4 OCNWDAF Installation
This chapter describes how to install Oracle Communications Network Data Analytics Function (OCNWDAF) on Oracle Communications Cloud Native Core, Cloud Native Environment (CNE).
The steps are divided into two categories:
You are recommended to follow the steps in the given sequence for preparing and installing OCNWDAF.
4.1 Preinstallation
To install OCNWDAF, perform the steps described in this section.
Note:
The kubectl commands might vary based on the platform used for deploying CNC Policy. Users are recommended to replacekubectl with environment-specific command line tool to configure kubernetes resources through kube-api server. The instructions provided in this document are as per the CNE’s version of kube-api server.
4.1.1 Creating Service Account, Role, and RoleBinding
This section describes the procedure to create service account, role, and rolebinding.
Important:
The steps described in this section are optional and you can skip them in any of the following scenarios:- If service accounts are created automatically at the time of OCNWDAF deployment.
- If the global service account with the associated role and rolebindings is already configured or if you are using any internal procedure to create service accounts.
If a service account with necessary rolebinding is already available, then update the
ocnwdaf/values.yamlwith the account details before initiating the installation procedure. In case of incorrect service account details, the installation fails.
Create Service Account
To create the global service account:
- Create an OCNWDAF service account resource file:
vi <ocnwdaf resource file>Example:
vi ocnwdaf-sampleserviceaccount-template.yaml - Update the resource file with the release specific information:
Note:
Update <helm-release> and <namespace> with its respective OCNWDAF namespace and OCNWDAF Helm release name.apiVersion: v1 kind: ServiceAccount metadata: name: <helm-release>-serviceaccount namespace: <namespace>
<helm-release> is the Helm deployment name.
<namespace> is the name of the Kubernetes namespace of OCNWDAF. All the microservices are deployed in this Kubernetes namespace.
Define Permissions using Role
- Create an OCNWDAF roles resource file:
vi <ocnwdaf sample role file>Example:
vi ocnwdaf-samplerole-template.yaml - Update the resource file with the role specific information:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: ClusterRole metadata: name: <helm-release>-role rules: - apiGroups: [""] resources: - pods - services - configmaps verbs: ["get", "list", "watch"]
Create Rolebinding
- Create an OCNWDAF rolebinding resource file:
vi <ocnwdaf sample rolebinding file>Example:
vi ocnwdaf-sample-rolebinding-template.yaml - Update the resource file with the role binding specific information:
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1 kind: RoleBinding metadata: name: <helm-release>-rolebinding namespace: <namespace> roleRef: apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io kind: Role name: <helm-release>-role subjects: - kind: ServiceAccount name: <helm-release>-serviceaccount namespace: <namespace>
Create Resources
kubectl -n <namespace> create -f <service account resource file>;kubectl -n <namespace> create -f <roles resource file>;kubectl -n <namespace> create -f <rolebinding resource file>Note:
Once the global service account is added, users must addglobal.ServiceAccountName in the ocnwdaf/values.yaml file; otherwise, installation may fail as a result of creating and deleting custom resource definitions (CRD).
4.1.2 Configuring Database, Creating Users, and Granting Permissions
This section explains how a database administrator can create the databases, users, and grant permissions to the users for OCNWDAF.
Perform the following steps to create the OCNWDAF MySQL database and grant permissions to the OCNWDAF user for database operations:
- Unzip the package nwdaf-installer.zip
mkdir nwdaf-installer unzip nwdaf-installer.zip -d nwdaf-installer/ - Log in to the server or machine with permission to access the SQL nodes of NDB cluster.
- Connect to the SQL node of the NDB cluster or connect to the cnDBTier.
- Run the following command to connect to the cnDBTier:
kubectl -n <cndbtier_namespace> exec -it <cndbtier_sql_pod_name> -c <cndbtier_sql_container_name> -- bash - Run the following command to log in to the MySQL prompt as a user with root permissions:
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot -p - Copy the file content from nwdaf-release-package/installer/nwdaf-installer/sql/ocn-nwdaf-db-script-23.2.0.0.0.sql and run it in the current MySQL instance.
4.1.3 Verifying and Creating OCNWDAF Namespace
This section explains how to verify or create a new namespace in the system.
