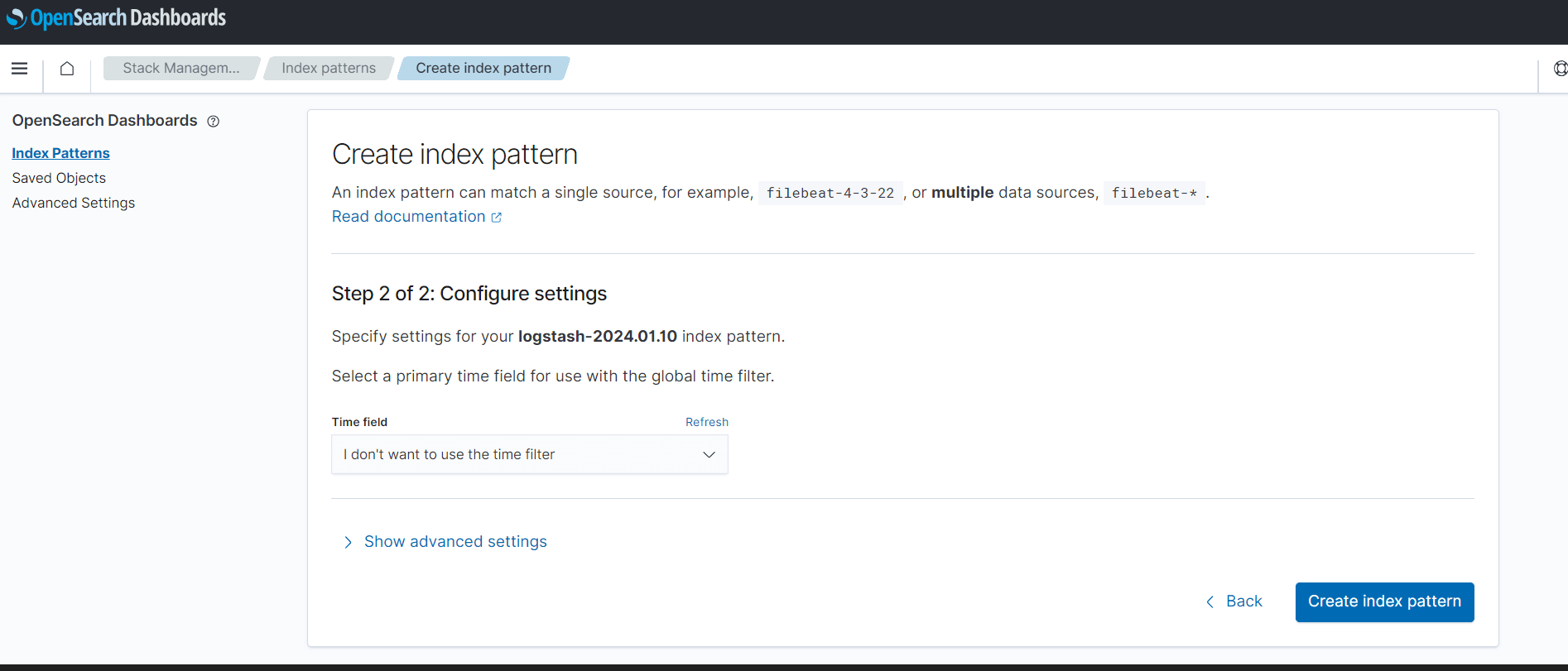
- Click Next step.
- Select I don't want to use the time filter and click Create index pattern.
- Ensure that the web page containing the indices appears on the main viewer frame.
- Click the Hamburger icon on the top left corner to open the sidebar menu and select Discover.
- Select your index from the drop-down. Add the required filter and search for logs.
- Select the log to remove all the remaining fields from filtered provisioning logs.
- Click Save to save the final filter logs.
- Click the Reporting option or View Report to download the logs.
For more information on OpenSearch, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE) Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Accessing Provisioning Logging by Copying the Logs from the Pod
- Run the following commands to get list of nudr-dr-provservice
pods.
kubectl get pods -n <namespace> | grep 'nudr-dr-provservice'The following pods will be listed.
ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-d48f787df-l5nbd 1/1 Running 0 111m - Run the following command to log in to the pod. Go to the path
home/udruser/provlogs/to get list of provisioning log files.kubectl exec -it ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-d48f787df-l5nbd -n <namespace> bash cd home/udruser/provlogs/ lsprovision.log provision.1.log.gz provision.2.log.gz - Run following command to copy the provisioning log files from the
pod. You must perform this step for all the files listed in Step
2.
kubectl cp ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-d48f787df-l5nbd:home/udruser/provlogs/provision.log provision.log -n prakash kubectl cp ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-d48f787df-l5nbd:home/udruser/provlogs/provision.1.log.gz provision.1.log.gz -n prakash kubectl cp ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice-d48f787df-l5nbd:home/udruser/provlogs/provision.2.log.gz provision.2.log.gz -n prakash - You must repeat the Step 2 and Step 3 for all the pods listed in Step 1.
- Transfer all the log files to a remote path.
2.9 Error Response and Logging Enhancement
This section describes the Error Response and Logging Enhancement feature.
2.9.1 Error Response Enhancement
{
"title":"Service Unavailable",
"status": "503",
"details":"Currently Congested. Could not process request.",
"cause":"NF_CONGESTION"
}With the enhanced error response mechanism, UDR sends additional pieces of information such as server FQDN, NF service name, vendor name, and error ID in the details field of the payload to investigate the errors.
{
"title":"[errorcodeProfiles[i].errorTitle]",
"status": "[errorcodeProfiles[i].status]",
"details":"[Server-FQDN]: [NF Service]: [errorcodeProfiles[i].errorDescription]: [VendorNF**-App-Error ID]",
"cause":"[errorcodeProfiles[i].errorCause]"
}{
"title": "Not Found",
"status": 404,
"detail": "slf01.abc.com: Nudr_GroupIDmap: Group Not Found: OSLF-DRS-SIG-E302",
"cause": "GROUP_IDENTIFIER_NOT_FOUND",
"invalidParams": null
}Sample ProblemDetails.detail as follows:
<nfFqdn>: <service-name>: <Readable Error details>:
<App-Error-Code>, example,
slf01.abc.com: Nudr_GroupIDmap: Request header Issue, Unsupported
Media Type: OSLF-DRS-HDRVLD-E001
Table 2-5 Parameters of the Details Field of the Payload
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nfFqdn |
Indicates the NF FQDN. It is obtained from the nfFqdn Helm Chart parameter. Sample Value: |
| service-name |
Indicates the microservice name. It is the originator of the error response. This value is static and cannot be configured. Sample Value:
|
| Readable Error details |
Provides a short description of the error. Sample Value: |
| App-Error ID |
Indicates the microservice ID and the error
ID Sample Value:
OSLF-DRS-SIG-E302, where,
|
| nftype |
Indicates the vendor or NF type. This parameter is prefixed with “O”, which indicates Oracle. For example, if the NF type is SLF, the vendor name becomes OSLF. It is obtained from the nfType Helm Chart parameter. Sample Value: |
| serviceId | It is either DRS (nudr-drservice) or DRP (nudr-dr-provservice). This value is set based on container name. |
| Category | Category to be used is fetched from error catalog.
Errors are classified into categories based on serviceid. Following
are the list of categories:
|
For the list of Error Code details, possible causes, and corrective actions, see Error Code Catalogue.
Enable
This feature is enabled automatically at the time of deployment.
Configure
nffqdn and nftype on the problemDetails.detail
parameter:
Table 2-6 Helm Configurations
| Configurations | Description |
|---|---|
|
nudr-drservice.nfType nudr-dr-provservice.nfType ingressgateway-prov.global.nfType ingressgateway-sig.global.nfType |
It is the configuration used to configure the NF type using the Helm charts for error detail. It is part of global section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. |
|
nudr-drservice.nfFqdn nudr-dr-provservice..nfFqdn ingressgateway-prov.global.nfFqdn ingressgateway-sig.global.nfFqdn |
It is the configuration used to configure the NF FQDN using Helm charts for error detail. It is part of global section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. |
Observe
There are no metrics, alerts, or KPIs for this feature.
2.9.2 Error Logging Enhancement
With the Error Response Logging feature, additional attributes are added to
the existing ERROR logs which gets populated with appropriate values during failure
scenarios. The new attributes that are added as part of this feature are errorStatus,
errorTitle, errorDetails, errorCause, sender, receiver, and subscriberId. Among these
errorStatus, errorTitle, errorDetails, and errorCause attributes are fetched from the
existing ProblemDetails attribute. The feature is enabled using the
additionalErrorLogging and logSubscriberInfo
feature flags in the logging API for each microservice. By default, the new attributes
are added to the logs. These new attributes is populated with appropriate values in
failure scenarios only when the feature is enabled.
{
"appLogLevel": "WARN",
"packageLogLevel": [
{
"packageName": "jetty",
"logLevelForPackage": "WARN"
},
{
"packageName": "springframework",
"logLevelForPackage": "WARN"
},
{
"packageName": "root",
"logLevelForPackage": "WARN"
}
],
"logSubscriberInfo": "DISABLED",
"additionalErrorLogging": "DISABLED"
}- nudr-datarepository-service:
Sample_logs_dr_signaling
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1718770954,"nanoOfSecond":523726788},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-2","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.exception.CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler","message":"Error Response Details","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":302,"threadPriority":5,"errorStatus":"404","errorTitle":"Not Found","errorDetails":"ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com: Nudr_DataRepository: Subscriber does not exist: OUDR-DRS-SIG-E272","errorCause":"USER_NOT_FOUND","sender":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com","receiver":"OCATS-UDR","messageTimestamp":"2024-06-19T04:22:34.523+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"24.2.0-rc.50","mktgVersion":"24.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-drservice","vendor":"Oracle","resourceId":"nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/sm-data","resultCode":"404","ocLogId":"1718770952081_520_ocudr-ingressgateway-sig-57d49b5767-fk4ht","requestType":"GET"}Sample_logs_dr_provisioning
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1718771274,"nanoOfSecond":165140206},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-2","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.exception.CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler","message":"Error Response Details","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":291,"threadPriority":5,"errorStatus":"400","errorTitle":"Bad Request","errorDetails":"ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com: Nudr_DataRepository: Payload should not be empty: OUDR-DRP-REQVLD-E102","errorCause":"MANDATORY_IE_INCORRECT","sender":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com","receiver":"OCATS-UDR","messageTimestamp":"2024-06-19T04:27:54.165+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"24.2.0-rc.50","mktgVersion":"24.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-4617722711377","resourceId":"nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data","resultCode":"400","ocLogId":"1718771274068_466_ocudr-ingressgateway-prov-7bf8c864cd-5dv47","requestType":"PUT"} - nudr-ondemand-migration:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1718771522,"nanoOfSecond":969319819},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-2","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"ocudr.migration.ondemand.exception.CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler","message":"Error Response Details","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger","threadId":434,"threadPriority":5,"errorStatus":"404","errorTitle":"Not Found","errorDetails":"ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com: nudr-ondemand-migration: Subscriber does not exist: OUDR-ODM-INTRNL-E272","errorCause":"USER_NOT_FOUND","sender":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com","receiver":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com","messageTimestamp":"2024-06-19T04:32:02.969+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"24.2.0-rc.50","mktgVersion":"24.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-ondemand-migration","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-59376755","ocLogId":"1718771522954_434_ocudr-nudr-ondemand-migration","requestType":"GET"} - nudr-config:
{"{"instant":{"epochSecond":1718771822,"nanoOfSecond":458471958},"thread":"XNIO-1task-6","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"com.oracle.nf.common.configurationService.exception.CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler","message":"Error Response Details","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger","threadId":190,"threadPriority":5,"errorStatus":"403","errorTitle":"Forbidden","errorDetails":"nudr-config: Read only field can not be modified, MODIFICATION_NOT_ALLOWED: OUDR-DRC-CFG-E559","errorCause":"MODIFICATION_NOT_ALLOWED","sender":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03","receiver":"PostmanRuntime/7.37.3","messageTimestamp":"2024-06-19T04:37:02.458+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"24.2.0-rc.50","mktgVersion":"24.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-config","vendor":"Oracle","resourceId":"/nudr-config/v1/udr.nudrservice.cfg/DR-SERVICE","resultCode":"400","ocLogId":"1718771822446_190_ocudr-nudr-config-549cdd85f9-vjf8r","requestType":"PUT"} - nudr-bulk-import:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1714996478,"nanoOfSecond":833348071},"thread":"Async-Writer-Thread - 7","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.bulkimport.util.ImportToolHelper","message":"Error Response Details","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":129,"threadPriority":5,"errorStatus":"400","errorTitle":"Bad Request","errorDetails":"udr001.oracle.com: Nudr_DataRepository: Invalid URI sent from client: OUDR-DRP-URIVLD-E021","errorCause":"MANDATORY_IE_INCORRECT","messageTimestamp":"2024-05-06T11:54:38.833+0000","application":"blk","engVersion":"24.2.0-beta.46","mktgVersion":"24.1.0.0.0","microservice":"blk-nudr-bulk-import","vendor":"Oracle","resourceId":"http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.prak:80/n5g-eir-prov/v1/equipment-status/imei-399236049675884","resultCode":"400","ocLogId":"1714996478722_328_blk-nudr-bulk-import-0","requestType":"PUT"} - nudr-notify-service:
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1720098082,"nanoOfSecond":762665335},"thread":"@575e572f-61","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.exception.CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler","message":"Error Response Details","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":61,"threadPriority":5,"errorStatus":"503","errorTitle":"Service Unavailable","errorDetails":"ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com: egressgateway: Service Unavailable: OUDR-EGW-E003","errorCause":"Encountered unknown host exception at EGW","sender":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com","receiver":"UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03 ocudr-ingressgateway-sig.oracle.com","messageTimestamp":"2024-07-04T13:01:22.762+0000","application":"ocudr-shriats","engVersion":"24.2.0-rc.50","mktgVersion":"24.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-shriats-nudr-notify-service","vendor":"Oracle"}
Managing the Error Logging Enhancements
Enable
You can enable the Error Logging Enhancements using Helm Configuration
You can enable or disable the feature by setting the
additionalErrorLogging parameter to enable or disable in the
logging section for each microservices. The default value is set as disabled.
You can enable or disable the logging of UE Identifier and subscriberid
by setting the logSubscriberInfo parameter to enable or disable in
the logging section for each microservices. The default value is set as
disabled.
# Logging level
logging:
additionalErrorlogging: “DISABLED”
logSubscriberlnfo: “DISABLEO"
level:
root: "WARN”Configure
- Configure using CNC Console: Enable the
Additional Error LoggingandLog Subscriber Infoparameter as enabled for each of the microservice in the Logging Level Configuration in the CNC Console. - Configure using REST API: Enable the
additionalErrorLoggingandlogSubscriberInfoparameter as ENABLED for each of the microservices. The default value is set as DISABLED. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.{ "appLogLevel": "WARN", "packageLogLevel": [ { "packageName": "jetty", "logLevelForPackage": "WARN" }, { "packageName": "springframework", "logLevelForPackage": "WARN" }, { "packageName": "root", "logLevelForPackage": "WARN" } ], "logSubscriberInfo": "DISABLED", "additionalErrorLogging": "DISABLED" }
Upgrade Impacts
- When you upgrade UDR from previous release version by setting
additionalErrorLoggingparameter as ENABLED, then additional information such as ProblemDetails IE is provided in all the published logs with error response details. - When you upgrade UDR from previous release version by setting
logSubscriberInfoparameter as ENABLED, then subscriberId is provided in all the published logs.
Rollback Impacts
When you rollback UDR from previous release version the configuration is also rolled back and Error Logging Enhancement feature does not work.
Log Throttling using Burst Filter
Burst filter is used to throttle the log when the log publishing rate exceeds the configured rate. The configured values are mentioned over a period of time and for maximum it is per second, and any excess logs after the rate is reached is ignored.
- level: It is the log level below which logs will be throttled. For example, DEBUG level will throttle TRACE and DEBUG logs.
- rate: It is the average log printing rate over a period of time after which the log throttling starts.
- max: It is the maximum number of logs allowed per second in case of maximum burst scenarios.
logging:
burstFilter:
level: "DEBUG"
rate: 500
max: 3000Note:
The time window is calculated as max/rate. For example, 3000/500 is six seconds. For six seconds you will not receive over 500 logs.- ERROR: ERROR, WARN, INFO, and DEBUG are filtered
- WARN: WARN, INFO, and DEBUG are filtered
- INFO: INFO and DEBUG are filtered
- DEBUG: DEBUG is filtered
Observe
There are no metrics, alerts, or KPIs for this feature.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.10 Ingress Gateway Pod Protection
This feature protects the Ingress Gateway pods from congestion conditions due to uneven traffic distribution, network fluctuations, traffic bursts, or unexpected high traffic volume. It ensures the protection and mitigation of Ingress Gateway pods from entering congestion condition and also facilitating necessary actions for recovery. As a front end microservice for HTTP traffic, it is important for Ingress Gateway to have pod protection implemented.
The pod protection is performed based on the CPU consumption of the Ingress Gateway Pods as explained in the Congestion State Parameters. It is measured at different load states mentioned in the Ingress Gateway Load States.
Congestion State Parameters
CPU Usage
In the Pod Protection feature, each Ingress Gateway microservice pod monitors its congestion state. This state is tracked in terms of CPU consumption, measured in nanoseconds, using Kubernetes cgroup (cpuacct.usage).
It is periodically monitored and calculated using the following formula. Then, it is compared against the CPU thresholds configured through the Rest API to determine the congestion state. For more information about the parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
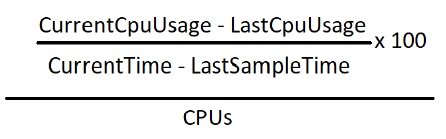
Where,
CurrentCpuUsage is the counter reading at current periodic cycle.
LastCpuUsage is the counter reading at previous periodic cycle.
CurrentTime is the current time snapshot.
LastSampletime is the previous periodic cycle time snapshot.
CPUs is the total number of CPUs for a given pod.
Ingress Gateway Load States
The following states are used to detect overload conditions. This ensures the protection and mitigation of pods from entering an overload condition, while also facilitating necessary actions for recovery.
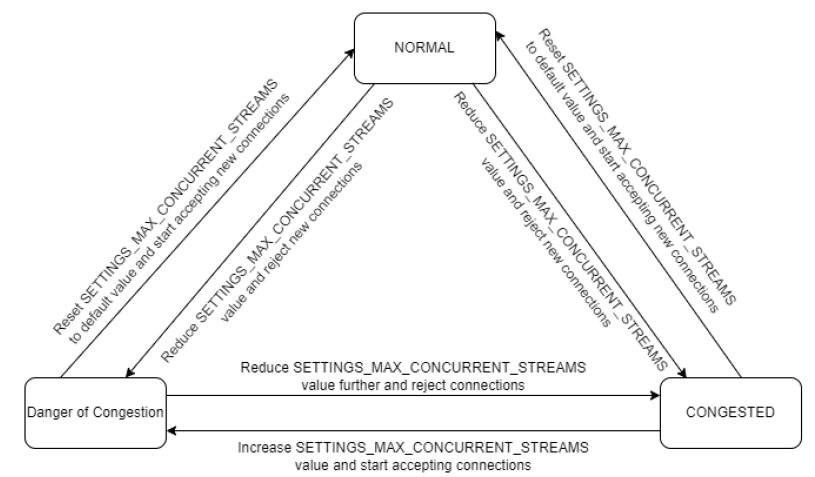
Note:
The transition can occur between any states based on the congestion parameters. The threshold for these congestion parameters is preconfigured and must not be changed.- Congested State: This is the upper bound state where the pod
is congested. This means one or more congestion parameters are above the
configured thresholds for the congested state. For more information about the
configuration using REST API, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core,
Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide. The pod can be
transitioned to the Congested State either from the Normal State or the DoC
state. When the pod reaches this state, the following actions are performed:
- new incoming HTTP2 connection requests are not accepted.
- the pod gradually decrements the number of concurrent
streams by updating SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS parameter in a
SETTINGS frame to the configured
maxConcurrentStreamsPerConvalue at a regular interval. The concurrent streams are decremented based on the value configured indecrementByparameter. And, the regular interval is configured in thedecrementSamplingPeriodparameter.
- Danger of Congestion (DOC): This is the intermediate state
where the pod is approaching a congested state. This means if CPU is above the
configured thresholds for the DoC state.
- any new incoming HTTP2 connection requests are not accepted.
- if the pod is transitioning from the Normal State to the
DoC state, the pod gradually decrements the number of concurrent streams
by updating SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS parameter in a SETTINGS
frame to the configured
maxConcurrentStreamsPerConvalue at a regular interval. The concurrent streams are decremented based on the value configured indecrementByparameter. And, the regular interval is configured in thedecrementSamplingPeriodparameter. - if the pod is transitioning from the Congested State to the
DoC state, the pod gradually increments the number of concurrent streams
by updating SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS parameter in a SETTINGS
frame to the configured
maxConcurrentStreamsPerConvalue at a regular interval. The concurrent streams are incremented based on the value configured inincrementByparameter. And, the regular interval is configured in theincrementSamplingPeriodparameter.
Note:
In any service mesh based deployment, if any incoming connections to the pod get terminated at the sidecar container then the sidecar container creates a new connection toward the application container. These incoming connections from the peer are managed by the sidecar and outside the purview of the application container.
Hence when the Ingress Gateway container reaches DOC or Congested level, in a service mesh based deployment, the Ingress Gateway container will only be able to stop accepting new connections from the sidecar container. Also in this state, the Ingress Gateway container will reduce the concurrency of the existing connections between the sidecar container and the Ingress Gateway container.
- Normal State: This is the lower bound state where all the
congestion parameters for the pod are below the configured thresholds for DoC
and Congested states. When the pod reaches this state, the following actions are
performed:
- the pod will continue accepting new incoming HTTP2 connection requests.
- the pod will continue accepting requests on the existing HTTP2 connections.
- in case the pod is transitioning from the Congested or DoC
state to Normal state, the pod gradually increments the number of
concurrent streams by updating SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS parameter
in a SETTINGS frame to the configured
maxConcurrentStreamsPerConvalue at a regular interval. The concurrent streams are incremented based on the value configured inincrementByparameter. And, the regular interval is configured in theincrementSamplingPeriodparameter.
To avoid toggling between these states due to traffic pattern, it is required for the pod to be in a particular state for a given period before transitioning to another state. The below configurations are used to define the period till which the pod has to be in a particular state:
stateChangeSampleCountmonitoringInterval
Formula for calculating the period is as follows:
(stateChangeSampleCount * monitoringInterval)
For more information about the configuration using REST API, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Pending Requests
Pending request count is the number of pending requests that are waiting for a response. The counter is incremented for all incoming requests and decremented when there is a response.
The following table provides the threshold configurations.
Table 2-7 Threshold configurations
| Type | CPU and Pending Count | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Normal |
Threshold start CPU: 0 Threshold end CPU: 79% Threshold start Pending Count : 0 Threshold end Pending Count : 4999 |
New connections will be accepted in normal state |
| DOC Alert |
Threshold start CPU: 80% Threshold end CPU: 89% Threshold start Pending Count : 5000 Threshold end Pending Count : 6999 |
New connection will be rejected in DOC STATE. |
| Congested Alert |
Threshold start CPU: 90% Threshold end CPU: 100% Threshold start Pending Count : 7000 Threshold end Pending Count : 7000+ |
New connection will be rejected in CONGESTED STATE. |
Managing Ingress Gateway Pod Protection
This section explains the procedure to enable and configure the feature.
Enable
- Use the API path as
http://<nudr-config svc IP>:<port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-prov/podprotectionorhttp://<nudr-config svc IP>:<port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/podprotection. - Set
enabledandcongestionControl.enabledtotrue. -
Run the API using PUT method with the proposed values given in the Rest API. For more information about API path, see "Configuration APIs for Common Services" section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Note:
You should not use memory as a congestion state parameter for pod protection feature because the memory accumulated by the pod during the traffic run is not released by the pod even when the traffic is reduced. This causes the pod to remain in DOC or CONEGSTED state.Given below is a sample REST API configuration to enable this feature:
{ "enabled": true, "congestionControl": { "states": [ { "name": "Normal", "weight": 0, "entryAction": [ { "action": "MaxConcurrentStreamsUpdate", "arguments": { "incrementBy": 30, "maxConcurrentStreamsPerCon": 100, "incrementByActionSamplingPeriod": 3 } }, { "action": "AcceptIncomingConnections", "arguments": { "accept": true } } ] }, { "name": "DoC", "weight": 1, "entryAction": [ { "action": "AcceptIncomingConnections", "arguments": { "accept": false } }, { "action": "MaxConcurrentStreamsUpdate", "arguments": { "decrementBy": 30, "incrementBy": 30, "maxConcurrentStreamsPerCon": 50, "decrementByActionSamplingPeriod": 1, "incrementByActionSamplingPeriod": 3 } } ], "resourceThreshold": { "cpu": 60, "pendingMessage": 5000 } }, { "name": "Congested", "weight": 2, "entryAction": [ { "action": "AcceptIncomingConnections", "arguments": { "accept": false } }, { "action": "MaxConcurrentStreamsUpdate", "arguments": { "decrementBy": 30, "maxConcurrentStreamsPerCon": 10, "decrementByActionSamplingPeriod": 1 } } ], "resourceThreshold": { "cpu": 75, "pendingMessage": 7000 } } ], "enabled": true, "actionSamplingPeriod": 3, "stateChangeSampleCount": 10 }, "monitoringInterval": 100 }
Observe
Metrics
- oc_ingressgateway_pod_congestion_state{namespace='$namespace'}
- oc_ingressgateway_pod_resource_state{type="CPU/PENDING_REQUEST",namespace='$namespace'}
- oc_ingressgateway_pod_resource_stress{type="CPU/PENDING_REQUEST",namespace='$namespace'}
- oc_ingressgateway_incoming_pod_connections_rejected_total{namespace="$namespace"}
- oc_ingressgateway_pod_congestion_state{namespace='$namespace'}
- oc_ingressgateway_incoming_pod_connections_rejected_total{namespace="$namespace"}
Alerts:
- IngressgatewayPodProtectionDocState
- IngressgatewayPodProtectionCongestedState
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.11 Support for cnDBTier APIs in CNC Console
With the implementation of this feature, cnDBTier APIs are integrated into the CNC Console, and UDR users can view specific cnDBTier APIs, such as checking the available backup lists, cnDBTier version, database statistics, heartbeat status, local cnDBTier cluster status, georeplication status, and initiating on-demand backup on the CNC Console.
- Backup List: This API displays the details of stored backups, such as the ID and size of the backup.
- cnDBTier version: This API displays the cnDBTier version.
- Database Statistics Report: This API displays the number of available database.
- Georeplication Recovery: This API provides the recovery status of georeplication
for the cnDBTier cluster:
- Update Cluster As Failed: This API is used to mark a disrupted cluster as failed.
- Start Georeplication Recovery: This API is used to start the georeplication recovery process for any failed cluster. Only one cluster can be recovered at a time.
- Georeplication Recovery Status: This API is used to monitor the recovery status of georeplication for both FAILED and ACTIVE cnDBTier sites.
- Geo Replication Status:
- Real Time Overall Replication Status: This API displays the overall replication status in multisite deployments. For example, in a four-site deployment, it provides the replication status between the following sites: site1-site2, site1-site3, site1-site4, site2-site3, site2-site4, and site2-site1. This is applicable for all other sites.
- Site Specific Real Time Replication Status: This API displays the site-specific replication status.
- HeartBeat Status: This API displays the connectivity status between the local site and the remote site name to which UDR is connected.
- Local Cluster Status: This API displays the status of the local cluster.
- On-Demand Backup: This API displays the status of initiated on-demand backups.
- cnDBTier Health: This API displays the health status of the
available databases.
- Backup Manager Health Status: This API displays the health status of the backup manager service. It checks whether the backup manager service is up or not and if the service can connect to database or not.
- Monitor Health Status: This API displays the health status
of the monitor service. It checks the following:
- If the monitor service is up or not
- If the service can connect to database or not
- If the metrics are fetched or not (the metrics are fetched when the service is up and vice versa)
- NDB Health Status: This API displays the health status of
the replication service whether the pod is connected to PVC or not and
checks whether the pods status is up or not.
Note:
PVC is not applicable to some of the pods. - Replication Health Status: This API displays the health status of the replication service. It checks whether the replication service is up or not and the service can connect to database or not.
Enable
The CNC console section for accessing the cnDBTier APIs is available in UDR if the cnDBTier is configured as an instance during the CNC Console deployment. For more information about integrating cnDBTier APIs in CNC Console, see the "NF Single Cluster Configuration With cnDBTier Menu Enabled" section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
There is no option to disable this feature.
Configure
cnDBTier APIs can be accessed or configured using the CNC Console. For more information, see cnDBTier in the CNC Console.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.12 Diameter Connection Configuration
The Diameter Connection Configuration feature provides the capability to trigger a Connection Establishment Request (CER) from the Diameter Gateway pod to each of the configured diameter endpoints. This feature enables the distribution of the diameter connection in a controlled manner by balancing the diameter traffic evenly between the Diameter Gateway pods. This is achieved by adding peer node details as a configuration in the Diameter Gateway.
Figure 2-4 Diameter Connection Configuration
When you configure the peer node details in the allowed client node list of the Diameter Gateway, the Diameter Gateway initiates one connection by sending Connection Establishment Request (CER) to the peer node from each Diameter Gateway pod. Diameter endpoints, such as Diameter Proxy and On-Demand Migration are added as peer nodes during deployment from the configuration map. Migration Tool configurations are added during tool installation using hooks.
Till UDR Release 23.2.0, the Diameter Gateway accepts connections only from the peer node. Since this is a Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) connection, there is only one connection from peer node to one of the Diameter Gateway pods. Due to this, traffic is not load balanced between the Diameter Gateway pods. In this feature, peer node details are configured in the Diameter Gateway. The Diameter Gateway uses these details to establish one connection from each of the Diameter Gateway pods to the peer node. This enables even distribution of traffic between the Diameter Gateway pods.
Configure using REST API:
In the Diameter Gateway configurations,
peerNodesForNotifications and migrationPeers
fields, which was used to store peer nodes details are removed. The
allowedClientNodes field is used to store peer nodes details,
peer node identity, and realm to allow incoming connection from peer nodes.
You can perform the PUT operation on the
http://10.75.229.85:31430/nudr-config/v1/udr.diamgateway.cfg/DIAMETER-GATEWAY
to update the peer node details.
If the responseOnly parameter is set to true, then
Diameter Gateway initiates a connection to the peer node. If the parameter is set to
false, the Diameter Gateway uses the peer node details for verifying and accepting
the incoming connections. Parameters host and port
are mandatory only if the responseOnly parameter is set to true.
For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native
Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
{
"realm": "oracle.com",
"identity": "nudr.oracle.com",
"reconnectDelay": 3,
"responseTimeout": 4,
"connectionTimeOut": 3,
"watchdogInterval": 6,
"reconnectLimit": 50,
"onDemandMigrationEnabled": false,
"allowedClientNodes": [{
"port": 7867,
"identity": "local1.tekelec1.com",
"responseOnly": true,
"host": "10.0.7.500",
"realm": "tekelec1275.com",
"type": "4GUDROndemandConnection"
}, {
"port": 3868,
"identity": "sh-server",
"host": "10.75.185.161",
"responseOnly": true,
"realm": "seagull",
"type": "server"
}]
}2.13 Conflict Resolution
In a multisite deployment, during replication down time, UDR updates subscriber data on all the sites. When the replication is restored, the updates are resolved automatically to all the database tables by MySQL NDB Cluster in the cnDBTier. In some cases, automatic resolution by MySQL causes subscriber data conflicts and anomalies in the database model. This feature provides an application-defined resolution to resolve the subscriber data conflicts by adding a timestamp column to determine whether an update is required on the replica.
Note:
- Conflict resolution feature must be enabled during maintenance activity to avoid service disruptions.
- Rollback of conflict resolution feature must be avoided.
To Enable
Note:
Following SQL files are available in ocudr_custom_configtemplates file:ALL_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sqlSLF_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql.EIR_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql.ALL_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql.fileSLF_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sqlEIR_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql.
- Post installation of cnDBTier and before installing UDR, SLF, or
EIR across the sites, do one of the following based on deployment mode, on
one of the ndbappmysqld nodes on one of the sites. In the SQL files, replace
the string
<database_name>with the UDR subscriber database name, which is common to all UDR sites:Note:
In case of a two or three site setup, perform this step only on site one, on one of the ndbappmsqld nodes, preferably ndbappmysql-0 node.- Run the SQL commands in the
ALL_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sqlfile, if installed in ALL mode. - Run the SQL commands in the
SLF_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql.file, if installed in SLF mode. - Run the SQL commands in the
EIR_mode_ndb_replication_insert.sql.file, if installed in EIR mode.
- Run the SQL commands in the
- Set the following configurations under appinfo section on all
UDR sites to enable the database and replication monitoring from UDR
deployment. This is also used by dbcr service before triggering an audit
operation.
appinfo: watchMySQL: true replicationStatusCheck: true scrapeInterval: 5 dbStatusUri: http://mysql-cluster-db-monitor-svc.cndb-site1:8080/db-tier/status/local realtimeDbStatusUri: http://mysql-cluster-db-monitor-svc.cndb-site1:8080/db-tier/status/cluster/local/realtime replicationUri: http://mysql-cluster-db-monitor-svc.cndb-site1:8080/db-tier/status/replication replicationInterval: 30 - Set the IP/FQDN list of the mate sites ingressgateway-prov
services in the following configuration under nudr_dbcr_auditor_service
section. Enable the
dbConflictResolutionEnabledparameter in the global section of the ocudr-custom values.yaml file. For more information about the configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation Guide.global: dbConflictResolutionEnabled: "true" nudr_dbcr_auditor_service: # Provide MateSite IGW IP List, Comma separated values. Provide fqdn or IP with port mateSitesIgwIPList: 'http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.myudr2:80,http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.myudr3:80' - Perform a helm upgrade of UDR using the helm upgrade command.
Note:
Steps 2 to 4 must be performed on all UDR sites during deployment.- To modifying the existing UDR database tables from cnDBTier, you must enable
the
ndb_allow_copying_alter_tableparameter in the cnDBTier custom yaml file and perform a Helm upgrade.Note:
Before executing the scripts you must make sure that the subscriber size in the tables must have lesser entries than theMaxDMLOperationsPerTransactionparameter on MySQL. It is recommended to perform the following procedure before provisioning. For the existing subscribers you must configure theMaxDMLOperationsPerTransactionparameter accordingly before the following procedure is performed. - Once the cnDBTier Helm upgrade is successful, manually run the
SQL commands mentioned on one of the following SQL files based on deployment
mode, on one of the ndbappmysqld nodes on one of the sites:
Note:
In case of a two or three site setup, perform this step only on site one, on one of the ndbappmsqld nodes, preferably ndbappmysql-0 node.- Run the SQL commands in the
ALL_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql, if installed in all mode. - Run SQL commands in the
SLF_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sqlfile, if installed in SLF mode. - Run the SQL commands in the
EIR_mode_ndb_replication_insert_UPGRADE.sql.file, if installed in EIR mode.
- Run the SQL commands in the
- Set the following configurations under appinfo section on all
UDR sites to enable the database and replication monitoring from UDR
deployment. This is also used by dbcr service before triggering an audit
operation.
appinfo: watchMySQL: true replicationStatusCheck: true scrapeInterval: 5 dbStatusUri: http://mysql-cluster-db-monitor-svc.cndb-site1:8080/db-tier/status/local realtimeDbStatusUri: http://mysql-cluster-db-monitor-svc.cndb-site1:8080/db-tier/status/cluster/local/realtime replicationUri: http://mysql-cluster-db-monitor-svc.cndb-site1:8080/db-tier/status/replication replicationInterval: 30 - Set the IP/FQDN list of the mate sites ingressgateway-prov
services in the following configuration under nudr_dbcr_auditor_service
section. Enable the
dbConflictResolutionEnabledparameter in the global section of the ocudr-custom values.yaml file. For more information about the configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation Guide. .global: dbConflictResolutionEnabled: "true" nudr_dbcr_auditor_service: # Provide MateSite IGW IP List, Comma separated values. Provide fqdn or IP with port mateSitesIgwIPList: 'http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.myudr2:80,http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov.myudr3:80' - Perform a helm upgrade of UDR using the helm upgrade command. This enables database conflict resolution auditor service and you must perform the required configurations on appinfo service.
- Use REST API to activate the UDR database conflict resolution
feature on all the sites. The following configuration under global section
of the ocudr-custom values.yaml file is used for this
feature:
curl -v -X PUT -i 'http://ocudr-nudr-config.<site-namespace>:5001/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL' -d '{"dbServiceName":"mysql-connectivity-service.sitea","udrServices":"All","udsfEnabled":false,"ingressHttpPort":"","ingressHttpsPort":"","snssai":"2-FFFFFF","dnn":"dnn1","autoCreate":true,"autoEnrolOnSignalling":true,"etagEnabled":false,"version":"v3","sbiCorrelationInfoEnable":false,"consumerNF":"PCF,UDM,NEF","nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03","vsaDefaultBillingDay":1,"subscriberActivityEnabled":false,"addDefaultBillingDay":true,"enableControlledShutdown":false,"keyType":"msisdn","keyRange":"1013020001-1013020002","dbConflictResolutionEnabled":true,"subscriberIdentifers":{"msisdn":[],"imsi":[],"nai":[],"extid":[]}}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" - You must restart all the ndbappmysqld and ndbmysqld pods on the cnDBTier deployment to activate the feature on MYSQL.
Note:
Steps 2 to 5 must be performed on all UDR sites during deployment. Step 6 must be performed on all cnDBtier sites.- Disable the conflict resolution, see To Disable.
- Perform a Helm rollback for cnDBTier and then NF.
To Disable
-
You can disable the database Conflict Resolution feature on all the sites using the REST API. A new configuration, dbConflictResolutionEnabled, under global section has been introduced for this.
URI and Payload Sample:curl -v -X PUT -i 'http://ocudr-nudr-config.<site-namespace>:5001/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL-d '{"dbServiceName":"mysql-connectivity-service.sitea","udrServices":"All","udsfEnabled":false,"ingressHttpPort":"","ingressHttpsPort":"","snssai":"2-FFFFFF","dnn":"dnn1","autoCreate":true,"autoEnrolOnSignalling":true,"etagEnabled":false,"version":"v3","sbiCorrelationInfoEnable":false,"consumerNF":"PCF,UDM,NEF","nfInstanceId":"5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03","vsaDefaultBillingDay":1,"subscriberActivityEnabled":false,"addDefaultBillingDay":true,"enableControlledShutdown":false,"keyType":"msisdn","keyRange":"1013020001-1013020002","dbConflictResolutionEnabled":false,"subscriberIdentifers":{"msisdn":[],"imsi":[],"nai":[],"extid":[]}}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" - Disable the
dbConflictResolutionEnabledparameter in the global section of the ocudr-custom values.yaml file and upgrade the NF. You can ignore this step for rollback, since this feature is not available in the previous release. - Run the SQL command on one of the ndbappmysqld nodes on one of
the sites. You must run the SQL command to the ndbappmysqld pod by logging
in to the SQL terminal.
Note:
In case of a two or three site setup, perform this step only on site one, on one of the ndbappmsqld nodes, preferably ndbappmysql-0 node.- Run the following command to log in to the SQL
terminal.
"mysql -h127.0.0.1 -u<udruser> -p<udrpassword"> - Run the following SQL command on one of the
ndbappmysqld nodes on one of the
sites.
"delete from mysql.ndb_replication where db='<udr_subscriber_database_name>';"
- Run the following command to log in to the SQL
terminal.
Note:
For PCF data, the sm-data components such as umdata or umdata limits modifies individually during replication down time. The conflict resolution for the data happens for the complete sm-data based on the latest time stamp. This is applicable for 4G attributes such as quota or dynamic quota.Database Conflict Resolution (DBCR) Service Logging Info
Debug logs are written when exceptions are cleared from data tables on SLF, UDR, or EIR. There will be one log per exception table. Info logs are written when specific IDs are cleared from the IDXTODATA tables and data tables during audit operation.2.14 Network Function Scoring for a Site
The Network Function (NF) Scoring feature calculates the score for a site based on NF specific factors such as alerts. This feature determines the health of a site as compared to other sites and allows you to select an appropriate site by comparing the NF scores within or across multiple sites.
One of the use cases is the Controlled Shutdown feature that allows the operator to partially or completely isolate the site. The NF Scoring feature helps the operators to select which site to partially or completely isolate based on the NF scoring.
App-Info service queries and calculates the NF score based on the site information.
App-Info Scoring Mechanism: App-Info service reads the configurations from the common config server to check if NF Scoring functionality is enabled. It works in the following ways:
- Continuous NF Score Calculation: When you enable the NF Scoring feature, app-info periodically reads the configurations to calculate the score.
- On-Demand NF Score Calculation: When you enable the NF Scoring feature, app-info fetches all the factors or criteria to calculate the NF Score. It fetches the factors in real-time and calculates the NF score on demand.
Table 2-8 NF Scoring Criteria
| Factors | Default Score | Formula to Calculate Factor Score | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| TPS | 20 | min (Current-TPS / Max-TPS * Max-TPS-Score, Max- TPS-Score) |
Current-TPS includes both ingressgateway-sig and ingressgateway-prov. Max-TPS specifies the maximum TPS. Max- TPS-Score specifies the maximum score of the TPS. |
| Service | 30 | A / N * SVC-Score |
A specifies number of available services N specifies number of configured services Max-SVC-Score specifies the maximum score of the Service Health. |
| Connection | 20 | min(Site-Current / Site-Total * Replication-health Score, Replication-health Score) |
Connection specifies the number of connections accepted by IGW and DGW from the network. Site-Current specifies the available replication links for a particular site. Site-Total specifies the total number of sites in a geo-redundant cluster. Replication-health Score specifies the score for the replication-health. |
| Replication-health | 30 | min(Site-Current / Site-Total * Site-Score, Site-Score) |
Site-Total specifies the total number of sites in a geo-redundant cluster. Site-Current specifies the available replication links for a particular site. |
| Locality-Preference | 5 | NA | The value of Locality-Preference is added for NF score calculation. |
| Critical-Alerts | 2 | CrN * Configured-Score-Critical-Alerts |
CrN is the number of active critical alarms. Configured-Score-Critical-Alerts specifies the score configured by the user. |
| Major-Alerts | 1 | MaN * Configured-Score-Major-Alerts |
MaN is the number of active Major alarms. Configured-Score-Major-Alerts specifies the score configured by the user. |
| Minor-Alerts | 0 | MaN * Configured-Score-Minor-Alerts |
MiN is the number of active Minor alarms. Configured-Score-Minor-Alerts specifies the score configured by the user. |
NF Scoring based on Custom Criteria
- Ratio-based: This method takes a ratio of the obtained
metric value.
Formula: Minimum (calcuated_value_from_prometheus/maxValue*maxScore, maxScore). For example, min((100/1000)*20,20) = min (20,10) = 10.
- Weightage-based: This method performs a scalar
multiplication of the obtained metric value.
Formula: weightage*calculated_value_from_prometheus. For example, 2*40 = 80.
Table 2-9 Custom Criteria
| Site Score | Criteria | Operator Configuration | Runtime | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | - | Name | Metric Name (Name of the metric on which custom criteria calculation is based) | Enable (Indicates criteria is enabled or disabled) | Base/Total (Maximum value expected for corresponding attribute) | Scoring Type | Max Score | Weightage | Formula |
| Add | NF Specific | Bulk Import | nudr_bulk_import_records_processed_total | true/false | 20 | Ratio | 20 | 5 | Minimum (calcuated_value_from_prometheus/maxValue*maxScore, maxScore) |
| Add | NF Specific | Export Tool | export_tool_status_total | true/false | 20 | Ratio | 20 | 5 | Minimum (calcuated_value_from_prometheus/maxValue*maxScore, maxScore) |
Note:
- For weightage-based calculation, the maximum score of the criteria is not considered.
- For ratio based-calculation, the weightage of the criteria is not considered.
Note:
enableCustomCriteria and customCriteria fields are optional.{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-07/schema#",
"title": "sample config json",
"description": "json validator",
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"logging": {
"type": "object",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance.",
"properties": {
"appLogLevel": {
"enum": [
"CRITICAL",
"FATAL",
"ERROR",
"WARN",
"WARNING",
"INFO",
"DEBUG",
"TRACE"
],
"type": "string",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance."
},
"packageLogLevel": {
"type": "array",
"minItems": 0,
"maxItems": 6,
"uniqueItems": true,
"items": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"packageName": {
"enum": [
"namespace_runtime_info",
"service_monitor",
"mysql_monitor",
"replication_status_monitor",
"service_status_scraper",
"log_level_agent"
],
"type": "string",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance."
},
"logLevelForPackage": {
"enum": [
"CRITICAL",
"FATAL",
"ERROR",
"WARN",
"WARNING",
"INFO",
"DEBUG",
"TRACE"
],
"type": "string",
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance."
}
},
"required": [
"packageName",
"logLevelForPackage"
],
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance."
}
]
},
"description": "An explanation about the purpose of this instance."
}
},
"required": [
"appLogLevel"
]
},
"nfScoring": {
"type": "object",
"description": "NF scoring configuration.",
"properties": {
"enableNFScoring": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "flag used to enable and disable NF Scoring feature"
},
"enableCustomCriteria": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "flag used to enable or disable custom criteria"
},
"tps": {
"type": "object",
"description": "TPS data.",
"required": ["enable"],
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"maxScore": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 20
},
"maxTps": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 1000000
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"serviceHealth": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Service Health data.",
"required": ["enable"],
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"maxScore": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 30
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"signallingConnections": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Signalling Connections data.",
"required": ["enable"],
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"maxScore": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 20
},
"maxConnections": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 10000
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"replicationHealth": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Replication Health data.",
"required": ["enable"],
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"maxScore": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 30
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"localitySitePreference": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Locality and Site Preference data.",
"required": ["enable"],
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"score": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 5
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"activeAlert": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Active Alert Weightage.",
"required": ["enable"],
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"criticalAlertWeightage": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 2
},
"majorAlertWeightage": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 1
},
"minorAlertWeightage": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 0
}
},
"additionalProperties": false
},
"customCriteria": {
"type": "array",
"description": "list of custom criterias",
"items": {
"type": "object",
"description": "Data related to custom criteria",
"properties": {
"enable": {
"type": "boolean"
},
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"metricName": {
"type": "string"
},
"scoringType": {
"type": "string"
},
"maxScore": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": -1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 30
},
"maxValue": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": -1,
"maximum": 10000
},
"weightage": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": -1,
"maximum": 100,
"default": 1
}
}
},
"required": ["enable"]
}
},
"additionalProperties": false,
"required": [
"enableNFScoring",
"tps",
"serviceHealth",
"signallingConnections",
"replicationHealth",
"localitySitePreference",
"activeAlert"
]
}
}
}Formula for NF scoring of a site: Sum of TPS-Score, SVC-Score, Conn-Score, Replication-health, and Locality-Preference score subtracted from Alerts scores.
Call Flow
This section describes call flows for the NF Scoring feature:
Figure 2-5 NF Scoring Configuration

