6 EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Configuration
Chapter 7, EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Configuration, describes the Eagle 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature and the procedures necessary to configure the EAGLE to support this feature.
Introduction
The EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature allows the network traffic on the EAGLE’s signaling links to be monitored by an ESP (extended services platform) or IMF (integrated message feeder) without additional intrusive cabling.
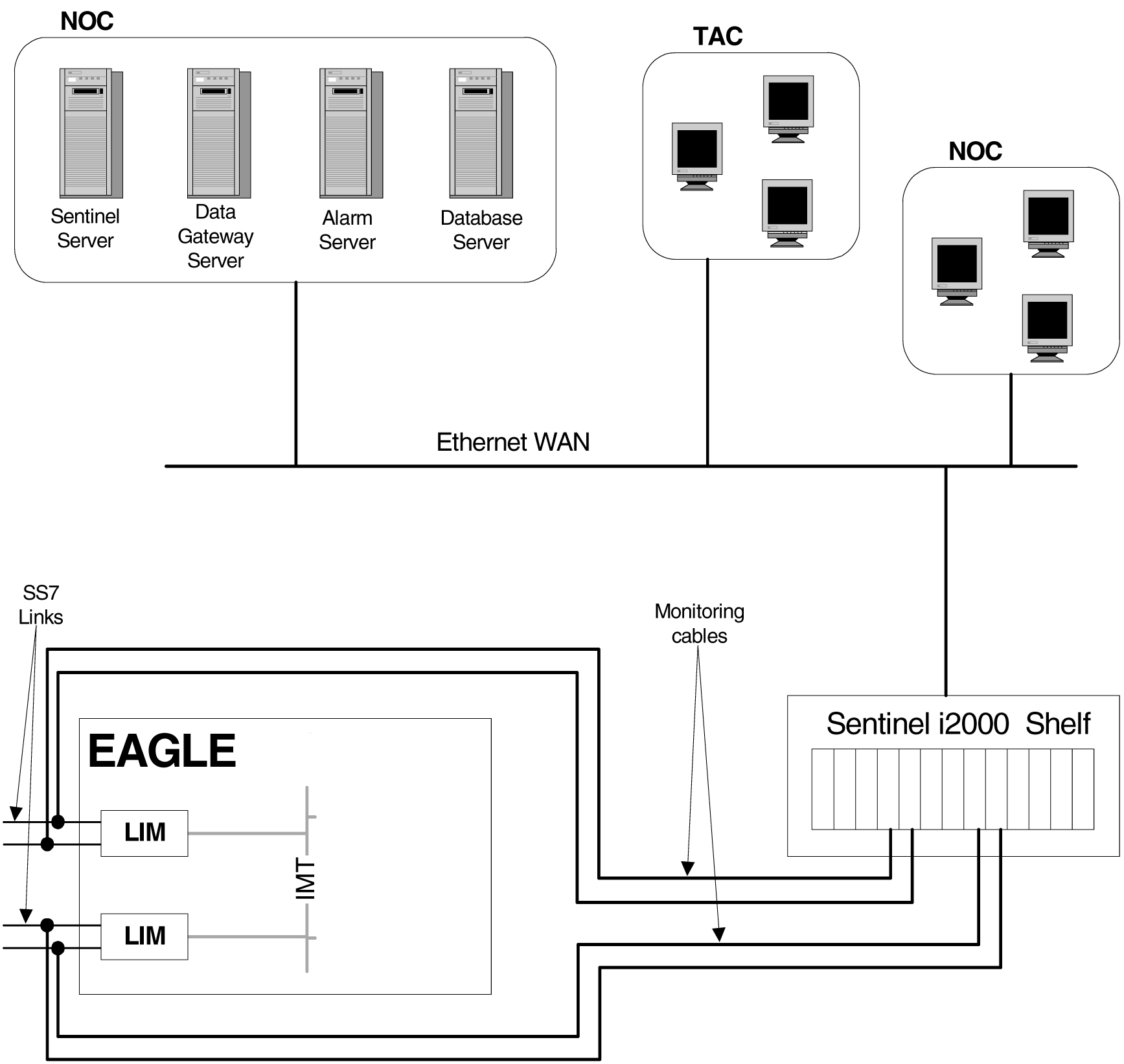
To monitor the network traffic on the EAGLE’s signaling links without this feature requires physical, clamp-on connections to the EAGLE's SS7 signaling links (see Figure 6-1). This monitoring method involves costs for cable installation and maintenance for each SS7 link that is to be monitored.