To verify if the required namespace already exists in the system, run the following command:
$ kubectl get namespacesIn the output of the above command, check if the required namespace is available. If the namespace is not available, create the namespace using the following command:
$ kubectl create namespace <required namespace>Example:
$ kubectl create namespace oc-nwdafNaming Convention for Namespaces
While choosing the name of the namespace where you wish to deploy OCNWDAF, make sure the namespace:
- starts and ends with an alphanumeric character
- contains 63 characters or less
- contains only alphanumeric characters or '-'
Note:
It is recommended to avoid using prefixkube- when creating namespace as this prefix
is reserved for Kubernetes system namespaces.
4.1.4 Verifying Installer
A folder named installer is obtained on decompressing the release package, copy this folder to the Kubernetes bastion home. To verify if the installer has all the valid files, run the following commands:
[ -d "./nwdaf-release-package/helmChart" ] && echo "helmChart exist"
[ -d "./nwdaf-release-package/nwdaf-ats" ] && echo "nwdaf-ats exist"
[ -d "./nwdaf-release-package/nwdaf-pre-installer" ] && echo "nwdaf-pre-installer exist"
[ -d "./nwdaf-release-package/nwdaf-pre-installer/scripts/prepare-dependencies.sh" ] && echo "prepare-depencies.sh script exist"
[ -d "./nwdaf-release-package/nwdaf-pre-installer/etc/nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-prod-properties" ] && echo "nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-prod-properties exist"
[ -d "./nwdaf-release-package/nwdaf-pre-installer/etc/kafka-topics.txt" ] && echo "kafka-topics.txt exist"Sample output:
helmChart exist
nwdaf-ats exist
nwdaf-pre-installer exist
prepare-depencies.sh script exist
nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-prod-properties exist
kafka-topics.txt exist4.2 Installation Tasks
This section describes the tasks that the user must follow for installing OCNWDAF.
4.2.1 Update OCNWDAF Preinstaller Files
Note:
This is an optional procedure.To update the preinstaller file, perform the following steps:
- Make the required changes in config files present in the extracted nwdaf-pre-installer directory and create a fresh tar file by running the following command:
tar -zcvf nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gz nwdaf-pre-installer/ -
Replace the existing tar file in the /helmChart directory with the new tar file.
4.2.2 Setup Encrypted Credentials
To set up encrypted credentials, perform the following steps:
- To update the secret values, replace the existing values with updated values after encoding the values using Base64 encoding method. Listed below are the secrets files:
- ocnwdaf-hooks-secret.yaml under /helmchart/templates/ directory
- hook-secrets.yaml under /helmchart/charts/nrf-client/templates/ directory
- To read the secret values, decode the present values using Base64 decoding method.
4.2.3 Configure Database Flag
Note:
This is an optional step. Perform this step based on customer requirement.Update the dbConfigStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmchart with any of the following values (the default value is alldb):
- alldb: This is the default value of the flag. Set this flag to create a fresh database by removing the existing database. If this flag is present, proceed with the installation of the services.
- nodb: This flag disables the dbCreation hooks for the installation of the Helm chart. Set this flag to install the services if the database is present without deleting any data.
- nwdafdb: This flag is used to create or reinstall the database only for NWDAF services. Set this flag to run the dbCreation hook only for OCNWDAF services (standard installation is followed for the remaining services).
- cap4cdb: This flag is used to create or reinstall the database only for CAP4C services. Set this flag to run the dbCreation hook only for CAP4C services (standard installation is followed for the remaining services).
Note:
If there is a requirement to install only OCNWDAF or only CAP4C services, set the dbConfigStatus flag to create the required DB and the charts that are not needed can be set to 'enabled: false' in the "values. yaml" under "/helm chart".
For example, if a user wants to install CAP4C services only with its database, then set the dbConfigStatus flag to 'cap4cdb', and set the value of all the NWDAF FE services that are not required to 'enabled: false' and proceed with the installation procedure.
4.2.4 Configuring Service Mesh
Note:
This configuration step is optional and only applies when a service mesh is available.- Service discovery
- Routing and traffic configuration
- Encryption and authentication/authorization
- Metrics and monitoring
Note:
To configure OCNWDAF to support a service mesh, the service mesh must be available in the cluster in which OCNWDAF is installed.Enable or Disable Service Mesh
To enable or disable service mesh support, update the Istio sidecar section in the values.yaml file.