Operator use APIs to make configuration changes such as enable or disable the feature, set weightage, and parameters, which is then used by app-info.
Figure 2-6 NF Scoring

The GET NF score API and Nudr config service interacts with app-info which in turn interacts with perf-info and prometheus to calculate and return overall NF score.
Enhancements in App-Info and Perf-Info for the Signalling Connections and Transaction Per Second (TPS) Criteria
To fetch an overall score for Ingress Gateway for TPS score calculation, perf-info is modified to support changes in ingress gateway provisioning and signaling.
To fetch an overall score for Ingress Gateway for signaling score calculation, app-info is modified to support changes in ingress gateway provisioning and signaling.
multipleIgwEnabled
parameter to true in the global section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml
file.multipleIgwEnabled: true- name: MULTIPLE_IGW_ENABLED
value: {{ .Values.global.multipleIgwEnabled | quote }}{
"scoringFactors": [
{
"additionalInfo": {
"actualValue": 29.95,
"configuredValue": 33,
"igw_prov": 19.95,
"igw_sig": 10.0
},
"calculatedScore": 18.151515151515152,
"criteria": "tps",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"actualValue": 17.0,
"configuredValue": 40,
"igw_prov": 12,
"igw_sig": 4
},
"calculatedScore": 8.5,
"criteria": "signallingConnections",
"maxScore": 20
}
]
}Configure using CNC Console:
Enable
You can enable this feature by selecting the Enable NF Scoring field in the Settings page of NF Scoring. For more information about enabling the feature through CNC Console, see NF Scoring Configurations.
Configure
The NF Scoring feature can be configured through CNC Console. For more information, see NF Scoring Configurations.
Configure using REST API:
- You can perform the GET and PUT operations on the
http://<nudr-config-host>:<nudr-config-port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/app-info/nfScoringto enable and disable NF Scoring and set the weightage, maximum score, and maximum value for each criteria:{ "enableNFScoring": true, "tps": { "enable": true, "maxScore": 20, "maxTps": 33 }, "serviceHealth": { "enable": true, "maxScore": 30 }, "signallingConnections": { "enable": true, "maxScore": 20, "maxConnections": 40 }, "replicationHealth": { "enable": true, "maxScore": 30 }, "localitySitePreference": { "enable": true, "score": 5 }, "activeAlert": { "enable": true, "criticalAlertWeightage": 2, "majorAlertWeightage": 1, "minorAlertWeightage": 0 }, "customCriteria": [{ "name": "BulkImport", "enable": true, "metricName": "nudr_bulk_import_records_processed_total", "scoringType": "ratio", "maxScore": 20, "maxValue": 20, "weightage": 5 }, { "name": "BulkExport", "enable": true, "metricName": "export_tool_status_total", "scoringType": "ratio", "maxScore": 20, "maxValue": 20, "weightage": 5 }] }The below table provides NF Scoring settings for SLF:Table 2-10 NF Scoring Settings for SLF
Field Name Description Enable NF Scoring Specifies whether to enable or disable the NF Scoring. This is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
TPS Specifies the Transaction Per Second. Enable Enables the TPS. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Max Score Specifies the maximum score of the TPS. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 20
Range: 1 to 100.
Max TPS Specifies the maximum TPS. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Range: 1 to 1000000
Service Health Specifies the Service Health of a site. Enable Enables the Service Health. This is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Max Score Specifies the maximum score of the Service Health. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 30
Range: 1 to 100
Signaling Connections Specifies the Signaling Connections of a site. Enable Enables the Signaling Connections. This is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Max Score Specifies the maximum score of the Signaling Connections. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 20
Range: 1 to 100
Max Connections Specifies the maximum connections. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Range: 1 to 100
Replication Health Specifies the Replication Health of a site. Enable Enables the Replication Health. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Max Score Specifies the maximum score of the Replication Health. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 30
Range: 1 to 100
Locality or Site preference Specifies the Locality or Site Preference. Enable Enables the Locality or Site Preference. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Score Specifies the score of the Locality or Site Preference. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 5
Range: 1 to 100
Active Alert Specifies the Active Alerts of a site. Enable Enables the Active Alert. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Critical Alert Weightage The site with more critical alerts is unhealthy. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 2
Range: 0 to 100
Major Alert Weightage The site with more major alerts is unhealthy. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 1
Range: 0 to 100
Minor Alert Weightage The site with more minor alerts is unhealthy. If enable is set to true then this is a mandatory parameter. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 0
Range: 0 to 100
Custom Criteria Specifies the Custom Criteria of a site. Enable Specifies whether to enable or disable the Custom Criteria. Data Type: Boolean
Default Value: false
Range: true or false
Name Name of the Custom Criteria. The two applicable criteria are Subscriber Bulk Import tool and Subscriber Export tool. Data Type: String
Metric Name Specifies the name of the Metric. Data Type: String
Scoring Type Specifies the scoring type. The two scoring types are ratio and weightage. Data Type: String
Default Scoring Type: ratio
Max Score Specifies the maximum score. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 30
Range: 1 to 100
Max Value Specifies the maximum value. Data Type: Integer
Range: 1 to 10000
Weightage Specifies the weightage of the alert. Data Type: Integer
Default Value: 1
Range: 0 to 100
Note: If the scoring type is ratio the weightage is ignored.
- You can perform the GET operation on the
http://<nudr-config-host>:<nudr-config-port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/nfscoreto fetch overall NF Score and calculated score for each criteria:{ "NFScore": 96.65151515151516, "detailedReport": { "failedFactors": [ { "criteria": "activeAlert", "detail": "failed to calculate activeAlert score" } ], "scoringFactors": [ { "additionalInfo": { "actualValue": 29.95, "configuredValue": 33, "igw_prov": 19.95, "igw_sig": 10.0 }, "calculatedScore": 18.151515151515152, "criteria": "tps", "maxScore": 20 }, { "additionalInfo": { "totalSvcs": 21, "upSvcs": 21 }, "calculatedScore": 30.0, "criteria": "serviceHealth", "maxScore": 30 }, { "additionalInfo": { "actualValue": 17.0, "configuredValue": 40, "igw_prov": 12, "igw_sig": 4 }, "calculatedScore": 8.5, "criteria": "signallingConnections", "maxScore": 20 }, { "additionalInfo": { "availableLinks": 0.0, "totalSites": 0.0 }, "calculatedScore": 0.0, "criteria": "replicationHealth", "maxScore": 30 }, { "calculatedScore": 5.0, "criteria": "localityPreference" }, { "calculatedScore": 20, "criteria": "BulkImport", "maxScore": 20 }, { "calculatedScore": 15, "criteria": "BulkExport", "weightage": 5 } ] } }
Table 2-11 Description of Parameters
| Field Name | Mandatory (M)/Optional(O)/Conditional(C) | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| NF Score | M | Float | The score of a site based on NF specific factors (such as alerts). |
| detailedReport | M | NA | Detailed report of NF Score calculation |
| scoringFactors | M | NA | Includes the factors that contributed to the NF Score |
| criteria | C | NA |
Factors involved in NF Score calculation Criteria are present for a specific factor, if it is enabled for NF Scoring. |
| maxScore | C | Integer |
Maximum score of that factor maxScore is present for a specific factor, if it is enabled for NF Scoring. |
| calculatedScore | C | Float |
Calculated score of that factor calculatedScore are present for a specific factor, if it is enabled for NF Scoring. |
| additionalInfo | O | NA | Additional information related to factor's score calculation. |
| configuredValue | C | Integer |
An expected value configured for a factor. configuredValue is present for a specific factor, if it is enabled for NF Scoring. |
| actualValue | C | Float |
An actual value for a particular factor after doing factor-specific configuration. actualValue is present for a specific factor, if it is enabled for NF Scoring. |
| totalSvcs | C | Integer |
Total configured services. totalSvcs is present when the factor SVC-Health is enabled. |
| upSvcs | C | Integer |
Total running services. upSvcs is present when the factor SVC-Health is enabled. |
| totalSites | C | Integer |
Total configured sites totalSites is present when the factor replicationHealth is enabled. |
| availableLinks | C | Integer |
Total healthy sites. availableLinks is present when the factor replicationHealth is enabled. |
| critical | C | Integer |
Critical alert's contribution to alert's calculated score. This attribute is present when ActiveAlerts are enabled as NF Scoring factor. |
| major | C | Float |
Major alert's contribution to alert's calculated score. This attribute is present when ActiveAlerts are enabled as NF Scoring factor. |
| minor | C | Float |
Minor alert's contribution to alert's calculated score. This attribute is present when ActiveAlerts are enabled as NF Scoring factor. |
| failedFactors | C | Float |
Enabled factors that failed to contribute to NF Score. This attribute is present when an application fails to calculate the score for 1 or more factors. |
| detail | C | NA |
Factor's failure reason. This attribute is present when there are 1 or more failed factors. |
Table 2-12 SLF Deployment NF Scoring for Site 1
| Scoring Factors | Site 1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Configured Value | Calculated Value | Maximum Score | Calculated Score |
| TPS | 33 | 20 | 20 | 12.12 |
| Connections | 40 | 20 | 20 | 10 |
| SVCs | 21 | 21 | 30 | 30 |
| Replication | 30 | 2 | 30 | 2 |
| Custom Criteria Bulk Import | 20 | 405 | 20 | 20 |
| Custom Criteria Bulk Export | 20 | 2 | 20 | 2 |
| Site Preference | 5 | - | 5 | |
| Alerts | 2 | 2 | 4 | |
| Final NF score calculated | - | - | - | 77.12 |
Table 2-13 SLF Deployment NF Scoring for Site 2
| Scoring Factors | Site 2 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Configured Value | Calculated Value | MaximumScore | Calculated Score |
| TPS | 33 | 10 | 20 | 6.06 |
| Connections | 40 | 10 | 20 | 5 |
| SVCs | 21 | 12 | 30 | 17.14 |
| Replication | 30 | 2 | 30 | 2 |
| Custom Criteria Bulk Import | 20 | 100 | 20 | 20 |
| Custom Criteria Bulk Export | 20 | 4 | 20 | 4 |
| Site Preference | 10 | - | - | 10 |
| Alerts | 2 | 3 | - | 6 |
| Final NF score calculated | - | - | - | 58.2 |
The final NF score for Site 1 is 77.12 and Site 2 is 58.2. The preferred is Site 1.
{
"NFScore": 77.12,
"detailedReport": {
"failedFactors": [],
"scoringFactors": [{
"additionalInfo": {
"actualValue": 20,
"configuredValue": 33,
"igw_prov": 10,
"igw_sig": 10
},
"calculatedScore": 12.12,
"criteria": "tps",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"totalSvcs": 21,
"upSvcs": 21
},
"calculatedScore": 30,
"criteria": "serviceHealth",
"maxScore": 30
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"actualValue": 20,
"configuredValue": 40,
"igw_prov": 10,
"igw_sig": 10
},
"calculatedScore": 20,
"criteria": "signallingConnections",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"availableLinks": 2,
"totalSites": 30
},
"calculatedScore": 2,
"criteria": "replicationHealth",
"maxScore": 30
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"critical": -4.0,
"major": 0.0,
"minor": 0.0
},
"calculatedScore": -4.0,
"criteria": "activeAlert"
},
{
"calculatedScore": 5.0,
"criteria": "localityPreference"
},
{
"calculatedScore": 20,
"criteria": "BulkImport",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"calculatedScore": 2,
"criteria": "BulkExport",
"maxScore": 20
}
]
}
} {
"NFScore": 58.12,
"detailedReport": {
"failedFactors": [],
"scoringFactors": [{
"additionalInfo": {
"actualValue": 10,
"configuredValue": 33,
"igw_prov": 5,
"igw_sig": 5
},
"calculatedScore": 6.06,
"criteria": "tps",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"totalSvcs": 21,
"upSvcs": 12
},
"calculatedScore": 17.14,
"criteria": "serviceHealth",
"maxScore": 30
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"actualValue": 10,
"configuredValue": 40,
"igw_prov": 5,
"igw_sig": 5
},
"calculatedScore": 5,
"criteria": "signallingConnections",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"availableLinks": 2,
"totalSites": 30
},
"calculatedScore": 2,
"criteria": "replicationHealth",
"maxScore": 30
},
{
"additionalInfo": {
"critical": -6.0,
"major": 0.0,
"minor": 0.0
},
"calculatedScore": -6.0,
"criteria": "activeAlert"
}
{
"calculatedScore": 10.0,
"criteria": "localityPreference"
},
{
"calculatedScore": 20,
"criteria": "BulkImport",
"maxScore": 20
},
{
"calculatedScore": 4,
"criteria": "BulkExport",
"maxScore": 20
}
]
}
}To Observe
The following alert is introduced for NF Scoring feature:
- NFScoreCalculationFailed
See UDR Alert Details section for more information alerts.
2.15 Converged Quota Support
This section describes the Converged Quota Support feature.
2.15.1 Converged Quota Support for UDR
- Provisioning interface using SOAP/XML
- Bulk provisioning using file import in iXML and CSV format. For more information, see see Bulk Import Operations in iXML Format and Bulk Import Operations in CSV Format.
- N36 signaling interface. For more information, see Policy N36 APIs.
- Provisioning Interface using REST/JSON. For more information, see Provisioning Using REST/JSON.
- On-Demand Migration. For more information, see On-Demand Migration.
- Diameter-Sh. For more information, see Diameter-Sh.
- Migration Tool. For more information, see Migrating Subscriber Data from 4G UDR to 5G UDR.
- Bulk provisioning using file import in iXML and CSV format.
- Provisioning APIs using SOAP and REST
- N36 signaling operations from PCF
- Migration Tool
cnPCRF interacts with 5G UDR for both 4G and 5G signaling data. cnPCRF supports only the N36 interface toward 5G UDR for 4G call flows. The cnUDR must store the quota information under sm-data/umData and sm-data/umDataLimits.
Figure 2-7 Converged Quota Support

Using Provisioning Gateway, 4G provisioning system provisions 4G PCRF data over SOAP/XML interface on 5G UDR. Provisioning Gateway converts SOAP/XML to REST/JSON and forward to 5G UDR. 5G UDR converges the 4G policy quota and dynamic quota data to 5G data model and stores in 5G UDR. When 4G PCRF accesses this data in 5G UDR using Diameter-Sh interface, 5G UDR converts the 5G data to 4G data and respond through the Diameter-Sh interface.
The UDR provides Migration tool, On-Demand Migration and Diameter-Sh support for data transition from 4G to 5G UDR. For more information, see Migrating Subscriber Data from 4G UDR to 5G UDR, On-Demand Migration, and Diameter-Sh.
Migration Tool
The migration tool is an external tool that is used to migrate the subscriber data from source UDR (4G OCUDR) to target UDR (5G UDR). Migration tool is delivered as a separate Helm chart and you must install it manually. The migration tool supports migration of the subscribers in ranges, based on the configuration provided in the Helm chart. Migration tool supports the converged quota feature by default. For more information, see Migration Tool.
Diameter-Sh
- Sh-User Data Request (UDR)
- Sh-Profile Update Request (PUR)
- Sh-Subscribe Notification Request (SNR)
- Sh- Push Notification Request (PNR)
In the converged data model, ETag (Entity Tag) value is used to update quota and dynamic quota and sequence number is used to update subscriber and state entities. Sequence number is used on Diameter-Sh and ETag is used for SBI interface.
Sequence Number
5G UDR uses sequence number for subscriber and state entities that are
present under VSA attributes. Sequence number increments every time the subscriber
or state entities are updated.
E-Tag
- ETag value is 0, if auto create is enabled by default and quota or dynamic quota is created using PUR, SNR, or UDR request.
- When PUR request is sent, the sequence number in the request validates against the ETag value (Example 0). The ETag value is incremented by 1 for each quota or dynamic quota update.
- If two different sequence numbers (Example 2 and 3) are sent during PUR request, the sequence number with the highest value (Example 3) is selected to validate against the ETag value. ETag value increments accordingly.
Diameter-Sh request only sends the sequence number to 5G UDR. 5G UDR updates the versions using the ETag functionality. ETag value is used to update versions for both Diameter-Sh and N36 requests.
Table 2-14 Quota Mapping from 4G UDR to 5G UDR
| 4G UDR Attribute | 5G UDR Parent JSON Attribute | 5G UDR JSON Attribute |
|---|---|---|
| name
Data Type: String |
umData | name
Data Type: String |
| cid
Data Type: String |
umData | limitId
Data Type: String |
| time
Data Type: String |
umData/customAllowedUsage | duration
Data Type: DurationSec |
| totalVolume
Data Type: String |
umData/customAllowedUsage | totalVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| inputVolume
Data Type: String |
umData/customAllowedUsage | downlinkVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| outputVolume
Data Type: String |
umData/customAllowedUsage | uplinkVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| serviceSpecific
Data Type: String |
umData | serviceSpecific
Data Type: Volume |
| nextResetTime
Data Type: String |
umData | resetTime
Data Type: DateTime |
| Type
Data Type: String |
umData | type
Data Type: string |
| grantedTotalVolume
Data Type: String |
umData/grantedUsage | totalVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| grantedInputVolume
Data Type: String |
umData/grantedUsage | downlinkVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| grantedOutputVolume
Data Type: String |
umData/grantedUsage | uplinkVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| grantedTime
Data Type: String |
umData/grantedUsage | duration
Data Type: DurationSec |
| grantedServiceSpecific
Data Type: String |
umData | grantedServiceSpecific
Data Type: string |
| QuotaState
Data Type: String |
umData | quotaState
Data Type: string |
| RefInstanceId
Data Type: String |
umData | refInstanceId
Data Type: string |
| Custom 1-n
Data Type: Data type entered in schema |
umData | custom 1-n
Data Type: Data type entered in schema |
Table 2-15 Quota Mapping from 4G UDR to 5G UDR
| 4G UDR Attribute | 5G UDR Parent JSON Attribute | 5G UDR JSON Attribute |
|---|---|---|
| Type
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | type
Data Type: String |
| name
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | name
Data Type: String |
| InstanceId
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | limitId
Data Type: String |
| Priority
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | priority
Data Type: String |
| InitialTime
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit/usageLimit | duration
Data Type: DurationSec |
| InitialTotalVolume
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit/usageLimit | totalVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| InitialInputVolume
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit/usageLimit | downlinkVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| InitialOutputVolume
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit/usageLimit | uplinkVolume
Data Type: Volume |
| InitialServiceSpecific
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | initialServiceSpecific
Data Type: Volume |
| activationdatetime
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | activationdatetime
Data Type: DateTime |
| expirationdatetime
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | endDate
Data Type: DateTime |
| purchasedatetime
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | startDate
Data Type: DateTime |
| Duration
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | validityDuration
Data Type: DurationSec |
| InterimReportingInterval
Data Type: String |
umDataLimit | interimReportingInterval
Data Type: DurationSec |
| Custom 1-n
Data Type: Data type entered in schema |
umDataLimit | custom 1-n
Data Type:Data type entered in schema |
Mapping Custom Attributes
- Update the attribute mapping using management APIs. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide
- Update the Subscriber Entity Configuration (SEC) for SOAP/XML interface field validation. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Guide and Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Interface Specification Guide.
- Update the sm-data schema. For more information, see " PCF Schema Management" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- Update the SEC for SOAP/XML interface field validation. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Guide and Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Interface Specification Guide.
- Update the VSA schema. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide and Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Interface Specification Guide.
Note:
If the custom fields (under UM-data/UM-dataLimits or subscriber profile/state) are added but not defined in the sm-data schema, UDR accepts the custom fields received in the request payload and skips the schema validation for custom fields.Configuration to Add Quota and Dynamic Quota Version
#Quota version
quotaVersion: 3#Dynamic quota version
DynamicQuotaVersion: 3Adding SEC on Provisioning Gateway
To accept and validate new custom entries, you must add the custom entries to the SEC configuration on provisioning gateway. For more information about adding a new custom entity, see "Subscriber Entity Configuration (SEC)" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Guide.
Adding Schema and Attribute Mapping Table
Note:
For Multiple site deployment, attribute mapping updates using Management APIs must done on each site.Update sm-data Schema for Validation
Validate the added custom entities against schema after the 4G data is converged to 5G data. For more information, see " PCF Schema Management" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Provisioning Using SOAP/XML
Note:
SOAP/XML APIs are used for provisioning 4G only policy data only. SOAP/XML APIs cannot be used for 5G policy data.Provisioning Using REST/JSON
- The 4G subscriber profile fields and state must be under sm-data/VendorSpecific-000111
- Add all 4G quota and dynamic quota information under sm-data/umData and sm-data/umDataLimits respectively.
- All 5G policy data must be under sm-data.
For more information, see "Provisioning Operations for PCF Data" and "4G Policy Data Operations" in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
| Operation Type | Resource URI |
|---|---|
| PUT | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId} |
| GET | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId} |
| DELETE | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId} |
Table 2-16 REST APIs for 4G Policy Data
| Operation Type | Resource Name | REST URI |
|---|---|---|
| PUT, GET |
Update complete 4G policy data or update individual entities Retrieve complete 4G policy data |
{
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa |
| PUT | Update quota row operations | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/usage/quota/row |
| GET | Retrieve quota | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa?fields=usage |
| GET | Retrieve quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/usage/quota/row?name=Q1&cid=11223344 |
| GET | Retrieve quota row fields | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/usage/quota/row?fields=outputvolume&name=Q3&cid=11223344 |
| DELETE | Delete quota | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa?fields=usage |
| DELETE | Delete quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/usage/quota/row |
| PATCH | Patch quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/usage/quota/row |
| PUT | Update dynamic quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/definition/DynamicQuota/row |
| GET | Retrieve dynamic quota | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa?fields=
definition |
| DELETE | Delete dynamic quota | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa?fields=definition |
| DELETE | Delete dynamic quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/msisdn-33123654862/sm-data/vsa/definition/DynamicQuota/row?name=DQ1 |
| PATCH | Patch dynamic quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/definition/DynamicQuota/row |
| GET | Retrieve dynamic quota row | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/definition/DynamicQuota/row?name=Q1&cid=11223344 |
| GET | Retrieve dynamic quota row field | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/definition/DynamicQuota/row?name=DQ3&InstanceId=15678&fields=InstanceId,InitialTotalVolume,InitialInputVolume |
| DELETE | Delete complete 4G policy data | {
apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa?fields=all |
Provisioning Bulk Import Using iXML and CSV
For provisioning bulk import using iXML and CSV, see Bulk Import Operations in iXML Format and Bulk Import Operations in CSV Format.
Policy N36 APIs
If the On-Demand Migration feature is enabled and 4G subscriber information is not available on 5G UDR, 5G UDR reads and provisions the 4G policy sm-data on 5G UDR based on request received from PCRF.
Note:
The APIs mentioned for provisioning operation of policy data must not have the usage and definition information under sm-data/VendorSpecific-000111 content. The usage and definition information must be converted to 5G data and placed under sm-data/umData and sm-data/umDataLimits.2.16 Controlled Shutdown of an Instance
UDR SLF supports controlled shutdown feature to provide the partial or complete isolation of the site from the network so that the operator can perform necessary recovery procedures when required. It helps the operator to perform the recovery procedures as per the requirement.
Note:
Controlled Shutdown feature is supported by UDR only on SLF mode.- Dropping signaling and provisioning requests on Ingressgateway-Sig and Ingressgateway-Prov with error codes.
- Updating the NF status as SUSPENDED at NRF.
- Export is not initiated in the subscriber export tool when the instance is in SHUTDOWN phase. Alert is raised to indicate this state.
- Bulk provisioning operations using subscriber bulk import tool is terminated.
Operational State
- config database
- Ingressgateway-sig common configuration
- Ingressgateway-prov common configuration
Figure 2-8 Operational State of the NF
App-Info
Controlled shutdown feature
controlledshutdown:
operationlStateResourcePath: "/operationalState"
Ephemeral Storage Request Configurations
global:
logStorage: *containersl_ogStorageRequestsRef crictlStorage: *containersCrictlStorageRequestsRef
nfType: udr
enableControlledShutdown: *enableControlledShutDown
Ingress Gateway
# configuring routes
routesConfig:
- id: trafficjnapping_http
uri: http://-ff .Release.Name }}-nudr-drservice:5001
path: /nudr-dr/**
order: 1
metadata:
# oauthValidation route level
oauthValidator:
enabled: *oauthEnabled
# xfccHeaderValidation route level
xfccHeaderValidation:
# When enabled on global section, the same gets referred here
# Set to false, if needs to be disabled for this particular route
validationEnabled: *xfccValidationEnabled
filters:
controlledShutdownFilter:
applicableShutdownStates:
- "COMPLETE SHUTDOWN"For each route you must configure the error code using Helm or REST API.
The REST API is enabled by default and the errorcode mapping for each route is done
by performing a PUT operation using
v1/igw-sig/controlledshutdownerrormapping.
# Controlled shutdown feature
enableControlledShutdown: *enableControlledShutDown
controlledShutdownConfigMode: HELM
controlledShutdownErrorMapping:
routeErrorProfileList :
- routeld: traffic_mapping_http
errorProflleName: "error503"controlshutdownerrormapping URL is loaded with the
SLF group URL as part of ingress gateway as shown below:
- For Ingressgateway-Sig REST API
http://10.75.229.85:30168/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/controlledshutdownerrormappingigw-sig controlshutdownerrormapping{ "routeErrorProfileList": [ { "routeId":"traffic_mapping_http_group", "errorProfileName":"error503" } ] } - For Ingressgateway-Prov REST API
http://10.75.229.85:30168/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-prov/controlledshutdownerrormappingigw-prov controlshutdownerrormapping{ "routeErrorProfileList": [ { "routeId":"traffic_mapping_http_group_prov", "errorProfileName":"error503" }, { "routeId":"traffic_mapping_http_slf_group_prov", "errorProfileName":"error503" } ] }
To Enable
You can enable or disable the control shutdown feature by setting the
enableControlledShutdown parameter to true or false in the
global section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. For more information on this
parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository
Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
You can enable or disable the operation state by setting the
enableControlledShutdown parameter to true or false in the
Global Configurations in the CNC Console. You can configure the operation state of a
site through CNC Console. For more information, see Operational State.
Configure using REST API:
http://10.75.229.206:30240/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to configure the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud
Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb",
"udrServices": "All",
"udsfEnabled": false,
"ingressHttpPort": "",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"autoCreate": true,
"autoEnrolOnSignalling": true,
"etagEnabled": true,
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": false,
"addDefaultBillingDay": true,
"enableControlledShutdown" : true,
"keyType": "imsi",
"keyRange": "2013020001-2013020002",
"nfType": "UDR",
"nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com",
"suppressNotificationEnabled": true,
"configClientConnectTimeout": 1000,
"configClientReadTimeout": 1000,
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": [],
"imsi": [],
"nai": [],
"extid": []
}
}SLF operational state REST API is introduced to make the application COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN or NORMAL.
Perform the PUT operation on the
http://10.75.229.85:30254/udr/nf-common-component/v1/operationalState
{
"operationalState": "NORMAL"
}Perform the GET operation on the
http://10.75.229.85:30254/udr/nf-common-component/v1/operationalState
{
"operationalState": "NORMAL"
}REST API OperationalHistory is introduced to get the history of last five operations that is performed on the operationalState.
Perform the GET operation on the
http://10.75.229.85:30254/udr/nf-common-component/v1/operationalStateHistory
{
"operationalState": "NORMAL",
"operationalStateHistory": [
{
"operationalState": "NORMAL",
"timestamp": "2023-02-02 13:42:16.621639149",
"status": "SUCCESS"
},
{
"operationalState": "COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN",
"timestamp": "2023-02-02 13:42:08.148351775",
"status": "SUCCESS"
},
{
"operationalState": "NORMAL",
"timestamp": "2023-02-02 13:35:07.111230791",
"status": "SUCCESS"
},
{
"operationalState": "COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN",
"timestamp": "2023-02-02 13:33:22.06605161",
"status": "SUCCESS"
}
]
}Perform the GET operation on curl -v -XGET -H "Content-type:
application/json"
'http://ocudr-nudr-config:5001/udr/nf-common-component/v1/operationalStateHistory?limit=3'
to get last three operationalStateHistory.
Note:
You can get maximum of five operationalStateHistory.{
"operationalState": "NORMAL",
"operationalStateHistory": [
{
"operationalState": "NORMAL",
"timestamp": "2023-02-02 13:42:16.621639149",
"status": "SUCCESS"
},
{
"operationalState": "COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN",
"timestamp": "2023-02-02 13:42:08.148351775",
"status": "SUCCESS"
}Note:
- If controlled shutdown is enabled and if the status is COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN, the subscriber export tool rejects any new jobs that is triggered and a metric is raised for the rejection.
- If controlled shutdown is enabled and if the status is COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN, the subscriber bulk import tool terminates the ongoing jobs by generating report of the progress of the job. The jobs is marked as SUSPENDED in the configurationDB, and any new jobs that is triggered is rejected.
To Observe
- nudr_config_operational_status
- export_tool_controlled_shutdown
- nudr_config_operational_status
See UDR Metrics and Alert Details section for more information on metrics and alerts.
2.17 Auto Enrollment and Auto Create Features
This section describes auto enrollment and auto create features on UDR.
2.17.1 Auto Enrollment
UDR has various consumer NFs which store the NF specific data. The Nudr interface is used by the NF such as UDM, PCF, and NEF to access a particular set of the data that is stored in UDR database. The data must be provisioned by a provisioning system before the consumer NF can access the data. The provisioning system sends all the subscriber keys in the request as part of creating data using REST/JSON commands. Once the provisioning is successful the consumer NF can access the created subscriber record using GET or PATCH operations.
Consumer NF such as cnPCRF need UDR to enroll the subscriber record with policy data that is sent on the N36 interface. This is required for subscribers in roaming scenarios, where cnPCRF does a PATCH operation to update the subscriber data. Auto enrollment enables UDR to auto enroll the subscriber if the subscriber record does not exist.
Auto enrollment also supports UDR in creating mandatory attribute smPolicySnssaiData with configured default values when NFs such as cnPCRF does not include smPolicySnssaiData attribute in sm-data.
Figure 2-9 Data Storage Architecture
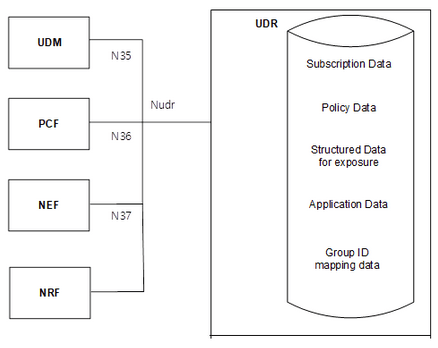
- PATCH on SessionManagementPolicyData
- PUT on UsageMonitoringInformation
The mandatory parameters in SessionManagementPolicyData such as SNSSAI data must be sent in PATCH request as per the 3GPP specifications.
If the mandatory parameters is not available for cnPCRF to send this information or SessionManagementPolicyData resource is not present for the subscriber. UDR supports addition of mandatory attributes with default values under SessionManagementPolicyData.
You can enable or disable the auto enrollment feature by setting the
autoEnrolOnSignalling parameter to true or false in the global
section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file.
- The following enhancements is made for PATCH operation:
Base URI:
{apiRoot}/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data)- If subscriber is not found on UDR database and when a PATCH
request is received with
smPolicySnssaiDataandautoEnrolOnSignallingis set to true, the subscriber is provisioned.If
smPolicySnssaiDatais not present in the request andautoEnrolOnSignallingis set to true, thensmPolicySnssaiDatais created with configured default values and the subscriber is provisioned. - If subscriber is found on UDR database and
SessionManagementPolicyData is not present. When a PATCH request without
smPolicySnssaiDatais received andautoEnrolOnSignallingis set to true, thensmPolicySnssaiDatais created with configured default values and the SessionManagementPolicyData is created.If
smPolicySnssaiDatais present in the request, SessionManagementPolicyData is created.
Figure 2-10 PATCH operation for Auto Enrollment
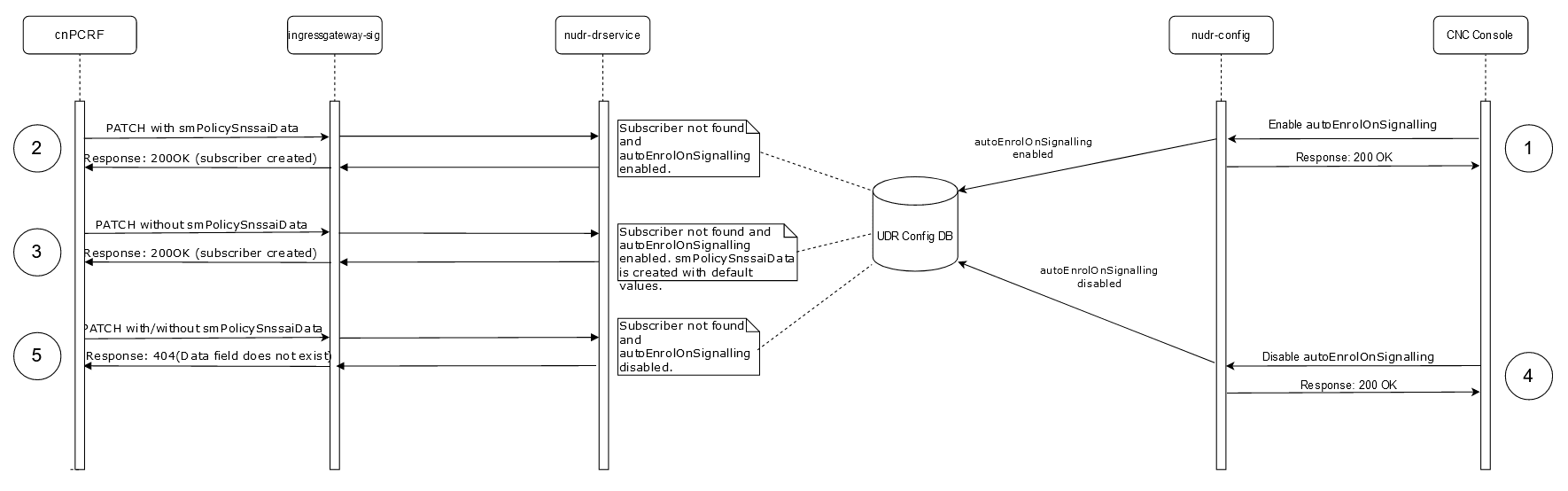
- If subscriber is not found on UDR database and when a PATCH
request is received with
- The following enhancements is made for PUT operation:
Base URI:
{apiRoot}/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data/{usageMonId}- If subscriber is not found on UDR database, when a PUT
request is received on
umDataandautoEnrolOnSignallingis set to true, then the subscriber is created with the given payload underumDatatag of SessionManagementPolicyData along with configured default values ofsmPolicySnssaiData. - If subscriber is found on UDR database and
SessionManagementPolicyData is not present, when a PUT request is
received on
umDataandautoEnrolOnSignallingis set to true, then the SessionManagementPolicyData is created with the given payload underumDatatag of SessionManagementPolicyData along with default values of smPolicySnssaiData.
Figure 2-11 PUT operation for Auto Enrollment
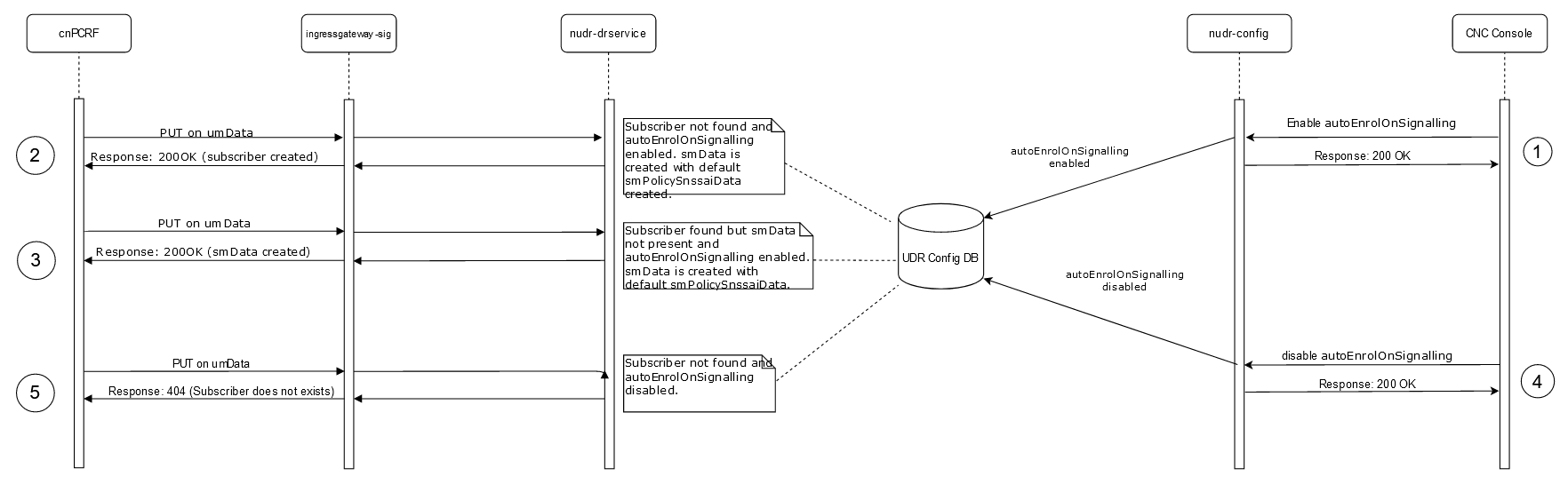
- If subscriber is not found on UDR database, when a PUT
request is received on
To Enable
autoEnrolOnSignalling parameter to true or false in the global
section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. For more information on this
parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository
Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Note:
This flag is applicable only for N36 signaling requests.You can enable or disable the feature by setting the
autoEnrolOnSignalling parameter to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console.
Configure using REST API
http://10.75.215.124:32523/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to configure the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud
Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb",
"udrServices": "All",
"udsfEnabled": false,
"ingressHttpPort": "",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"autoCreate": true,
"autoEnrolOnSignalling": true,
"etagEnabled": true,
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": false,
"addDefaultBillingDay": true,
"enableControlledShutdown" : true,
"keyType": "imsi",
"keyRange": "2013020001-2013020002",
"nfType": "UDR",
"nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com",
"suppressNotificationEnabled": true,
"configClientConnectTimeout": 1000,
"configClientReadTimeout": 1000,
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": [],
"imsi": [],
"nai": [],
"extid": []
}
}To Observe
- udr_default_smPolicySnssaiData_creation
- total_auto_enrol_requests
- udr_auto_enrol_subscriber_success
See UDR Metrics section for information on metrics.
Logging
Info loggers is added when default value of smPolicySnssaiData and SNSSAI is applied for the requests.
2.17.2 Auto Create
The auto create feature is used when a provisioning system updates a part of subscriber data instead of creating the subscriber profile, keys, or the policy data. In this feature the subscriber record is auto created on UDR with the information available in the provisioning request.
The feature is applicable from Provisioning Gateway. Provisioning Gateway supports SOAP/XML interface, when the provisioning systems does a PUT operation on policy data instead of a POST operation, the PUT operation auto creates the subscriber record.
Figure 2-12 Auto Create
To Enable
autoCreate parameter to true or false in the global section of
the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. For more information on this parameter, see
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository
Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Note:
This flag is applicable only for provisioning and diameter requests.You can enable or disable the feature by setting the autoCreate
parameter to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console.
Configure using REST API
http://10.75.215.124:32523/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to configure the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud
Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb",
"udrServices": "All",
"udsfEnabled": false,
"ingressHttpPort": "",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"autoCreate": true,
"autoEnrolOnSignalling": true,
"etagEnabled": true,
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": false,
"addDefaultBillingDay": true,
"enableControlledShutdown" : true,
"keyType": "imsi",
"keyRange": "2013020001-2013020002",
"nfType": "UDR",
"nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com",
"suppressNotificationEnabled": true,
"configClientConnectTimeout": 1000,
"configClientReadTimeout": 1000,
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": [],
"imsi": [],
"nai": [],
"extid": []
}
}Table 2-17 Supported APIs for Auto Create
| Operation Type | Resource Name | REST URI |
|---|---|---|
| PUT | ProfileData | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/profile-data/{ue-id} |
| PUT | AM,SM,UEPolicySet | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId} |
| PUT | Subscriber/Quota/State/DynamicQuota | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa |
| PATCH | Subscriber | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/{ueId}/sm-data/vsa/subscriber |
To Observe
See UDR Metrics section for information on metrics.
2.18 ETag (Entity Tag) support for UDR
ETag (Entity Tag) support for UDR helps to make sure that the update is successful only when the consumer has the latest set of data, which is determined by the ETag value received at UDR. When two different Cloud Native Policy and Charging Rules Function (cnPCRF) are connected to UDR in a georedundant setup and both the cnPCRF are updating the UsageMonData for the same subscriber simultaneously, there is possibility of data loss as the update can overwrite each other.
ETag is introduced in the HTTP header to resolve this data loss. When you send a GET sm-data request to update the UsageMonData, the ETag header with default value 0 is attached with the sm-data and added in the GET sm-data response. This ETag value is used in PUT or PATCH update request with if-match header to maintain concurrency control.
When the PUT or PATCH update request are received by database with if-match header, the database compares the header ETag value with the value attached with the sm-data. If both the values match, the request is processed and the ETag is updated with a different value, for example: 1, and this updated value is sent back in the PUT or PATCH response. If the ETag value does not match, the data update fails with error code 412 (etag out of sync). All provisioning and signaling operations to the sm-data will increment the ETag value.
Figure 2-13 ETag in HTTP response