Figure 6-1 Monitoring via Hardware Connection
This feature eliminates the need to have intrusive hardware for each link that is to be monitored. The monitoring is performed by an Ethernet connection from an STC (Signaling Transport Card) or an FC-capable card to the ESP/IMF (see Figure 6-2 ). An FC-capable card is a card that is configured to copy traffic directly to an IMF subsystem over its Fast Copy interfaces. Currently, cards running the IPGHC and IPSG GPLs are the only supported FC-capable cards. Message Signaling Units (MSUs), alarms, and events may be copied to the ESP/IMF subsystem over the Ethernet link to provide the network traffic monitoring.
Figure 6-2 EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Network Connectivity
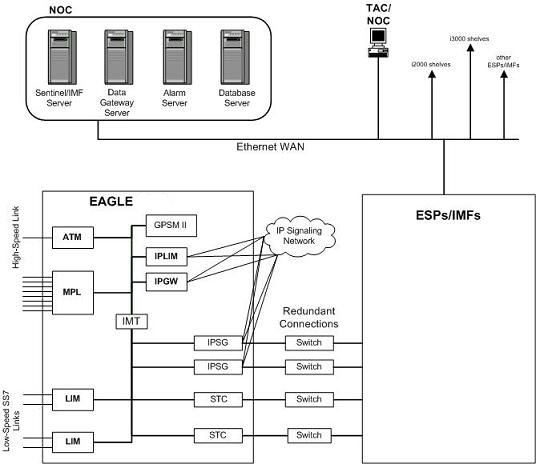
As can be seen in Figure 6-2 , this new method of connectivity removes the cabling and clamps from each monitored SS7 link. By incorporating a TCP/IP stack on each LIM and having the STCs or FC-capable cards serve as IP routers, the ESP/IMF subsystem may communicate directly with the SS7 LIMs. Figure 6-3 shows the logical communications pathway.
Figure 6-3 ESP/IMF/EAGLE Network
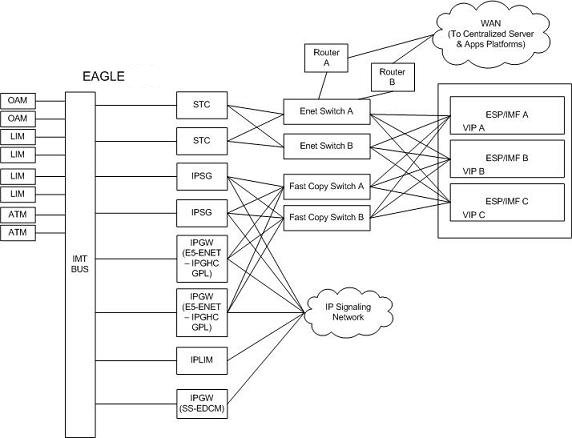
The STC communicates to the LIM by the IMT bus; the IP messages are simply encapsulated in an IMT wrapper between the cards. The STCs are provisioned in an n+1 configuration for redundancy. Each STC Ethernet port has a separate connection path to each Ethernet switch in order to provide an alternate path in the event of an Ethernet link failure. Note that the figure depicts a redundant network; this assures that a single network failure will not halt EAGLE or ESP/IMF operations. As shown in Figure 6-3 , one or more ESP/IMF may be connected to a single Ethernet switch. The number of STCs required corresponds to the number of SS7 links that are to be associated with the EAGLE Integrated Monitoring Support feature, plus an additional STC for redundancy.
The LIMs are assigned private network addresses. The IP message origination address specified is that of the LIM. The IP message destination address is that of the VIP (virtual IP address) contained within the ESP/IMF server. The STC serves as a router from the LIM to the ESP/IMF servers.