For example:
##########################
#ISTIO SIDECAR INJECTION #
##########################
istio:
## NOTE: The label of the namespace will take precedence over the injection field that is set here. If mesh is to be disabled, make sure the namespace has no istio-injection label or set to disabled if present
injection: false
readinessCheck: &readinessCheck falseFor more information, see Global Parameters.
Update the following NRF client parameters:
istioSidecarQuitUrlistioSidecarReadyUrlserviceMeshCheck
For more information, see NRF Client Parameters.
Update the following Ingress Gateway Parameters in the values.yaml file:
serviceMeshCheck
Table 4-1 Ingress Gateway Parameter
| Parameter | Description | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| serviceMeshCheck | This is a mandatory parameter. This flag must be set to true if a Service Mesh is present in the environment where OCNWDAF is deployed. If this parameter is set to true load balancing is handled by the Service Mesh.
|
Range: True or False
Default value: False Applicable to: OCNWDAF |
Update the following Egress Gateway parameters in the values.yaml file:
serviceMeshCheck
Table 4-2 Egress Gateway Parameter
| Parameter | Description | Detail |
|---|---|---|
| serviceMeshCheck | This is a mandatory parameter. This flag must be set to true if a Service Mesh is present in the environment where OCNWDAF is deployed. If this parameter is set to true load balancing is handled by the Service Mesh.
|
Range: True or False
Default value: False Applicable to: OCNWDAF |
After Service Mesh is enabled and deployed, the proxy containers run along with the OCNWDAF application pods.
Note:
The gateways and other services inside the Service Mesh are not accessible from outside the Service Mesh. In order to use OCNWDAF with a Service Mesh, ensure that the dependencies (such as, cnDBTier or analytics consumers) are deployed within the Service Mesh.
4.2.5 Configuring Routing Rules in Ingress Gateway
The routing rules are configured in the Ingress Gateway values.yaml file. Once the routing rules are configured, the Ingress Gateway reroutes the incoming traffic to the microservices based on the configured routing rules.
Ingress Gateway values.yaml file:
- id: prodcon
uri: http://10.123.158.150:31457
path: /relinquishOwnerShip
order: 1
#Below field is used to provide an option to enable/disable route level xfccHeaderValidation, it will override global configuration for xfccHeaderValidation.enabled
metadata:
# requestTimeout is used to set timeout at route level. Value should be in milliseconds.
requestTimeout: 4000
requiredTime: 3000
xfccHeaderValidation:
validationEnabled: false
oauthValidator:
enabled: false
svcName: "prodcon-1"
configurableErrorCodes:
enabled: false
errorScenarios:
- exceptionType: "NOT_FOUND_EXCEPTION"
errorProfileName: "ERR_NOT_FOUND"
- exceptionType: "UNKNOWN_HOST_EXCEPTION"
errorProfileName: "ERR_UNKNOWN_HOST"
- exceptionType: "CONNECT_EXCEPTION"
errorProfileName: "ERR_400"
- exceptionType: "XFCC_HEADER_NOT_PRESENT_OR_EMPTY"
errorProfileName: "ERR_1300"
- exceptionType: "GLOBAL_RATELIMIT"
errorProfileName: "ERR_RATE_LIMIT"
# Server header configuration if defined at Route level(irrespective of being enabled/disabled) will take precedence over the Global conf. Uncomment only if needed at Route level.
#serverHeaderDetails:
# enabled: false
# errorCodeSeriesId: E2 # If not defined here, value at Global level will be used as fallback. Value need to be one among "errorCodeSeriesList" resource defined later.
filters:
controlledShutdownFilter:
applicableShutdownStates:
- "PARTIAL_SHUTDOWN"
- "COMPLETE_SHUTDOWN"
unsupportedOperations:
- "GET"
- "PUT"
#Below are Request Custom Headers
customReqHeaderEntryFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-entry-headeReq-1
defaultVal: script:shm-02,x-exit-new-req
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-entry-current-user
- headerName: x-entry-current-user
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: test
customReqHeaderExitFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeReq-1
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-current-user
- headerName: x-exit-current-user
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: sbi-timer-feature
- methods:
- GET
- POST
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeReq-3
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-new-req
override: false
- headerName: x-exit-headeReq-4
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headeReq-1
override: false
- methods:
- DELETE
- GET
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headerReq-5
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerReq-new
override: false
- headerName: x-exit-headerReq-6
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerReq-temp
override: false
# Below are Response Custom Headers
customResHeaderEntryFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-entry-headerRes-1
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-entry-headeReq-1
override: false
- headerName: sbi-timer-feature-Res
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-new-req
customResHeaderExitFilter:
headers:
- methods:
- ALL
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headerRes-1
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerReq-1
override: false
- headerName: sbi-timer-feature
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: x-exit-headerRes-1
- methods:
- GET
- PUT
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-3
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: x-exit-SourceRes-a
override: true
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-4
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingReq
sourceHeader: x-exit-SourceRes-b
override: false
- methods:
- DELETE
headersList:
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-5
defaultVal: abc
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: ""
override: false
- headerName: x-exit-headeRes-6
defaultVal: 123
source: incomingRes
sourceHeader: ""
override: false
#Below field is used for blacklisting(removing) a request header at route level.