In the call flow above, If both PCRF 1 and PCRF 2 sends a GET sm-data request to update the UsageMonData, both the cnPCRFs receive data with ETag value "0". When cnPCRF 1 send a PUT or PATCH request with "if-match" in the request header, the ETag value is validated by the database and data is updated with new Etag value "1". If cnPCRF 2 tries to update UsageMonData with older ETag value "0", UDR rejects the request with 412 error code (etag out of sync). The cnPCRF need to fetch the updated sm-data from UDR and retry the request with the updated ETag value to successfully update the data.
When the request is send with "If-None-Match" scenario to find if the latest data is available in UDR. If-None-Match is successful the UDR has the latest data and this data need to be send to the cnPCRF. If-None-Match is failed the UDR has the older data and UDR send 304 response without any content in the response.
ETag in HTTP Response Scenarios
ETag for GET Response
GET /nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/imsi-450081000000018/sm-data HTTP/2
Host: ocudr-ingressgateway-sigHTTP/2 200 OK
date: Wed, 11 Jan 2023 09:59:03 GMT
ETag: "0"
Content-Length: 546
Content-type: application/jsonGET /nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/imsi-450081000000018/sm-data HTTP/2
Host: ocudr-ingressgateway-sig
if-none-match: "1"HTTP/2 200 OK
date: Wed, 11 Jan 2023 09:59:03 GMT
ETag: "0"
Content-Length: 546
Content-type: application/jsonGET /nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/imsi-450081000000018/sm-data HTTP/2
Host: ocudr-ingressgateway-sig
if-none-match: "0"HTTP/2 304
date: Wed, 11 Jan 2023 09:59:03 GMT
Content-type: application/jsonETag for PATCH operation
PATCH /nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/imsi-450081000000018/sm-data HTTP/2
Host: ocudr-ingressgateway-sig
If-Match: "0"
Content-Length: 496
Content-type: application/jsonHTTP/2 204 No Content
date: Wed, 11 Jan 2023 09:59:16 GMT
ETag: "1"
Content-Length: 0PATCH /nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/imsi-450081000000018/sm-data HTTP/2
Host: ocudr-ingressgateway-sig
If-Match: "2"
Content-Length: 496
Content-type: application/json HTTP/2 412
date: Wed, 11 Jan 2023 09:59:44 GMT
Content-Length: 0Etag Notifications
When usage monitoring data update is complete, UDR sends updated ETag notifications header to the consumer about the current state of the usage monitoring data. This enables the consumer to update the ETag values in the subsequent update operations.
Figure 2-14 Etag Notifications for Provisioning Requests
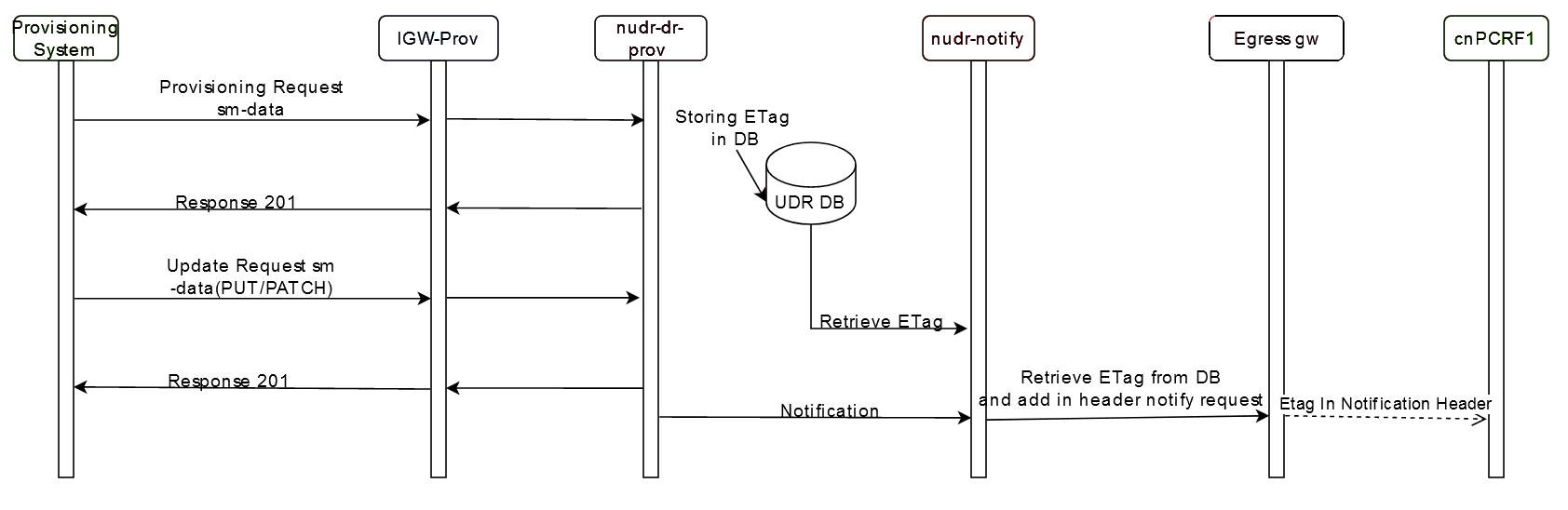
Figure 2-15 Notification for Signaling Requests
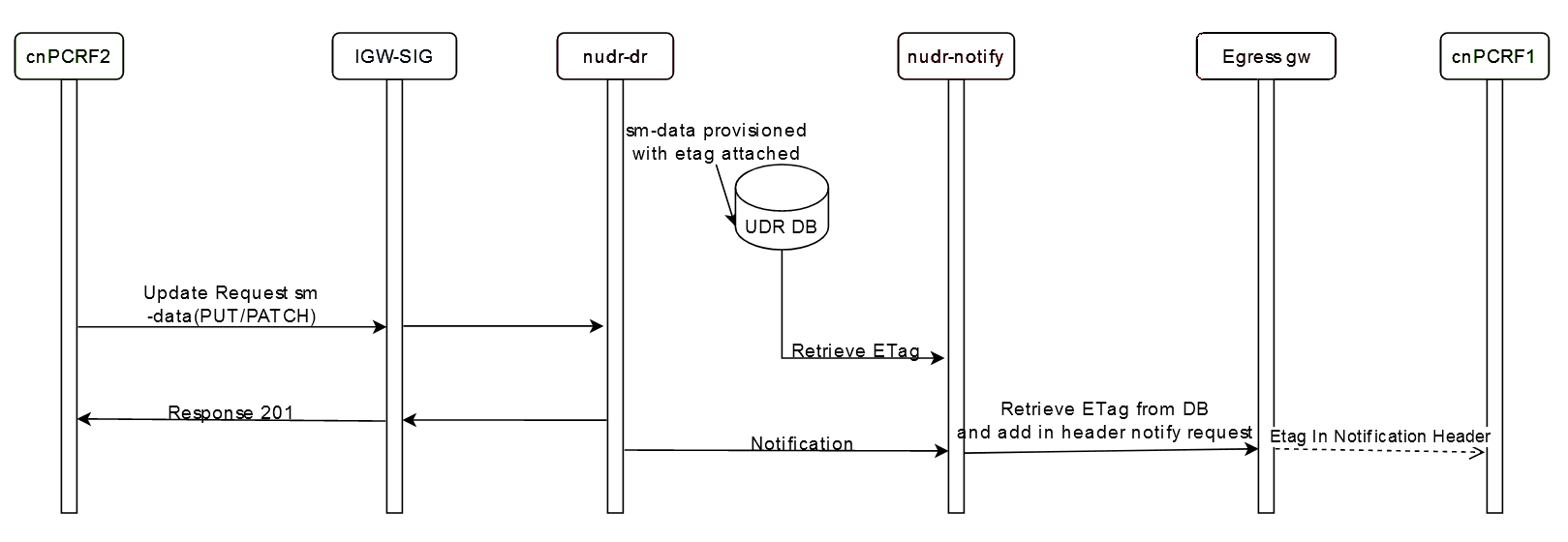
To Enable
etagEnabled parameter to true or false in the global section of
the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. For more information on this parameter, see
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository
Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery
Guide.global:
# Flag to enable/disable the addition of etag
etagEnabled: trueYou can enable or disable the feature by setting the etagEnabled
parameter to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console.
Configure using REST API:
http://nudr-config-service:PORT/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to configure the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud
Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb",
"udrServices": "All",
"udsfEnabled": false,
"ingressHttpPort": "",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"autoCreate": true,
"autoEnrolOnSignalling": true,
"etagEnabled": true,
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": false,
"addDefaultBillingDay": true,
"enableControlledShutdown" : true,
"keyType": "imsi",
"keyRange": "2013020001-2013020002",
"nfType": "UDR",
"nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com",
"suppressNotificationEnabled": true,
"configClientConnectTimeout": 1000,
"configClientReadTimeout": 1000,
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": [],
"imsi": [],
"nai": [],
"extid": []
}
}- PATCH:
https://localhost:9443/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/msisdn-1111111111/sm-data - PUT and DELETE:
https://localhost:9443/nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/msisdn-1111111111/sm-data/mk1
- PUT:
http://localhost:8080/nudr-dr-prov/v2/policy-data/msisdn-461772271137732
To Observe
- udr_etag_rest_request_total
- udr_etag_rest_response_total
- nudr_notif_etag_notifications_sent_total
See UDR Metrics section for more information on metrics.
Logging
Logs are generated only when there is a mismatch of the ETag value.
Upgrade and Rollback Support
etagEnabled flag set to true the below scenarios can occur:
- The new data created will have ETag value generated and attached to the data and the subsequent update operations will use this Etag value.
- The existing data which does not have ETag value attached, will send the default ETag value 0 in GET response header and new a ETag value is generated and attached to the data in the next update operation.
When rollback is performed on UDR to the previous release version, if there is ETag value attached to the data, the GET response does not add the ETag value in the response header and ETag validation is not performed for subsequent update operations even if the "If-match" header is sent in the request.
2.19 Subscriber Export Tool
- Supports configuration on periodicity of export and export time
- Supports monitoring the export status of the subscriber data
- Supports transfer of exported files in .csv, .exml, or .txt format to the remote server
- Supports deletion of exported files from PVC (Persistent Volume Claim) when files are successfully exported to the remote server
- Supports on-demand export of the subscriber data
- Supports secure transfer of exported files to the remote server using Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
Scheduling Subscriber Export Tool
- DAILY
- WEEKLY
- MONTHLY
- ONE TIME (used for ondemand export of subscriber data)
The start time of the export must be configured along with the configured frequency. You must use day-month-year-hours-minutes-seconds (dd-MM-YYYY hh:mm:ss) and 24 hours format for configuration. For more information, see Customizing Subscriber Export Tool.
2.19.1 Supports Export of SLF and EIR Subscriber Database
This feature supports periodic exporting of SLF subscriber data into Comma Separated Value (CSV) file format and supports periodic exporting of EIR subscriber database containing all International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI) and associated International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), and Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) using the subscriber export tool. The subscriber export tool is scheduled for periodic and on-demand runs and is deployed as a stand-alone tool. It also supports dynamic configuration of periodicity of export. For more information on subscriber export tool, see Subscriber Export Tool.
Configure using CNC Console:
You can configure different parameters of subscriber export tool using CNC Console. For more information, see Subscriber Export Tool Configurations in CNC Console.
Configure using REST API:
You can perform the GET and PUT operations to configure the feature. For more information about REST based APIs, see the Configuration APIs for UDR Microservices section in the Configuration API Specification chapter of the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Observe
See UDR Metrics and Alert Details sections for more information on metrics and configurable parameters, respectively.
2.19.1.1 Exporting SLF Subscriber Database
bash-4.4$ cat 2022-10-13-07-34-10-012118459_SLFSegment1.txt
accountId,imsi,nai,msisdn,extid,SLFGroupName,CHFGroupId
10000000000000001001000002,1001000002,,1001000002,,IMSGrp2,
10000000000000001001000004,1001000004,,1001000004,,IMSGrp4,timestamp_<ConfigurableFileName>.<configurable extension>The maximum file size for each exported file is 1 GB. If the exported file exceeds the maximum limit, then the file will split into multiple files.
- 2022-09-21-16-50-01-578894500_SLFTestSegment-1.txt → First set of subscribers
- 2022-09-21-16-50-01-578894500_SLFTestSegment-2.txt → Second set of subscribers
- 2022-09-21-16-50-01-578894500_SLFTestSegment.txt → Last set of subscribers
2.19.1.2 Exporting EIR Subscriber Database
bash-4.4$ cat 2022-11-12-21-10-00-211378929_EIRTestSegment.txt IMEI,SVN,ALLOW,GRAY,BLOCK,IMSI1,IMSI2,IMSI3,IMSI4,IMSI5,MSISDN1,MSISDN2,MSISDN3,MSISDN4,MSISDN5
111111111111111,0,y,y,y,1111111121,1111111131,0,0,0,11111111113,1111111112,0,0,0Note:
Multiple value delimiters are not applicable for EIR export, it is applicable only for SLF export.timestamp_<ConfigurableFileName>.<configurable extension>The count of IMSIs and MSISDNs are configurable. For example, if five IMSIs and MSISDNs are configured but not provisioned for that IMEI, then 0 is used.
The maximum file size for each exported file is 1 GB. If the exported file exceeds the maximum limit, then the file will split into multiple files.
- 2022-11-12-21-10-00-211378929_EIRTestSegment.txt-1.txt → First set of subscribers
- 2022-11-12-21-10-00-211378929_EIRTestSegment.txt-2.txt → Second set of subscribers
2.19.2 Support for EXML Format
- Supports configuring the export file to .exml format
- Supports configuration on periodicity of export and export time
- Supports monitoring the export status of the subscriber data
- Supports transfer of exported files in .exml format to the remote
server using
sftpEnabledflag. - Supports the deletion of exported files from PVC (Persistent Volume
Claim) when files are successfully exported to the remote server using
deletePVCflag.
Note:
When EXML file is generated using nudr-export-tool micro service, you must convert the EXML file to ixml file using ixml converter tool from 4G UDR. Once the file is converted to ixml format, use nudr-bulk-import micro service for import.- MSISDN
- IMSI
- NAI
- EXTID
- ACCOUNTID
Export of 4G Policy Data
- Export the total range of 4G policy subscriber data from the 5G UDR database
- Export of selected range of 4G policy subscriber data from the 5G UDR database
Export the Total Range of Subscriber Data
EXPORT_TOOL_CFG payload as
follows:
Table 2-18 Export Tool Parameter Values
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| exportMode | EXML_EXPORT |
| fileExtension | .exml |
| subscriberRangeEnabled | false |
Configure using REST API:
http://10.75.229.152:31964/nudr-config/v1/udr.exporttool.cfg/EXPORT_TOOL_CFG
to export the total range of subscriber data. For more information, see Oracle
Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"fixedDumpFileNamePrefix": "policydata",
"remoteUserName": "cloud-user",
"exportMode": "EXML_EXPORT",
"remotePath": "/home/cloud-user/ocudr/",
"pollingInterval": "1",
"msisdnCount": 5,
"pvcPath": "/home/udruser/export",
"fieldDelimiter": ",",
"serverPort": 22,
"multiValuedelimiter": "|",
"serverHost": "10.75.229.18",
"subscriberExportRange": {
"keyType": "msisdn",
"subscriberRanges": [
"33123654860-33123654864",
"33123654865-33123654870",
"33123654871-33123654874",
"33123654875-3123654880",
"33123654881-33123654885"
]
},
"subscriberRangeEnabled": false,
"fileExtension": ".exml",
"deleteFromPVC": true,
"sftpExportEnabled": false,
"startTime": "17/11/2022 07:02:04",
"imsiCount": 5,
"newFilePerRangeEnabled": false,
"frequencyOfPeriodicDump": "ONE_TIME",
"maxNumberOfDumps": 1
}Note:
For EXML mode,multiValuedelimiter and
fieldDelimiter parameters are not applicable.
Range Based Export of Subscriber Data
Range based support helps to migrate the 4G policy subscriber data to 5G UDR in a phase manner. This support is available for Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) or International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) key types. You can configure a single key (MSISDN or IMSI) with a maximum range support of five ranges per key.
- Export of 4G policy subscriber data to a single exml file.
- Export of 4G policy subscriber data to multiple exml files for each range.
Export of 4G Policy Subscriber Data to a Single EXML Files.
EXPORT_TOOL_CFG
payload as follows:
Table 2-19 Export Tool Parameter Values
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| subscriberRangeEnabled | true |
| exportMode | EXML_EXPORT |
| fileExtension | .exml |
| keyType | MSISDN or IMSI |
| subscriberRanges |
|
Configure using REST API:
http://10.75.229.152:31964/nudr-config/v1/udr.exporttool.cfg/EXPORT_TOOL_CFG
to export the subscriber data to a single exml file. For more information, see
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST
Specification
Guide.{
"fixedDumpFileNamePrefix": "policydata",
"remoteUserName": "cloud-user",
"exportMode": "EXML_EXPORT",
"remotePath": "/home/cloud-user/ocudr/",
"pollingInterval": "1",
"msisdnCount": 5,
"pvcPath": "/home/udruser/export",
"fieldDelimiter": ",",
"serverPort": 22,
"multiValuedelimiter": "|",
"serverHost": "10.75.229.18",
"subscriberExportRange": {
"keyType": "msisdn",
"subscriberRanges": [
"33123654860-33123654864",
"33123654865-33123654870",
"33123654871-33123654874",
"33123654875-3123654880",
"33123654881-33123654885"
]
},
"subscriberRangeEnabled": true,
"fileExtension": ".exml",
"deleteFromPVC": true,
"sftpExportEnabled": false,
"startTime": "17/11/2022 07:02:04",
"imsiCount": 5,
"newFilePerRangeEnabled": false,
"frequencyOfPeriodicDump": "ONE_TIME",
"maxNumberOfDumps": 1
}Export of 4G Policy Subscriber Data to Multiple Exml File
EXPORT_TOOL_CFG
payload as follows:
Table 2-20 Export Tool Parameter Values
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| subscriberRangeEnabled | true |
| newFilePerRangeEnabled | true |
| exportMode | EXML_EXPORT |
| fileExtension | .exml |
| keyType | MSISDN or IMSI |
| subscriberRanges |
|
Note:
To support multiple exml files, you must enable bothsubscriberRangeEnabled and
newFilePerRangeEnabled parameters to true.
Configure using REST API:
http://10.75.229.152:31964/nudr-config/v1/udr.exporttool.cfg/EXPORT_TOOL_CFG
to export the subscriber data to multiple exml files. For more information, see
Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST
Specification
Guide.{
"fixedDumpFileNamePrefix": "policydata",
"remoteUserName": "cloud-user",
"exportMode": "EXML_EXPORT",
"remotePath": "/home/cloud-user/ocudr/",
"pollingInterval": "1",
"msisdnCount": 5,
"pvcPath": "/home/udruser/export",
"fieldDelimiter": ",",
"serverPort": 22,
"multiValuedelimiter": "|",
"serverHost": "10.75.229.18",
"subscriberExportRange": {
"keyType": "msisdn",
"subscriberRanges": [
"33123654860-33123654864",
"33123654865-33123654870",
"33123654871-33123654874",
"33123654875-3123654880",
"33123654881-33123654885"
]
},
"subscriberRangeEnabled": true,
"fileExtension": ".exml",
"deleteFromPVC": true,
"sftpExportEnabled": false,
"startTime": "17/11/2022 07:02:04",
"imsiCount": 5,
"newFilePerRangeEnabled": true,
"frequencyOfPeriodicDump": "ONE_TIME",
"maxNumberOfDumps": 1
}Configure using CNC Console:
You can configure different EXMLsupport parameters in the subscriber export tool using CNC Console. For more information, see Subscriber Export Tool Configurations in CNC Console.
For more information on configuring subscriber export tool, see Customizing Subscriber Export Tool.
2.19.3 Secure File Transfer Support for Subscriber Export Tool
Subscriber export tool support the capability to securely transfer the exported data to a remote server using Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP).
To Enable using REST API:
http://10.75.215.124:32523/nudr-config/v1/udr.exporttool.cfg/EXPORT_TOOL_CFG
to configure the subscriber export tool and enable SFTP. For more information, see
Customizing Subscriber Export Tool and Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data
Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"fixedDumpFileNamePrefix": "SLFTestSegment",
"remoteUserName": "cloud-user",
"exportMode": "PDBI_EXPORT",
"remotePath": "/home/cloud-user/jaipal/",
"pollingInterval": "*/60 * * * * *",
"msisdnCount": 5,
"pvcPath": "/home/udruser/export",
"fieldDelimiter": ",",
"serverPort": "22",
"multiValuedelimiter": "|",
"serverHost": "10.75.229.18",
"fileExtension": ".txt",
"deleteFromPVC": true,
"sftpExportEnabled": true,
"startTime": "14/09/2022 17:32:10",
"imsiCount": 5,
"frequencyOfPeriodicDump": "DAILY",
"maxNumberOfDumps": 5
}To Enable using CNC Console or Helm Configuration:
- You can enable or disable the SFTP by setting the
sftpDetails.sftpExportEnabledparameter to true or false in custom-value.yaml file of the subscriber export tool. For more information on the parameters, see Customizing Subscriber Export Tool.sftpDetails: host: 10.75.229.18 port: 22 username: cloud-user path: /home/cloud-user/jaipal/ sftpExportEnabled: true deleteFromPvc: true pollingInterval: "*/60 * * * * *" secrets: privatekey: name: ocudr-ssh-private-key publickey: name: ocudr-ssh-public-key fileSizeCheck: false transferProtocol: sftpNote:
- transferProtocol: Transfers the files to remote location. The default protocol is SFTP. The two types of protocols supported are SFTP and SCP.
- fileSizeCheck: Checks the file size of the remote server once the file is successfully transferred to remote location. This confirms that the full log file is transferred to the remote location. This is an optional flag. If the flag to set to true, application will fetch the file sizee from the same remote location path.
- You can disable or enable the feature by setting the
RemoteTransferEnabledparameter to true or false in the Subscriber Export Tool Configurations in the CNC Console.
Note:
Perform the below procedure only if SFTP is enabled.kubectl create secret generic ocudr-ssh-private-key --from-file=id_rsa=/home/cloud-user/ocudr/secrets/id_rsa -n <namespace>
kubectl create secret generic ocudr-ssh-public-key --from-file=id_rsa.pub=/home/cloud-user/ocudr/secrets/id_rsa.pub -n <namespace>2.19.4 Installing Subscriber Export Tool
You can install the Subscriber Export Tool using helm. While installing the export tool, the "exporttoolpersistentclaim" PVC for bulk import container is created.
Before installing the Subscriber Export Tool using helm charts, you are required to configure its parameters in the nudr-export-tool-custom-values.yaml. For information about the Subscriber Export Tool configurable parameters, see Customizing Subscriber Export Tool.
Fresh Installation of the Subscriber Export Tool
- Extract the Subscriber Export Tool helm charts from the
software or CSAR package and run the following
command:
helm install <release name for export tool> -n <udr/slf namespace> nudr-export-tool/ -f nudr-export-tool-custom-values.yaml - Example of the Subscriber Export Tool pod deployed in UDR/SLF
namespace is given below:

Note:
Upgrading of the Subscriber Export Tool is not supported. Only clean installation of the Subscriber Export Tool is supported, all older configurations will be lost during clean installation.For scheduling the subscriber data export, see Scheduling Subscriber Export Tool in Subscriber Export Tool.
Installing of the Subscriber Export Tool on Multiple Sites
Note:
Follow this section to fresh install the Subscriber Export Tool on two-sites.Before installing the Subscriber Export Tool on site 2, you must have the Subscriber Export Tool installed in site 1.
If the Subscriber Export Tool needs to be deployed in site 2, ensure no export tool jobs are running in site 1 until the Subscriber Export Tool is deployed in site 2.
- Perform the following steps to install the Subscriber Export Tool in multiple
sites:
- Make sure the following tables are available across all the
sites before installing the Subscriber Export Tool on site 2.
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE
- If tables are missing from one of the sites, run the
following commands from the site where tables exist. Perform
georeplication recovery if there is replication failure:
Note:
Do not run the commands if tables are available across all the sites.- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_SEQ;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_SEQ;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_SEQ;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE;
- Install the Subscriber Export Tool on site 2, refer to Fresh Installation of the Subscriber Export Tool.
- Ensure that the following tables are replicated across all
the sites after Subscriber Export Tool is deployed on site 2:
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE
- Make sure the following tables are available across all the
sites before installing the Subscriber Export Tool on site 2.
Reinstallation of the Subscriber Export Tool on Multiple Sites
Note:
Follow this section if:- You are reinstalling the Subscriber Export Tool from an older release version to higher release version and vice versa.
- You are reinstalling the Subscriber Export Tool in the same release version.
- Perform the following steps to reinstall the Subscriber Export Tool in multiple
sites.
- Run the following command to uninstall the Subscriber
Export Tool from all the
sites.
helm uninstall <release name> -n <namespace> - Install the Subscriber Export Tool on two-sites. To identify the order of Subscriber Export Tool installation, see "Upgrade of Multiple Site Deployments" section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
- Run the following command to uninstall the Subscriber
Export Tool from all the
sites.
-
Ensure that the following tables are available across all the sites before installing the Subscriber Export Tool on site 1.
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE
-
If tables are missing from one of the sites, run the following commands from the site where tables exist. Perform georeplication recovery if there is replication failure:
Note:
Do not run the commands if tables are available across all the sites.- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_SEQ;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_SEQ;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_SEQ;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION;
- DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE;
-
Install the Subscriber Export Tool on site 1, refer to Fresh Installation of the Subscriber Export Tool.
Note:
Make sure that there are no export tool job running on site1 until the Subscriber Export Tool is deployed on site 2. -
Ensure that the following tables are replicated across all the sites after the Subscriber Export Tool is installed on site 1:
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_SEQ
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_CONTEXT
- EXPORT_BATCH_STEP_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION_PARAMS
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_EXECUTION
- EXPORT_BATCH_JOB_INSTANCE
- Perform the steps from 2 to 5 to install the Subscriber Export Tool on site 2.
2.19.5 Customizing Subscriber Export Tool
The following table lists the user parameters for installing and customizing the subscriber export tool.
Table 2-21 Subscriber Export Tool Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default value | Range or Possible Values (If applicable) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| global.dockerRegistry | Docker registry from where the images are pulled | ocudr-registry.us.abc.com:5000/ocudr | NA | NA |
| global.mysql.dbServiceName | Database service to connect | mysql-connectivity-service.occne-infra | NA | NA |
| global.mysql.port | Port for database service connection | 3306 | NA | NA |
| global.serviceAccountName | The entire pod should be associated with the serviceaccount used for ocudr deployment. | ocudr-serviceaccount | NA | NA |
| preInstall.image.name | Image name for the nudr-export-tool-prehook pod which will take care of DB and table creation for UDR deployment. | nudr_export_tool_pre_install_hook | NA | NA |
| preInstall.image.tag | Image version for nudr-export-tool-pre-install-hook pod image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| preInstall.config.logLevel | Log level for preinstall hook pod | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
NA |
| postUpgrade.image.name | Image name for the nudr-export-tool-post-upgrade pod which will take care of DB and table creation for UDR deployment. | nudr_export_tool_post_upgrade_hook | NA | NA |
| postUpgrade.image.tag | Image version for nudr_export_tool_post_upgrade_hook pod image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| postUpgrade.config.logLevel | Log level for postUpgrade hook pod | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.cpu | CPU limit for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well. | 1 | NA | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.memory | Memory limit for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well. | 1Gi | NA | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.ephemeral-storage | Ephemeral Storage limits for hook pods | 1024Mi | Unit MB | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.cpu | CPU requests for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well. | 0.5 | NA | The cpu to be allocated for hooks during deployment |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.memory | Memory requests for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well. | 0.5Gi | NA | The memory to be allocated for hooks during deployment |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.ephemeral-storage | Ephemeral Storage request for hook pods | 72Mi | Unit MB | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.tolerations | When global.tolerationSetting is ENABLED configure tolerations here. | [] | Example:
tolerations:
|
NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion | Node Selector API version setting | v1 | Allowed Values:
|
NA |
| gloabl.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector.nodeKey |
NodeSelector key configuration for UDR hooks, This excludes the common service hooks. When hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration will come into use. |
' ' | Valid key for a label for a particular node | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector.nodeValue |
NodeSelector Value configuration for UDR hooks, This excludes the common service hooks NodeSelector Value configuration for UDR hooks, This excludes the common service hooks |
' ' | Valid value pair for the above key for a label for a particular node | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector |
NodeSelector configuration when hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion at micro service level is set to v2 Uncomment and use this configuration when required or keep this commented. |
{} | Valid key value pair matching a node for nodeSelection by a pod | |
| dbCredSecretName | Database Credentioal Secret Name | ocudr-secrets | NA | NA |
| configServerEnable | Enable configuration updates via config REST APIs | true | true or false | NA |
| customExtension.allResources.labels | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to all the OCUDR k8s resources | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.allResources.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to all the OCUDR k8s resources | null | NA | ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section |
| customExtension.lbServices.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.lbServices.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.lbDeployments.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR Deployments that are associated to a Service which is of Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.lbDeployments.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR Deployments that are associated to a Service which is of Load Balancer type | null | NA | ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section |
| customExtension.nonlbServices.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as not Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbServices.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as not Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbDeployments.labels | CustomLabels that needs to be added to OCUDR Deployments that are associated to a Service which is not of Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbDeployments.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR Deployments that are associated to a Service which is not of Load Balancer type | null | NA | ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section |
| extraContainers | Configuration to enable debug tool container | DISABLED | DISABLED or ENABLED | NA |
| extraContainerTpl | The template for extraContainer will be defined in this configuration. For now we have the debugContainer template defined here. Applicable for all microservices under ocudr umbrella. |
|
NA | NA |
| extraContainersVolumesTpl | Debug container volume template | - name: debug-tools-dir emptyDir: medium:
Memory sizeLimit: "4Gi" |
NA | NA |
| image.name | Docker Image name | nudr_export_tool | NA | NA |
| image.tag | Tag of Image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| image.pullPolicy | This setting will tell if image need to be pulled or not | IfNotPresent | Possible Values -
Always IfNotPresent Never |
NA |
| createExportToolPVC.name | Name of PVC | exporttoolpersistentclaim | NA | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.storageClassName | Storage class name for PVC | standard |
Possible Values - standard |
NA |
| createExportToolPVC.storage | Storage allocation for PVC | 10Gi | NA | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.pathLocation | Path mounted on PVC for export file generation | /home/udruser/export | NA | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.fileName | Fixed file name suffix for export dump files genarted | SLFTestSegment | NA | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.fileExtension | Export file extension | .txt | .csv/.txt | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.fieldDelimiter | Delimiter used in dump files to separate out different fields | , | NA | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.multivalueDelimiter | Delimiter used in dump files to separate out multiple values in a single field | | | NA | NA |
| createExportToolPVC.fileSize | File size of the generated CSV files. Beyond this limit there will be a new file generated Do not change this value, this is for Engineering. | 1GB | NA | NA |
| service.type | UDR service type | ClusterIP |
Possbile Values- ClusterIP NodePort LoadBalancer |
The kubernetes service type for exposing UDR
deployment
Recommends to be set as ClusterIP default value always |
| service.port.http | HTTP port | 5001 | NA | The http port to be used in notify service to receive signals from nudr-notify-service pod. |
| service.port.management | bulk import Management port | 9000 | NA | The actuator management port to be used for notify service |
| service.customExtension.labels | Custom Labels that need to be added tonudr-diameterproxyspecific Service. | null | NA | This can be used to add custom label(s) to nudr-diameterproxy Service |
| service.customExtension.annotations | Custom Annotations that need to be added to nudr-diameterproxy specific Services. | null | NA | This can be used to add custom annotation(s) to nudr-diameterproxy Service |
| deployment.replicaCount | Number of replicas for export tool | 1 | NA | NA |
| deployment.customExtension.labels | Custom Labels that need to be added to nudr-diameterproxy specific Deployment. | null | NA | This can be used to add custom label(s) to nudr-diameterproxy Deployment |
| deployment.customExtension.annotations | Custom Annotations that need to be added to nudr-diameterproxyspecific Deployment | null | NA | This can be used to add custom annotation(s) to nudr-diameterproxy Deployment |
| hikari.poolsize | Mysql Connection pool size | 10 | NA | The hikari pool connection size to be created at start up |
| hikari.connectionTimeout | MYSQL connection timeout | 1000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| hikari.minimumIdleConnections | Minimum idle MYSQL connections maintained | 2 | Valid No, less than poolsize configured | NA |
| hikari.idleTimeout | Idle MYSQL connections timeout | 10000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| hikari.queryTimeout | Query timeout for a single database query. If you set the value to -1 there will be no timeout for database queries | -1 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| logging.level.root | Log Level | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
Log level of the export tool pod |
| logging.level.ocudr | Application Log Level | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
App Log level of the export tool pod |
| resources.requests.cpu | Cpu Allotment for nudr-notify-service pod | 2 | NA | The cpu to be allocated for notify service pod during deployment |
| resources.requests.memory | Memory allotment for nudr-bulk-import pod | 2Gi | NA | The memory to be allocated for nudr-bulk-import pod during deployment |
| resources.requests.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation request | 50 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.requests.crictlStorage | Crictl storage for ephemeral storage allocation request | 2 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.limits.cpu | Cpu allotment limitation | 2 | NA | NA |
| resources.limits.memory | Memory allotment limitation | 2Gi | NA | NA |
| resources.limits.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit | 1000 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.limits.crictlStorage | Crictl storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit | 2 | Unit: MB | NA |
| readinessProbe.initialDelaySeconds |
Configurable wait time before performing the first readiness probe by the kubelet Do not change this value. If you see delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you should consider tuning these parameters. |
30 |
Not Applicable Unit: Seconds |
NA |
| readinessProbe.periodSeconds | Time interval for every readiness probe check.
Do not change this value. If you see delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you should consider tuning these parameters. |
3 |
Not Applicable Unit: Seconds |
NA |
| livenessProbe.initialDelaySeconds | Configurable wait time before performing the first
liveness probe by the kubelet.
Do not change this value. If you see delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you should consider tuning these parameters. |
30 |
Not Applicable Unit: Seconds |
NA |
| livenessProbe.periodSeconds | Time interval for every liveness probe check
Do not change this value. If you see delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you should consider tuning these parameters. |
3 |
Not Applicable Unit: Seconds |
NA |
| extraContainers | This configuration decides at this microservice level the extra container need to be used or not. | USE_GLOBAL_VALUE | Allowed
Values:
ENABLED DISABLED USE_GLOBAL_VALUE |
This configuration decides service level extraContainer support. The default value will let it be dependent on what is configured in the global level |
| serviceMeshCheck | Enable when deployed in serviceMesh, referred to the serviceMeshCheck in global section. Set to false when side car is not included for this service | *serviceMeshFlag | NA | Do not change this value unless it is different from the value configured in global section reference |
| istioSidecarReadyUrl |
Readiness url configurable for side car, referred to global section istioSidecarReadyUrl Change only if the url is different for the side car container in this microservice |
*istioReadyUrl | NA | Do not change this value unless it is different from the value configured in global section reference |
| ocudrReleaseName | Release Name of OCUDR, To form config-server/ocudr endpoint fqdn | ocudr | NA | NA |
| dbRetry.maxRetry | Number of DB transaction retires for failed DB transactions | 3 | NA | Do not change the default values. Used for Engineering purpose |
| dbRetry.interval | Interval for each transaction attempt during retries | 4 | NA | Do not changes default values. Used for Engineering purpose |
| tolerations | When tolerationsSetting is ENABLED configure tolerations here | [] | NA | Example:
|
| helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion | Node Selector API version setting | v1 | Allowed Values:
v1 v2 |
NA |
| nodeSelector.nodeKey | Micro service level NodeSelector key configuration.
When helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration will come into use. The configuration does not depend on nodeSelection flag. Once configured, this is used for all microservices. |
' ' | Valid key for a label for a particular node | NA |
| nodeSelector.nodeValue | Global level NodeSelector Value configuration.
When helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration will come into use. The configuration does not depend on nodeSelection flag. Once configured, this is used for all microservices. |
' ' | Valid value pair for the above key for a label for a particular node | NA |
| nodeSelector | NodeSelector configuration when helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v2. Uncomment and use this configuration when required or keep this commented. | {} | Valid key value pair matching a node for nodeSelection by a pod | |
| periodicDumpFrequency | Frequency for periodic dump generation. By default only one time is set | ONE_TIME | ONE_TIME/DAILY/WEEKLY/MONTHLY | NA |
| startTime |
Start time for dump generation. If left empty, then now will be considered for dump generation. Date is required, so for WEEKLY dump the date is used for identifying day in the week and for subsequent weeks the same day is used |
14/09/2022 17:32:10 | Valid time in the format as shown in default value/Empty ("") | NA |
| maxDumps | Max dumps that will be retained in the PVC storage. Rest of the dumps older in age will be cleared. | 5 | [1 - 5] | NA |
| numberOfSubscribers | Internal Engineering Configuration. Do not change | 1000 | NA | NA |
| batch.corePoolSize | Internal Engineering Configuration. Do not change | 5 | NA | NA |
| batch.maxPoolSize | Internal Engineering Configuration. Do not change | 5 | NA | NA |
| batch.queueCapacity | Internal Engineering Configuration. Do not change | 30000 | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.host | Remote Host IP | 10.75.229.18 | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.port | Remote Host Port | 22 | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.username | Remote Host Username | cloud-user | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.path | Path of Remote host server where the exported files are stored | /home/cloud-user/ocudr/ | NA | Do not delete the backslash / in the default value. It is mandatory to include the backslash. This is also applicable during the REST API operation. |
| sftpDetails.sftpExportEnabled | Indicates if the sftp export is enabled or not | true | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.deleteFromPvc | Indicates whether files should be deleted from PVC after export | true | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.pollingInterval | Interval at which files are polled for sftp export in minutes | 1 | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.secrets.privatekey.name | Private key name of the remote server in secrets | ocudr-ssh-private-key | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.secrets.publickey.name | Public key name of remote server in secrets | ocudr-ssh-public-key | NA | NA |
| exportMode | Indicates SLF or EIR subscribers export mode. Values of export should be CSV_EXPORT(SLF Mode)/PDBI_EXPORT(EIR Mode) | EIR Mode | SLF_Export/EIR_Export | |
| imsiCount | Applicable for PDBI_EXPORT. The max number of IMSIs as part of a single subscriber that will be exported | 5 | [1-10] | |
| msisdnCount | Applicable for PDBI_EXPORT. The max number of MSISDNs as part of a single subscriber that will be exported | 5 | [1-10] | |
| startupProbe.failureThreshold | It is the configurable number of times the startup probe
is retried for failures.
Note: Do not change this value. If there is delay in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then tune these parameters |
40 | NA | NA |
| startupProbe.periodSeconds | It is the time interval for every startup probe check. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delay in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then tune these parameters | 5 | NA | NA |
| maxConcurrentPushedStreams | Maximum number of concurrent requests that is pushed per destination | 6000 | NA | NA |
| maxRequestsQueuedPerDestination | Maximum number of requests that is queued per destination | 5000 | NA | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerDestination | Maximum connection allowed per destination | 10 | NA | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerIp | Maximum connection allowed per IP | 10 | NA | NA |
| requestTimeout | Client Request timeout | 5000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| connectionTimeout | Client connection timeout | 10000 | NA | NA |
| idleTimeout | Client connection idle timeout | 0 | NA | NA |
| dnsRefreshDelay | Server DNS refresh delay | 120000 | NA | NA |
| pingDelay | Server ping delay | 60 | NA | NA |
| connectionFailureThreshold | Client connection failure threshold | 10 | NA | NA |
| jettyserviceMeshCheck | Flag to enable or disable jetty service mesh check for ASM deployment | false | true/false | NA |
| subscriberRangeEnabled | Flag to enable or disable the range based subscriber export. Default is set to false for full range of 4G policy subscriber data export. | false | true/false | NA |
| keyType | To export the range based subscriber data with keys. The two key type are IMSI and MSISDN. | msisdn | msisdn/imsi | NA |
| subscriberRanges | Configures the start and end ranges that is given to
export the data. This works only if
subscriberRangeEnabled parameter is
enabled.
|
|
NA | NA |
| newFilePerRangeEnabled | When enabled creates a separate EXML file for each range. Default is set to false. | false | true/false | NA |
| sftpDetails.fileSizeCheck | Checks the file size of the remote server once the file is successfully transferred to remote location. | false | true/false | NA |
| sftpDetails.transferProtocol | Transfers the files to remote location. the default protocol uses SFTP | sftp | sftp or scp | NA |
| gracefulShutdown.gracePeriod | It is the graceful shutdown time limit. | 30s | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| fileStatusInterval | It is the file status update interval. This is an engineering configurations. | 30 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| jobStatusInterval | It is the Jib status update interval. This is an engineering configurations. | 30 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
To Configure on-demand and schedule periodic dumps on the export tool post the installation, see the Configuration APIs for UDR Microservices and Configuration APIs for Loglevel sections in the Configuration API Specification chapter of the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- frequencyOfPeriodicDump: When the frequencyOfPeriodicDump parameter is configured as ONE_TIME, it will act as ondemand dump and the startTime must be set to a value from the current time
- startTime: Start time of the dump must be configured in day-month-year-hours-minutes-seconds (dd-MM-YYYY hh:mm:ss) and 24 hours format. In case of WEEKLY start time the date is used to identify the day of the week the dump is scheduled
- maxNumberOfDumps: Maximum number of dumps that are retained on the Persistent Volume Claim (PVC). When the maximum limit is reached, the oldest dump is cleared
- fixedDumpFileNamePrefix: Configurable name suffix for each dump file that is generated. This is used along with the timestamp
- multiValuedelimiter: This is used as the delimiter when we have multiple keys of the same type
- fieldDelimiter: Field delimiter is used as the delimiter for each field on the dump file
- fileExtension: Configurable file extension is used for the generated dump files
- exportMode: This is the mode of export. The values of the export should be SLF_EXPORT for SLF Mode and EIR_EXPORT for EIR Mode. This field is not editable
- imsiCount: Configurable imsi count. It is used to write that many imsi column in export file
- msisdnCount: Configurable msisdn count. It is used to write that many msisdn column in export file
- remoteUserNam: Configurable user name of remote host
- remotePath: Configurable path in remote server where exported files is stored
- serverHost: ConfigurableIP address of remote host
- serverPort: Configurable Port of remote host
- sftpExportEnabled: Used to indicate if the SFTP is enabled or disabled
- deleteFromPVC: Configurable flag to control deletion of files from sftp
- pollingInterval: Polling interval for SFTP functionality measured in minutes
- subscriberRangeEnabled: Flag to enable or disable the range based subscriber export. Default is set to false for full range of 4G policy subscriber data export.
- keyType : This is used to export the range based subscriber data with keys. The two key type are IMSI and MSISDN.
- subscriberRanges: Configures the start and end ranges that is given to export the data.
- newFilePerRangeEnabled : Creates a separate EXML file for each range. Default is set to false.
- sftpDetails.fileSizeCheck: Checks the file size of the remote server once the file is successfully transferred to remote location.
- sftpDetails.transferProtocol: Transfers the files to remote location. The default protocol is SFTP.
2.19.6 Upgrade and Rollback support for Subscriber Export Tool
Upgrade Procedure
Note:
Helm Upgrade and Helm rollback of Subscriber Export Tool is not supported.Helm Upgrade of Subscriber Export Tool is not supported. You must uninstall the current version Subscriber Export Tool and install the higher version. For more information, see Installing Subscriber Export Tool.
Rollback Procedure
Note:
UDR and the Subscriber Export Tool must be rolled back together.- Uninstall the current version of the Subscriber Export Tool.
- Install the older version of the Subscriber Export Tool. For more information, see Installing Subscriber Export Tool.
- Perform the rollback procedure for UDR. For more information, see Rolling BackUDR chapter in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.19.7 Monitoring the Subscriber Export Tool Status
This section provides details of monitoring subscriber export tool status.
Monitoring the Subscriber Export Tool Operation
You can monitoring the export operation is supported using REST API and CNC Console. It also supports monitoring the status of exported data and overall export operation through CNC Console.
- fileName: Export file name
- startTime: The start time of subscriber export to the particular file
- completeTime: Current File dumping completion time
- filePath: The path where the file is stored on the container, and the same is mounted on the PVC
- status: Status are INPROGRESS or COMPLETED
- jobId: Unique ID for Export
- subscriberCount: 220
- exportedSubscriberCount: 220
- jobProgress: 100 (In percentage)
- jobId: Unique ID for Export
- status: RUNNING/COMPLETED/SKIPPED/FAILED
Subscriber Export Tool Job Status
- If any resource is not found, for example: database connectivity.
- If the subscriber export tool fails to connect to the database.
- In case of failure of the subscriber export tool.
Figure 2-16 Subscriber Export Tool Export Status

Subscriber Export Tool File Status
- When the subscriber export tool is triggered by configuring the frequency and start time using the CNC Console, the file status shows FILE_EXPORT_IN_PROGRESS.
- When the subscriber data is exported from database to CSV or TXT file, the file status shows FILE_EXPORT_COMPLETE.
- When the file export is completed, the SFTP scheduler exports the subscriber data from the database to CSV or TXT file and the file is placed in the PVC. The file status shows FILE_TRANSFER_IN_PROGRESS.
- If the transfer is successful, file status shows FILE_TRANSFER_COMPLETED.
- If the file transfer is failed, file status shows FILE_TRANSFER FAILED and the SFTP scheduler picks up the file again for transfer and the file status shows FILE_TRANSFER_IN_PROGRESS.
Figure 2-17 Subscriber Export Tool File Status

2.20 Subscriber Activity Logging
UDR supports multiple log levels which the operator can set based on the requirement. The default log level enabled is ERROR or WARN. Subscriber Activity Logging enhances the logging functionality of UDR to support subscriber specific logging. This feature enables the operators to log the subscriber activity for the configured list of subscribers. A list of subscribers for which the logging is required can be defined and this is controlled irrespective of the log level that is enabled for UDR. You can collect the message exchanges, subscriber specific decision making, and logic handling for specific subscribers.
- 5G signaling traffic - SBI
- Diameter traffic - Sh Interface
- Provisioning traffic
To Enable
- You can disable or enable the feature by setting the
subscriberActivityEnabledparameter to true or false in the global section of the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. For more information on this parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide . - You can disable or enable the feature by setting the
subscriberActivityEnabledparameter to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console
Note:
When the requested subscriber logging is enabled the corresponding subscriber Identifier must be cleared because additional logging can impact performance.subscriberActivityEnabled:falseConfigure using CNC Console:
You can configure different subscriber identifiers for each keys. Subscriber activity is enabled only for values which are configured. For more information, see Global Configurations in the CNC Console.
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": ["1111111123","1111111124","1111111125","1111111111"],
"imsi": ["2222222221","2222222222","2222222223"],
"nai": ["3333333331","3333333332","3333333333"],
"extid": ["2333333331"]
}Configure using REST API:
You can perform the PUT operation on the
http://10.75.214.219:32113/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to configure the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud
Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
{
"ingressHttpPort": "80",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-asmndb",
"autoCreate": true,
"udsfEnabled": false,
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": "1",
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": true,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"nai": [],
"imsi": ["0908338283"],
"extid": [],
"msisdn": ["1234567890","1234567891"]
},
"udrServices": "All"
}Sample logs
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658758894,"nanoOfSecond":319666506},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-1","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :msisdn-1111111124 : Incoming Request received ","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":45,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-25T14:21:34.319+0000","application":"reddy1","engVersion":"22.2.3012","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"reddy1-nudr-drservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-1111111124","resourceId":"nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/ue-policy-set","ocLogId":"1658758874753_269_reddy1-ingressgateway-sig-666c94f6b8-lnxhw","requestType":"PUT"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658758894,"nanoOfSecond":398003490},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-1","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :msisdn-1111111124 : schema validation success","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":45,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-25T14:21:34.398+0000","application":"reddy1","engVersion":"22.2.3012","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"reddy1-nudr-drservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-1111111124","resourceId":"nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/ue-policy-set","ocLogId":"1658758874753_269_reddy1-ingressgateway-sig-666c94f6b8-lnxhw","requestType":"PUT"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658758894,"nanoOfSecond":610396593},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-1","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :msisdn-1111111124 : Subscriber not exist in 5G ","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":45,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-25T14:21:34.610+0000","application":"reddy1","engVersion":"22.2.3012","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"reddy1-nudr-drservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-1111111124","resourceId":"nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/ue-policy-set","ocLogId":"1658758874753_269_reddy1-ingressgateway-sig-666c94f6b8-lnxhw","requestType":"PUT"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658758894,"nanoOfSecond":626709333},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-1","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :msisdn-1111111124 : Auto create is disabled- Subscriber not found","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":45,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-25T14:21:34.626+0000","application":"reddy1","engVersion":"22.2.3012","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"reddy1-nudr-drservice","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"msisdn-1111111124","resourceId":"nudr-dr/v2/policy-data/ues/ue-policy-set","ocLogId":"1658758874753_269_reddy1-ingressgateway-sig-666c94f6b8-lnxhw","requestType":"PUT"}{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827381,"nanoOfSecond":998796077},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : Received PUR msg","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:01.998+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827381,"nanoOfSecond":999854337},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : Data-Reference validation successful","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:01.999+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827382,"nanoOfSecond":3210128},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : Schema Validation Successful","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:02.003+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827382,"nanoOfSecond":13014813},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : inserting or updating data into 5G UDR","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:02.013+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827382,"nanoOfSecond":16845880},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : caught exception from dao operation","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:02.016+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","resultCode":"409","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827382,"nanoOfSecond":17614851},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : DIAMETER_ERROR_TRANSPARENT_DATA_OUT_OF_SYNC","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:02.017+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","resultCode":"409","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1658827382,"nanoOfSecond":18276262},"thread":"DiamMsgBuffer:WorkerThread-5","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.common.metrics.SubscriberActivityLogger","message":"Subscriber Acitivty Logging :imsi-111111111111 : request resulCode: 5105","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":5,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-07-26T09:23:02.018+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.40","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy","vendor":"Oracle","subscriberId":"imsi-111111111111","resultCode":"409","ocLogId":"1658827381997_5_ocudr-nudr-diameterproxy-55f6b54cb6-cdwx5","requestType":"PUR","originHost":"Route-Record (282,M,l=27) = diamcli1.oracle.com"}Figure 2-18 Sample Kibana Logs
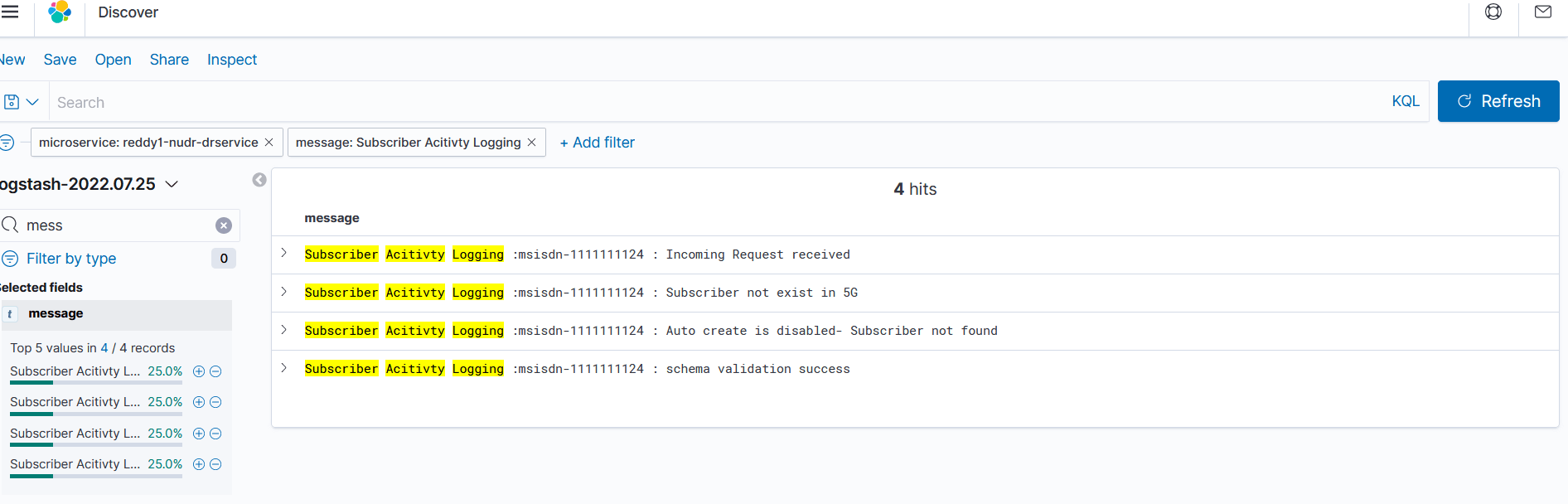
To Observe
See UDR Metrics section for more information on metrics.
2.21 Support for 5G EIR Signaling
- REST/JSON based provisioning of 5G EIR profile
- Provisioning of 5G EIR entries using CNC Console or REST API
- N5g-eir_EquipmentIdentityCheck Service API. N5g-eir is the service based interface as defined by 3GPP.
- NRF registration of the EIR service
- EIR Access Log for blacklisted and greylisted Permanent Equipment Identifier (PEI). 5G EIR supports 14 digit International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI).
- Bulk import of 5G EIR subscriber data by using Provisioning Database Interface (PDBI) interface and Comma Separated Value (CSV)
Figure 2-19 Reference Model – 5G-EIR

The NF Service Consumer (for example: AMF) checks the status of the PEI by using the HTTP GET method. The NF Service Consumer sends a GET to the resource representing the PEI equipment status. The request includes the PEI as the query parameter and if required, Subscription Permanent Identifier (SUPI) or Generic Public Subscription Identifier (GPSI) can be included.
When the request is successful, "200 OK" is received with the message body containing the equipment status of the PEI.
If the equipment status of the PEI is not known, 404 Not Found error is returned with the message body containing problem details. The details attribute is set to ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN.
EIR Signaling Interface
- The TLS and oauth2 authentication features provided by the ingressgateway-sig microservice.
- The overload control feature provided by the ingressgateway-sig microservice.
- The User-Agent, LCI and OCI, XFCC, and server header support on the ingressgateway-sig microservice.
- The Rate Limiting feature provided by ingressgateway-sig microservice.
EIR Equipment Identity Check
The URL supported for N5g-eir_EquipmentIdentityCheck is
defined in 3GPP 29.511 specification. For example,
{api-root}/n5g-eir-eic/v1/equipment-status?pei={pei}&supi={supi}&gpsi={gpsi}
EirResponseData. For
example:
{
"status": "WHITELISTED"
}nudr-drservice.defaultResponse. The configuration is set to
EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN by default. The response will be 404 with
cause as ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN as
follows.{
"title": "Not Found",
"status": 404,
"detail": "Provided SUPI/GPSI does not match with PEI association",
"cause": "ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"invalidParams": []
}{
"title": "Not Found",
"status": 404,
"detail": "Mobile Equipment Not Known in the EIR",
"cause": "ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"invalidParams": []
}To Install 5G EIR
- set value of the
global.udrServicesparameter ton5g-eir-eic. - Set the
appinfo.coreservicesparameters as below.# Service to be monitored by appinfo, we need to add to list as and when required #If UDR service is ALL OR nudr-dr use *allordr, use *slf if udrServices=nudr-group-id-map core_services: #udr: *allordr #if EIR mode then comment udr and uncomment below 5g_eir: *eir - Uncomment EIR
appProfiesinnrf-clientsection.#uncomment below appProfiles if EIR mode is enabled appProfiles= [{"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "nfStatus": "REGISTERED", "fqdn": "ocudr-ingressgateway.myudr.svc.cluster.local", "nfType": "5G_EIR", "allowedNfTypes": ["AMF"], "plmnList": [{ "mnc": "14", "mcc": "310" }], "priority": 10, "capacity": 500, "load": 0, "locality": "bangalore", "nfServices": [{ "load": 0, "scheme": "http", "versions": [{ "apiFullVersion": "2.1.0.alpha-3", "apiVersionInUri": "v1" }], "fqdn": "ocudr-ingressgateway.myudr.svc.cluster.local", "ipEndPoints": [{ "port": "80", "ipv4Address": "10.0.0.0", "transport": "TCP" }], "nfServiceStatus": "REGISTERED", "allowedNfTypes": ["AMF"], "serviceInstanceId": "ae870316-384d-458a-bd45-025c9e748976", "serviceName": "n5g-eir-eic", "priority": 10, "capacity": 500 }], "heartBeatTimer": 90, "nfServicePersistence": false, "nfProfileChangesSupportInd": false, "nfSetIdList": ["setxyz.udrset.5gc.mnc012.mcc345"]}]
For more information about above parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
To support 5G EIR bulk provisioning a new container (pdbiToCsv container) has been added in the bulk import tool. To configure bulk import with this enhancement, see Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.
5G EIR Provisioning
5G EIR provisioning interface is supported on the ingressgateway-prov microservice and utilizes the TLS and oauth2 authentication features provided by the ingressgateway-prov microservice. EIR provisioning interface supports HTTP1.1 and HTTP2. Internally, provisioning requests are routed to nudr-dr-provservice, which creates subscriber records on the EIR database. For more information, see Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.
EIR Access Logs
- Date and Time
- Source
- IMSI
- IMEI
- Status
Note:
- The status of the IMEI is indicated as below:
- IMEI in black list is 1
- IMEI in grey list is 2
- Access logs are applicable when
defaultResponseis used and it is set as GREYLISTED or BLACKLISTED.
The access logs can be filtered on the kibana for a specific time period
using EIR access log filter on nudr-drservice logs. EIR access log is flag driven
feature. A new configuration, nudr-drservice.accessLogEnabled, is
introduced to enable or disable the feature.
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1656481285,"nanoOfSecond":195874715},"thread":"XNIO-1 task-1","level":"ERROR","loggerName":"ocudr.udr.services.util.EIRAccessLogger","message":"EIR Access Log: pei-1111111113, supi-1111111112, gpsi-1111111121, status: 2","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.log4j.spi.AbstractLogger","threadId":44,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-06-29T05:41:25.195+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"22.2.30-m1","mktgVersion":"22.2.0.0.0","microservice":"ocudr-nudr-drservice","vendor":"Oracle","resourceId":"n5g-eir-eic/v1/equipment-status","ocLogId":"1656481291296_128_ocudr-ingressgateway-sig-65f875b999-cc5zd","requestType":"GET"}To Observe
See UDR Metrics section for more information on metrics.
2.21.1 User Equipment Optimization Support for EIR
- 200 OK - WHITELISTED/BLACKLISTED/GREYLISTED
- 404 Not Found - Equipment Not Found
When the PEI or IMEI are received in the GET request but PEI or IMEI are not
found in the EIR database, EIR responds with a configured default response. The default
response is set as Equipment Not Found. The sample response from the
Equipment Identity Check (EIC) is as follows:
{
"title": "Not Found",
"status": 404,
"detail": "Equipment not found",
"cause": "ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"invalidParams": []
}Configure using REST API:
http://10.75.215.124:32523/nudr-config/v1/udr.nudrservice.cfg/DR-SERVICE
to configure the default response. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST
Specification
Guide.{
"hikariPoolSize": 25,
"tracingEnabled": false,
"subscriptionDataSubscriptionsOnly": false,
"defaultGroupIdEnabled": false,
"defaultSlfGroupName": "DefaultGrp",
"onDemandMigrationEnabled": true,
"defaultResponse": "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"accessLogEnabled": false,
"defaultResponseIMEINotFound": "WHITELISTED"
}defaultResponseIMEINotFound parameter in the
nudr-drservice section is set to WHITELISTED, EIR response in EIC
as follows:{
"status": "WHITELISTED"
}{ "title": "Not Found",
"status": 404,
"detail": "Provided SUPI/GPSI does not match with PEI association",
"cause": "ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"invalidParams": []
}To Observe
- eir_default_response_imei_not_found
See UDR Metrics section for more information on metrics.
2.21.2 International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) Fallback Lookup Enhancement for EIR
Earlier in EIR, if the incoming message had International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI), International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI), and Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) and if only the IMEI was provisioned in the EIR database without IMSI or MSISDN, then EIR used to respond with a configured default response for the user equipment status. Using IMSI Fallback Lookup Enhancement feature, EIR returns user equipment status as WHITELISTED, BLACKLISTED, or GREYLISTED for the matched IMEI in the EIR database.
The feature is enabled using the imsiLookupFallbackEnabled
feature flag. The default value is set as false.
Note:
The incoming request message must contain the Subscription Permanent Identifier (SUPI)/Generic Public Subscription Identifier (GPSI) and Permanent Equipment Identifier (PEI)/IMEI.- Search for PEI and IMSI received in the request message with the PEI and IMSI in the EIR database. If matched, EIR responds with the associated equipment status. The equipment status values are WHITELISTED, BLACKLISTED, or GREYLISTED.
- Search for only PEI match in the EIR database. If matched, EIR responds with the associated equipment status.
- Search for PEI match in the EIR database with any other IMSIs. If
found, EIR responds as per the default configuration in
defaultResponseparameter. The default values are EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN, WHITELISTED, BLACKLISTED, or GREYLISTED. - If PEI match is not found in the EIR database, then EIR responds as
per the default configuration in
defaultResponseIMEINotFoundparameter. The default values are EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN, WHITELISTED, BLACKLISTED, or GREYLISTED.
Managing IMSI Fallback Lookup Enhancement
Enable
- You can enable or disable the feature by setting the
imsiLookupFallbackEnabledparameter to true or false in the global section of theocudr-custom-values.yaml file. The default value is set to false. For more information on this parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.# EIR Configurations eirConfigurat ions : defaultResponse: "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN" accessLogEnabled: "true" defauItResponselMEINotFound: "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN imsiLookupFallbackEnabled: "false"
Configure
- Configure using CNC Console: You can enable or disable
the feature by setting the
imsiLookupFallbackEnabledfield to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console. - Configure using REST API: You can perform the PUT
operation on the
http://10.75.229.45:30015/nudrconfig/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBALto enable or disable the feature. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.{ "dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-rs1", "udrServices": "n5g-eir-eic", "udsfEnabled": false, "ingressHttpPort": "", "ingressHttpsPort": "", "snssai": "2-FFFFFF", "dnn": "dnn1", "sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false, "autoCreate": true, "autoEnrolOnSignalling": true, "etagEnabled": true, "version": "v3", "consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF", "nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03", "vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1, "subscriberActivityEnabled": false, "addDefaultBillingDay": true, "enableControlledShutdown": false, "keyType": "msisdn", "keyRange": "000000-000000", "dbConflictResolutionEnabled": false, "maxNumberOfSubscriptions": 30, "suppressNotificationEnabled": true, "configClientConnectTimeout": 1000, "configClientReadTimeout": 1000, "s13InterfaceEnabled": false, "defaultResponse": "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN", "accessLogEnabled": true, "defaultResponseIMEINotFound": "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN", "imsiLookupFallbackEnabled": true, "subscriberIdentifers": { "msisdn": [], "imsi": [], "nai": [], "extid": [] } }
Observe
There are no metrics, alerts, or KPIs for this feature.
Upgrade and Rollback of IMSI Fallback Lookup Enhancement Feature
- Upgrade scenario: When you upgrade UDR from previous release
version by setting
imsiLookupFallbackEnabledparameter as true, then the feature is enabled in the upgraded release version. - Rollback scenario: When you rollback UDR to previous release version the configuration is also rolled back and the feature does not work.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.21.3 Diameter S13 Interface
Equipment Identity Register (EIR) is a database containing records of all User Equipment (UE) that are allowed or disallowed from accessing the network. Each UE is identified by its International Mobile Equipment Identity (IMEI). When an UE is identified by the network, the Mobility Management Entity (MME) requests the IMEI of the UE, which is sent to the EIR for authorization. This feature supports diameter interface between EIR and MME to retrieve the UE equipment status of the subscriber.
- nudr-diam-gateway: It is used to establish and maintain the diameter connection.
- nudr-diameterproxy: It is used to retrieve the equipment status from the EIR database, which is provisioned using provisioning system or PDBI subscriber bulk import tool.
Equipment Data Provisioning
The equipment data is provisioned in EIR using the PDBI subscriber bulk import tool or provisioning API. For more information, see Subscriber Bulk Import Tool and Support for 5G EIR Signaling.
Figure 2-20 Equipment Data Provisioning

Diameter Gateway Support
- Establishing and maintaining the diameter connection with the WHITELISTED peer
- Horizontal pod auto scaling and High Availability (HA) for the traffic load distribution
- Georedundancy deployment models
- Diameter Gateway Pod Congestion feature, which protects the pod by rejecting the traffic when congested. For more information about the feature, see Diameter Gateway Pod Congestion Control.
- Diameter peer must be WHITELISTED to establish the connection
with EC. Configure the diameter peer details under
allowedClientNodesin the diameter gateway configurations. - Perform the PUT operation on the
http://10.75.229.85:31430/nudr-config/v1/udr.diamgateway.cfg/DIAMETER-GATEWAYto whitelist the diameter peer. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.{ "realm": "oracle.com", "identity": "nudr.oracle.com", "reconnectDelay": 3, "responseTimeout": 4, "connectionTimeOut": 3, "watchdogInterval": 6, "reconnectLimit": 50, "onDemandMigrationEnabled": false, "allowedClientNodes": [{ "port": 3868, "identity": "peer1", "host": "10.75.185.161", "responseOnly": false, "realm": "seagull", "type": "server" }] }
Mobile Equipment Identity Check Request (ECR)
- A connection is established from the diameter peer using the Capability Exchange Request (CER) request. The Capability Exchange Answer (CEA) responds to the request and maintains the connection.
- ECR request is sent from diameter peer to diameter gateway. The request is then sent to diameter proxy from diameter gateway to get the equipment status from the EIR database.
- Equipment status of the subscriber is returned to the diameter peer.
Figure 2-21 Diameter S13 Interface Call Flow
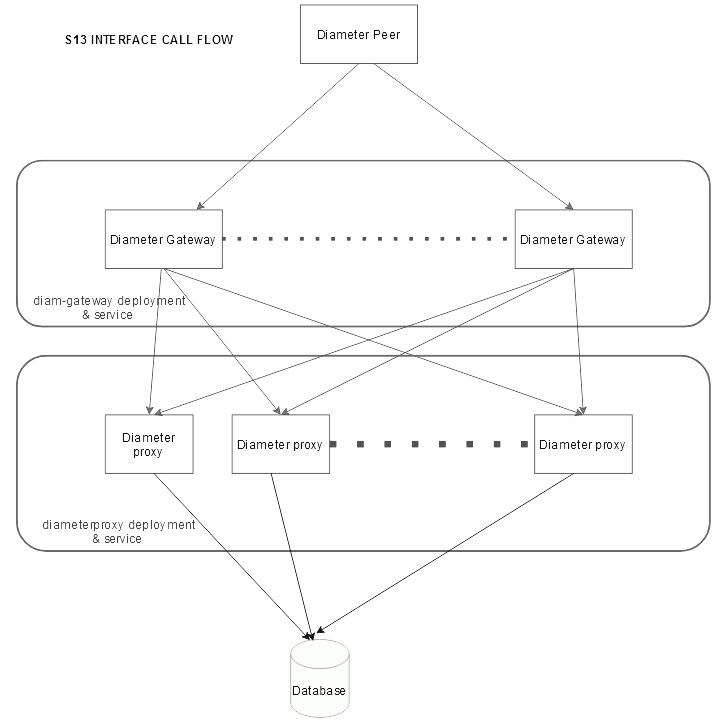
Figure 2-22 ECR Request