TCP/IP Link Provisioning
The IP communications link, used to transmit copied MSUs between the EAGLE and the ESP/IMF subsystem, is dynamically configured by the Sentinel/IMF. This is performed automatically as part of the operations for coming into service. A special function, part of the card's application software, is to establish communications with the ESP/IMF subsystem by sending a service request message (see Figure 6-4, Figure 6-5, and Figure 6-6).
Figure 6-4 Ethernet Link Establishment - EMP Link Data
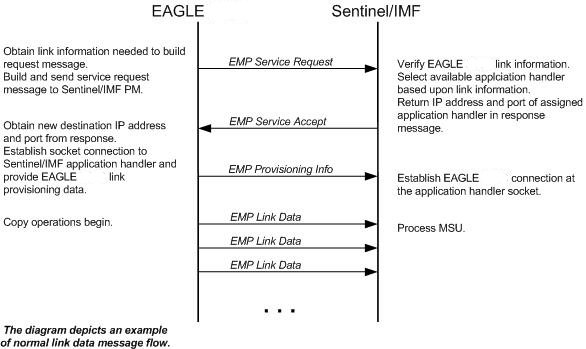
Figure 6-5 Ethernet Link Establishment - EMP Fast Copy Link PDU
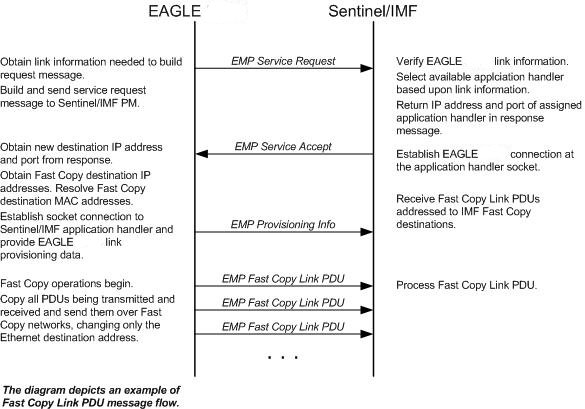
Figure 6-6 Ethernet Link Establishment - EMP Fast Copy Link PDU Modified for the IPGHC GPL

The LIM receiving the service accept response then opens a new socket using the specified IP address and port as the destination using standard TCP/IP socket messaging. The ESP/IMF server configured to service the port responds to the connect request and the socket is now available for normal operations. MSUs are copied from the LIM through the STC or FC-capable cards (if the Fast Copy function is being used) to the ESP/IMF server, then to the Sentinel/IMF.
The IPGHC GPL supports up to 50 associations per E5-ENET card. Each card hosts one SS7 signaling link. Sending information for 50 associations to the IMF requires a large UDP message. Network elements generally restrict broadcasting large UDP data. It is not guaranteed that the large Service Request Message (UDP broadcast) can reach the IMF in all networks. The Service Config Request Message and Service Config Data Message, shown in Figure 6-6, are used to send the large configuration information to the IMF.
The Service Request Message is sent with the “Service Type” field set to “LINK DATA SEGMENTED”. The IMF responds with a Service Config Request Message querying the configuration data by specifying the IP address and UDP port where the large configuration data needs to be sent. The card running the IPGHC GPL sends (UDP unicast) the configuration data to the specific IP address and UDP port included in the Service Config Request Message.
If the LIM is unsuccessful with its initial link service request, it will re-attempt link establishment with the ESP/IMF subsystem after delaying for a short period (that is, approximately 15 seconds). The LIM continuously repeats the link establishment procedure until it is successful. If the LIM ever loses its IP connection to the ESP server, the LIM will automatically begin reestablishment operations.
The STCs use Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol to provision themselves with IP addresses. The ESP/IMF subsystem contains a DHCP server and a DHCP client resides on the STC. The STC receives its IP address from the DHCP server in accordance with the DHCP standard.
The IP addresses of an FC-capable card is automatically assigned to the card as the card is brought into service. Each card is assigned two IP addresses, one for Fast Copy network A and the other for Fast Copy network B. The network portion of the IP addresses is determined from the FCNA and FCNAMASK (for the Fast Copy network A IP addresses) and the FCNB and FCNBMASK (for the Fast Copy network B IP addresses) values shown in the rtrv-netopts command output. The value of the host portion of the IP address for an FC-capable card is the IMT address of the card+1.