removeRequestHeader:
- name: myheader1
- name: myheader3
#Below field is used for blacklisting(removing) a response header at route level.
removeResponseHeader:
- name: myresponseheader1
- name: myresponseheader3id: prodconuri: http://10.123.158.150:31457path: /relinquishOwnerShip
For more information on the customizable Ingress Gateway parameters, see Ingress Gateway Parameters.
Note:
It is recommended to retain the default values of other routesConfig parameters.4.2.6 Install Ingress and Egress Gateways
helm install <chart-name> <chart-path> -n <namespace>After a successful installation, both the Ingress and Egress Gateway pods must be running in your namespace.
Sample output:
Figure 4-1 Sample Output

4.2.7 Installing OCNWDAF Package
To install the OCNWDAF package, perform the following steps:
- Update the values in the
<replace here>tag in the values.yaml file under the <release directory>/ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/ directory according to the setup.... cluster: name: &clusterName '<replace here>' namespace: &nameSpace '<replace here>' dbConfig: MYSQL_HOST: &mySQLHost '<replace here>' MYSQL_PORT: &mySQLPort '<replace here>' MYSQL_ENGINE: &mySQLEngine '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_NAMESPACE: &cndbNameSpace '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_SQL_POD_NAME: &cndbSQLPodName '<replace here>' ... - Update the values in the
<replace here>tag in the values.yaml file under the <release directory>/ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/charts/nrf-client directory according to the setup.... # Mysql Host envMysqlHost: &mySqlHostRef '<replace here>' # <enter here> envMysqlSecondaryHost: '' # Mysql Port envMysqlPort: &mySqlPortRef '<replace here>' # <enter here> envMysqlSecondaryPort: '' dbEngine: &mySqlEngine '<replace here>' # <enter here> ... - Set the Subcharts flag in the centralized values.yaml file under the <release directory>/ocn-nwdaf-helmChart/helmChart/ directory. The allowed values are true or false. The services with the flag set to "false" are not deployed.
- Optionally, update any other parameter in centralized or subchart values.yaml files.
For example, Prometheus monitoring details or hooks environment variables in the centralized values.yaml under the /helmchart directory. Any microservice specific values like image name or tag, environment variables in microservices subchart values.yaml file.
The following list is the default variables used to configure OCNWDAF, these variables are present in the centralized values.yaml files and in the secrets:
- MYSQL_HOST
- MYSQL_PORT
- KAFKA_BROKERS
- REDIS_HOST
- REDIS_PORT
- CAP4C_KAFKA_INGESTOR_DB
- CAP4C_KAFKA_INGESTOR_DB_USER
- CAP4C_KAFKA_INGESTOR_DB_PASSWORD
- CAP4C_MODEL_CONTROLLER_DB
- CAP4C_MODEL_CONTROLLER_DB_USER
- CAP4C_MODEL_CONTROLLER_DB_PASSWORD
- CAP4C_MODEL_EXECUTOR_DB_USER
- CAP4C_MODEL_EXECUTOR_DB_PASSWORD
- CAP4C_STREAM_ANALYTICS_DB
- NWDAF_CAP4C_REPORTING_SERVICE_USER
- NWDAF_CAP4C_REPORTING_SERVICE_PASSWORD
- NWDAF_CAP4C_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_DB
- NWDAF_CAP4C_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_DB_USER
- NWDAF_CAP4C_SCHEDULER_SERVICE_DB_PASSWORD
- NWDAF_CONFIGURATION_HOST
- NWDAF_USER
- NWDAF_DB_PASSWORD
- Install OCNWDAF, run the following Helm installation command:
helm install <installation name> <path to the chart directory> -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout <timeout>hFor example:
helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n ocnwdaf-ns --timeout 5hNote:
The parameter--timeoutis optional. It is recommended to use this parameter to avoid any installation failure due to slow internet or CPU speeds. Use appropriate value for this parameter depending on the speed of image pull from the nodes of the Bastion host. The recommended timeout value is 30 minutes.Mandatory Installation Instruction
Note:
Some services are release name dependent, use "nwdaf" for <installation name> in the Helm install command.Sample terminal screen once the installation starts:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ]$ helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n nwdaf-test --timeout 30m W0404 04:44:48.456730 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:44:48.459573 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:51:41.957767 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscalerSample output of resources in the namespace:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ~]$ kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACE NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE pod/ocn-nwdaf-db-creation-hook-jj9mx 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 15s NAME COMPLETIONS DURATION AGE job.batch/ocn-nwdaf-db-creation-hook 0/1 15s 15sSample output after installation is complete:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-1 ]$ helm install nwdaf helmChart/ -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout 30m W0404 04:44:48.456730 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:44:48.459573 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:51:41.957767 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler W0404 04:51:41.963127 3847781 warnings.go:70] autoscaling/v2beta2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler is deprecated in v1.23+, unavain v1.26+; use autoscaling/v2 HorizontalPodAutoscaler NAME: nwdaf LAST DEPLOYED: Tue Apr 4 04:44:47 2023 NAMESPACE: nwdaf-test STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: None - Run the following command to verify if all the dependencies are in Running state (if any pod is not in Running state wait for a maximum of five restarts):
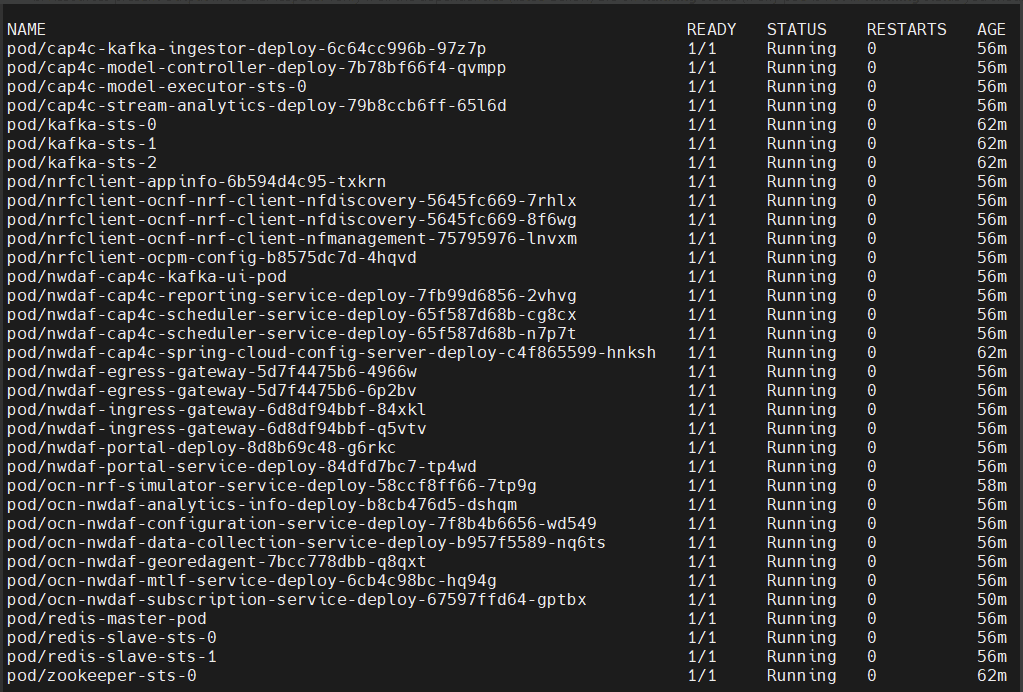
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output:
Figure 4-2 Sample Output
OCNWDAF Microservices Port Mapping
Table 4-3 Port Mapping
| Service | Port Type | IP Type | Network Type | Service Port | Container Port |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ocn-nwdaf-analytics | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-egress-gateway | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-ingress-gateway | External | NodePort | External/ K8s | 80/TCP | 8081/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-configuration-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-data-collection | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-mtlf | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-subscription | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-analytics-info | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-configuration | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| ocn-nwdaf-georedagent | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 9181/TCP | 9181/TCP |
| cap4c-kafka-ingestor | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-model-controller | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| cap4c-model-executor | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 9092/TCP | 9092/TCP |