Equipment Status Retrieval Call Flow
- If ECR contains software version as part of terminal information along with IMEI, lookup will be based on IMEI and software version, if the software version is not available, then look up is based on IMEI only.
- If IMEI or IMEI software version is not found in the EIR
database, then ECA returns with configured
defaultResponseIMEINotFound. - If IMEI or IMEI software version is found in EIR database, then
you must check if user name is present in the ECR request. If user name is
not present in the ECR request, then ECA returns with
DIAMETER SUCCESSand equipment status. - If user name is present, then you must check if a match is present in the EIR database.
- If user name match is not present with IMEI or IMEISV, then you
must send ECA with configured
defaultResponse. - If user name match is present with IMEI or IMEI software
version, then ECA returns with
DIAMETER SUCCESSand equipment status.
Figure 2-23 Equipment Status Retrieval Call Flow
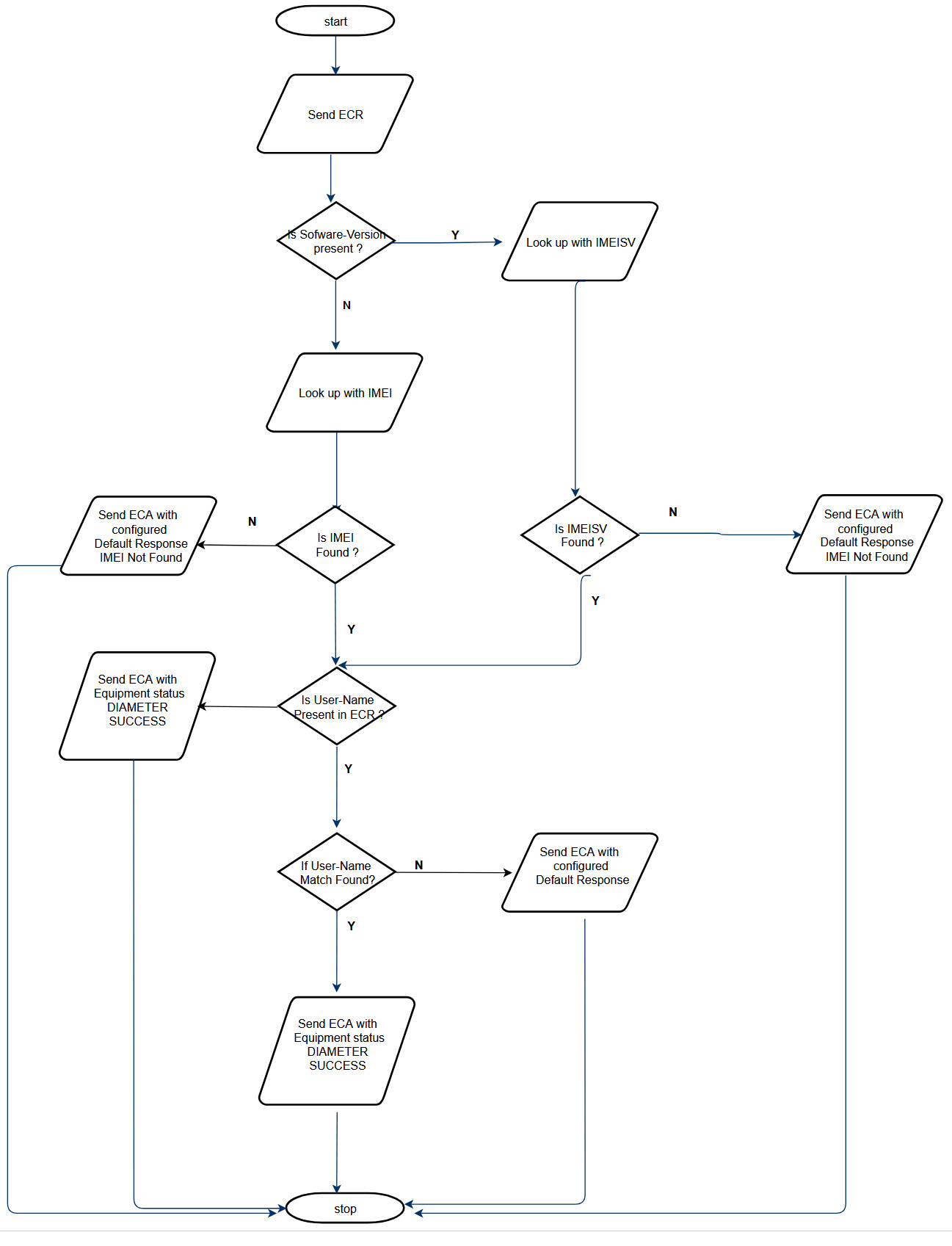
Table 2-22 Possible Error Codes
| Result Code | Details |
|---|---|
| 2001 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_SUCCESS Error Message: diameter success |
| 5422 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_ERROR_EQUIPMENT_UKNOWN Error Message: unknown equipment |
| 5005 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_MISSING_AVP Error Message: missing avp |
| 5004 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_INVALID_AVP_VALUE Error Message: invalid avp value |
| 5001 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_AVP_UNSUPPORTED Error Message: diameter avp not supported |
| 5009 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_AVP_OCCUR_TOO_MANY_TIMES Error Message: diameter avp occurs too many times |
| 5010 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_NO_COMMON_APPLICATION Error Message: no common application |
| 3004 |
Error Response: DIAMETER_TOO_BUSY Error Message: diameter is busy |
EIR Access Log and Default Response
This feature supports EIR access logs and default response implementation. For more information, see Support for 5G EIR Signaling.
Managing Diameter S13 Interface
Enable
Note:
The existing EIR configurationsdefaultResponse,
defaultResponseIMEINotFound, and
accessLogEnabled parameters are applicable for this
feature.
- You can enable or disable the feature by setting the
s13InterfaceEnableparameter to true or false in the global section of theocudr-custom-values.yaml file. The default value is set to false. For more information on this parameter, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.s13InterfaceEnable: true # EIR Configurations eirConfigurations: defaultResponse: "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN" accessLogEnabled: "true" defaultResponseIMEINotFound: "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN"
Configure
You can configure this feature using REST API and CNC Console.
Configure using CNC Console
You can enable or disable the feature by setting the
s13InterfaceEnable field to true or false in the Global Configurations in the CNC Console.
Configure using REST API
http://10.75.229.45:30015/nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to enable or disable the feature. For more information, see Oracle
Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb",
"udrServices": "All",
"udsfEnabled": false,
"ingressHttpPort": "",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"autoCreate": true,
"autoEnrolOnSignalling": true,
"etagEnabled": true,
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": false,
"addDefaultBillingDay": true,
"enableControlledShutdown": true,
"keyType": "msisdn",
"keyRange": "000000-000000",
"nfType": "UDR",
"nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com",
"suppressNotificationEnabled": true,
"configClientConnectTimeout": 1000,
"configClientReadTimeout": 1000,
"s13InterfaceEnable": true,
"defaultResponse": "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"accessLogEnabled": true,
"defaultResponseIMEINotFound": "EQUIPMENT_UNKNOWN",
"imsiLookupFallbackEnabled":false,
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": [],
"imsi": [],
"nai": [],
"extid": []
}
}Observe
Metrics
eir_default_response_imei_not_foundeir_txn_default_response_sent
Alerts:
NudrDiameterProxyServiceDownNudrDiameterGatewayDownOceirDiameterCongestionDocStateOceirDiameterCongestionCongestedStateDiameterPeerConnectionsDropped
Upgrade and Rollback of Diameter S13 Interface Feature
During upgrade from 24.2.x release to 24.3.0, all the existing configurations under
nudr-drservice configuration such as defaultResponse,
defaultResponseIMEINotFound, and
accessLogEnabled are present under the global configuration.
During rollback from 24.3.0 release version to previous release versions the
configurations are restored to nudr-drservice configuration.
Note:
Parameterss13InterfaceEnabled and
imsiLookupFallbackEnabled are added to the global
configurations.
Maintain
If you encounter alerts at system or application levels, see the Alert Details section for resolution steps.
- Collect the logs: For more information on collecting logs, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
- Raise a service request: See My Oracle Support for more information on how to raise a service request.
2.22 Support for LCI and OCI Header
This feature introduces Load Control Information (LCI) and Overload Control Information (OCI) Headers in the HTTP request(s) and response(s). These headers send the operating status of the producer resources to the consumer Network Functions (NFs).
The load information in the headers include the following:
- LCI Header: This header sends the current load information of the producer Network Function (NF). This information helps the consumer NF in load balancing the traffic in the network. 3gpp-Sbi-Lci denotes LCI Header. When the conditions for generating LCI Header are met, the NF service producer includes this header at the NF scope, back-end service scope, or both.
- OCI Header: This header sends the current overload information so that the peer NF can reduce the traffic towards the overloaded NF. 3gpp-Sbi-Oci denotes OCI Header. When the conditions for generating OCI Header are met, the NF service producer includes this header at the NF scope, back-end service scope, or both.
Following are the examples of LCI and OCI Headers:
Note:
For LCI and OCI headers, reporting of the load is considered based on localLciHeaderValidity and loadThreshold. Once the localLciHeaderValidity expires the loadThreshold value will not be considered. Threshold value will be validated only within the validity period.3gpp-Sbi-Lci: Timestamp: "Tue, 07 Jun 2021 01:11:22 GMT"; Load-Metric: 25; slf-FQDN: slf.example.com3gpp-Sbi-Oci: Timestamp: "Tue, 04 Feb 2020 08:49:37 GMT"; Period-of-Validity: 120s; Overload-Reduction-Metric: 75; SLF-FQDN: slf.example.comModify the ocudr-custom-values.yaml file with the following
configuration parameters:
LCI and OCI Header Priorities
- oAuth token (1st priority)
- User-Agent (2nd priority)
- Via (3rd priority)
If there are multiple headers available at ingressgateway-sig, then the consumer NF identity must be extracted based on the priority order of the header as mentioned above.
oAuth token header
Authorization → NF instance ID is extracted after decoding the below token eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJFUzI1NiJ9.eyJpc3MiOiI2ZmFmMWJiYy02ZTRhLTQ0NTQtYTUwNy1hMTRlZjhlMWJjMTEiLCJzdWIiOiJmZTdkOTkyYi0wNTQxLTRjN2Qt YWI4NC1jNmQ3MGIxYjAxYjEiLCJhdWQiOiJTTUYiLCJzY29wZSI6Im5zbWYtcGR1c2Vzc2lvbiIsImV4cCI6MTY0NDQ5MjExOH0.xGud7dIwEugyXV-I8M-xld9OAr_rKbB3y 4_SWVVAwHyb6DxtWUz5uB-KtXwozbRJorMNkF6rwz5D0G6VAm9WLw
User agent header
User-Agent → NFType-NFInstanceId fqdn
UDR-6faf1bbc-6e4a-4454-a507-a14ef8e1bc11 abc.com
Via header
Via → HttpVersion fqdn
2.0 abc.5gc.mnc012.mcc311.pub.3gppnetwork.org
(Note - Since NF-Instance ID is not a part of Via header, fqdn will be used as the required key)Configuration
Ingress Gateway
Enable
You can enable LCI and OCI Headers globally by setting the lciHeaderConfig.enabled and ociHeaderConfig.enabled parameters as true, respectively.
Configure
You can configure LCI and OCI Headers using the Helm based configuration:
Sample Helm configuration:
lciHeaderConfig:
enabled: true
loadThreshold: 30
localLciHeaderValidity: 60000 #(value in milliseconds)
producerSvcIdHeader: "UDRHeader"
ociHeaderConfig:
enabled: true
producerSvcIdHeader: "UDRHeader"
validityPeriod: 30000 #(value in milliseconds)
overloadConfigRange: #Note - minor, major and critical conditions should cover complete range of 0 to 100 both inclusive for it to be a valid config
minor: "[75-80]"
major: "[81-90]"
critical: "[91-100]"
reductionMetrics:
minor: 5 #(Possible values 1 to 9 both inclusive)
major: 15 #(Possible values 5 to 15 both inclusive)
critical: 25 #(Possible values 10 to 50 both inclusive)
nfInstanceId: *nfInsId #Producer NF Instance ID
svcToSvcInstanceIdMapping:
- svcName: "ocudr-nudr-drservice"
serviceInstanceId: *nfInsId
perfInfoConfig:
pollingInterval: 5000 #(value in milliseconds)
serviceName: "nudr-perf-info"
host: nudr-perf-info
port: 5905
perfInfoRequestMap: "/load"Note:
During configuring the minor, major, or critical range numbers make sure that the range numbers specified do not overlap each other. For example 75-80 and 80-85. This can give you incorrect result.Egress Gateway
Enable
You can enable LCI and OCI Headers globally by setting the lciHeaderConfig.enabled and ociHeaderConfig.enabled parameters as true, respectively.
Configure
You can configure LCI and OCI Headers using the Helm based configuration:
Sample Helm configuration:
lciHeaderConfig:
enabled: true
loadThreshold: 40
localLciHeaderValidity: 1000 #(value in milliseconds)
consumerSvcIdHeader: "ConsumerHeader"
producerSvcIdHeader: "UDRHeader"
ociHeaderConfig:
enabled: true
consumerSvcIdHeader: "ConsumerHeader"
producerSvcIdHeader: "UDRHeader"
validityPeriod: 5000 #(value in milliseconds)
overloadConfigRange: #Note - minor, major and critical conditions should cover complete range of 0 to 100 both inclusive for it to be a valid config
minor: "[75-80]"
major: "[81-90]"
critical: "[91-100]"
reductionMetrics:
minor: 5 #(Possible values 1 to 9 both inclusive)
major: 15 #(Possible values 5 to 15 both inclusive)
critical: 25 #(Possible values 10 to 50 both inclusive)
nfInstanceId: *nfInsId #Producer NF Instance ID
svcToSvcInstanceIdMapping:
- svcName: "ocudr-nudr-drservice"
serviceInstanceId: *nfInsId
perfInfoConfig:
pollingInterval: 5000 #(value in milliseconds)
serviceName: "nudr-perf-info"
host: nudr-perf-info
port: 5905
perfInfoRequestMap: "/load"Note:
During configuring the minor, major, or critical range numbers make sure that the range numbers specified do not overlap each other. For example 75-80 and 80-85. This can give you incorrect result.2.23 Support for User-Agent Header
User Agent Header Validation in Ingress Gateway
User-Agent header helps the producer Network Function (NF) to identify the consumer NF that has sent the request. To implement this, 3GPP introduced the use of User-Agent header for consumers to include the same in service requests. Additionally, producers may require to support the validation of the User-Agent headers to complete the request identification process in the network.
This feature validates the User-Agent header in the incoming request against the configured values in Ingress Gateway.
The following format is used to generate User-Agent header:
<NFTYPE>-<NFInstanceID> <NF FQDN>where, <NFType> is the type of the Network
Function.
<NFInstanceID> is the instance
ID of the NF.
<NF FQDN> is the FQDN of the
NF.
Note:
You must provide the correct format as follows for this feature to work, providing only theNFType without the hyphen will lead to request failure.
User-Agent headers must be in one of the following sample formats:
PCF-6c03761c-fc42-47a5-9c37-cb8c520fb56fPCF-PCF-6c03761c-fc42-47a5-9c37-cb8c520fb56f pcf.oracle.com
Below screenshot shows how the User-Agent header is passed in the
request:
- If the user-agent header is present, then it is matched with the configured NF types. If a match is found, then validation is successful and request is allowed to pass. If a match is not found, then request is rejected with a configurable error code.
- If the user-agent header is present and has multiple values, then the request is rejected with a configurable error code. Hence, the user-agent header, if present should have a single value.
- If the user-agent header is not present and validationType is relaxed, then validation is not made and request is allowed to pass. If validationType is strict, then request will be rejected with a configurable error code.
- If the configured NF types are not PCF and NRF, then the configuration is rejected in the REST mode. In case of Helm mode, the startup probe fails.
Managing User-Agent Header
Enable
- Helm: Set the value for property
userAgentHeaderValidationConfigModeto Helm and parameteruserAgentHeaderValidationto true in thecustom-values.yamlfile under the Ingress Gateway section. For more information, see the section Server Header at Ingress Gateway under Chapter Customizing Cloud Native Core Policy in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Converged Policy Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide . - REST API: Set the value for property
userAgentHeaderValidationConfigModeto REST, and send a PUT request, along with payload by setting flaguserAgentHeaderValidationto true.Note:
By default, this feature is disabled withuserAgentHeaderValidationConfigModeas REST.For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Configure
You can configure this feature either through HELM or REST.
The configuration applies to all the routes. By default, feature is disabled and mode of configuration is REST. Scope of configuration remains same throughout the deployment lifecycle. That is, If configMode is HELM, then only HELM based configuration is supported throughout the deployment. REST based configuration is not supported in between.
- Configure using
Helm:
#User-Agent header validator configuration #Mode of configuration. Can be either HELM or REST userAgentHeaderValidationConfigMode: REST userAgentHeaderValidation: enabled: false # If User-Agent header is not present or it's value is null in the incoming request then validation type can be used to skip or perform validation. If set to strict then validation will be performed. # If set to relaxed then validation will be skipped. validationType: strict # List of consumer NF Types to be matched against the value of User-Agent header in the request consumerNfTypes: - "PCF" - "NRF" - Configure using REST API: You can perform the PUT operation
on the
http://10.75.229.75:31187/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/useragentheadervalidation
REST API to configure the feature.
For more information about REST API configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.{ "enabled": false, "validationType": "strict", "consumerNfTypes": [ "PCF","NRF" ] }
Observe
See UDR Metrics and Alert Details sections for more information on metrics and configurable parameters, respectively.
User Agent Header Generation in Egress Gateway
This feature generates the User-Agent header to help the producer NF identify the consumer NF that sent the request.
The generated User-Agent header is in the following format:
<NF Type>-<Instance-Id>
<FQDN>, only if addFqdnToHeader is set to true.
Otherwise, the generated header is in the following format:
<NF Type>-<Instance-Id>where,
<NF Type> is the type of the Network Function.
<Instance-Id> is the instance ID of the
NF.
<FQDN> is the FQDN of the
NF.
'User-Agent': 'UDR-6c03761c-fc42-47a5-9c37-cb8c520fb56f udr.oracle.com' #If addFqdnToHeader is set to true
'User-Agent': 'UDR-6c03761c-fc42-47a5-9c37-cb8c520fb56f' #If addFqdnToHeader is set to falseManaging User-Agent Header
Enable
- Helm: Set the value for property
userAgentHeaderConfigModeto Helm and parametersuserAgentHeaderandoverwriteHeaderto true in thecustom-values.yamlfile under the Egress Gateway section. - REST API: Set the value for property
userAgentHeaderConfigModeto REST, and send a PUT request, along with payload by setting flagsenabledandoverwriteHeaderto true.Note:
By default, this feature is disabled withuserAgentHeaderValidationConfigModeas REST. For egressgateway, to generate the User Agent header using the<NF Type>and<Instance-Id>provided in the custom values, theoverwriteHeaderflag should always be set to true. If theaddFqdnToHeaderflag is set to true, egressagteway adds fqdn to the header only if the<FQDN>value is provided in the payload.For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Configure
You can configure this feature either through HELM or REST.
The configuration applies to all the routes. By default, feature is disabled and mode of configuration is REST. Scope of configuration remains same throughout the deployment lifecycle. That is, If configMode is HELM, then only HELM based configuration is supported throughout the deployment. REST based configuration is not supported in between.
- Configure using
Helm:
#User-Agent header generation configuration userAgentHeaderConfigMode: REST userAgentHeader: enabled: false # flag to enable or disable the feature nfType: "" # NF type of consumer NF nfInstanceId: "" # NF type of consumer NF addFqdnToHeader: false # Flag to add fqdn. If enabled then user-agent header will be generated along with the fqdn configured otherwise fqdn will not be added nfFqdn: "" #fqdn of NF. This is not the fqdn of gateway overwriteHeader: false oauthClient: enabled: false nfInstanceId: fe7d992b-0541-4c7d-ab84-c6d70b1b01b1 nfType: PCF - Configure using REST API: You can perform the PUT operation
on the http://10.75.229.75:31187/udr/nf-common-component/v1/egw/useragentheader
REST API to configure the feature.
For more information about REST API configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.."useragentheader": { "enabled": false, "nfType": " UDR", "nfInstanceId": "fe7d992b-0541-4c7d-ab84-c6d70b1b01b1", "nfFqdn": "udr.oracle.com", "addFqdnToHeader": false, "overwriteHeader": true }
2.24 Diameter Gateway Pod Congestion Control
The Diameter Gateway is a diameter proxy agent for UDR. Being a front-end microservice for diameter traffic for both Ingress Gateway and Egress Gateway, the Diameter Gateway can get congested due to higher traffic, higher CPU usage, and higher memory utilization. Thus, it is imperative to have suitable congestion control features in place for Diameter Gateway pods to avoid adverse impacts on latency and performance. Another reason for the need for a congestion control mechanism for Diameter Gateway is the nature of diameter connections. These connections are long lived and are distributed by external LoadBalancer. When LoadBalancer routes an incoming request from network to Diameter Gateway pod, it does not take into account health or load of the pod. As a result, uneven distribution of traffic may happen and gateway pods experience congestion.
- Determine the pod congestion state
- Trigger Congestion Control
Determining Pod Congestion State
- Normal
- DOC (Danger of Congestion)
- Congested
- CPU: CPU usage of the container is monitored and congestion state is calculated based on the following parameter - cpuacct.usage that provides current CPU usage in nano seconds.
- Memory: Memory usage of the container is monitored and congestion
state is calculated based on the following parameter.
- memory.limit_in_bytes is the memory limit
- memory.usage_in_bytes is the current memory usage
- Queue: Pending requests count is the number of pending requests waiting for a response from the backend microservice. The counter is incremented for all incoming requests and decremented when there is a response.
Triggering Congestion Control
Note:
Congestion control does not apply to response messages as they are always accepted.The priority value for a request can be from 0 to 15 where 0 is the highest priority and 15 is the lowest priority.
Enable
To enable the feature:
In the Diam-gateway section of the custom-values.yaml file, set the value of the podCongestion.enabled flag to true. By default, it is false.
Configure
- Default priority configuration for all the messages.
- Sample count threshold for congestion state change.
- Diameter Request message priority configuration when pod in DOC and CONGESTED state.
- DOC and CONGESTED state configuration.
- Threshold percentage for Cpu, Memory and Queue usage for DOC and CONGESTED state.
- Configure using CNC Console: Perform the feature configurations on the Diameter Gateway Congestion Configuartions page. For more information about the configurations, seeDiameter Gateway Congestion .
- Configure using REST API: UDR provides the REST API for configurating diameter gateway pod congestion control feature. You can perform the PUT operation to configure the feature. For more information about REST API configuration, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
The default configuration details for Diameter Pod Congestion Control feature are:
Deployment resource
- 1 Diameter Gateway pod with default resource (2cpu, 2 Gb memory)
- 3 diameterproxy pods with default resource (2cpu, 2Gb memory)
and Diameter traffic model
- 33% Subscription with getting profile
- 33% update the profile data
- 33% get profile data
Table 2-23 Congestion Configuration
| Pod state | CPU Usage | Memory Usage | Queue Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | < 60% | 40% | NA |
| DOC (Danger of Congestion) | 60% to 80% | 40% to 50% | NA |
| Congested | > 80% | 50% | NA |
Note:
Initial pod state set to NORMAL and state will change based on sample count and one of the resource usage goes more than configured number.Observe
- ocudr_pod_congestion_state
Note:
Prometheus automatically injects name of the pod with label name "kubernetes_pod_name" to metric. This information is further used for alerting purposes.Maintain
Error logs are generated when the system is congested and the actions taken to bring the system back to normal. Warning logs are generated to indicate the congestion level. However, error logs are not generated when messages are rejected to avoid additional resource usage to write error logs.
{"instant":{"epochSecond":1644819199,"nanoOfSecond":415860635},"thread":"pool-7-thread-1","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocpm.cne.common.congestion.CongestionStateManager","message":"Abrupt
change in congestion state, current state : NORMAL, calculated state : CONGESTED,
transientStateSampleCount :
0","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger","threadId":44,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-02-14T06:13:19.415+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"1.15.50","mktgVersion":"1.15.0.0.0","microservice":"diam-gateway","vendor":"Oracle"}{"instant":{"epochSecond":1644819200,"nanoOfSecond":722676387},"thread":"pool-7-thread-1","level":"WARN","loggerName":"ocpm.cne.common.congestion.CongestionStateManager","message":"Current
Congestion state changed, old state : DOC, new state : NORMAL, transientStateSampleCount : 10
","endOfBatch":false,"loggerFqcn":"org.apache.logging.slf4j.Log4jLogger","threadId":44,"threadPriority":5,"messageTimestamp":"2022-02-14T06:13:20.722+0000","application":"ocudr","engVersion":"1.15.50","mktgVersion":"1.15.0.0.0","microservice":"diam-gateway","vendor":"Oracle"}2.25 Support for Network Exposure Function API
- UDR to support exposure data for signaling (Access and Mobility data and PduSessionManagementData) and NEF Subscription and Notification APIs.
- Provisioning of the exposure data into the UDR by enhancing the existing provisioning interface.
Figure 2-24 NEF Integration
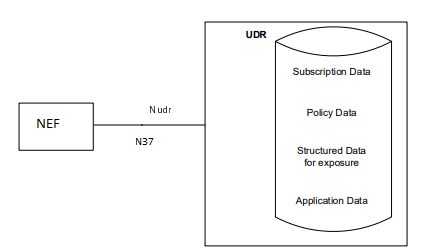
- Query: The Query service operation is used for the NEF to retrieve the data stored in the UDR.
- Create: The Create service operation is used for the NEF to create the data into the UDR.
- Update: The Update service operation is used for the NEF to update the data stored in the UDR.
- Delete: The Delete service operation is used for the NEF to remove the data from the UDR.
- Subscribe: The Subscribe service operation is used for the NEF to subscribe to the data change notification from the UDR.
- Unsubscribe: The Unsubscribe service operation is used for the NEF to unsubscribe to the data change notification from the UDR.
- Notify: The Notify service operation is used for the UDR to notify the data change notification to the NEF.
Note:
For more information, see 3GPP specification 29.519.For more information on operations supported for NEF data, see the Operations Supported for NEF Data section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
2.26 Supports Unstructured Data Storage Function
Figure 2-25 Relation between Any NF and UDSF
Note:
For structured data types, see 3GPP specification 29.504 and 29.5192.27 Support for Default Group ID in SLF
Overview
When a subscriber is not provisioned in the Subscriber Location Function (SLF), the SLF responds with an error stating "Subscriber does not exist". This feature provides an option of not responding with an error but instead provides a default group or default NF for the subscribers that are not provisioned in the SLF.
Based on the default group nfgroupId configured we can control the NFType for which default group ID is applicable. If the feature is disabled, then the response for non provisioned subscribers will be "Subscriber does not exist". Default slfGroupName gets inserted during installation or upgrade to SLF_GROUP_NAME table using helm hooks. You can update the Default slfGroupName using the SLF GroupName Configuration API. For information about SLF GroupName Configuration API, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Note:
If subscriber is not provisioned in the SLF and default ID group feature is enabled, then SLF look up will give a response as 200 OK, provided that the default group is configured with nfGroupID including the nfType requested in the query parameter.To Enable
To enable this feature using CNC Console or Helm chart changes:
- Enable Using CNC Console: To enable this feature using CNC Console, set the defaultGroupIdEnabled field as true in the Data Repository Service Configurations page under Service Configurations.
- Enable Using values.yaml file: To enable this feature, set the defaultGroupIdEnabled flag as 'true' under the nudr-drservice section of default SLFGroupName.
To Configure default SLFGroupName
To configure default SLFGroupName using CNC Console or helm chart changes:
- Configure Using CNC Console: To configure default SLFGroupName using CNC Console application, set the defaultSLFGroupName field as DefaultGrp.
- Configure Using REST API: To configure default SLFGroupName using the values.yaml file, set the value of the defaultSLFGroupName parameter in the file. For information about these parameters, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
To Observe
See UDR Metrics and UDR KPIs sections for more information on metrics, alerts, and KPIs respectively.
2.28 Subscriber Location Function
Overview
In large deployments, network operators may choose to deploy an SLF, which helps in identifying a subscriber to the particular Network Function(NF). This allows the network operators to support ranges based on subscriber identities for NF's.
You can configure UDR to support the storage and retrieval of this information by acting as a Subscriber Location Function (SLF). This SLF information is consumed by NRF. This 5G SLF solution supports Nudr-groupid-map service as defined by 3GPP and registers with NRF for this service. UDR supports REST or JSON based provisioning APIs for SLF data.
Note:
To understand SLF Lookup Support on UDR, it is recommended to see the SLF Lookup APIs as defined in the 3GPP 29.504 v16.2.0To Configure
To configure SLF over UDR network using CNC Console or REST API:
- Configure Using CNC Console: To configure SLF using CNC Console application, see Provisioning - SLF Data.
- Configure Using REST API: To configure SLF using REST APIs,
see the following sections in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core,
Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- Operations Supported for SLF Data
- Provisioning Operations for SLF Data
To Observe
See UDR Metrics and UDR KPIs sections for more information on metrics, configurable parameters, and KPIs respectively.
2.28.1 Error Response Enhancement for SLF Lookup Request
SLF supports the “cause” attribute in the problem details for all error responses as per 3GPP 29.504 specification. The "cause" attribute in the problem details object of the HTTP error response payload is used to indicate the application-related information for that specific occurrence of the error. This enables the HTTP client to take appropriate action. The error response is enhanced to support error causes scenario for SLF lookup requests.
The following table lists the error response code for SLF.
Table 2-24 Error Response Code
| Protocol or Application Error | Description | Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| USER_NOT_FOUND |
When the subscriber UE ID received in the NF Group ID retrieval request does not exist in the database. HTTP Status Code: 404 NOT Found |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| GROUP_IDENTIFIER_NOT_FOUND |
When the subscriber UE ID retrieval request is received in the NF Group ID and the subscriber exists in the database but the NF Group ID is not configured for the NF type requested. HTTP Status Code: 404 NOT Found |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| MANDATORY_QUERY_PARAM_MISSING |
Query parameter which is defined as mandatory or conditional but which is mandatory requirement for an HTTP method is not included in the URI of the request. HTTP Status Code: 400 BAD REQUEST |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| MANDATORY_QUERY_PARAM_MISSING |
A mandatory query parameter or conditional query parameter but which is mandatory requirement for an HTTP method that was received in the URI with semantically incorrect value. HTTP Status Code: 400 BAD Request |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| INVALID_QUERY_PARAM |
The HTTP request contains an unsupported query parameter in the URI. HTTP Status Code: 400 BAD REQUEST |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| MANDATORY_IE_INCORRECT |
A mandatory IE (which can be within the JSON body, a
variable part of an HTTP Status Code: 400 BAD REQUEST |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| OPTIONAL_IE_INCORRECT |
An optional Information Element (IE) (which can be within the JSON body or an HTTP header) for an HTTP method that was received with a semantically incorrect value which prevents successful processing of the service request. HTTP Status Code: 400 BAD Request |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
| SUBSCRIBER_LINKED_TO_GROUP |
When deleting a group which has subscribers linked to that particular group. HTTP Status Code: 403 FORBIDDEN |
This error response is caused due to the following
scenario:
|
2.29 Server Header Inclusion in Error Response
The Network Function interacting with UDR can determine the originator of HTTP error response only if the originator of an error includes a Server header. You can add the Server header attribute in the outgoing error response of UDR or SLF with NF name and NF instance id registered with NRF.
Format:
Server:
<NF_Name_registered_in_NRF>-<NFInstanceID_Registered_In_NRF>
Example: Server:
UDR-5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03
You can enable and configure the server header feature using Helm configuration and REST API.
Configure using HELM
You can enable the server header by setting the
serverHeaderDetails: enabled parameter to true in the
ocudr-custom-values.yaml file. This includes all UDR or SLF 4xx and 5xx responses
indicating details of the server header, where the problem originated. To change the
default configuration, modify the serverHeaderDetails and
errorCodeSeriesList values in the ocudr-custom-values.yaml
file. For more information about the ocudr-ingressgateway microservice parameters,
see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository
Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Configure using REST API
- Configure the
errorcodeserieslistonhttp://< NUDR_CONFIG_SERVICE_IP>:<NUDR_CONFIG_PORT>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/errorcodeserieslist.[ { "id": "E1", "errorCodeSeries": [ { "errorSet": "4xx", "errorCodes": [ -1 ] }, { "errorSet": "5xx", "errorCodes": [ -1 ] } ] }, { "id": "E2", "errorCodeSeries": [ { "errorSet": "4xx", "errorCodes": [ -1 ] } ] } ] - Configure
serverheaderdetailsonhttp://< NUDR_CONFIG_SERVICE_IP>:<NUDR_CONFIG_PORT>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/serverheaderdetailsNote:
- The
errorCodeSeriesIdis a mandatory attribute. The value must be one among theerrorCodeSeriesListresource defined in/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/errorcodeserieslistendpoint. - The
nfTypeis a mandatory attribute. Server header will not be included in the response, ifnfTypeis not defined. - The
nfInstanceIdis an optional attribute. OnlynfTypeis used for server header value, ifnfInstanceIdis not defined. You must provide the same value used in customs values.yaml file fornfInstanceId.
{ "enabled": true, "errorCodeSeriesId": "E1", "configuration": { "nfType": "UDR", "nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03" } } - The
To Maintain
In case of failure or misconfiguration, server header does not populate in UDR or SLF responses. In this case, it is recommended to follow the instructions given in the Configure using HELM and Configure using REST API sections.
2.30 Rate Limiting
Rate Limiting means setting the number of HTTP requests that UDR can receive in a given period. With the implementation of this feature, UDR can restrict the traffic for a particular route.
Note:
This feature supports only priority based discard.- All the routes configured under the routesconfiguration REST API and its corresponding rate limit configuration details are screened.
- Starts calculating the number of requests that should be dropped in each sampling period specific to the incoming request route + HTTP method.
- At the end of each sampling period, rate calculator notifies the route level, rate limit about the rate calculated per route+{Method}.
- Requests with sbi-priority header with a value greater than the configured number are discarded. Requests with lesser values are rejected based on configured error code.
- The number of messages dropped in the current sampling period are decided based on the extra number of messages received than configured limit in previous sampling period.
To Enable
By default, UDR loads all the rate limiting configuration payloads while installing
or upgrading UDR when Ingress Gateway default configuration is used. Once the UDR
installation or upgrade completes, the user can edit the routelevelratelimiting.json
payload to send a PUT request to
http://10.75.229.75:31187/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw/routelevelratelimiting.
To enable the rate limiting feature, set the ratelimit parameter to 'true' in the routelevelratelimiting.json payload.
To Configure
To configure the rate limiting feature on UDR, the user is required to do the REST based configurations on Ingress Gateway, which are stored in the configuration database of UDR.
For more information about REST based APIs, see the Configuration APIs for Rate Limit section in the Configuration API Specification chapter of the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
2.31 Overload Handling
Overload occurs when 100% of the planned capacity is exhausted. It can be due to uneven distribution of traffic towards a given UDR service instance, network fluctuations leading to traffic bursts, or unexpected high traffic volume at any given point of time.
During overload conditions, the service's response time may grow to unacceptable levels, and exhaustion of resources may force service to unexpected behavior or even downtime. Overload management helps to control services downtime and ensures service availability during extreme overload conditions.
Using Ingress Gateway and perf-info microservices, UDR provides options to control network congestion and handle the overload scenarios.
REST API's support for Overload Control Feature
- GET:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocpolicymapping - PUT:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocpolicymapping
{
"enabled": true,
"mappings": [
{
"svcName": "testDeploy-nudr-drservice",
"policyName": "OCDP1"
}
],
"samplingPeriod": 6000
}Table 2-25 Request/Response Parameters
| Field Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| enabled | boolean | Set the values to true or false to enable or disable the overload control feature. |
| mappings.svcName | string | The SVC entry determine mapping between services and discards policy name per service. |
| mappings.policyName | string | The discard policy entry determine mapping between services and discards policy name per service. |
| samplingPeriod | integer | Time frame for each cycle of overload control per service. The value is in milliseconds. |
- GET:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocdiscardpolicies - PUT:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocdiscardpolicies
[
{
"name": "OCDP1",
"scheme": "PercentageBased",
"policies": [
{
"level": "L1",
"value": 0,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error429"
},
{
"level": "L2",
"value": 5,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error429"
},
{
"level": "L3",
"value": 15,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error429"
},
{
"level": "L4",
"value": 25,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error503"
}
]
},
{
"name": "OCDP2",
"scheme": "PriorityBased",
"policies": [
{
"level": "L1",
"value": 30,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error429"
},
{
"level": "L2",
"value": 24,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error429"
},
{
"level": "L3",
"value": 15,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error429"
},
{
"level": "L4",
"value": 10,
"action": "RejectWithErrorCode",
"errorCodeProfile": "error503"
}
]
}
]Table 2-26 Request/Response Parameters
| Field Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| name | string | Name of the discarded policy. |
| scheme | string | Discarded policy scheme. |
| policies.value | integer | Value of priority, above which requests are considered as potential candidates for drop. It is the percentage of requests to drop in the current sampling period over the calculated rate in the previous sampling period. |
| policies.action | string | Defines the action to be taken on selected request rejections based on the error code. |
| policies.level | string | Defines the overload level. |
| policies.errorCodeProfile | string | The error code profiles. |
- GET:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/errorcodeprofiles - PUT:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/errorcodeprofiles
[
{
"name": "error429",
"errorCode": 429,
"errorCause": "Too many reequests",
"errorTitle": "Too many reequests",
"redirectURL": "",
"retry-after": "",
"errorDescription": "Too many reequests"
},
{
"name": "error503",
"errorCode": 503,
"errorCause": "Backend not able to handle traffic",
"errorTitle": "Backend not able to handle traffic",
"redirectURL": "",
"retry-after": "",
"errorDescription": "Backend not able to handle traffic"
}
]Table 2-27 Request/Response Parameters
| Field Name | Data type | Mandatory (M) or Optional (O) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | M | Name of the error. |
| errorCode | string | M | The errorCode field in an errorScenario which determines the HttpStatusCode that need to be populated in the ProblemDetails (HttpStatus field) response from ingress gateway, when the exception occurred at ingress gateway matches the configured errorScenario exceptionType field. |
| errorCause | string | O |
The errorCause field in an errorScenario determines the error cause that need to be populated in the ProblemDetails (cause field) response from ingress gateway when the exception occurred at ingress gateway matches the configured errorScenario exceptionType parameter. |
| errorTitle | string | O | The errorTitle field in an errorScenario determines the title that needs to be populated in ProblemDetails (Title field) response from ingress gateway, when the exception occurred at ingress gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. |
| redirectURL | string | O |
The redirectUrl field in an errorScenario determines the redirection URL, this value is populated in location header when sending the response from ingress gateway. The header is populated only when the exception occurred at ingress gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. The errorCode configured for the particular errorScenario lies in 3xx error series and the redirectUrl field for the particular errorScenario is configured appropriately. |
| retry-after | string | O |
The retryAfter field in an errorScenario determines the value in seconds/particular date after which the service must be retried. This value is populated inRetry-After header when sending the response from ingress gateway. The header is populated only when the exception occurred at ingress gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType parameter. The errorCode configured for the particular errorScenario lies in 3xx error series and the retryAfter field for the particular errorScenario is configured appropriately in seconds. |
| errorDescription | string | O |
The errorDescription field in an errorScenario determines the description that need to be populated in ProblemDetails (Detail field) response from ingress gateway when the exception occurred at ingress gateway matches the configured errorScenario's exceptionType field. |
- GET:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/perf-info/overloadLevelThreshold - PUT:
/udr/nf-common-component/v1/perf-info/overloadLevelThreshold
[
{
"svcName": "ocudr-nudr-drservice",
"metricsThresholdList": [
{
"metricsName": "svc_failure_count",
"levelThresholdList": [
{
"level": "L1",
"onsetValue": 13000,
"abatementValue": 12500
},
{
"level": "L2",
"onsetValue": 14000,
"abatementValue": 13500
},
{
"level": "L3",
"onsetValue": 15000,
"abatementValue": 14500
},
{
"level": "L4",
"onsetValue": 16000,
"abatementValue": 15500
}
]
},
{
"metricsName": "memory",
"levelThresholdList": [
{
"level": "L1",
"onsetValue": 50,
"abatementValue": 45
},
{
"level": "L2",
"onsetValue": 70,
"abatementValue": 65
},
{
"level": "L3",
"onsetValue": 85,
"abatementValue": 82
},
{
"level": "L4",
"onsetValue": 90,
"abatementValue": 88
}
]
},
{
"metricsName": "cpu",
"levelThresholdList": [
{
"level": "L1",
"onsetValue": 65,
"abatementValue": 60
},
{
"level": "L2",
"onsetValue": 75,
"abatementValue": 70
},
{
"level": "L3",
"onsetValue": 80,
"abatementValue": 75
},
{
"level": "L4",
"onsetValue": 90,
"abatementValue": 85
}
]
},
{
"metricsName": "svc_pending_count",
"levelThresholdList": [
{
"level": "L1",
"onsetValue": 13000,
"abatementValue": 12500
},
{
"level": "L2",
"onsetValue": 14000,
"abatementValue": 13500
},
{
"level": "L3",
"onsetValue": 15000,
"abatementValue": 14500
},
{
"level": "L4",
"onsetValue": 16000,
"abatementValue": 15500
}
]
}
]
} ]Table 2-28 Request/Response Parameters
| Field Name | Data type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| svcName | string | Name of the back end service (svcName). |
| metricsThresholdList | array | List of criteria used to calculate the load level. |
| metricsThresholdList.metricsName | string | Name of the criteria |
| metricsThresholdList.levelThresholdList | array | List of threshold values |
| metricsThresholdList.levelThresholdList.level | string | Specifies the name of the level. The name specified in this parameter must match with the level name in the Ingress Gateway's ocdiscardpolicies. |
| metricsThresholdList.levelThresholdList.onsetValue | string |
If the metric level goes below this value, load level goes to a lower value.
|
| metricsThresholdList.levelThresholdList.abatementValue | string | If the metric level goes above this value, load level is set. |
To Enable Overload Control
- custom-values.yaml file:
- In the global section of the custom-values.yaml file, enable the overloadManagerEnabled flag.
- In the perf-info section of the custom-values.yaml
file, perform the following changes:
envMysqlDatabase: Provide the configdb name of the deployed setup.The configdbName is the value, which is assigned while creating Kubernetes secret at the time of UDR installation.
prometheus: Provide the prometheus url of the deployed setup. For Example :10.75.229.87:31403/cne-2230-rc2/prometheus/.
- Using REST API endpoint:
- To enable the ocpolicymapping API:
- Send the GET request to
http://<nudr-configsvcname:port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocpolicymapping.{ "enabled": false, "mappings": [ { "svcName": "<ReleaseName>-nudr-drservice", "policyName": "OCDP1" } ], "samplingPeriod": 6000 } - Edit the following parameters in the response
payload:
- Set the enabled flag as 'true' in the ocpolicymapping json file and
- Change svcName to <ReleaseName>. For example, if svcName is testDeploy, you must update as testDeployin the below payload.
- Send the PUT request to
http://<nudr-configsvcname:port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocpolicymapping{ "enabled": true, "mappings": [ { "svcName": "testDeploy-nudr-drservice", "policyName": "OCDP1" } ], "samplingPeriod": 6000 }
- Send the GET request to
- To validate ocdiscardpolicy API:
- Send the GET request to
http://<nudr-configsvcname:port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocdiscardpolicies
By default the percentages are configured for OCDP1.[ { "name": "OCDP1", "scheme": "PercentageBased", "policies": [ { "level": "L1", "value": 0, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error429" }, { "level": "L2", "value": 5, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error429" }, { "level": "L3", "value": 15, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error429" }, { "level": "L4", "value": 25, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error503" } ] }, { "name": "OCDP2", "scheme": "PriorityBased", "policies": [ { "level": "L1", "value": 30, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error429" }, { "level": "L2", "value": 24, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error429" }, { "level": "L3", "value": 15, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error429" }, { "level": "L4", "value": 10, "action": "RejectWithErrorCode", "errorCodeProfile": "error503" } ] } ] - To changes the percentage, send PUT request
along with above discardpolicy payload
http://<nudr-configsvcname:port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocdiscardpolicies.
- Send the GET request to
-
Set the
Note:
You should not use memory as a overload threshold configuration for overload control feature because the memory accumulated by the pods during the traffic run is not released by the pods even when the traffic is reduced. This causes the service to remain in high overload levels causing the traffic to be discarded.overloadthresholdconfigurationsAPI to control the overload levels. By default below configurations are present when you deploy UDR:- Send the GET request to
http://<nudr-configsvcname:port>/udr/nf-common-component/v1/perf-info/overloadLevelThreshold.[ { "svcName": "ocudr-nudr-drservice", "metricsThresholdList": [ { "metricsName": "svc_failure_count", "levelThresholdList": [ { "level": "L1", "onsetValue": 13000, "abatementValue": 12500 }, { "level": "L2", "onsetValue": 14000, "abatementValue": 13500 }, { "level": "L3", "onsetValue": 15000, "abatementValue": 14500 }, { "level": "L4", "onsetValue": 16000, "abatementValue": 15500 } ] }, { "metricsName": "memory", "levelThresholdList": [ { "level": "L1", "onsetValue": 50, "abatementValue": 45 }, { "level": "L2", "onsetValue": 70, "abatementValue": 65 }, { "level": "L3", "onsetValue": 85, "abatementValue": 82 }, { "level": "L4", "onsetValue": 90, "abatementValue": 88 } ] }, { "metricsName": "cpu", "levelThresholdList": [ { "level": "L1", "onsetValue": 65, "abatementValue": 60 }, { "level": "L2", "onsetValue": 75, "abatementValue": 70 }, { "level": "L3", "onsetValue": 80, "abatementValue": 75 }, { "level": "L4", "onsetValue": 90, "abatementValue": 85 } ] }, { "metricsName": "svc_pending_count", "levelThresholdList": [ { "level": "L1", "onsetValue": 13000, "abatementValue": 12500 }, { "level": "L2", "onsetValue": 14000, "abatementValue": 13500 }, { "level": "L3", "onsetValue": 15000, "abatementValue": 14500 }, { "level": "L4", "onsetValue": 16000, "abatementValue": 15500 } ] } ] } ]
- Send the GET request to
- To enable the ocpolicymapping API:
- Send the GET request to
http://ocudr-ingress-gateway:80/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocpolicymapping. - Change the policyName to 'OCDP2' from OCDP1. OCPD1 denotes the percentage based discard policy.
- Send the PUT request to
http://ocudr-ingress-gateway:80/udr/nf-common-component/v1/igw-sig/ocpolicymapping.
This enables the overload control feature for priority based discard policy.
For more information about the configurable parameters related to overload handling, see the Configuring Unified Data Repository section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
To Validate
- If traffic reaches L1 level, traffic will not be discarded and alarm will be raised
- If traffic reaches L2 level , 5 percentage traffic will be discarded and alarm will be raised
- If traffic reaches L3 level ,15 percentage traffic will be discarded and alarm will be raised
- If traffic reaches L4 level , 25 percentage traffic will be discarded and alarm will be raised
If priority based discard policy is enabled, then UDR identifies requests with
sbi-priority defined and discards all the requests that has
header value greater than 30. When the CPU reaches the 65-70 percentage, it is on
L1.
If percentage based discard policy is enabled, then discard percentage is 0 and no traffic is discarded.
- L1Alert name: OcudrOverload60Percent
Note:
You should not use memory as a overload threshold configuration for overload control feature because the memory accumulated by the pods during the traffic run is not released by the pods even when the traffic is reduced. This causes the service to remain in high overload levels causing the traffic to be discarded.Table 2-29 Default Configuration Details for Overload Threshold Levels
Type L1Alert name: OcudrOverload60Percent - Onset Abatement Discard % Discard Priority CPU 65 60 0 30 Memory 50 45 0 30 Pending Count 13000 12500 0 30 Failure Count 13000 12500 0 30 - L2 Alert name:OcudrOverload75Percent
Table 2-30 Default Configuration Details for Overload Threshold Levels
Type L2 Alert name:OcudrOverload75Percent - Onset Abatement Discard % Discard Priority CPU 75 70 5 24 Memory 70 65 5 24 Pending Count 14000 13500 0 30 Failure Count 14000 13500 0 30 Note:
The default error code for a discard is 429 for all the types defined above. - L3 Alert name:OcudrOverload80Percent
Table 2-31 Default Configuration Details for Overload Threshold Levels
Type L3 Alert name:OcudrOverload80Percent - Onset Abatement Discard % Discard Priority CPU 80 75 15 15 Memory 85 82 15 15 Pending Count 15000 14500 15 15 Failure Count 15000 14500 15 15 Note:
The default error code for a discard is 429 for all the types defined above. - L4 Alert name:OcudrOverload90Percent
Table 2-32 Default Configuration Details for Overload Threshold Levels
Type L4 Alert name:OcudrOverload90Percent - Onset Abatement Discard % Discard Priority CPU 90 85 25 10 Memory 90 88 25 10 Pending Count 16000 15500 25 10 Failure Count 16000 15500 25 10 Note:
The default error code for discard is 503 for all the types defined above.
Note:
If there is any breach at multiple threshold levels, then the highest threshold level is considered and appropriate action is taken. UDR also sends an alert for appropriate levels.To configure this feature, you can use REST based API configurations. For more information, see the Configuration APIs for Overload Handling section of the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
To Observe
If there is a breach at any threshold level, then UDR sends an alert. For more information about alerts, see Alert Details.
Overload Control to Support Provisioning Traffic
To support overload control for provisioning traffic, additional perf-info-prov service and ingressgateway-prov service are needed.
Ingressgateway-prov fetches the load values of the provisioning traffic from perf-info-prov.
The following configurations are required to support overload control for provisioning traffic:
- custom-values.yaml file
- Enable the perf-info-prov.enabled flag. By default, it is false.
- REST
- Modify all the configuration Rest URLs related to the Ingress Gateway overload configurations to igw-prov in place of igw-sig in the URL .
- Modify all the configuration Rest URLs related to the perf-info overload configurations to perf-info-prov in place of perf-info in the URL.
- Modify all the payloads svcName to ocudr-nudr-dr-provservice in place of ocudr-nudr-drservice.
Metrics
Table 2-33 Overload Control Feature Metrics
| Metric Name | Metric Description | Metric Type | Labels |
|---|---|---|---|
| load_level | Tracks load_level of a service. | Gauge | Service = <ReleaseName>-nudr-drservice |
| service_resource_stress | Tracks CPU, failures, and pending requests based on which the service calculates the overload level. | Gauge | type = "PendingRequest","CPU","Memory","FailureCount" Service = <ReleaseName>-nudr-drservice |
| service_resource_overload_level | Tracks individual resource overload level. | Gauge | type = "PendingRequest","CPU","Memory","FailureCount" Service = <ReleaseName>-nudr-drservice |
2.32 Oauth2.0
Overview
Oauth 2.0 is a security feature that authenticate requests received from valid consumer NFs. The consumer NF requests for access token from the issuer, 'NRF' and uses this access token to send the request to UDR.
- NF Type and NF Instance ID of UDR
- Services hosted at UDR
- NRF public Key certificate
Note:
By default, the Oauth2.0 feature is not enabled for Ingress Gateway Provisioning.validationType. There are two
types of validation as follows:
- Strict validation type: If Oauth token is received in the request header, then Ingress Gateway validates the token. If the request do not have the Oauth token, then the request fails with missing token.
- Relaxed validation type: If Oauth token is received in the request header, then Ingress Gateway validates the token. If the request do not have the Oauth token, then the request is processed further ignoring the validation.
To Enable and Configure
To enable Oauth2.0 validation, configure both Helm based and REST based configurations on Ingress Gateway.
Helm based Configuration
- Enable the oauthValidatorEnabled parameter on Ingress Gateway
- Create a secret that stores NRF public key certificate. To
create a secret, run the following
command:
kubectl create secret generic oauthsecret --from-file=public_key.crt -n ocudrIn the above command:- oauthsecret is the secret name
- ocudr is the namespace
- public_key.crt is the public key certificate
Note:
You can have any number of certificates in the secret.
- Configure the secret and namespace on Ingress Gateway in the
OAUTH CONFIGURATION section of the values.yaml using following
fields:
nrfPublicKeyKubeSecret: oauthsecret nrfPublicKeyKubeNamespace: ocudr
REST based Configuration
Using REST based configuration, you can distinguish between the certificates configured on different NRFs and can use these certificates to validate the token received from a specific NRF.
Note:
The CNCC GUI uses config API and payload as follows:/{nfType}/nf-common-component/v1/{serviceName}/{resource}” with
service name as "igw" and resource as
"oauthvalidatorconfiguration".Payload:
{
"keyIdList": [{
"keyId": "664b344e74294c8fa5d2e7dfaaaba407",
"kSecretName": "samplesecret1",
"certName": "samplecert1.crt",
"certAlgorithm": "ES256"
}],
"instanceIdList": [{
"instanceId": "664b344e74294c8fa5d2e7dfaaaba407",
"kSecretName": "samplesecret2",
"certName": "samplecert2.crt",
"certAlgorithm": "ES256"
}],
"oAuthValidationMode": "INSTANCEID_ONLY"
}Using CNCC GUI, you can configure multiple keyId and instanceId objects of different NRFs. Based on NRF instanceId received in token, UDR validates the token. It allows you to configure instanceId of NRF or keyId configured in NRF, secret name in which the certificate is stored, certificate name and certificate algorithm. After the REST request is sent, Oauth validator considers a certificate from the secret configured.
Using oAuthValidationMode, you can select the mode of validation as either INSTANCEID_ONLY, KID_ONLY or KID_PREFERRED. Based on the mode of validation selected, it checks keyIdList or instanceIdList. The KID_PREFERRED is a fall back mode where it checks for keyId in the token. If keyId is present in the token and matches with the configured keyId, then the validation mode is KID_ONLY otherwise it is INSTANCEID_ONLY.
Oauth validation should not be enabled for specific type of requests such as all provisioning requests sent to UDR. In the routesConfig section of custom-values.yaml file, set the oauth validator flag as 'false'.
Figure 2-26 oauthValidator not enabled
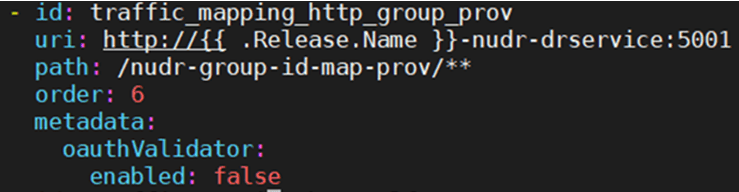
Oauth Error Codes
Table 2-34 Application Error Codes
| Error Details | Error Description | Error Causes |
|---|---|---|
|
App Error Codes: E171 HTTP Error Code: 401 Error Type: OAUTH_TOKEN_VALIDATION_FAILURE |
This error code indicates that validation of Oauth token failed at Ingress Gateway. | Oauth token passed with the request and is enclosed with the values which are incorrect to the configuration present at the Ingress Gateway. |
|
App Error Codes: E172 HTTP Error Code: 408 Error Type: OAUTH_CERT_EXPIRED |
This error code indicates that Oauth certificate expired is received at Ingress Gateway. | Indicates that all the attributes are present and in the correct format, but the token has expired with respect to ingress gateway configuration. |
|
App Error Codes: E173 HTTP Error Code: 407 Error Type: OAUTH_MISMATCH_IN_KID |
This error code indicates that Oauth miss match in KID at Ingress Gateway. | Incorrect issuer and KID value are included in the request. |
|
App Error Codes: E174 HTTP Error Code: 406 Error Type: OAUTH_PRODUCER_SCOPE_NOT_PRESENT |
This error code indicates that producer scope not present in the Oauth token received at Ingress Gateway. | The producer scope is not present in the token of the request. |
|
App Error Codes: E175 HTTP Error Code: 405 Error Type: OAUTH_PRODUCER_SCOPE_MISMATCH |
This error code indicates that producer scope present in the Oauth token do not match with the producer scope configured in Ingress Gateway. | The producer scope sent through the token either has a wrong format, is used incorrectly, or incorrect value is present. |
|
App Error Codes: E177 HTTP Error Code: 404 Error Type: OAUTH_PRODUCER_PLMNID_MISMATCH |
This error code indicates that the received Oauth token do not match with producer PLMN configured in Ingress Gateway. | The configured PLMN ID in ingress gateway is not matching with the PLMN ID received through the Oauth token. |