A custom routing protocol manages the multiple redundant links and provides a faster network convergence than is possible with standard routing protocols.
Time Stamping
The MSU information will be delivered to the ESP/IMF subsystem with an accurate time stamp (± 5 milliseconds). This allows the Sentinel/IMF to correlate a call's messages for CDR (Call Detail Record) operations.
EAGLE Provisioning
To provision this feature, these items are required:
- STC cards are installed in the EAGLE
- If the Fast Copy function is being used to copy traffic from IPSG cards (the
FCMODE=FCOPYandFCGPL=IPSGvalues are shown in thertrv-eisoptsoutput), cards running the IPSG GPL must be installed in the EAGLE. The state of at least one of the cards running the IPSG GPL must be IS-NR. - If the Fast Copy function is being used to copy traffic from cards running the IPGHC GPL (the
FCMODE=FCOPYandFCGPL=IPGHCvalues are shown in thertrv-eisoptsoutput), cards running the IPGHC GPL must be installed in the EAGLE. The state of at least one of the cards running the IPGHC GPL must be IS-NR. -
The TSC (Time Slot Counter) Synchronization feature is enabled in the EAGLE 5. TSC synchronization is supplied by the E5-MASP or E5-MCAP cards in card locations 1113 and 1115.
- A timing source for the low-speed signaling links and for the TSC (Time Slot
Counter) synchronization feature
If the EAGLE does not contain LIMDS0 cards, but contains TDM part numbers 870-0774-15 or later, the clock source for any low-speed links and for the TSC (Time Slot Counter) synchronization feature used by the Sentinel/IMF can be generated from the high-speed source clock source. An external BITS clock is not required.
If an external BITS clock is connected to an EAGLE without LIMDS0 cards, but with TDM part numbers 870-0774-15 or later, the external BITS clock must be used as the clock source for any low-speed links and for the TSC (Time Slot Counter) synchronization feature.
If LIMDS0 cards are present in the EAGLE, the external BITS clock is required for timing of the DS0 signaling links and for TSC (Time Slot Counter) synchronization used by the Sentinel/IMF. If the EAGLE also contains TDM part numbers 870-0774-15 or later along with the LIMDS0 cards, this procedure can be used to select the source of the high-speed source clock for the high-speed links using external timing.The high-speed source clock source cannot be used to generate the clock source for any low-speed links and for the TSC (Time Slot Counter) synchronization feature.
- A Network Time Protocol (NTP) timing source from the ESP/IMF server
- The EAGLE shelves can contain HIPR2 cards. Shelves containing IPLIMx, IPSG or IPGWx cards that are being monitored must contain HIPR2 cards.
An “n + 1" STC configuration is required to provide redundancy for this feature.
The connection from the EAGLE to the ESP is an Ethernet connection with a minimum bandwidth of 10 Mbps. The dual-slot STC contains two 10 Mbps Ethernet ports. The single-slot STC contains two 100 Mbps Ethernet ports. FC-capable cards require a 100 Mbps/full duplex configuration for copying traffic to the ESP. If the IP port on the FC-Capable card is not able to auto-negotiate to this speed/duplex configuration, then the traffic will not be copied from this port to the ESP.
Refer to Hardware User Reference for more information about the E5-MCAP cards and STCs.
The n+1 STC configuration requires that a minimum of two STCs must be provisioned in the database. If single-slot STCs are being provisioned in the database, a minimum of two single-slot STCs must be provisioned.
Table 6-1 shows the signaling links on these cards can be monitored by this feature.