| cap4c-stream-analytics | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
| nwdaf-portal | External | NodePort | External / K8s | 80/TCP | |
| nwdaf-portal-service | Internal | ClusterIP | Internal / K8s | 8080/TCP | 8080/TCP |
Note:
For NodePort services the Service Port will be allocated by the Kubernetes.Installation of Simulator Chart
Follow the procedure below to install the simulator chart:
- Update the values in the
<replace here>tag present in values.yaml under/simulator-helmchart/based on the setup:... cluster: name: &clusterName '<replace here>' namespace: &nameSpace '<replace here>' dbConfig: MYSQL_HOST: &mySQLHost '<replace here>' MYSQL_PORT: &mySQLPort '<replace here>' MYSQL_ENGINE: &mySQLEngine '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_NAMESPACE: &cndbNameSpace '<replace here>' CNDBTIER_SQL_POD_NAME: &cndbSQLPodName '<replace here>' ... - Set the Subcharts flag in the centralized values.yaml file under the /simulator-helmchart directory. The allowed values are true or false. The services with the flag set to false are not deployed.
- Optionally, update any other parameter in centralized or subchart values.yaml files.
For example, Prometheus monitoring details or hooks environment variables in the centralized values.yaml under the /simulator-helmchart directory. Any microservice specific values like image name or tag, environment variables in microservices subchart values.yaml file.
- Install simulators, run the following Helm installation command:
helm install <installation name> <path to the chart directory> -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout <timeout>hFor example:
helm install simulators simulator-helmchart/ -n ocnwdaf-ns --timeout 30mNote:
The parameter--timeoutis optional. It is recommended to use this parameter to avoid any installation failure due to slow internet or CPU speeds. Use appropriate value for this parameter depending on the speed of image pull from the nodes of the Bastion host. The recommended timeout value is 30 minutes.Sample terminal screen once the installation starts:
[cloud-user@occne224-cluster-bastion-2 ocn-nwdaf-helmChart]$ helm install simulators simulator-helmChart/ -n ttest --timeout 30m W0511 10:38:19.670067 2848359 warnings.go:70] spec.template.spec.containers[0].env[61].name: duplicate name "SPRING_KAFKA_CONSUMER_PROPERTIES_MAX_POLL_INTERVAL_MS" NAME: simulators LAST DEPLOYED: Thu May 11 10:38:12 2023 NAMESPACE: ttest STATUS: deployed REVISION: 1 TEST SUITE: None - Run the following command to verify if all the dependencies are in Running state (if any pod is not in Running state wait for a maximum of five restarts):
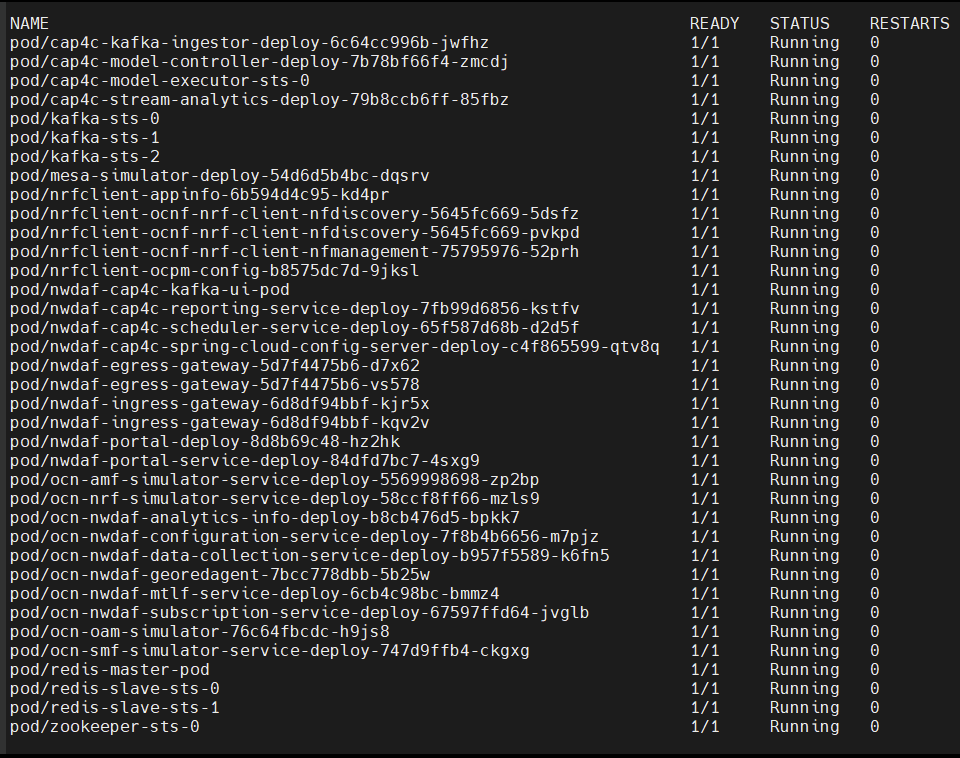
kubectl get all -n $K8_NAMESPACESample output:
Figure 4-3 Sample Output
- The following services with port mapping are deployed:
Table 4-4 Port Mapping
Service Port Type IP Type Network Type Service Port Container Port ocn-nrf-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP ocn-amf-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP mesa-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP ocn-smf-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP ocn-oam-simulator Internal ClusterIP Internal / K8s 8080/TCP 8080/TCP
Configure Service Parameters
In the values.yaml under /helmchart/ select the services to deploy, the Helm chart parameters are listed below:
nrfclient.enabled: true
ocn-nrf-simulator.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-zookeeper.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-kafka.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-kafka-ui.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-keycloak.enabled: false
nwdaf-cap4c-redis.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-stream-analytics.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-model-executor.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-model-controller.enabled: true
nwdaf-cap4c-kafka-ingestor.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-configuration-service.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-subscription.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-data-collection.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-mtlf.enabled: true
ocn-nwdaf-analytics.enabled: true
ocnNwdafGeoredagent.enabled: false
nwdaf-portal-service.enabled: true
nwdaf-portal.enabled: tru
common-services-gateways.enabled: true
cap4cDeployTemp.enabled: falseIn the values.yaml under /simulator-helmChart/ select the simulators to deploy, the simulator Helm chart parameters are listed below:
ocn-smf-simulator.enabled: true
ocn-mesa-simulator.enabled: true
ocn-amf-simulator.enabled: true
ocn-oam-simulator.enabled: true4.3 Postinstallation Tasks
This section explains the postinstallation tasks for OCNWDAF.
4.3.1 Performing Helm Test
Helm Test is a feature that validates the successful installation of OCNWDAF and determines if the NF is ready to take traffic. The pods are tested based on the namespace and label selector configured for the helm test configurations.
Note:
Helm Test can be performed only on helm3.Prerequisite: To perform the helm test, you must have the helm test configurations completed under the "Global Parameters" section of the custom_values.yaml file. For more information on parameters, see Global Parameters.
Run the following command to perform the helm test:
helm3 test <helm-release_name> -n <namespace>where:
helm-release-name is the release name.
namespace is the deployment namespace where OCNWDAF is installed.
Example:
helm3 test ocnwdaf -n ocnwdaf
Sample output:
NAME: ocnwdaf
LAST DEPLOYED: Mon Nov 14 11:01:24 2022
NAMESPACE: ocnwdaf
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: ocnwdaf-test
Last Started: Mon Nov 14 11:01:45 2022
Last Completed: Mon Nov 14 11:01:53 2022
Phase: Succeeded
NOTES:
# Copyright 2022 (C), Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved4.3.2 Configuring OCNWDAF GUI
This section describes how to configure Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function (OCNWDAF) GUI using the following steps:
Configure OCNWDAF GUI in CNC Console
Prerequisite: To configure OCNWDAF GUI in CNC Console, you must have CNC Console installed. For information on how to install CNC Console, refer to Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Before installing CNC Console, ensure that the instances parameters are updated in the occncc_custom_values.yaml file.
If CNC Console is already installed, ensure all the parameters are updated in the occncc_custom_values.yaml file. For information refer to Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.
Access OCNWDAF GUI
To access OCNWDAF GUI, follow the procedure mentioned in the "Accessing CNC Console" section of Oracle Communications Cloud Native Configuration Console Installation, Upgrade, and Fault Recovery Guide.