|
App Error Codes: E178 HTTP Error Code: 403 Error Type: OAUTH_AUDIENCE_NOT_PRESENT_OR_INVALID |
This error code indicates that the received Oauth token does not contain an audience or invalid audience at Ingress Gateway. | Token is passed with audience parameter containing only correct nfType but in a different case. An audience parameter with missing or incorrect values for NfType and NfInstanceId can also cause this error. |
|
App Error Codes: E179 HTTP Error Code: 402 Error Type: OAUTH_TOKEN_INVALID |
This error code indicates that invalid Oauth token received at Ingress Gateway. | Indicates that the Oauth token received at Ingress Gateway is not valid, or not in the correct format. |
|
App Error Codes: E180 HTTP Error Code: 400 Error Type: OAUTH_TOKEN_ABSENCE |
This error code indicates that request received at ingress gateway with no Oauth token or empty Oauth token. | Oauth token is missing in the request. |
To Maintain
- Delete an existing secret and create a new secret with updated
public key certificate. To delete a secret, run the following command:
kubectl delete secret oauthsecret -n ocudr - Send the certificate configuration update request using CNCC GUI. The request should include the keyIdList and instanceIdList with new certificates.
2.33 Multiple Site Redundancy
Overview
UDR or SLF supports multiple site redundancy using the cnDBTier multi-site deployment model. All sites of UDR are active and can take traffic. The replication of database is handled by configuring DBTier for multiple site deployment.
Each UDR site has its own copy of the configuration database and subscriber database. All databases are replicated across all sites. Each site accesses its own configuration database. Each site access same subscriber databases, which are replicated.
Any updates of subscriber database are immediately replicated across all sites and hence, the redundancy is achieved.
When local site is down, UDR application fails due to database not being available. UDR starts failing the readiness checks and after configurable number of times, UDR deregisters from NRF. UDR does not connect to remote site of database.
Once the local database connectivity is restored, UDR application starts processing the traffic and also registers again with NRF.
Other sites where database is up, the UDR application has no impact.
To Enable and Configure
To enable and configure multiple site redundancy, see the 'Create Database User or Group' section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.34 Migrating Subscriber Data from 4G UDR to 5G UDR
Overview
Converged UDR provides the capabilities of both 5G UDR and 4G OCUDR. It supports migrating subscriber data from 4G OCUDR to the cloud-native UDR (cnUDR or 5G UDR). The cnUDR provides functionality such as migration tools and On-Demand Migration features to migrate the 4G policy subscriber data from 4G OCUDR to cnUDR.
- Migration Tool : Provides the capability to migrate bulk of subscribers from 4G OCUDR to cnUDR. For more information, see Migration tool.
- On-Demand Migration: You can migrate 4G OCUDR subscriber information to 5G UDR, provided the 4G UDR subscriber information is not already using Migration Tool or Subscriber Bulk Import Tool. On-Demand Migration triggers on provisioning or signaling request. For more information, see On-Demand Migration.
Note:
It is recommended to use Migration Tool in combination with On-Demand Migration feature to ensure that the signaling and provisioning traffic are migrated to cnUDR without data loss. To rollback the exported subscriber data to 4G OCUDR, see Support for EXML Format section.To Observe
See Migration Metrics and Alert Details section for more information on metrics and alerts respectively.
For troubleshooting information, see "nudr-migration" section in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Troubleshooting Guide.
2.34.1 Migration Tool
The migration tool is an external tool that is used to migrate the subscriber data from source UDR (4G OCUDR) to target UDR (cnUDR). Migration tool is delivered as a separate Helm chart and you must install it manually. The migration tool supports migration of the subscribers in ranges, based on the configuration provided in the Helm chart.
The migration tool uses the following sequence to migrate the subscriber from 4G OCUDR to cnUDR:
- Migration tool connects to 4G OCUDR using diameter gateway.
- Migration tool reads the subscriber information from 4G OCUDR and send the provisioning requests to cnUDR through Ingress Gateway provisioning.
- On completion of migration, creates a report with INFO log level. The report includes summary of the subscriber migration.
Prerequisites
- Before you install the yaml file, 4G OCUDR and cnUDR must be in active and running state to start the migration process.
- The XSI IP network of 4G MP nodes must be accessible from kubernetes nodes, where you are deploying.
- Enable subscriber auto create as true in the nudr-dr section of the values yaml file.
2.34.1.1 Installing the Migration Tool
Migration tool is delivered as a separate Helm chart and you must install it manually. The migration tool supports migration of the subscribers in ranges, based on the configuration provided in the Helm chart. To install the migration tool, you must edit the custom value.yaml file that has configuration details of the migration tool.
migration:
startRange: "5556555531"
endRange: "5556555541"
realm: "oracle.com"
identity: "migration.oracle.com"
nodePort: 3868
nodeHost: "ocudr-nudr-migration-service"
fourG:
realm: "oracle.com"
identity: "tekelec.oracle. com"
nodePort: 3868
nodeHost: "10.196.7.118"
maxConnectionRetry: 10
gateway:
realm: "oracle.com"
identity: "nudr.oracle.com"
port: 3868
keyType: "msisdn"Table 2-35 Migration Tool Parameters
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
| migration.startRange/endRange | It is the subscriber range value that is migrated from 4G UDR to 5G UDR. |
| migration.realm | It is the realm of the migration tool that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the migration tool. |
| migration.identity | It is the identity of the migration tool that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the migration tool. |
| migration.nodePort | It is the nodePort of the migration tool that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the migration tool. |
| migration.nodeHost | It is the nodeHost of the migration tool that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the migration tool. |
| fourG.realm | It is the realm of the 4G that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the 4G. This must be configured as the 4G server details. |
| fourG.identity | It is the identity of the 4G that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the 4G. This must be configured as the 4G server details. |
| fourG.nodePort | It is the nodePort of the 4G that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the 4G. This must be configured as the 4G server details. |
| fourG.nodeHost | It is the nodeHost of the 4G that is used by the diameter gateway to establish connection to the 4G. This must be configured as the 4G server details. |
| fourG.maxConnectionRetry | Maximum number of retry for migration tool to connect to the diameter gateway. |
| gateway.realm | It is the realm of the diameter gateway. |
| gateway.identity | It is the identity of the diameter gateway. |
| gateway.port | It is the port of the diameter gateway. |
| keyType | It is key type that must be migrated from the configured range. |
Migration Tool Support for Multiple Pods
deployment:
# Replica count for deployment
replicaCount: 1Note:
It is recommended to use ReplicaCount as 1 when migrating less than 10 subscribers. The replicaCount must be less than the difference betweenstartRange and endRange.
In a multiple pod deployment the configured ranges are equally distributed
among all the pods. When configuring multiple replicas make sure that the difference between
startRange and endRange values are sufficient to
distribute to all the pods.
helm install migration -n <namespace>kubectl get pods -n <namespace>
You can configure the migration tool using CNC Console. For more information, see Migration Tool Configurations and Migration Tool Status.
2.34.1.2 Configuring Migration Tool
The following table list the parameters for initContainer and mainContainer used for installing Migration Tool.
Table 2-36 Migration Tool Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default value | Range or Possible Values (If applicable) |
|---|---|---|---|
| global.dockerRegistry | Docker registry from where the images are pulled. | ocudr-registry.us.abc.com:5000/ocudr | NA |
| global.mysql.dbServiceName | DB service to connect | mysql-connectivity-service.occne-infra | NA |
| global.mysql.port | Port for DB Service Connection | 3306 | NA |
| global.serviceAccountName | The entire pod must be associated with the serviceaccount used for ocudr deployment. | ocudr-serviceaccount | NA |
| preInstall.image.name | Image name for the nudr_pre_migration_hook pod which will take care of DB and table creation for UDR deployment. | nudr_pre_migration_hook | NA |
| preInstall.root.logLevel | Log level for preinstall hook pod root level | WARN | Possible
Values:
WARN INFO DEBUG |
| preInstall.ocudr.logLevel | Log level for preinstall hook pod app log level | WARN | Possible
Values:
WARN INFO DEBUG |
| preInstall.image.tag | Image version for nudr_pre_migration_hook pod image | 25.1.100 | NA |
| postUpgrade.config.logLevel | Log level for postUpgrade hook pod | WARN |
Possible Values: WARN INFO DEBUG |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.cpu | CPU limit for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. This is applicable for Helm test job too. | 1 | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.memory | Memory limit for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. This is applicable for Helm test job too | 1Gi | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.ephemeral-storage | Ephemeral Storage limits for hook pods | 1024Mi | Unit MB |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.cpu | CPU requests for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. This is applicable for Helm test job too. The CPU to be allocated for hooks during deployment. | 0.5 | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.memory | Memory requests for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. This is applicable for Helm test job too. The memory to be allocated for hooks during deployment. | 0.5Gi | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.ephemeral-storage | Ephemeral Storage request for hook pods. | 72Mi | Unit MB |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.tolerations | When global.tolerationSetting is ENABLED configure
tolerations here.
Example:
|
[] | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion | Node Selector API version setting | v1 |
Allowed Values:
|
| gloabl.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector.nodeKey |
NodeSelector key configuration for UDR hooks. This excludes the common service hooks When hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration will come into use. |
' ' | Valid key for a label for a particular node. |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector.nodeValue |
NodeSelector Value configuration for UDR hooks. This excludes the common service hooks. When hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration is in use. |
' ' | Valid value pair for the above key for a label for a particular node. |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector |
NodeSelector configuration when hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion at micro service level is set to v2. Uncomment and use this configuration when required. Else keep this commented. |
{} | Valid key value pair matching a node for nodeSelection by a pod. |
| dbCredSecretName |
DB Credentioal Secret Name |
ocudr-secrets | NA |
| configServerEnable |
Enable configuration updates using config REST APIs |
true | true or false |
| customExtension.allResources.labels |
Custom Labels that needs to be added to all the OCUDR k8s resources. |
null | NA |
| customExtension.allResources.annotations |
Custom Annotations that needs to be added to all the OCUDR k8s resources. Note: ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section. |
null | NA |
| customExtension.lbServices.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as Load Balancer type. | null | NA |
| customExtension.lbServices.annotations |
Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as Load Balancer type. |
null | NA |
| customExtension.lbDeployments.labels |
Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR deployments that are associated to a Service which is of Load Balancer type. |
null | NA |
| customExtension.lbDeployments.annotations |
Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR deployments that are associated to a Service which is of Load Balancer type. Note: ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section. |
null | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbServices.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR services that are considered as not load balancer type. | null | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbServices.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR services that are considered as not load balancer type. | null | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbDeployments.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to OCUDR Deployments that are associated to a Service which is not of load balancer type. | null | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbDeployments.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR
deployments that are associated to a Service which is not of load
balancer type.
Note: ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section. |
null | NA |
| extraContainers | Configuration to enable debug tool container | DISABLED | DISABLED or ENABLED |
| extraContainerTpl | The template for extraContainer will be defined in this configuration. The debugContainer template defined here. This is applicable for all microservices under ocudr umbrella. |
|
NA |
| extraContainersVolumesTpl | Debug container volume template |
|
NA |
| image.name | Docker Image name | nudr_migration | NA |
| image.tag | Tag of Image | 25.1.100 | NA |
| image.pullPolicy | This setting will tell if image need to be pulled or not | IfNotPresent |
Possible Values: Always IfNotPresent Never |
| configservice.port.http | Config service port | 5001 | Valid Port |
| migration.startRange | Defines the range of subscriber data in which migration should start | "5556555531" | NA |
| migration.endRange | Defines the range of subscriber data in which migration should end | "5556555541" | NA |
| migration.realm | It is the migration tool realm | "oracle.com" | NA |
| migration.identity | It is the migration tool identity | "migration.oracle.com" | NA |
| migration.nodePort | It is the migration tool port | 3868 | Valid Port |
| migration.nodeHost | It is the migration tool host | "ocudr-nudr-migration-service" | Valid Port |
| migration.migrationPauseEnabled | Migration Pause Feature Enabled | false | true/false |
| fourG.realm | Fourg realm details | "oracle.com" | NA |
| fourG.identity | Fourg identity details | "tekelec.oracle.com" | NA |
| fourG.nodePort | Fourg nodeport details | 3868 | Valid Port |
| fourG.nodeHost | Fourg nodehost details | "10.196.7.118" | Valid IP |
| fourG.maxConnectionRetry | Fourg maxConnection Retry Times | 10 | NA |
| gateway.realm | It is the realm of Diameter Gateway | "oracle.com" | NA |
| gateway.identity | It is the rort of Diameter Gateway | "3868" | "3868" |
| gateway.port | It is the identity of Diameter Gateway | "nudr.oracle.com" | NA |
| keyType | Defines the range of subscriber data in which migration should start. | msisdn | NA |
| batchConfig.chunkSize | This is engineering configurations. | 2500 | NA |
| batchConfig.throttlelimit | This is engineering configurations. | 100 | NA |
| batchConfig.coreThreadPool | This is engineering configurations. | 10 | NA |
| batchConfig.maxThreadPool | This is engineering configurations. | 10 | NA |
| batchConfig.queueCapacity | This is engineering configurations. | 30000 | NA |
| batchConfig.writerCoreThreadPool | This is engineering configurations. | 10 | NA |
| batchConfig.writerMaxThreadPool | This is engineering configurations. | 10 | NA |
| batchConfig.writerQueueCapacity | This is engineering configurations. | 30000 | NA |
| service.type |
It is the UDR service type. The kubernetes service type for exposing UDR deployment. Note: Suggested to be set as ClusterIP (default value) always. |
ClusterIP |
Possbile Values- ClusterIP NodePort LoadBalancer |
| service.port.http |
The HTTP port to be used in notify service to receive signals from nudr-migration-service pod. |
5001 | NA |
| service.port.management | Bulk import Management port.
The actuator management port to be used for notify service. |
9000 | NA |
| service.customExtension.labels |
Custom Labels that needs to be added to nudr-migration specific Service. This can be used to add custom label(s) to nudr-diameterproxy Service. |
null | NA |
| service.customExtension.annotations |
Custom Annotations that needs to be added to nudr-migration specific Services. This can be used to add custom annotation(s) to nudr-migration Service. |
null | NA |
| deployment.replicaCount |
Number of replicas for export tool |
1 | NA |
| deployment.customExtension.labels |
Custom Labels that needs to be added to nudr- migration specific Deployment. This can be used to add custom label(s) to nudr-migration Deployment. |
null | NA |
| deployment.customExtension.annotations |
Custom Annotations that needs to be added to nudr-migration specific Deployment. This can be used to add custom annotation(s) to nudr-migration Deployment. |
null | NA |
| hikari.poolsize | It is the Mysql connection pool size. The hikari pool connection size to be created at start up. | 10 | NA |
| hikari.connectionTimeout | It is the MYSQL connection timeout. | 1000 | Unit: Milliseconds |
| hikari.minimumIdleConnections | It is the minimum idle MYSQL connections maintained. | 2 | Valid No, less than poolsize configured |
| hikari.idleTimeout | It is the Idle MYSQL connections timeout. | 1000 | Unit: Milliseconds |
| hikari.queryTimeout | It is the Query Timeout for a single DB query. If set to -1, there will be no timeout set for DB queries. | -1 | Unit: Seconds |
| logging.level.root | Log level of the export tool pod. | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
| logging.level.ocudr | It is the application Log Level. App Log level of the migration tool pod. | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
| resources.requests.cpu | CPU Allotment for nudr-notify-service pod. The CPU to be allocated for migration service pod during deployment. | 2 | NA |
| resources.requests.memory | Memory allotment for nudr-bulk-import pod. The memory to be allocated for nudr-migration pod during deployment. | 2Gi | NA |
| resources.requests.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation request. | 50 | Unit: MB |
| resources.requests.crictlStorage | Critical storage for ephemeral storage allocation request. | 2 | Unit: MB |
| resources.limits.cpu | CPU allotment limitation. | 2 | NA |
| resources.limits.memory | Memory allotment limitation. | 2Gi | NA |
| resources.limits.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit. | 1000 | Unit: MB |
| resources.limits.crictlStorage | Critical storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit. | 2 | Unit: MB |
| readinessProbe.initialDelaySeconds |
Configurable wait time before performing the first readiness probe by the kubelet. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you must consider tuning these parameters. |
30 | Unit: Seconds |
| readinessProbe.periodSeconds |
Time interval for every readiness probe check. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you must consider tuning these parameters. |
3 | Unit: Seconds |
| livenessProbe.initialDelaySeconds |
Configurable wait time before performing the first liveness probe by the kubelet. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you must consider tuning these parameters. |
30 | Unit: Seconds |
| livenessProbe.periodSeconds |
Time interval for every liveness probe check. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delays in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then you must consider tuning these parameters. |
3 | Unit: Seconds |
| tolerations | When tolerationsSetting is ENABLED configure tolerations
here.
Example:
|
[] | NA |
| helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion | Node Selector API version setting. | v1 |
Allowed Values:
|
| nodeSelector.nodeKey |
Micro service level NodeSelector key configuration When helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration is used. This configuration do not depend on nodeSelection flag. once configured this will be used for all microservices. |
' ' | Valid key for a label for a particular node |
| nodeSelector.nodeValue |
Global level NodeSelector Value configuration When helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration is used. This configuration do not depend on nodeSelection flag. once configured this will be used for all microservices. |
' ' | Valid value pair for the above key for a label for a particular node |
| nodeSelector | NodeSelector configuration when helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v2. Uncomment and use this configuration when required. Else keep this commented. | {} | Valid key value pair matching a node for nodeSelection by a pod |
| maxConcurrentPushedStreams | Maximum number of concurrent requests that is pushed per destination | 6000 | NA |
| maxRequestsQueuedPerDestination | Maximum number of requests that is queued per destination | 5000 | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerDestination | Maximum connection allowed per destination | 10 | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerIp | Maximum connection allowed per IP | 10 | NA |
| requestTimeout | Client Request timeout | 5000 | Unit: Milliseconds |
| connectionTimeout | Client connection timeout | 10000 | NA |
| idleTimeout | Client connection idle timeout | 0 | NA |
| dnsRefreshDelay | Server DNS refresh delay | 120000 | NA |
| pingDelay | Server ping delay | 60 | NA |
| connectionFailureThreshold | Client connection failure threshold | 10 | NA |
| jettyserviceMeshCheck | For ASM deployment jetty service mesh check | false | true or false |
| diameterServer | Diameter Server flag | true | true or false |
| diameterPort | Diameter port | "3868" | Valid Port |
| deletSourceUDR | Delete content from source UDR | false | true or false |
| sourceEndPointURL | 4G endpoint URL | "http://<4GRESTURL>:PORT" | NA |
| udrServiceBaseURL | 5G UDR Service endpoint | "http://ocudr-ingressgateway-prov:80" | NA |
| gracefulShutdown.gracePeriod | Graceful Shutdown time limit | 30s | Unit: Seconds |
| internalTracingEnabled | The flag enables jaeger tracing for the service | false | true or false |
2.34.1.3 Using the Migration Tool
You can use the migration tool only if:
- There exists an active source such as 4G connections are enabled and diameter gateway is running and destination source such as 5G UDR is up and running.
- The diameter gateway connections on 4G UDR are configured. It means the peer node information and connections are created with diameter gateway.
- Subscribing Client Permission is available for migration identity on 4G UDR for connecting to the migration tool.
- It is installed as per the installation process shared at Installing the Migration Tool.
You can verify 5G UDR databases for all the 4G UDR records once the migration job completes. You can observe its metrics that are pegged in the Grafana dashboard.
Below sample report shows the success and failure records count in the INFO logs of nudr-migration job.
Migration Tool Summary Report:
| Time taken for processing: 0min 11sec |
| Per Pod Number of records: 10 |
| Per Pod Number of source UDR success: 10 |
| Per Pod Number of source UDR subscriber not found: 0 |
| Per Pod Number of target UDR keys already exists: 0 |
| Per Pod Number of source UDR failure: 0 |
| Per Pod Number of target UDR success: 10 |
| Per Pod Number of target UDR failure: 0 |
| List of failed source UDR keys Per Pod: |
| List of failed subscriber not exist keys at source Per Pod: |
| List of keys already exists in target UDR Per Pod: |
| List of failed target UDR keys Per Pod: |The success and failure records counts are published in the INFO logs of nudr-migration job.
- If the data migration from 4G UDR to 5G UDR fails due to target 5G UDR INFO log. For example: List of failed target UDR keys: 63612000056, 63612000057.
- If the data migration from 4G UDR to 5G UDR fails due to source 4G UDR INFO log. For example: List of failed source UDR keys: 63612000058 63612000059.
- If the data migration from 4G UDR to 5G UDR fails due to subscriber does not exist at source 4G UDR INFO log. For example: List of failed subscriber keys does not exist at source: 63612000060 63612000061.
- If the data migration from 4G UDR to 5G UDR fails due to already existing keys in target 5G UDR INFO log. For example: List of keys already existing in target UDR: 63612000062 63612000063.
Migration Tool Upgrade and Rollback
Upgrade and rollback of migration tool is not supported. Migration tool must be uninstalled when the migration job is completed.
helm uninstall <release name> -n <namespace>2.34.2 On-Demand Migration
The on-demand migration feature is supported as part of Converged Policy database solution of UDR. By enabling this feature, you can migrate 4G UDR subscriber information to 5G UDR, provided the 4G UDR subscriber information is not already provisioned on 5G platform. For more information on converged quota, see Converged Quota Support for UDR.
This following diagram depicts the call flow between microservices when on-demand migration is triggered from the external clients such as cnPCRF, PCF and so on. When the on-demand migration requests reaches the microservices, it uses the Diameter Gateway to connect to 4G UDR and migrates the data to cnUDR. The diagram shows on-demand migration is triggered from various microservices when different types of requests are processed.
Figure 2-27 On-Demand Migration
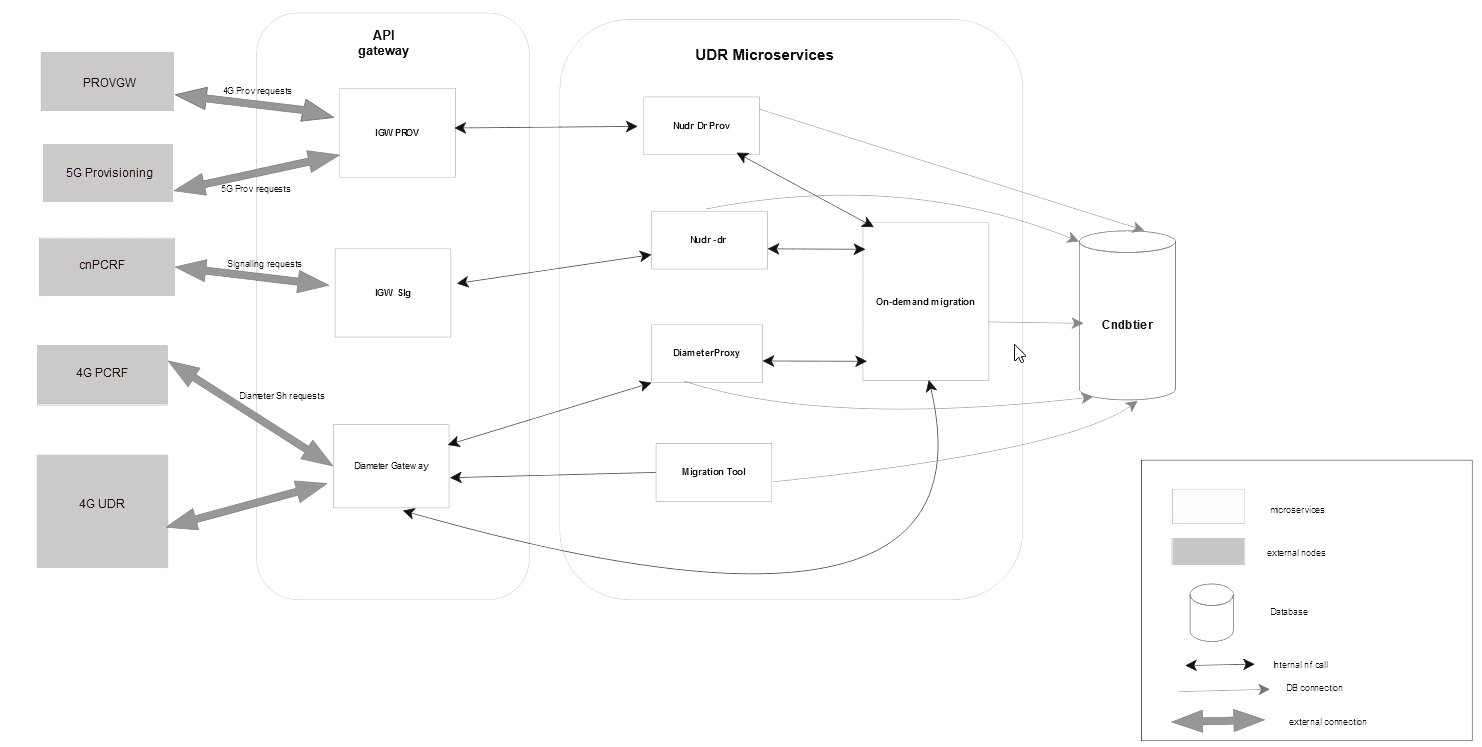
- Provisioning Event: Provisioning Gateway sends the provisioning
requests such as read or update subscriber information to cnUDR. If the on-demand
migration feature is enabled and if the subscriber does not exist on cnUDR, the
subscriber information is read from 4G UDR and provisioned on cnUDR before sending back
the response to the Provisioning Gateway. cnUDR reads and provisions the 4G policy quota
data using the data model defined in Table 2-14 and supports:
- Provisioning request for read and update using SOAP/XML provisioning interface. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Provisioning Gateway Interface Specification Guide.
- GET, PUT, and PATCH operations using REST/JSON provisioning interface. For more information, see in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- Nudr Event: Based on a 5G session request initiated by PCF and an
Nudr request received on cnUDR, the subscriber information is read from 4G UDR and
provisioned on cnUDR.
- Provided the on-demand migration feature is enabled on cnUDR
- Subscriber information does not exist on cnUDR
- Sh-event: Based on request (Diameter-Sh) received from PCRF to
access the subscriber profile or entities using the UDR/PUR/SNR requests, the subscriber
information is read from 4G UDR and provisioned on cnUDR
- Provided the on-demand migration feature is enabled on cnUDR
- Subscriber information does not exist on cnUDR
Note:
On-demand migration can be enabled or disabled for each Provisioning Event, Nudr Event, and Sh-event independently.Deleting Source UDR Subscriber Information
deleteSubscriberOnSource parameter to true or false. The
default configuration is false.
Note:
You may experience delay in response from cnUDR if the on-demand migration feature is enabled.To Enable
Pre-requisite: The on-demand migration service reads subscriber information from 4G UDR using Diameter connection(Sh) with 4G UDR. To read subscriber information from 4G UDR, it is important to configure 4G UDR with peer Diameter connections of cnUDR.
- In the global values.yaml file, under nudr-dr service section, set the
ondemandmigrationproperty as 'true' and run the Helm upgrade command. By default, it is set as false. - Upon setting the
ondemandmigrationproperty as 'true', data is fetched from 4G UDR and provisioned on cnUDR when any of the event occurs (provisioning event, Nudr event or sh-event).Note:
After enabling theondemandmigrationparameter, the on-demand migration service runs as a separate service. The nudr-dr and diameter-proxy microservice uses it for handling subscriber migration. - After migrating the subscriber information to cnUDR, set the
deleteSubscriberOnSourceparameter to 'true' to delete that subscriber from 4G UDR.Figure 2-28 Enabling ondemandmigration and deleteSubscriberOnSource parameter
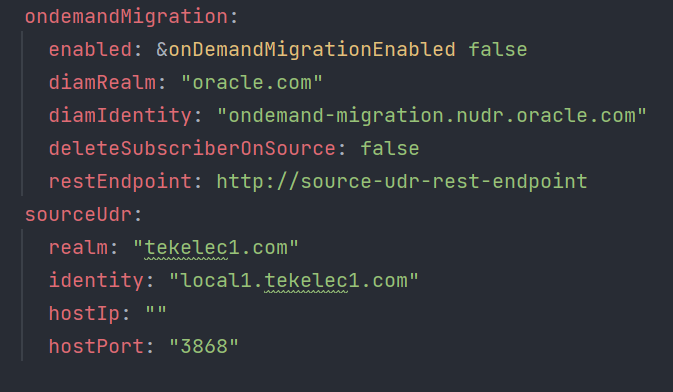
Note:
You can set the above parameter either from the CNC Console or the yaml file. If you opt to use yaml file then ensure that the nudr_config parameter is not enabled. After updating the yaml file, run the Helm upgrade command.Range Support for On-Demand Migration
Range support for On-demand migration helps to migrate the 4G subscriber data to 5G UDR in a phase manner. You can initiate migration for small range of subscriber data and validate the call flows. Once the migration is successful, you can migrate another small range of subscriber data in a phase manner.
- Key Type: This defines the type of key for the key range. The key type can either be Mobile Station Integrated Services Digital Network (MSISDN) or International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI). Key type is not validated, if the default key range is set.
- Key Range: This defines the range of subscribers for on-demand migration. Multiple key ranges are not allowed. The default value is 000000-000000.
To Configure
- Edit the Helm config file while installing UDR. This flag is not available on CNC Console.
- Configure Diameter-Sh peers on the Helm charts or CNC Console. 5G UDR uses these Diameter-Sh connections with 4G UDR to read its subscribers information.
Using this configuration, you can also delete the subscriber information migrated to 5G UDR from source 4G UDR.
Configuring Range Support
global:
# Key type and range for ondemand qouta migration
key:
type: msisdn
range: 000000-000000Configuring Range Support using REST API
http://nudr-config-service:PORT/ nudr-config/v1/udr.global.cfg/GLOBAL
to configure the range support. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native
Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"dbServiceName": "mysql-connectivity-service.occne-ndb",
"udrServices": "All",
"udsfEnabled": false,
"ingressHttpPort": "",
"ingressHttpsPort": "",
"snssai": "2-FFFFFF",
"dnn": "dnn1",
"autoCreate": true,
"autoEnrolOnSignalling": true,
"etagEnabled": true,
"sbiCorrelationInfoEnable": false,
"consumerNF": "PCF,UDM,NEF",
"nfInstanceId": "5a7bd676-ceeb-44bb-95e0-f6a55a328b03",
"vsaDefaultBillingDay": 1,
"subscriberActivityEnabled": false,
"addDefaultBillingDay": true,
"enableControlledShutdown" : true,
"keyType": "imsi",
"keyRange": "2013020001-2013020002",
"nfType": "UDR",
"nfFqdn": "udr001.oracle.com",
"suppressNotificationEnabled": true,
"configClientConnectTimeout": 1000,
"configClientReadTimeout": 1000,
"subscriberIdentifers": {
"msisdn": [],
"imsi": [],
"nai": [],
"extid": []
}
}Upgrade and Rollback Impacts for Range Support
- If On-demand migration is enabled, then range support works for all key type and key range.
- If you modify the key type and key range through REST API, then the On-demand migration triggers only if the key type is valid and key is in the range value.
Note:
Range support for on-demand migration is disabled when rollback is performed to a previous version.2.34.2.1 Configuring On-Demand Migration
The following table list configurable parameters for nudr-ondemand-migration microservice.
Table 2-37 nudr-ondemand-migration microservice parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default value | Range or Possible Values (If applicable) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| enabled | Flag to enable nudr-ondemand-migration microservice | false | NA | NA |
| image | Image from the Docker registry along with the image name and tag | ocudr-registry.us.abc.com:5000/ocudr/nudr_pre_migration_hook:25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| image.name | Name of Docker Image | nudr_ondemand_migration | NA | NA |
| image.tag | Tag or version of Image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| image.pullPolicy | This setting indicates if need to be pulled or not | IfNotPresent | Possible Values:
Always IfNotPresent Never |
NA |
| service.type | Kubernetes service type for exposing UDR deployment | ClusterIP | Possible Values:
ClusterIP NodePort LoadBalancer |
Suggested to be set as ClusterIP (default value) always |
| service.port.http | HTTP port used in nudr-ondemand-migration service | 5001 | NA | NA |
| service.port.https | HTTPS port used for nudr-ondemand-migration service | 5002 | NA | NA |
| service.port.management | Management port number used for nudr-ondemand-migration service | 9000 | NA | NA |
| service.customExtension.labels | Use to add custom label(s) to nudr-ondemand-migration service | null | NA | NA |
| service.customExtension.annotations | This can be used to add custom annotation(s) to nudr-ondemand-migration service | null | NA | NA |
| drservice.port.http | dr-service HTTP port required in nudr-ondemand-migration application | 5001 | NA | NA |
| drservice.port.https | dr-service HTTPS port required in nudr-ondemand-migration application | 5002 | NA | NA |
| deployment.replicaCount | Number of nudr-ondemand-migration pods maintained by replica set created with deployment | 2 | NA | NA |
| deployment.customExtension.labels | Used to add custom label(s) to nudr-ondemand-migration deployment | null | NA | NA |
| deployment.customExtension.annotations | To add custom annotation(s) to nudr-ondemand-migration deployment | null | NA | NA |
| logging.level.root | Log level of the nudr-ondemand-migration server pod | WARN | Possible Values:
WARN INFO DEBUG |
NA |
| resources.requests.cpu | Number of CPUs allocated for nudr-ondemand-migration pod during deployment | 3 | NA | NA |
| resources.requests.memory | Memory allocated for nudr-ondemand-migration pod during deployment | 4Gi | NA | NA |
| resources.requests.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation request | *containersLogStorageRequestsRef | Unit: MB | Change the reference to a different value if allocation needs to be different for this container |
| resources.requests.crictlStorage | Crictl storage for ephemeral storage allocation request | *containersCrictlStorageRequestsRef | Unit: MB | Change the reference to a different value if allocation needs to be different for this container |
| resources.limits.cpu | Maximum number of CPUs allocated for nudr-ondemand-migration pod | 3 | NA | NA |
| resources.limits.memory | Maximum memory allocated for nudr-ondemand-migration pod | 4Gi | NA | NA |
| resources.limits.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit | *containersLogStorageLimitsRef | Unit: MB | Change the reference to a different value if allocation needs to be different for this container |
| resources.limits.crictlStorage | Crictl storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit | *containersCrictlStorageLimitsRef | Unit: MB | Change the reference to a different value if allocation needs to be different for this container |
| resources.target.averageCpuUtil | CPU utilization limit for auto scaling (creating HPA) | 80 | NA | NA |
| minReplicas | Minimum number of pods allocated for nudr-diameterproxy | 2 | NA | NA |
| maxReplicas | Maximum number of pods allocated for nudr-diameterproxy | 4 | NA | NA |
| serviceToCheck | Essential services on which INIT container performs readiness checks | nudr-drservice | Comma separated microservice names | NA |
| hikari.poolsize | Hikari pool connection size to be created at start up | 20 | NA | NA |
| hikari.connectionTimeout | MYSQL connection timeout | 1000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| hikari.minimumIdleConnections | Minimum idle MYSQL connections maintained | 2 | Valid No, less than poolsize configured | NA |
| hikari.idleTimeout | Idle MYSQL connections timeout | 10000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| hikari.queryTimeout | Query timeout for a single database query. If you set the value to -1 there will be no timeout for database queries | -1 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| maxConcurrentPushedStreams | Maximum number of concurrent requests that is pushed per destination | 6000 | NA | NA |
| maxRequestsQueuedPerDestination | Maximum number of requests that is queued per destination | 5000 | NA | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerDestination | Maximum connection allowed per destination | 10 | NA | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerIp | Maximum connection allowed per IP | 10 | NA | NA |
| requestTimeout | Client Request timeout | 5000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| connectionTimeout | Client connection timeout | 10000 | NA | NA |
| idleTimeout | Client connection idle timeout | 0 | NA | NA |
| dnsRefreshDelay | Server DNS refresh delay | 120000 | NA | NA |
| pingDelay | Server ping delay | 60 | NA | NA |
| connectionFailureThreshold | Client connection failure threshold | 10 | NA | NA |
| jettyserviceMeshCheck | For ASM deployment jetty service mesh check | false | true/false | NA |
| diameter.identity | Identity (FQDN) of nudr-ondemand migration in diameter messages | ondemand-migration.udr.oracle.com | String value | NA |
| startupProbe.failureThreshold | It is the configurable number of times the startup probe
is retried for failures.
Note: Do not change this value. If there is delay in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then tune these parameters |
40 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| startupProbe.periodSeconds | It is the time interval for every startup probe check. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delay in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then tune these parameters | 5 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| extraContainers | This configuration decides whether service level extra container need to be used or not | USE_GLOBAL_VALUE | Allowed Values:
|
NA |
| serviceMeshCheck | Flag to check service mesh. Set this to false when side car is not included for this service | *serviceMeshFlag | NA | Do not change this value unless it is different from the value configured in global section |
| istioSidecarReadyUrl | Readiness URL configurable for side car
Change only if the URL is different for side car container in this microservice |
*istioReadyUrl | NA | Do not change this value unless it is different from the value configured in global section reference |
| nodeNameAffinity | Slave nodename in which ondemand pod should to run | NA | NA | NA |
| tolerationsSetting | Flag to enable the toleration setting at the
microservice level or global level.
If set to USE_GLOBAL_VALUE global.tolerations configured value is used. If set to ENABLED tolerations configuration in the same section is used. |
USE_GLOBAL_VALUE |
Allowed Values:
|
NA |
| nodeSelection | Flag to enable the nodeSelection setting at the
microservice level or global level.
If set to USE_GLOBAL_VALUE global.tolerations configured value is used. If set to ENABLED then tolerations configuration in the same section are used. This is applicable for v2 apiVersion nodeSelector configuration. |
USE_GLOBAL_VALUE |
Allowed Values:
|
NA |
| tolerations | When tolerationsSetting is ENABLED, then configure tolerations. | [] | Example: |
NA |
| helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion | Node Selector API version setting | v1 |
Allowed Values:
|
NA |
| nodeSelector.nodeKey | NodeSelector key configuration at the microservice level when helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration is used. And this configuration does not depend on nodeSelection flag, once configured this is used for all microservices. | ' ' | Valid key for a label for a particular node. | NA |
| nodeSelector.nodeValue | NodeSelector value configuration at the global level when helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration is used. And this configuration does not depend on nodeSelection flag, once configured this is used for all microservices. | ' ' | Valid value pair for the above key for a label for a particular node. | NA |
| nodeSelector | NodeSelector configuration when
helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v2.
Uncomment and use this configuration when required. Else keep this commented. |
{} | Valid key value pair matching a node for nodeSelection by a pod. | NA |
| maxUnavailable | Number of pods that can be terminated during disruptions | 1 | NA | NA |
| gracefulShutdown.gracePeriod | It is the graceful shutdown time limit | 30s | Unit: Seconds | NA |
2.35 Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
This section describes the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool feature.
2.35.1 Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
The Subscriber Bulk Import tool has three containers: a main container, xmlToCsv container, and pdbiToCsv container.
To support EIR functionality, pdbiToCsv container is added to the bulk import tool.
- Read the subscriber data from a CSV file in a pre-determined format
and then process the records.
Note:
The CSV file is located in a specified directory on the pod. - Process each record and send requests to UDR for provisioning the subscribers
- Support PCF subscriber data (5G PCF and VSA), SLF, and EIR subscriber data
- Support Subscribers CREATE, MODIFY, and DELETE operations
- Reads the ixml subscriber data from the ixml file in a specified directory path on the pod.
- Converts ixml subscriber information to JSON format and generates CSV file as output.
- Uses the converted CSV file to provision subscribers on 5G UDR in PCF-VSA provisioning requests
- Supports different types of operations: CREATE, MODIFY, DELETE, and PATCH.
- Reads the PDBI record from the pdbi file in a specified directory path on the pod.
- Converts PDBI record to JSON format and generates CSV file as output.
- Uses the converted CSV file to provision subscribers on 5G EIR.
- Supports different types of operations: MODIFY, DELETE, and DELETE-KEY.
Note:
- The Bulk Import tool uses PVC (Persistent Volume Claim) and PV (Persistent Volume) that is created before deploying the tool. For more information about creating PVC and PV, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
- You are required to manually copy all the CSV files to the PV mountpath inside the container, which is /home/udruser/import/.
Support for 5G EIR Bulk Provisioning
5G EIR supports bulk provisioning of subscriber data by using the batch files in both CSV and PDBI format. This feature provides the capability of processing the batch files containing EAGLE Provisioning Application Processor (EPAP) supported PDBI provisioning commands that enables deployment of 5G EIR in stand alone mode and also in conjunction with the Oracle offered legacy EAGLE EPAP based 3G and 4G EIR deployments.
Figure 2-29 5G EIR Bulk Provisioning
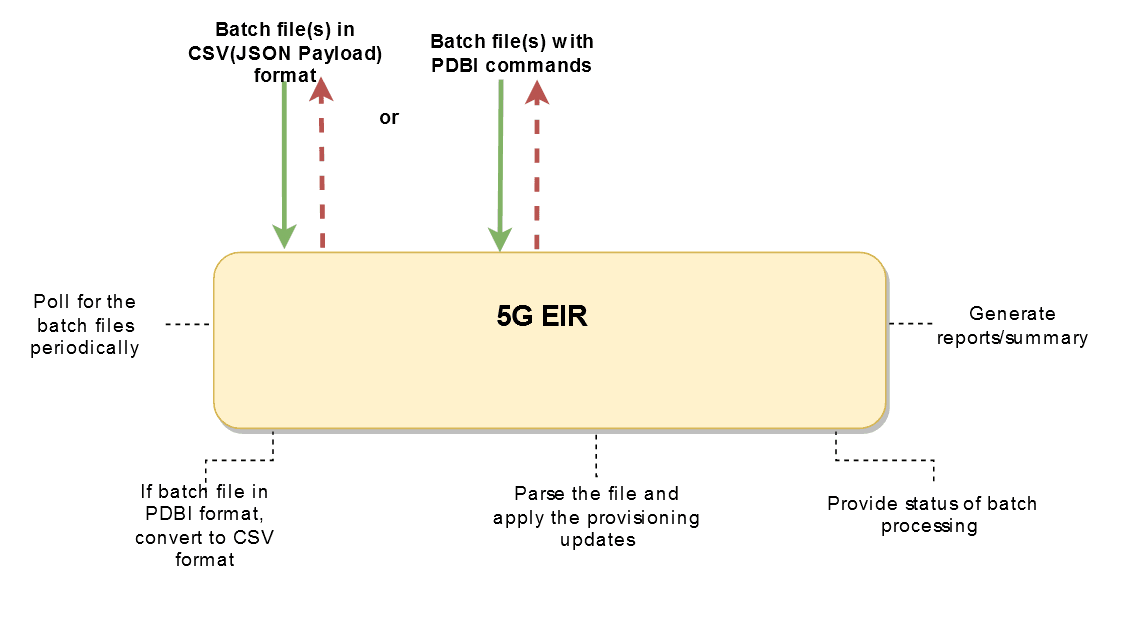
Bulk Import File Format for PDBI Commands
PDBI provides commands that communicate provisioning information from the customer database to the Provisioning Database (PDB) in the Active Provisioning Database Application (PDBA) in an EAGLE. The customer can executes provisioning commands using a provisioning application. The provisioning application uses the PDBI request and response messages to communicate with the EPAP PDBA over the customer network.
sample_msg(field1 #, field2 #, [field3 <yes/no>], field4 <0..255>)
ent_eir(iid 1, imei 355171053475189, white yes, gray yes, imsi 111111111111115, imsi 111111111111116)
ent_eir(iid 2, imei 11111110000001, imsi 111111111111111, black yes)
ent_eir(iid 3, imei 11111110000002, msisdn 1111111114, black yes)
dlt_eir(iid 4, imei 355171053475189)keyType,keyValue,operationType,nfType,jsonPayload
IMEI,11111110000001,MODIFY,EIR,"{"cmd":"ent_eir(iid 2, imei 11111110000001, imsi 111111111111111, black yes)","profile-data":{"imei":["11111110000001"],"imsi":["111111111111111"]},"equipment-status":{"black":true}}"
IMEI,11111110000002,MODIFY,EIR,"{"cmd":"ent_eir(iid 3, imei 11111110000002, msisdn 1111111114, black yes)","profile-data":{"imei":["11111110000002"],"msisdn":["1111111114"]},"equipment-status":{"black":true}}"
IMEI,355171053475189,MODIFY,EIR,"{"cmd":"ent_eir(iid 1, imei 355171053475189, white yes, gray yes, imsi 111111111111115, imsi 111111111111116)","profile-data":{"imei":["355171053475189"],"imsi":["111111111111115","111111111111116"]},"equipment-status":{"white":true,"grey":true}}"
IMEI,355171053475189,DELETE,EIR,"{"cmd":"dlt_eir(iid 4, imei 355171053475189)"}"ent_eir(iid 3, imei 355171053475189, svn 01, white yes, gray yes, imsi 111111111111115, imsi 111111111111116)
dlt_eir(iid 6, imei 355171053475189, svn 01)- PDBI commands supported:
- ent_eir
- upd_eir
- dlt_eir
- PDBI commands not supported:
- ent_sub
- upd_sub
- dlt_sub
- ent_entity
- upd_entity
- dlt_entity
To Observe
See Bulk Import Metrics for more information on metrics respectively.
2.35.1.1 Subscriber Bulk Import Operations
The Subscriber Bulk Import tool supports following operation types:
- CREATE: Allows to create subscribers with all keys mentioned in the payload. The PCF create and SLF create request payloads are available in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- UPDATE: Allows to update the existing subscribers with new data
mentioned in the subs_data column.
Note:
While using this operation, you should provide complete subscriber information as it replaces the old information with new data. - DELETE: Allows to delete complete subscriber information with all keys attached to the subscriber.
- PATCH: Updates the existing subscribers with new data in the payload. It updates only particular field or element.
Note:
For information about bulk import tool keyTypes, see Sample Bulk Import File in CSV Format.The Bulk Import tool supports following NF Types:
- PCF: Using this tool, you can provision all 5G PCF data in bulk for all resource types: AM data, SM Data, and UEPolicySet. For more information, see the Operations supported for PCF Data section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- SLF: You can create SLF Subscribers with all keys and
SLFGroupName in the payload. For more information, see the Operations supported
for SLF Data section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core,
Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Note:
The Bulk Import tool does not support SLFGroupName provisioning. You can provision this using REST APIs or CNC Console GUI. - PCF-VSA: You can provision all 4G policy data in bulk for all entity types: subscriber, quota, state, and dynamicQuota. For more information, see the Operations supported for Policy Data section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- EIR: You can create EIR Subscribers. For more information, see the Provisioning Operations for EIR Data section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
Table 2-38 API for Provisioning
| NF Types | CREATE | UPDATE | DELETE | PATCH |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCF | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| SLF | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| PCF-VSA | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| EIR | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
2.35.1.2 Bulk Import Operations in iXML Format
- MSISDN
- IMSI
- NAI
- EXTID
- AccountId
- Entitlement
The below table provides operation details of bulk import tool in iXML format.
Table 2-39 iXML Format for Bulk Import
| Opertion Detail | iXML Format |
|---|---|
| Transaction block with single request of Entity Dynamic Quota (createEntity request) |
|
| Transaction block with uploadField and deleteField requests |
|
| Transaction block with multiple requests of updateField, deleteField, and deleteFieldSet of State entity |
|
| Transaction block request with all entities (createSubscriber along with Create request for Quota, DynamicQuota, and State) |
|
| Transaction block request with all Entities (createSubscriber along with updateFieldSet request for Quota, DynamicQuota, and State) |
|
| Non transaction request to Create Subscriber |
|
| Non transaction request to Update Subscriber |
|
| Non transaction request to Delete Subscriber |
|
| Non transaction request with Create request to create Quota Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with Create request to create State Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with Create request to create Dynamic Quota entity |
|
| Non transaction request with UpdateFieldSet request to update Quota entity |
|
| Non transaction request with UpdateFieldSet request to update State entity |
|
| Non transaction request with UpdateFieldSet request to update DynamicQuota entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request to delete Quota entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request for Quota to delete row Q2 |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request todelete State entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request for State entity to delete field mcc |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request to delete Dynamic Quota Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request for Dynamic Quota to delete row PDQ1 |
|
| Non transaction request with updateField request to update a subscriber profile and set the value of the BillingDay field to 23 and the Tier field to Gold. |
|
Non transaction request with updateField request to update a
subscriber profile. The request performs the following functions:
|
|
| Non transaction request with deleteField request to delete a subscriber profile and set the value of the BillingDay field to 23 and the Tier field to Gold |
|
| Non transaction request with updateField request to update the inputVolume and the outputVolume fields in the Q1 Quota row in the Quota entity. The two rows are called Q1 exist, one row with a CID of 111 and another row with a CID of 222. The request is to update the instance with the CID of 111. |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldrequest to delete the inputVolume and the outputVolume fields in the Q1 Quota row in the quota entity. The Two rows are called Q1 exist, one row with a CID of 111 and another row with a CID of 222. The request is to delete the instance with the CID of 111. |
|
| Non Transaction Request with updateField request to update the InitialInputVolume and the InitialOutputVolume fields in the DQ1DynamicQuota row in the DynamicQuota entity. The two rows are called DQ1 exist, one row with an InstanceId of 11111 and another row with an InstanceId of 22222. The request is to update the instance with the InstanceId of 11111 |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteField request to delete the InitialInputVolume and the InitialOutputVolume fields in the DQ1DynamicQuota row in the DynamicQuota entity. The two rows are called DQ1 exist, one row with an InstanceId of 11111 and another row with an InstanceId of 22222. The request is to delete the instance with the InstanceId of 11111 |
|
| Non transaction request with updateField request to update a property value in the State entity. The two properties exist, one with a propertyname of MCC and another with name of approved. The request is to update the property value with the name of MCC. |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteField request to delete a property value in the State entity. The two properties exist, one with a propertyname of MCC and another with name of approved. The request is to delete the property value with the name of MCC. |
|
2.35.1.3 Bulk Import Operations in CSV Format
The below table provides operation details of bulk import tool in CSV format.
Table 2-40 CSV Format for Bulk Import
| Opertion Detail | CSV |
|---|---|
| Transaction block with single request of Entity Dynamic Quota (update request) |
|
| Transaction block with uploadField and deleteField requests |
|
| Transaction block with multiple requests of updateField, deleteField, and deleteFieldSet of State entity |
|
| Transaction block request with all entities (createSubscriber along with Create request for Quota, DynamicQuota, and State) |
|
| Transaction block request with all Entities (createSubscriber along with updateFieldSet request for Quota, DynamicQuota, and State) |
|
| Non transaction request to Create Subscriber |
|
| Non transaction request to Update Subscriber |
|
| Non transaction request to Delete Subscriber |
|
| Non transaction request with Create request to create Quota Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with Create request to create State Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with Create request to create Dynamic Quota Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with UpdateFieldSet request to update Quota Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with UpdateFieldSet request to update State Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with UpdateFieldSet request to update DynamicQuota entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request to delete Quota entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request for Quota to delete row Q2 |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request todelete State entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request for State entity to delete field MCC |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request to delete Dynamic Quota Entity |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldSet request for Dynamic Quota to delete row PDQ1 |
|
| Non transaction request with updateField request to update a subscriber profile and set the value of the BillingDay field to 23 and the Tier field to Gold. |
|
Non transaction request with updateField request to update a
subscriber profile. The request performs the following functions:
|
|
| Non transaction request with deleteField request to delete a subscriber profile and set the value of the BillingDay field to 23 and the Tier field to Gold |
|
| Non transaction request with updateField request to update the inputVolume and the outputVolume fields in the Q1 Quota row in the Quota entity. The two rows are called Q1 exist, one row with a CID of 111 and another row with a CID of 222. The request is to update the instance with the CID of 111. |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteFieldrequest to delete the inputVolume and the outputVolume fields in the Q1 Quota row in the quota entity. The Two rows are called Q1 exist, one row with a CID of 111 and another row with a CID of 222. The request is to delete the instance with the CID of 111. |
|
| Non Transaction Request with updateField request to update the InitialInputVolume and the InitialOutputVolume fields in the DQ1DynamicQuota row in the DynamicQuota entity. The two rows are called DQ1 exist, one row with an InstanceId of 11111 and another row with an InstanceId of 22222. The request is to update the instance with the InstanceId of 11111 |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteField request to delete the InitialInputVolume and the InitialOutputVolume fields in the DQ1DynamicQuota row in the DynamicQuota entity. The two rows are called DQ1 exist, one row with an InstanceId of 11111 and another row with an InstanceId of 22222. The request is to delete the instance with the InstanceId of 11111 |
|
| Non transaction request with updateField request to update a property value in the State entity. The two properties exist, one with a propertyname of MCC and another with name of approved. The request is to update the property value with the name of MCC. |
|
| Non transaction request with deleteField request to delete a property value in the State entity. The two properties exist, one with a propertyname of MCC and another with name of approved. The request is to delete the property value with the name of MCC. |
|
| 5G PCF Data includes complete policy data information |
|
| 5G and 4G PCF Data includes complete policy data information along with VSA data |
|
Multiple Pod Subscriber Bulk Import Support
deployment:
# Replica count for deployment
replicaCount: 1replicaCount. Pod name must be used when copying the CSV, XML,
or PDBI
files.kubectl cp <csv file> <namespace>/<nudr-bulk-import pod name>:/home/udruser/importkubectl cp create_pcf.csv bulktest/bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-0:/home/udruser/importkubectl cp create_pcf.csv bulktest/bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-1:/home/udruser/xmlkubectl cp create_pcf.csv bulktest/bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-2:/home/udruser/pdbiNote:
- SFTP do not support multiple pod bulk import.
- Copying files into or from PVC must be within the pod.
2.35.2 Installing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
You can install the subscriber bulk import and xmltocsv containers using helm. While installing the bulk import and xmltocsv containers, the "bulkimportpersistentclaim" PVC for bulk import container and the "xmltocsvpersistentclaim" PVC for xmltocsv container are created automatically. This is because the tool uses Kubernetes StatefulSet for deployment and it has a limitation to create PVC when the tool is installed.
maxConnectionsPerDestination parameter value
range between 4 to 200 in the custom-value.yaml
file.
#Jetty client config
maxRequestsQueuedPerDestination: 20000
maxConnectionsPerDestination: 4
requestTimeout: 5000 #(ms)
jettyMaxPoolSize: 1000
jettyMinPoolSize: 50
jettyldleTimeout: 0 #(ms,<=0 -> to make timeout infinite)Installing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
Before installing the bulk import tool using helm charts, you are required to configure its parameters in the nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml file. For information about the bulk import tool configurable parameters, see Configuring Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.
To install the bulk import tool as a separate deployment with different release name:
- Extract the bulk import helm charts from the software or CSAR
package and run the following command:
helm3 install <release name for bulk import> -n <udr namespace> nudr-bulk-import/ -f nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml
Note:
Run the following command to upgrade the bulk import microservice:helm3 upgrade <release name for bulk import> -n <udr namespace> -f nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml - Once the pod is up and running, copy the CSV file. The container
starts processing the records.
Figure 2-30 Bulk Import Install