Table 6-1 Monitored Card Types
| Card Application (APPL Value Used by the ent-card Command | Card Type (TYPE Value Used by the ent-card Command) | Card Name |
|---|---|---|
| SS7ANSI | LIMDS0 | E5-E1T1, E5-E1T1-B card |
| SS7ANSI, CCS7ITU | LIME1 | E5-E1T1, E5-E1T1-B card |
| LIMT1 | E5-E1T1, E5-E1T1-B card | |
| ATMANSI | LIMATM | E5-ATM , E5-ATM-B |
| ATMITU | LIME1ATM | E5-ATM, E5-ATM-B |
| SS7IPGW | DCM | E5-ENET, E5-ENET-B card |
| IPGWI | DCM | E5-ENET, E5-ENET-B card |
| IPSG | ENET | E5-ENET, E5-ENET-B card |
|
Notes: Only signaling links assigned to M2PA associations can be monitored on the cards running the IPLIM and IPLIMI applications. This can be verified by entering the Signaling links assigned to M3UA associations can be monitored on the cards running the SS7IPGW and IPGWI applications. This can be verified by entering the Monitoring can be performed on E5-E1T1 cards, E5-E1T1-B cards, E5-ENET cards, and E5-ENET-B cards using only the IMF. Monitoring can be performed on channelized E1 signaling links and unchannelized E1 signaling links (assigned to the LIME1 card type). A channelized E1 signaling link is a signaling link that is assigned to a channelized E1 port, shown by the entry |
||
The signaling links assigned to the cards running either the ss7ansi or ccs7itu applications are low-speed signaling links transmitting at either 56 kbps or 64 kbps. Signaling links assigned to the atmansi and atmitu applications are high-speed signaling links transmitting at 1.544 Mbps (atmansi) or 2.048 Mbps (atmitu). Signaling links assigned to the iplim, iplimi, ss7ipgw, ipsg, and ipgwi applications are IP signaling links.
Because the performance of a single-slot STC is higher than a dual-slot STC, a dual-slot STC cannot replace a single-slot STC. If a single-slot STC replaces a dual-slot STC, and it is the only single-slot STC in the EAGLE, another single-slot STC must be added to the EAGLE. To add the additional single-slot STC, go to Adding a Signaling Transport Card (STC).
In order to perform the necessary IP routing within the EAGLE switch, a private virtual network (PVN) is incorporated; the PVN represents the internal IP addressing scheme for every STC within the EAGLE switch. Each card has an auto-assigned, default, Class B private IP address (for example, 172.28.60.16).
Note:
The EAGLE uses a default value of 172.20.48.0 for the PVN address. You may change the default value by specifying a new network portion of an IP address and a network mask; the host portion is auto-configured. The EAGLE requires use of the lower 8 bits of address space for auto-configuration of internal networking schemes. The entered mask value may be up to 255.255.255.0Network Considerations
There are three networks used to connect the EAGLE to the ESP/IMF subsystem (see Figure 6-3 :
- The EAGLE containing the STCs and FC-capable cards (if the Fast Copy function is being used).
- The two Ethernet switches
- The ESP/IMF servers
The monitored information is sent from the EAGLE to the ESP/IMF servers through the Ethernet switches, then forwarded to the Sentinel/IMF by the isolation routers. Each router will have one Ethernet port designated as the physical demarcation point between the customer network and the ESP/IMF subsystem.
IP Address Provisioning
The ESP/IMF subsystem requires IP addresses for these items:
- ESP/IMF external network:
- Three IP addresses on the customer network for the ESP/IMF isolation routers, one IP address for HSRP, one IP address for each router (two total)
- One netmask
- One IP address for the default router.
- ESP/IMF internal network – Contiguous IP block routed within their network (last octet range 1-67 for 17 servers). The Sentinel/IMF considers each ESP/IMF server a separate processing element, therefore each ESP/IMF server needs its own IP address.
- Routes to their network to route to the VIP network already defined within ESP/IMF subsystem.
Caution:
These IP addresses can be changed, as well as the PVNIP address in the EAGLE, contact the Customer Care Center (refer to unresolvable-reference.html#GUID-3FA61F5C-C612-4DBC-B090-8EF65AD958FD for the contact information) before changing these IP addresses.
Route Configuration
No explicit routing tables are provisioned in the ESP/IMF subsystem. Use of the single customer provided default router address is assumed for outgoing traffic. All incoming traffic will use the HSRP address provided by the isolation routers.
Enabling the Time Slot Counter Synchronization (TSCSYNC) and EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support (E5IS) Features
The EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature requires that the Time Slot Counter Synchronization (TSCSYNC) and EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support (E5IS) features are enabled with the chg-feat command using the tscsync and e5is parameters. This procedure is used to enable these features.
Note:
Once the Time Slot Counter Synchronization and EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support features are turned on with thechg-feat command, they cannot be turned off.
The Time Slot Counter Synchronization and EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support features must be purchased before turning on these features. If you are not sure whether you have purchased the Time Slot Counter Synchronization or EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support features, contact your Oracle Sales Representative or Account Representative.
Figure 6-7 Enabling the Time Slot Counter Synchronization (TSCSYNC) and EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support (E5IS) Features
Configuring the EISCOPY Option for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
This procedure is used to configure the
EISCOPY option for the
EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support
feature using the
chg-eisopts command with the
eiscopy parameter.
The
chg-eisopts command can also be used
to configure the
FCMODE option. Perform
Configuring the FCMODE Option for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
to configure the
FCMODE option.
The
eiscopy parameter contains two values,
on and off. The
eiscopy=on parameter enables the
EISCOPY function for the EAGLE 5 Integrated
Monitoring Support feature. The
eiscopy=off parameter turns off the
EISCOPY function for the EAGLE 5 Integrated
Monitoring Support feature. The
EISCOPY function allows the EAGLE to copy
MSUs to the
ESP/IMF subsystem. The default value for the
eiscopy parameter is
off.
To change the
EISCOPY option, the EAGLE 5 Integrated
Monitoring Support feature (E5IS) must be
turned on.
Figure 6-8 Configuring the EISCOPY Option for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
Configuring the FCMODE Option for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
This procedure is used to configure the FCMODE option
for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature with the
chg-eisopts command
and these parameters.
fcmode parameter specifies a
system-wide control to enable or disable monitoring on FC-capable cards. A card
that can run the Fast Copy interface is referred to as an FC-capable card.
E5-ENET-B
and SLIC cards running the IPSG and IPGHC GPLs
are the supported FC-capable cards. The
fcmode parameter has three values.
off- Monitoring is not performed on FC-capable cards.stc- STC monitoring is performed on FC-capable cardsfcopy- FC monitoring is performed on FC-capable cards
The system default value for the
fcmode parameter is
off.
fcgpl parameter specifies the type of
cards that the monitoring specified by the
FCMODE value will be applied to. The
fcgpl parameter has three values.
ipsg- monitoring is performed on E5-ENET-B and SLIC cards running the IPSG GPL (IPSG cards).ipghc- monitoring is performed on E5-ENET-B and SLIC cards running the IPGHC GPL.all- monitoring is performed on E5-ENET-B and SLIC cards running the IPSG and IPGHC GPLs.
The system default value for the
fcgpl parameter is
all.
To change the
FCMODE
values, the
EISCOPY value, shown
in the
rtrv-eisopts output, must be
on. See the
Configuring the EISCOPY Option for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
procedure for information about changing the
EISCOPY value.
Figure 6-9 Configuring the FCMODE Option for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
Sheet 1 of 3
Sheet 2 of 3
Sheet 3 of 3
Configuring the IP Addresses for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
This procedure is used to configure the IP addresses and the PVNMASK value used for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature using the chg-netopts command with the pvn, pvnmask, fcna, and fcnb parameters.
The pvn and pvnmask parameters define the network used by the STCs to transmit copied MSUs between the EAGLE and the ESP/IMF subsystem. The IP communications link to the ESP/IMF subsystem is dynamically configured by the Sentinel/IMF. The LIMs are assigned Class B private network IP addresses (for example, 172.28.60.0), creating a PVN). The IP message origination address is the address of the LIM. The IP message destination address is that of the VIP (virtual IP address) contained within the ESP/IMF server.
The EAGLE uses a default value of 172.20.48.0 for the PVN address (pvn parameter). The default value may be changed by specifying a new network portion of an IP address and a network mask. The host portion of these PVN addresses are configured automatically. The default value for the pvnmask parameter is 255.255.252.0.
To change the network portion of the PVN address and the PVN submask used by the PVN addresses within the EAGLE, enter the chg-netopts command with the pvn and pvnmask parameters. The EISCOPY function must be disabled (eiscopy=off) in order to make these changes. For the EISCOPY value to be OFF, the FCMODE values for all the GPLs must be OFF. If the FCMODE values for all the GPLs are OFF, the FCNA and FCNB values can also be changed.