Verifying Subscriber Bulk Import PVC
- Run the following command to check PVC creation:
kubectl get pvc -n <namespace>Figure 2-31 Verifying PVC

OR
Run the following command to verify the PV creation:
kubectl get pvFigure 2-32 Verifying PV
- Update the values.yaml file available at
ocudr/charts/nudr-bulk-importand run the following command to upgrade the bulk import tool.helm3 upgrade <release name for bulk import> -n <udr namespace> .;
Installing xmltocsv converter
- Enable the following flag in the custom-values.yaml file. The
custom-values.yaml file is available at
/nudr-bulk-importlocation.nudr-bulk-import: xmlToCsv: enabled: true(default value is false) - Run the following command to install the bulk import tool:
helm3 install <release name for bulk import> -n <udr namespace> -f nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml - Once the pod is up and running, copy the ixml file. The xmltocsv
container starts processing the records.
Figure 2-33 xmltocsv install
Verifying xmltocsv PVC Creation
- Run the following command to verify bulk import and xmltocsv
PVC creation:
kubectl get pvc -n <namespace>Figure 2-34 Verifying xmltocsv pvc

- Run the following command to verify the PV creation:
kubectl get pvFigure 2-35 Verifying xmltocsv pv

Note:
- If the bulk import tool is already running on your system, then you
cannot upgrade to add xmltocsv container to an existing bulk import
container. Uninstall the existing bulk import container and enable
xmlToCsv flag by running the following command:
helm3 install <release name for bulk import> -n <udr namespace> -f nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml - If both the containers are already running, then update the
custom-values.yaml file in the at
/nudr-bulk-importlocation and run the following command to upgrade bulk import tool.helm3 upgrade <release name for bulk import> -n <udr namespace> -f nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml
To Install the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool for EIR Provisioning
- Enable the following flag in the
nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml
file.
pdbiToCsv: enabled: true - Configure the PDBI file path, where the PDBI
nudr-bulk-import-custom-values.yaml file are replaced, using the following
configuration.
createPdbiToCsvPVC: pathLocation: /home/udruser/pdbi - Run the following command to install the bulk import tool for EIR
provisioning.
helm install <release-Name> -n <namespace> -f <nudr-bulk-import-customvalues.yaml file> nudr-bulk-import-23.1.2.tgzThe bulk import will start running with 2 container. The container starts processing the records.