The fcna and fcnb parameters define, along with the FCNAMASK and FCNBMASK values shown in the rtrv-netopts output, the network used by the Fast Copy networks A and B. The IP address is assigned to the FC-capable cards dynamically based on the fcna and fcnb parameter values. A card that can run the Fast Copy interface is referred to as an FC-capable card. Currently, cards running the IPGHC and IPSG GPLs are the only supported FC-capable cards. The default value for the fcna parameter is 172.21.48.0. The default value for the fcnb parameter is 172.22.48.0. The FCNAMASK and FCNBMASK values are 255.255.254.0 and cannot be changed. To change the fcna and fcnb parameter values, the FCMODE values for all the GPLs shown in the rtrv-eisopts output must be either off or stc. The fcna and fcnb parameter values can be a Class A, B, or C IP address. The third segment of the IP address can only contain an even number. The value of the fourth segment of the IP address must be 0 (zero).
The subnet address that results from the PVN and PVNMASK, FCNA and FCNAMASK, or FCNB and FCNBMASK values cannot be the same as the subnet address resulting from the ipaddr and submask parameter values of the chg-ip-lnk command, or the dest and submask parameter values of the ent-ip-rte command.
This interaction applies to the PVN and PVNMASK values only if the ipaddr or dest parameter values are Class B IP addresses.
The ipaddr, dest, and submask parameter values can be verified by entering the rtrv-ip-lnk and rtrv-ip-rte commands. Choose pvn and pvnmask, fcna, or fcnb parameter values whose resulting subnet address is not be the same as the subnet address resulting from the ipaddr and submask parameter values of the chg-ip-lnk command, or the dest and submask parameter values of the ent-ip-rte command.
Caution:
When configuring the IP addresses, make sure that the IP addresses do not conflict with the DHCP IP addresses that are leased to the STC cards. Any conflicting IP addresses can adversely affect the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature.To change the IP addresses and the PVNMASK value, the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature (E5IS) must be turned on.
Figure 6-10 Configuring the IP Addresses for the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support Feature
Sheet 1 of 2
Sheet 2 of 2
Adding a Signaling Transport Card (STC)
This procedure is used to add an STC (Signaling Transport Card) to the database using the ent-card command. The STC provides an interface between the EAGLE and the ESP (EAGLE Integrated Monitoring Support feature). The STC allows the ESP subsystem to monitor the EAGLE’s signaling links without additional intrusive cabling.
The ent-card command uses these parameters.
:loc – The location of the card being added to the database.
:type – The type of card being added to the database. For this procedure, the value of this parameter is stc.
:appl – The application software that is assigned to the card. For this procedure, the value of this parameter is eroute.
:force – Allow the LIM to be added to the database even if there are not enough service modules to support the number of LIMs in the EAGLE. This parameter is obsolete and is no longer used.
The STC can be either a single-slot STC, a dual-slot STC, or an E5-STC card as shown in Table 6-2.
Table 6-2 STC Part Numbers
| Card Type | Card Name (as shown on the card Label) | Part Number |
|---|---|---|
| E5-STC | E5-ENET | 870-2212-02 |
| E5-ENET-B | 870-2971-XX |
The dual-slot STC can be inserted only in card slots 01, 03, 05, 07, 11, 13, 15, and 17 of the extension shelf. The dual-slot STC can be inserted in the control shelf, but only in slots 01, 03, 05, 07, and 11. The dual-slot STC occupies two card slots, so the even numbered card slot must be empty and not provisioned in the database, as shown in Table 6-3. The dual-slot STC is connected to the network through the odd numbered card slot connector.
Table 6-3 Dual-Slot STC Locations
| Location of the STC | Empty Card Location | Location of the STC | Empty Card Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slot 01 | Slot 02 | Slot 11 | Slot 12 |
| Slot 03 | Slot 04 | Slot 13 | Slot 14 |
| Slot 05 | Slot 06 | Slot 15 | Slot 16 |
| Slot 07 | Slot 08 | Slot 17 | Slot 18 |
The single-slot STC can be inserted into any card slot, except an even numbered card slot adjacent to a dual-slot card, shown in Table 6-3, slots 9 and 10 in each shelf, and slots 1113 through 1118.
The shelf to which the card is to be added, must already be in the database. This can be verified with the rtrv-shlf command. If the shelf is not in the database, see the “Adding a Shelf” procedure in Database Administration - System Management User's Guide.
In order to enable the EISCOPY option, with the chg-eisopts command, and to comply with the n+1 STC configuration requirement, a minimum of two STCs must be provisioned in the database. A minimum of two STCs must be provisioned.
The number of SS7 signaling links that can be monitored by an STC varies depending the following criteria:
- Whether the STC is a dual-slot STC or single-slot STC
- The type of signaling link (defined by the application running on the card the signaling link is assigned to)
- The amount of traffic and the size of the MSUs being handled by the EAGLE
Note:
Perform the “Changing the High-Capacity Card Temperature Alarm Thresholds” procedure in Database Administration -SS7 User's Guide to verify the temperature threshold settings for the E5-STC card.STC Provisioning
The following rules apply to provisioning STCs.
- A minimum of two STCs must be provisioned in the EAGLE.
- The maximum number of STCs that can be provisioned in the EAGLE is 32.
- Only single-slot STCs can be installed and provisioned in the EAGLE if IP signaling links are being monitored. Dual-slot STCs cannot be installed or provisioned.
- HIPR2 cards must be installed in the shelf that contains E5-STCs.
- For shelves containing HIPR2 cards in card slots 9 and 10, these rules apply to provisioning STCs.
- STCs should be provisioned in the same shelf that contains the cards being monitored.
- More than three STCs can be provisioned in the shelf depending on the number of empty cards slots the shelf has.
- To monitor signaling links on these cards, HIPR2 cards must be installed in slots 9 and 10 of the shelf that contains these cards.
- E5-ENET cards that contain IP signaling links.
- E5-E1T1 cards that contain E1 or T1 signaling links.
- If the E5-STC card is an E5-ENET-B card, the FAN feature must be turned on and fans must be installed on the shelf that contains the E5-ENET-B card. Enter the
rtrv-featcommand to verify whether or not the FAN feature is turned on. Perform the procedures in Installation Guide to install fans on the shelf that contains the E5-ENET-B card if fans must be installed. The MFC (message flow control) option must be on. Enter thertrv-stpoptscommand to verify whether or not the MFC option is on. Perform the Configuring the MFC Option procedure to turn the MFC option on, if required.
Note:
Contact your Sales Representative or Account Representative to determine the number of STCs that must be provisioned in your EAGLE, and to determine where in the EAGLE these STC cards must provisioned before performing this procedure.The examples in this procedure are used to add an STC card in these card locations: 1303, 2101, and 2102.
Figure 6-11 Adding a Signaling Transport Card (STC)
Sheet 1 of 3
Sheet 2 of 3
Sheet 3 of 3
Removing a Signaling Transport Card (STC)
This procedure is used to remove an STC from the database using the dlt-card command.
Caution:
If the STC is the last STC in service, removing this card from the database will disable the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature.Caution:
If removing the STC reduces the quantity of STCs in the EAGLE below number of STCs required by the ESP subsystem, the performance of the EAGLE 5 Integrated Monitoring Support feature will be degraded.The examples in this procedure are used to remove the STC in card location 1303.
Canceling the REPT-STAT-CARD Command
Because the rept-stat-card command used in this procedure can output information for a long period of time, the rept-stat-card command can be canceled and the output to the terminal stopped. There are three ways that the rept-stat-card command can be canceled.
- Press the F9 function key on the keyboard at the terminal where the
rept-stat-cardcommand was entered. - Enter the
canc-cmdwithout thetrmparameter at the terminal where therept-stat-cardcommand was entered. - Enter the
canc-cmd:trm=<xx>, where<xx>is the terminal where therept-stat-cardcommand was entered, from another terminal other that the terminal where therept-stat-cardcommand was entered. To enter thecanc-cmd:trm=<xx>command, the terminal must allow Security Administration commands to be entered from it and the user must be allowed to enter Security Administration commands. The terminal’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-secu-trmcommand. The user’s permissions can be verified with thertrv-userorrtrv-secu-usercommands.
For more information about the canc-cmd command, go to Commands User's Guide.
Figure 6-12 Removing a Signaling Transport Card (STC)