Running and Monitoring the Bulk Import Tool for EIR
- Place the PDBI files in the configured PDBI file path location
/home/udruser/pdbifolder. - The PDBI file is converted to CSV file and is placed in
/home/udruser/importfolder. - The bulk import main container processes the CSV file where the provisioning API's for EIR are called and the log files are also generated.
Sample Logs Files:
Containers generate summary report log file and the final result log file in configured PDBI file path/logs. Below are the samples of the log files:
Sample log file after processing PDBI file to CSV file: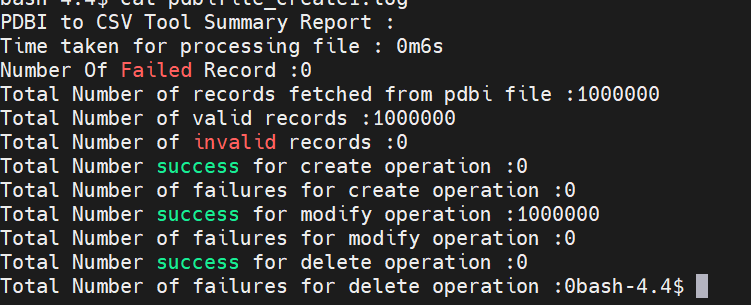
Sample log file after processing CSV file: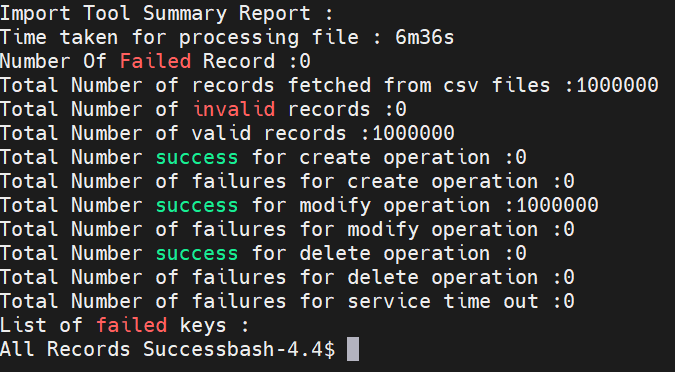
Sample PDBI result log file: PDBI result log file is stored in the
configured PDBI file path/logs (example: /home/udruser/pdbi/logs).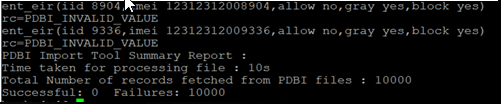
Change the Configuration for an Existing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool using Helm
Perform the following steps to change the configuration for an existing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool deployment:
Note:
This configuration is not exposed through the REST API.- Modify the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool custom yaml file with the required configuration.
- Run the following command to delete the existing subscriber bulk import tool
Helm
deployment
helm delete <release name> -n <name space> - Run the following command to install the subscriber bulk import tool with the
modified custom yaml
file
helm install <release name> -n <name space> <chart path> -f <values.yaml path with latest configuration>
2.35.2.1 Configuring Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
The following table lists the user parameters for creating PVC and template for installing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.
Table 2-41 Subscriber Bulk Import Tool User Parameters
| Parameter | Description | Default value | Range or Possible Values (If applicable) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| global.dockerRegistry | Docker registry from where the images are pulled | ocudr-registry.us.abc.com:5000/ocudr | NA | NA |
| global.mysql.dbServiceName | Database service to connect | mysql-connectivity-service.occne-infra | NA | NA |
| global.mysql.port | Port for database service connection | 3306 | NA | NA |
| global.udrTracing.enable | Flag to enable UDR tracing on Jaeger | false | true or false | NA |
| global.udrTracing.host | Jaegar service name installed in CNE | occne-tracer-jaeger-agent.occne-infra | NA | NA |
| global.udrTracing.port | Jaegar Service Port installed in CNE | 6831 | NA | NA |
| global.serviceAccountName | The entire pod should be associated with the service account used for UDR deployment. | ocudr-serviceaccount | NA | NA |
| global.preInstall.image.name | Image name for the nudr-bulk-import-prehook pod which will take care of DB and table creation for UDR deployment. | nudr_bulk_import_pre_install_hook | NA | NA |
| global.preInstall.image.tag | Image version for nudr-bulk-import-pre-install-hook pod image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| global.preInstall.createUser | Creates user and grants access to UDR database. | false
Note: Do not change this value. |
true or false | NA |
| global.preInstall.config.logLevel | Log level for preinstall hook pod | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
NA |
| global.postUpgrade.image.name | Image name for the nudr-bulk-import-post-upgrade pod which will take care of DB and table creation for UDR deployment. | nudr_bulk_import_post_upgrade_hook | NA | NA |
| global.postUpgrade.image.tag | Image version for nudr_bulk_import_post_upgrade_hook pod image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| global.postUpgrade.config.logLevel | Log level for postUpgrade hook pod | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.cpu | CPU limit for pods created k8s hooks and jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job too. | 1 | NA | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.memory | Memory limit for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well. | 1Gi | NA | NA |
| global.hookJobResources.limits.ephemeral-storage | Ephemeral Storage limits for hook pods | 1024Mi | Unit MB | |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.cpu | CPU requests for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well. | 0.5 | NA | The cpu to be allocated for hooks during deployment |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.memory | Memory requests for pods created k8s hooks/jobs created as part of UDR installation. Applicable for helm test job as well | 0.5Gi | NA | The memory to be allocated for hooks during deployment |
| global.hookJobResources.requests.ephemeral-storage | Ephemeral Storage request for hook pods | 72Mi | Unit MB | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.tolerations | When global.tolerationSetting is ENABLED configure tolerations here. | [] | Example:
tolerations:
|
NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion | Node Selector API version setting | v1 | Allowed Values:
|
|
| gloabl.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector.nodeKey |
NodeSelector key configuration for UDR hooks, This excludes the common service hooks When hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration will come into use. |
' ' | Valid key for a label for a particular node | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector.nodeValue |
NodeSelector Value configuration for UDR hooks. This excludes the common service hooks. When hooksCommonConfig.hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion is set to v1 then this configuration will come into use. |
' ' | Valid value pair for the above key for a label for a particular node | NA |
| global.hooksCommonConfig.nodeSelector |
NodeSelector configuration when hooksCommonConfig.helmBasedConfigurationNodeSelectorApiVersion at micro service level is set to v2 Uncomment and use this configuration when required. Else keep this commented. |
{} | Valid key value pair matching a node for nodeSelection by a pod | NA |
| dbCredSecretName | Database credential secret name | ocudr-secrets | NA | NA |
| customExtension.allResources.labels | Custom Labels that needs to be added to all the UDR Kubernetes resources | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.allResources.annotations | Custom annotations that needs to be added to all the UDR Kubernetes resources | null | NA | ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section |
| customExtension.lbServices.labels | Custom labels that needs to be added to UDR services that are considered as Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.lbServices.annotations | Custom Annotations that needs to be added to OCUDR Services that are considered as Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.lbDeployments.labels | Custom labels that needs to be added to UDR deployments that are associated to a service of Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.lbDeployments.annotations | Custom annotations that needs to be added to UDR deployments that are associated to a service of Load Balancer type | null | NA | ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section |
| customExtension.nonlbServices.labels | Custom labels that needs to be added to UDR services that are not considered as Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbServices.annotations | Custom annotations that needs to be added to UDR services are not considered as Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbDeployments.labels | Custom labels that needs to be added to UDR deployments that are associated to a service which is not of Load Balancer type | null | NA | NA |
| customExtension.nonlbDeployments.annotations | Custom annotations that needs to be added to UDR deployments that are associated to a service, which is not of Load Balancer type | null | NA | ASM related annotations to be added under ASM Specific Configuration section |
| extraContainerTpl | The template for extraContainer is defined in this configuration. The debugContainer template defined here which is applicable for all microservices under ocudr umbrella. |
|
NA | NA |
| extraContainersVolumesTpl | Debug container volume template |
|
NA | NA |
| image.name | Docker Image name | nudr_bulk_import | NA | NA |
| image.tag | Tag of Image | 25.1.100 | NA | NA |
| image.pullPolicy | This setting indicates whether image needs to be pulled or not | IfNotPresent |
Possible Values - Always IfNotPresent Never |
NA |
| createBulkImportPVC.name | name of PVC | bulkimportpersistentclaim | NA | NA |
| createBulkImportPVC.storageClassName | storage class name for PVC | standard | Possible Values - standard | NA |
| createBulkImportPVC.storage | storage for PVC | 10Gi | NA | NA |
| createXmlToCsvPVC.name | name of PVC | xmltocsvpersistentclaim | NA | NA |
| createXmlToCsvPVC.storageClassName | storage class name for PVC | standard | Possible Values - standard | NA |
| createXmlToCsvPVC.storage | storage for PVC | 10Gi | NA | NA |
| xmlToCsv.enabled | flag for enabling or disabling nudr-xmltocsv | false | true or false | NA |
| xmlToCsv.management | management port of xmltocsv container | 9001 | NA | NA |
| service.type | The Kubernetes service type for exposing UDR deployment | ClusterIP |
Possbile Values- ClusterIP NodePort LoadBalancer |
Suggested to be set as ClusterIP (default value) always |
| service.port.http | The HTTP port to be used in notify service to receive signals from nudr-notify-service pod. | 5001 | NA | NA |
| service.port.management | The actuator management port to be used for notify service. | 9000 | NA | NA |
| hikari.poolsize | The Hikari pool connection size to be created at start up | 10 | NA | NA |
| hikari.connectionTimeout | MYSQL connection timeout | 1000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| hikari.minimumIdleConnections | Minimum idle MYSQL connections maintained | 2 | Valid. No, less than poolsize configured | NA |
| hikari.idleTimeout | Idle MYSQL connections timeout | 10000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| hikari.queryTimeout | Query timeout for a single database query. If you set the value to -1 there will be no timeout for database queries | -1 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| logging.level.root | Log level of the notify service pod | WARN |
Possible Values - WARN INFO DEBUG |
NA |
| resources.requests.cpu | The CPU to be allocated for notify service pod during deployment | 2 | NA | NA |
| resources.requests.memory | The memory to be allocated for nudr-bulk-import pod during deployment | 2Gi | NA | NA |
| resources.requests.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation request | 50 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.requests.crictlStorage | Crictl storage for ephemeral storage allocation request | 2 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.limits.cpu | CPU allotment limitation | 2 | NA | NA |
| resources.limits.memory | Memory allotment limitation | 2Gi | NA | NA |
| resources.limits.logStorage | Log storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit | 1000 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.limits.crictlStorage | Crictl storage for ephemeral storage allocation limit | 2 | Unit: MB | NA |
| resources.target.averageCpuUtil | CPU utilization limit for auto scaling (creating HPA) | 80 | NA | NA |
| extraContainers | This configuration decides service level extraContainer support. The default value lets it to be dependent on what is configured in the global level | USE_GLOBAL_VALUE |
Allowed Values:
|
NA |
| serviceMeshCheck | Enable when deployed in serviceMesh, referred to the serviceMeshCheck in global section. Set to false when side car is not included for this service | false | NA | Do not change this value unless it is different from the value configured in global section. |
| istioSidecarReadyUrl | Readiness URL configurable for side car,
referred to global section istioSidecarReadyUrl. Change only if the url is different for the side car container in this microservice |
http://127.0.0.1:15000/ready | NA | Do not change this value unless it is different from the value configured in global section. |
| ocudrReleaseName | Release Name of UDR to form config-server/ocudr endpoint FQDN | ocudr | NA | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.enabled | If this parameter is enabled, then only pdbiToCsv container is used to convert PDBI format to CSV format. Otherwise, not. | false |
Possible Values - true or false |
NA |
| pdbiToCsv.managementPort | Management Port of PDBI to CSV container | 9002 | NA | NA |
| createPdbiToCsvPVC.name | Name of Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) for PDBI to CSV | pdbitocsvpersistentclaim | NA | NA |
| createPdbiToCsvPVC.storageClassName | Storage class name for PVC | standard | Possible Values - standard | NA |
| createPdbiToCsvPVC.storage | Storage for PVC | 10Gi | NA | NA |
| createPdbiToCsvPVC.pathLocation | Directory from where PDBI files are polled | /home/udruser/pdbi | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.enable | To enable the sftp feature on bulk-import | false |
Possible Values - true or false |
NA |
| sftpDetails.host | Remote Host IP | 10.75.229.18 | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.port | Remote Host Port | 22 | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.username | Remote Host Username | cloud-user | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.path | Remote Host server path where .pdbi files present | home/cloud-user/ocudr/sftppath/ | NA | Do not delete the backslash / in the default value. It is mandatory to include the backslash. This is also applicable during the REST API operation. |
| sftpDetails.transferOutPath | Remote Host server path where generated .log files are placed | /home/cloud-user/transferOut/ | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.extension | Extension of the files to be transferred, as of now support will be for .pdbi | .pdbi | .pdbi | NA |
| sftpDetails.pollingImport | Periodic lookup interval for sftp transfer-in | "2" | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.pollingExport | Periodic lookup interval for sftp transfer-out | "1" | NA | NA |
| sftpDetails.deleteLogFilePvc | This flag is used to delete the log files from pvc path once the file transfer is successfully done to the remote host | false |
Possible Values - true or false |
NA |
| startupProbe.failureThreshold | It is the configurable number of times the startup probe
is retried for failures.
Note: Do not change this value. If there is delay in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then tune these parameters |
40 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| startupProbe.periodSeconds | It is the time interval for every startup probe check. Note: Do not change this value. If there is delay in pod coming up and probe is killing the pod then tune these parameters | 5 | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| maxConcurrentPushedStreams | Maximum number of concurrent requests that is pushed per destination | 6000 | NA | NA |
| maxRequestsQueuedPerDestination | Maximum number of requests that is queued per destination | 5000 | NA | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerDestination | Maximum connection allowed per destination | 10 | NA | NA |
| maxConnectionsPerIp | Maximum connection allowed per IP | 10 | NA | NA |
| requestTimeout | Client Request Timeout | 5000 | Unit: Milliseconds | NA |
| connectionTimeout | Client connection timeout | 10000 | NA | NA |
| idleTimeout | Client connection idle timeout | 0 | NA | NA |
| dnsRefreshDelay | Server DNS refresh delay | 120000 | NA | NA |
| pingDelay | Server ping delay | 60 | NA | NA |
| connectionFailureThreshold | Client connection failure threshold | 10 | NA | NA |
| jettyserviceMeshCheck | For ASM deployment jetty service mesh check | false | true/false | NA |
| batchConfig.asynchronous | To enable multiple thread bulk import and single thread bulk import | false | true/false | NA |
| batchConfig.coreThreadPool | Number of minimum and core thread pool size for spring batch | 2 | NA | NA |
| batchConfig.maxThreadPool | Number of maximum thread pool size for spring batch | 2 | NA | NA |
| batchConfig.queueCapacity | Number maximum queue size | 2000 | NA | NA |
| batchConfig.writerCoreThreadPool | Number of minimum or core thread pool size for task executor | 5 | NA | NA |
| batchConfig.writerMaxThreadPool | Number of maximum thread pool size for task executor | 5 | NA | NA |
| batchConfig.writerQueueCapacity | Maximum queue size of task executor | 2000 | NA | NA |
| xmlToCsv.batchConfig.coreThreadPool | Number of minimum and core thread pool size for spring batch | 10 | NA | NA |
| xmlToCsv.batchConfig.maxThreadPool | Number of maximum thread pool size for spring batch | 10 | NA | NA |
| xmlToCsv.batchConfig.queueCapacity | Maximum queue size | 2000 | NA | NA |
| xmlToCsv.batchConfig.chunkSize | Reading file chunk size | 500 | NA | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.batchConfig.coreThreadPool | Number of minimum and core thread pool size for spring batch | 5 | NA | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.batchConfig.maxThreadPool | Number of max thread pool size for spring batch | 5 | NA | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.batchConfig.queueCapacity | Maximum queue size | 2000 | NA | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.batchConfig.chunkSize | Reading file chunk size | 500 | NA | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.mandatoryFields.create | Mandatory field for create operation import though PDBI | imei | Valid field | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.mandatoryFields.update | Mandatory field for update operation import though PDBI | imei | Valid field | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.mandatoryFields.delete | Mandatory field for delete operation import though PDBI | imei | Valid field | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.allFields.create | Fields list for create operation import though PDBI | iid,imei,svn,allow,white,grey,gray,black,block,imsi,msisdn,force,timeout | Valid field | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.allFields.update | Fields list for updateoperation import though PDBI | iid,imei,svn,allow,white,grey,gray,black,block,imsi,msisdn,force,timeout | Valid field | NA |
| pdbiToCsv.allFields.delete | Fields list for delete operation import though PDBI | iid,imei,imsi,msisdn,timeout,svn | Valid field | NA |
| sftpDetails.fileSizeCheck |
Check the file size of the remote server once the file is successfully transferred to the remote location. This flag is used check file size of transfer out log files from PVC to remote location. |
false | true or false | NA |
| sftpDetails.transferProtocol |
Transfer the files to remote location. The default protocol is SFTP. |
sftp | sftp or scp | NA |
| sftpDetails.secrets.privatekey.name | SFTP transfer private key holding secret. | ocudr-ssh-private-key | Valid K8s secret name | NA |
| sftpDetails.secrets.publickey.name | SFTP transfer public key holding secret. | ocudr-ssh-public-key | Valid K8s secret name | NA |
| gracefulShutdown.gracePeriod | It is the graceful shutdown time limit. | 30s | Unit: Seconds | NA |
| deployment.replicaCount | Configures the number of pod replicas to deploy. | 1 | Positive integers | The deployment is StatefulSet. |
| deployment.customExtension.labels | Custom labels that must be added to specific subscriber bulk import deployment resource. | {} (empty flow mapping) | Valid yaml mapping | NA |
| deployment.customExtension.annotations | Custom annotations that must be added to specific subscriber bulk import deployment resource. | {} (empty flow mapping) | Valid yaml mapping | NA |
2.35.2.2 Initiating the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
By default, the Subscriber Bulk Import tool polls the /home/udruser/import path every 5000 ms. Before initiating the tool, ensure the nudr-bulk-import pod is up and running.
- Run the following command to place the file inside the container:
kubectl cp <csv file> <namespace>/<nudr-bulk-import pod name>:/home/udruser/importExample:
kubectl cp create_pcf.csv bulktest/bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-pgh2p:/home/udruser/import - To verify whether the file is present inside the container or not,
log in to the bash of container and run the following command:
kubectl exec -it <nudrbulk-import pod name>-n <namespace> -- bashExample:
kubectl exec -it bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-pgh2p -n bulktest -- bashNote:
After log in to bash, you can find the file under /home/udruser/import location.bash-4.2$ pwd /home/udruser/import bash-4.2$ ls -l -rw-r--r--. 1 root udruser 28471 Aug 19 09:33 create_pcf.csvThe Bulk Import tool processes each CSV file at a time and provisions the subscribers on 5G UDR. The summary report is available in the /home/udruser/import path with filename (<CSV_filename>.log).
bash-4.2$ pwd /home/udruser/import bash-4.2$ ls -l -rw-r--r--. 1 root udruser 28471 Aug 19 09:33 create_pcf.csv create_pcf.logA sample summary report is as follows:
Import Tool Summary Report Time taken for processing file 0m26s Number Of Failed Record 0 Total Number of records fetched from csv files 4 Total Number success for create operation 4 Total Number of failures for create operation 0 Total Number success for modify operation 0 Total Number of failures for modify operation 0 Total Number success for delete operation 0 Total Number of failures for delete operation 0 Total Number of failures for service time out 0 List of failed keys All Records SuccessNote:
The Bulk Import container logs contains the summary report, when the INFO logging level is enabled. - Run the following command to copy the report from pod container:
kubectl cp <pod name>:home/udruser/import/modify_slf.log <file name> -n <namespace>Example:
kubectl cp ocudr-nudr-bulk-import-8g8c8:home/udruser/import/modify_slf.log modify_slf.log -n myudr
Note:
- The metrics of bulk import tool can be observed on the Grafana dashboard. For more information about Bulk import metrics, see nudr-bulk-import-service Metrics.
- To monitor the status of bulk import tool, see Subscriber Bulk Import Status.
2.35.2.2.1 Using xmltocsv Converter
- Run the following command to place the ixml file in the path
(/home/udruser/xml) inside the container:
kubectl cp <csv file> <namespace>/<nudr-bulk-import pod name>:/home/udruser/xml -c nudr-xmltocsvExample:
kubectl cp createSubscriber.ixml bulktest/bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-pgh2p:/home/udruser/xml -c nudr-xmltocsv - Log in to bash of the container and run the following commands to
check the ixml file inside the container:
kubectl exec -it <nudrbulk-import pod name> -c nudr-xmltocsv -n <namespace> bashExample:kubectl exec -it bulktest-nudr-bulk-import-pgh2p -c nudr-xmltocsv -n bulktest bashbash-4.2$ pwd /home/udruser/xml bash-4.2$ ls -l -rw-r--r--. 1 root udruser 28471 Aug 19 09:33 createSubscriber.ixml createSubscriber.logNote:
After log in to bash, you can find the file under /home/udruser/xml location.The xmltocsv convertor processes the ixml file, converts XML format to JSON format, and then generate CSV file as output. This CSV file is automatically placed in the
The bulk import container processes this CSV file and provisions the subscribers on 5G UDR. You can check this CSV file in the/home/udruser/importfolder./home/udruser/importfolder.
You can see the progress of XML file processing in logs only if the INFO logs are enabled.bash-4.2$ pwd /home/udruser/import bash-4.2$ ls -l -rw-r--r--. 1 root udruser 28471 Aug 19 09:33 createSubscriber.csvRun the following command to generate a summary report of xmltocsv convertor in the same path (/home/udruser/xml) with file name as <CSV_filename>.log.
cat createSubscriber.logA summary report of xmltocsv container is created in same path(/home/udruser/xml) with filename <CSV_filename>.log.
bash-4.2$ pwd /home/udruser/xml bash-4.2$ ls -l -rw-r--r--. 1 root udruser 28471 Aug 19 09:33 createSubscriber.ixml createSubscriber.logA sample summary report which is created in xmltocsv container is as follows:
A summary report of bulk import container is created in same path (/home/udruser/import) with file name as <CSV_filename>.logXML to CSV Tool Summary Report : Time taken for processing file : 0m0s Number Of Failed Record :0 Total Number of records fetched from xml file :100 Total Number success for create operation :100 Total Number of failures for create operation :0 Total Number success for modify operation :0 Total Number of failures for modify operation :0 Total Number success for delete operation :100 Total Number of failures for delete operation :0 List of failed keys : All Records SuccessA summary report of bulk import container is created in same path(/home/udruser/import) with filename <CSV_filename>.log
bash-4.2$ pwd /home/udruser/import bash-4.2$ ls -l -rw-r--r--. 1 root udruser 28471 Aug 19 09:33 createSubscriber.csv createSubscriber.logA sample summary report created in bulk import is as follows:
Import Tool Summary Report Time taken for processing file 0m26s Number Of Failed Record 0 Total Number of records fetched from csv files 4 Total Number success for create operation 4 Total Number of failures for create operation 0 Total Number success for modify operation 0 Total Number of failures for modify operation 0 Total Number success for delete operation 0 Total Number of failures for delete operation 0 Total Number of failures for service time out 0 List of failed keys All Records SuccessThis summary report is also available in the xmltocsv and bulk import containers logs when INFO logging level is enabled. To copy the report from a pod container to the current location (<file name>), run the following command:
kubectl cp <pod name>:home/udruser/xml/createSubscriber.log <file name> -c nudr-xmltocsv -n <namespace>Example:
kubectl cp ocudr-nudr-bulk-import-8g8c8:home/udruser/xml/createSubscriber.log createSubscriber.log -c nudr-xmltocsv -n myudr
Note:
- The metrics of bulk import tool can be observed on the Grafana dashboard. For more information about bulk import metrics, see nudr-bulk-import-service Metrics.
- You can monitor the xmltocsv metrics on Prometheus or Grafana.
2.35.2.3 Upgrade and Rollback support for Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
Upgrade Procedure
Helm upgrade is supported. To change the configuration for an existing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool, see Change the Configuration for an Existing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool using Helm.
helm upgrade <release name> -n <name space> <chart path>- UDR must be upgraded first and then Subscriber Bulk Import Tool must be upgraded. For more information, see "Upgrading UDR" section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
- Only existing container is enabled when upgrading. For example, if in the previous deployment only the nudr-bulk-import container is enabled then when upgrading you can only enable nudr-bulk-import container.
- PVC size cannot be modified as part of the upgrade process.
Rollback Procedure
Note:
Helm rollback is not supported for Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.Note:
UDR and the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool must be rolled back together.- Uninstall the current version of the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.
- Install the older version of the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool. For more information, see Installing Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.
- Perform the rollback procedure for UDR. For more information, see Rolling Back UDR chapter in Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
2.35.2.4 Sample Subscriber Bulk Import File
This section provides sample subscriber bulk import files.
2.35.2.4.1 Sample Bulk Import File in CSV Format
The Bulk Import file should be in CSV file format, which is shared below:
Sample: CSV File Format
keyType,keyValue,operationType,nfType,jsonPayload
msisdn,1111111114,CREATE,PCF,"{"profile-data": {"MSISDN": ["9111111112","9211111112","1111111114"]},"policy-data": {"am-data": {"praInfos": {"p1": {"praId": "p1","trackingAreaList": [{"plmnId": {"mcc": "976","mnc": "32"},"tac": "5CB6"},{"plmnId": {"mcc": "977","mnc": "33"},"tac": "5CB7"}],"ecgiList": [{"plmnId": {"mcc": "976","mnc": "32"},"eutraCellId": "92FFdBE"},{"plmnId": {"mcc": "977","mnc": "33"},"eutraCellId": "8F868C4"}],"ncgiList": [{"plmnId": {"mcc": "976","mnc": "32"},"nrCellId": "b2fB6fE9D"},{"plmnId": {"mcc": "977","mnc": "33"},"nrCellId":"5d1B4127b"}],"globalRanNodeIdList": [{"plmnId": {"mcc": "965","mnc": "235"},"n3IwfId": "fFf0f2AFbFa16CEfE7"},{"plmnId": {"mcc": "967","mnc": "238"},"gNbId": {"bitLength": 25,"gNBValue": "1A8F1D"}}]}},"subscCats": ["cat1", "cat2"]}}}"
accountID,12345678912345678912345678,MODIFY,SLF,"{"profile-data": {"imsi": ["2222222221","2222222222"],"nai": ["test@abc.com"],"accountID": ["12345678912345678912345678"],"msisdn": ["19195225555","19195225556"],"extid": ["user@abc.com"]},"slfGroupName": "IMSGrp1"}"
msisdn,63612000056,DELETE,PCF-VSA
msisdn,1111111114,DELETE,PCFThe bulk import tool supports following keyTypes:
Table 2-42 CSV File Format Details
| keyType | keyValue | OperationType | nfType | Subs_data(JSON) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MSISDN | 1234 | CREATE | PCF | { .. } |
| IMSI | 6786677 | MODIFY | PCF | { .. } |
| NAI | abcd@oracle.com | DELETE | PCF | { .. } |
| EXTID | user@abcd.com | CREATE | PCF | { .. } |
| NAI | test@abcd.com | CREATE | PCF | { .. } |
| IMEI | 355171053475182 | CREATE | EIR | { .. } |
Note:
The subs_data column must have JSON body enclosed in double quotes(").2.35.2.4.2 Sample iXML format for Bulk Import
The sample iXML format for bulk import is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<transaction>
<txRequest id="1">
<createSubscriber>
<key>
<MSISDN>6666666100</MSISDN>
</key>
<entity>
<data>
<name>Subscriber</name>
<interface>XMLIMPORT</interface>
</data>
<content><![CDATA[<subscriber><field name="MSISDN">6666666100</field><field name="IMSI">222222222222222</field><field name="BillingDay">31</field><field name="Entitlement">DayPass</field><field name="Entitlement">DayPassValue</field></subscriber>]]></content>
</entity>
</createSubscriber>
</txRequest>
</transaction>2.35.2.4.3 Sample Bulk Import File in CSV Format for EIR
The bulk import file should be in CSV file format, as below:
Sample: CSV File Format
keyType,keyValue,operationType,nfType,jsonPayload,addInfo
IMEI,355171053475182,MODIFY,EIR,"{"cmd":"ent_eir(iid 3237536, imei 355171053475182, black yes, force yes)","profile-data":{"imei":["355171053475182"]},"equipment-status":{"white":false,"gray":false,"black":false}}"keyType,keyValue,operationType,nfType,jsonPayload,addInfo
IMEI,356508052681576,DELETE-KEY,EIR,"{"cmd":"dlt_eir(iid 3237532, imei 356508052681576, imsi 12345678)","profile-data":{"IMSI":["12345678"]}}"2.35.3 Monitoring the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool Status
Monitoring the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool Status for UDR and SLF Mode
- When the file is copied to the PVC path, the subscriber bulk import tool shows the status as STARTED.
- When the subscriber bulk import tool picks the file from the PVC, the status is shows as IN-PROGRESS.
- When the provisioning is complete, the status shows COMPLETED and the result log file is generated and placed in the PVC path.
Figure 2-36 Bulk Import Tool Status for UDR and SLF

Monitoring the Subscriber Bulk Import Tool Status for EIR Mode
- If SFTP is enabled in the subscriber bulk import tool, the status shows TRANSFER_IN_STARTED. When the file transfer is complete, the status shows TRANSFER_IN_COMPLETED and provisioning starts.
- If SFTP disabled in the subscriber bulk import tool, the status is shown as STARTED.
- When the file is present in the PVC, the subscriber bulk import tool will pick the file and the status shows IN-PROGRESS.
- When the provisioning is completed, the status shows COMPLETED and the result log file is generated and placed in the PVC path.
- If SFTP is enabled in the subscriber bulk import tool, the result log file is transferred to the remote host and the status shows TRANSFER_OUT_COMPLETED.
Figure 2-37 Bulk Import Tool Status for EIR

For more information, see the CNC Console section Subscriber Bulk Import Status.
2.35.4 Secure File Transfer Support for Subscriber Bulk Import Tool
Subscriber bulk import tool supports the capability to securely transfer the files from the remote server using Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP). This feature supports transferring-in the Provisioning Database Interface (PDBI) import files and transferring out the result log files to a remote server.
Using Helm Configuration:
- You can enable or disable the SFTP by setting the
sftpDetails.enableparameter to true or false in custom-value.yaml file of the subscriber bulk import tool. For more information on the parameters, see Configuring Subscriber Bulk Import Tool.sftpDetails: enable: true host: 10.75.229.127 port: 22 username: cloud-user path: /home/cloud-user/ocudr/sftppath1/ extension: .pdbi pollingImport: "2" pollingExport: "1" deleteLogFilePvc: false secrets: privatekey: name: ocudr-ssh-private-key publickey: name: ocudr-ssh-public-key fileSizeCheck: false transferProtocol: sftp - Configure the private and public keys for the remote host. The
operator must provide the private key (id_rsa) and the public key
(id_rsa.pub) for the remote
host.
kubectl create secret generic ocudr-ssh-private-key --from-file=id_rsa=/home/cloud-user/ocudr/secrets/id_rsa -n <namespace> kubectl create secret generic ocudr-ssh-public-key --from-file=id_rsa.pub=/home/cloud-user/ocudr/secrets/id_rsa.pub -n <namespace>
When the SFTP is enabled the scheduler looks for the .pdbi files from
the remoteHost for the path that is configured under the
remoteDirPath parameter and transfers the files to the PVC
location. When the files processing are completed the resultant log files are
transferred to the same remoteHost from PVC location to a separate
path that is configured under the transferOutPath parameter.
Using REST API:
http://10.75.215.124:32523/nudr-config/v1/udr.bulkimportservice.cfg/BULK_IMPORT_CFG
to configure the SFTP feature. For more information, see Configuring Subscriber Bulk Import Tool and Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data
Repository REST Specification
Guide.{
"pollingTimeInterval": 5000,
"lastModifiedTimeInterval": 30,
"pdbiFilePath": "/home/udruser/pdbi",
"pdbiFileExpiryTime": "7d",
"remoteHost": "10.75.229.128",
"remoteHostPort": "22",
"remoteDirPath": "/home/cloud-user/ocudr/sftppath/",
"remoteHostUsername": "cloud-user",
"fileExt": ".pdbi",
"sftpEnabled": true,
"deleteFileFromPVC": false,
"periodicImportPoll": "2",
"periodicExportPoll": "1",
"resultLogFilePath": "/home/udruser/pdbi/logs"
"transferOutPath": "/home/cloud-user/transferOut/"
}
kubectl create secret generic ocudr-ssh-private-key --from-file=id_rsa=/home/cloud-user/ocudr/secrets/id_rsa -n <namespace>
kubectl create secret generic ocudr-ssh-public-key --from-file=id_rsa.pub=/home/cloud-user/ocudr/secrets/id_rsa.pub -n <namespace>2.36 Alternate Route Service
Overview
UDR uses Alternate Route Service to connect to other NFs, especially to NRF, for egress traffic. Alternate Route service supports static and dynamic configurations of virtual FQDN of NRF.
Note:
Before routing to NRF2, UDR retries NRF1 configured number of times and then, route to NRF2.To Enable
To enable Alternate Route Service, set the alternateRouteServiceEnable flag as 'true' under the Alternate Route section of values.yaml file.
To Configure
You can configure Alternate Route Service in the nrf-client-service section of the Values.yaml file as shown below:
Figure 2-38 Configuring Alternate Route Service
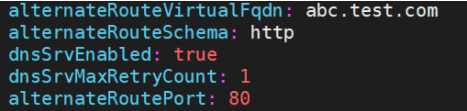
This service runs in a separate microservice in which you need to configure virtual FQDN as shown below:
Figure 2-39 Configuring Virtual FQDN
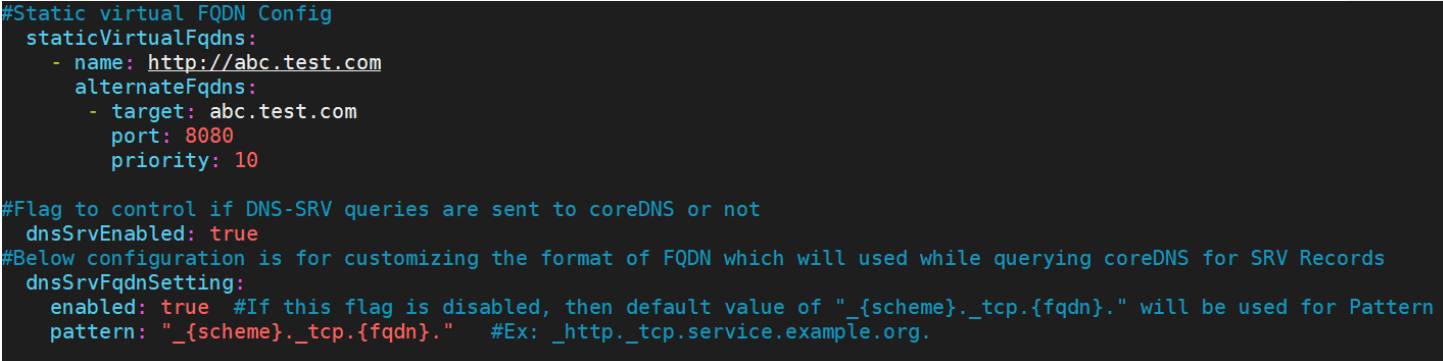
2.37 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info Header
The implementation of 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header enables network analytic tools or probes to easily identify the messages exchanged for a given User Equipment (UE). The Network Function (NF) service consumer or NF service producer can include any one of the UE identifiers (such as imsi, msisdn, extiid) in its 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header. The identifier helps to identify the UE related to the HTTP request or response.
If the HTTP request contains the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header, then the HTTP server (if it supports this header) includes the header details in the response and sends it to the HTTP client with the same UE identity that was present in the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header of the received HTTP request.
- Stores the UE identifier received in the header
- Includes the header in subsequent callback notification requests
- There exists only one entry for its header.
- The header has only one identifier from the following list:
- imsi
- msisdn
- extid
- accountid
- nai
- impi
- suci
- gci
- gli
- impu
- imei
- imeisv
- mac
- eui
Note:
Unified Data Repository (UDR) supports only imsi, msisdn, extid, accountid, and nai identifiers.
To Enable
sbiCorrelationInfoEnable: true. You can use any one of the following ways
to enable the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header.
- REST API: Set the enabled value to 'true' in request JSON of the Options configuration API. For more information, see the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
- User Configurable Parameter: Set the sbiCorrelationInfoEnable parameter to 'true'. For more information, see the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide .
- CNC Console: In the Global Configurations page, set the SBI Correlation Info Enable field to 'true'. For more information, see the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository User Guide.
For all success responses (2xx), the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header is added by default. For all error responses (4xx and 5xx), the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header is added only if the request has a header.
To Maintain
In case of failure or misconfiguration, the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header does not populate in UDR or Subscriber Location Function (SLF) responses. It is recommended to follow the instructions shared in the To Enable section.
2.37.1 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info Header for Ingress Gateway
For the incoming requests, the nudr-dr service of UDR fetches the correlation header value from R-URI (Request - Uniform Resource Identifier) of the nudr-dr service and populates it into the correlation header of the nudr-dr service response. UDR ignores the correlation header value in the request and uses the R-URI value for the correlation header value in the response.
If the correlation header is not present in the incoming requests, then it is not sent in the error responses and the correlation header is populated with the identity used for subscriber data retrieval from the UDR database.
Example: Header: 3gpp-sbi-correlation-info: imsi-4411111114
Note:
If the nudr-dr microservice is slow or down, then Ingress Gateway rejects the requests and does not add the correlation header.The correlation header is added for all the success and failures responses of UDR, SLF, or EIR for only signaling APIs such as "nudr-dr" and "nudr-group-id-map". The list of APIs that support 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header are as follows:
Table 2-43 APIs Supporting 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info Header
| Resource | URI |
|---|---|
| policy-data | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/am-data |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/ue-policy-set |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/policy-data/ues/{ueId}/sm-data/{usageMonId} |
| subscription-data | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/authentication-data/authentication-subscription |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/authentication-data/authentication-status |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/context-data |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/context-data/amf-3gpp-access |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/context-data/amf-non-3gpp-access |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/context-data/smf-registrations |
| - | {apiRoot}/nudr-dr/{apiVersion}/subscription-data/{ueId}/context-data/smsf-non-3gpp-access |
| nf-group-ids | {apiRoot}/nudr-group-id-map/{apiVersion}/nf-group-ids?subscriber-id=msisdn-1111111111&nf-type=UDM,AUSF,NEF |
2.37.2 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info Header for Egress Gateway
If the incoming request creates a subscription to notifications (subs-to-notify) and has 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header, then UDR stores this header in its database and includes the stored header in subsequent callback notification requests.
For all the provisioning or update resource requests and Network Function (NF) resource update requests subscribed for notifications, the 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header is retrieved from the database and added in the PCF or UDM notification requests if subscription to notifications (subs-to-notify) has 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info header. All the responses from Egress Gateway are validated irrespective of presence of header and respective metric is being pegged.
Table 2-44 APIs Supporting 3gpp-Sbi-Correlation-Info Header
| Resource | URI |
|---|---|
| subs-to-notify | https://pcf12.example.com/serviceY/abc |
For more information about the APIs that support this feature, see the Subscription Notification Formats for PCF Data section in the Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Unified Data Repository REST Specification Guide.
2.38 Automated Test Suite Support
UDR provides Automated Test Suite (ATS) for validating different functionalities. ATS allows you to execute UDR, SLF, and EIR test cases using an automated testing tool, and then compares the actual results with the expected or predicted results. In this process, there is no intervention from the user is required. For more information, see Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, ATS User Guide.