4 Troubleshooting OCNWDAF
This chapter provides information to troubleshoot the common errors which can be encountered during the preinstallation and installation procedures of OCNWDAF.
4.1 Generic Checklist
The following sections provide a generic checklist for troubleshooting tips.
Deployment related tips
Perform the following checks after the deployment:
- Are OCNWDAF deployment, pods, and services created?
Are OCNWDAF deployment, pods, and services running and available?
Run the following the command:
Inspect the output, check the following columns:# kubectl -n <namespace> get deployments,pods,svc- AVAILABLE of deployment
- READY, STATUS, and RESTARTS of a pod
- PORT(S) of service
- Check if the microservices can access each other through the REST interface.
Run the following command:
# kubectl -n <namespace> exec <pod name> -- curl <uri>
Application related tips
Run the following command to check the application logs and look for exceptions:
# kubectl -n <namespace> logs -f <pod name>You can use '-f' to follow the logs or 'grep' for specific pattern in the log output.
4.2 Deployment Related Issue
This section describes the most common deployment related issues and their resolution steps. It is recommended to perform the resolution steps provided in this guide. If the issue still persists, then contact My Oracle Support.
4.2.1 Installation
This section describes the most common installation related issues and their resolution steps.
- Pod Creation Failure
- Pod Startup Failure
- NRF Registration Failure
- Install Timeout Error
- Resource Creation Failure
- Pods Enter Pending State
- Incorrect Service Account Creation
- Service Nodeport Error
- Service Configuration or Parameter Mismatch
- Run Only DB Creation Hook
- Helm Chart Upgrade
- Incorrect Values in Helm Chart
- Service Account Creation in Openshift Environment
- Stream Transformation or Storage Not Working
- Data Director Integration - Certificates Not Working
4.2.1.1 Pod Creation Failure
A pod creation can fail due to various reasons. Some of the possible scenarios are as follows:
Verifying Pod Image Correctness
To verify pod image:
- Check whether any of the pods is in the ImagePullBackOff state.
- Check if the image name used for all the pods are correct. Verify the image names and versions in the OCNWDAF installation file. For more information about the custom value file, see Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function Installation and Fault Recovery Guide.
Verifying Resource Allocation Failure
To verify any resource allocation failure:
- Run the following command to verify whether any pod is in the pending state.
kubectl describe <nwdaf-drservice pod id> --n <ocnef-namespace> - Verify whether any warning on insufficient CPU exists in the describe output of the respective pod. If it exists, it means there are insufficient CPUs for the pods to start. Address this hardware issue.
Verifying Resource Allocation Issues on Webscale Environment
Webscale environment has openshift container installed. There can be cases where,
- Pods does not scale after you run the installation command and the installation fails with timeout error. In this case, check for preinstall hooks failure. Run the oc get job command to create the jobs. Describe the job for which the pods are not getting scaled and check if there are quota limit exceeded errors with CPU or memory.
- Any of the actual microservice pods do not scale post the hooks completion. In this case, run the oc get rs command to get the list of replicaset created for the NF deployment. Then, describe the replicaset for which the pods are not getting scaled and check for resource quota limit exceeded errors with CPU or memory.
- Installation times-out after all the microservice pods are scaled as expected with the expected number of replicas. In this case, check for post install hooks failure. Run the oc get job command to get the post install jobs and do a describe on the job for which the pods are not getting scaled and check if there are quota limit exceeded errors with CPU or memory.
- Resource quota exceed beyond limits.
Verifying Resources Assigned to Previous Installation
If a previous installations, uninstall procedure was not successful and the uninstall process was forced, it is possible that some resources are still assigned to the previous installation. This can be detected by running the following command:
kubectl -n <namepsace> describe pod <podname>While searching for events, if you detect messages similar to the following message, it indicates that there are resources still assigned to the previous installation and should be purged.
0/n nodes are available: n pods has unbound immediate PersistenVolumeClaims4.2.1.2 Pod Startup Failure
- If dr-service, diameter-proxy, and diam-gateway services are stuck in the Init state, then the reason could be that config-server is not yet up. A sample log on these services is as follows:
"Config Server is Not yet Up, Wait For config server to be up."To resolve this, you must either check for the reason of config-server not being up or if the config-server is not required, then disable it.
- If the notify and on-demand migration service is stuck in the Init state, then the reason could be the dr-service is not yet up. A sample log on these services is as follows:
"DR Service is Not yet Up, Wait For dr service to be up."To resolve this, check for failures on dr-service.
4.2.1.3 NRF Registration Failure
- Confirm whether registration was successful from the nrf-client-service pod.
- Check the ocnwdaf-nrf-client-nfmanagement logs. If the log has "OCNWDAF is Unregistered" then:
- Check if all the services mentioned under allorudr/slf (depending on OCNWDAF mode) in the installation file has same spelling as that of service name and are enabled.
- Once all services are up, OCNWDAF must register with NRF.
- If you see a log for SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE(503), check if the primary and secondary NRF configurations (primaryNrfApiRoot/secondaryNrfApiRoot) are correct and they are UP and Running.
4.2.1.4 Incorrect Service Account Creation
Problem
Pods display an error when appropriate service accounts are not created for the pods.
Error Code or Error Message
Sample error message:
Figure 4-1 Sample Error Message
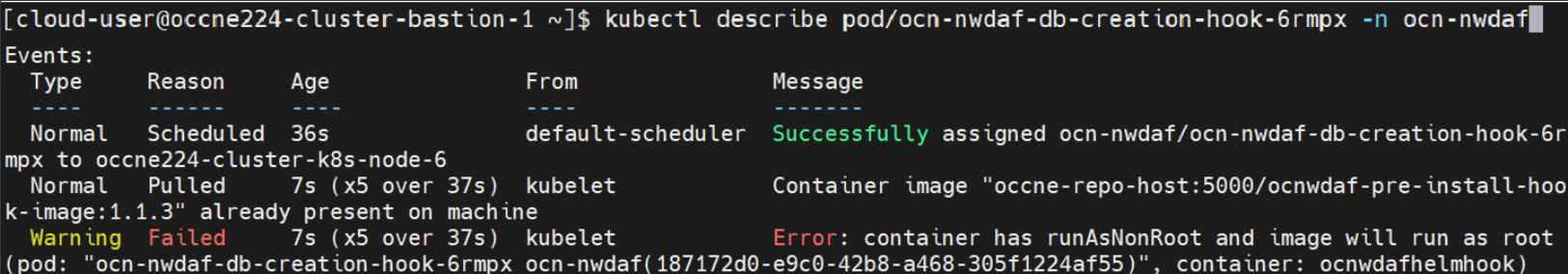
Solution
Ensure the service account creation hook in the parent chart's values.yaml file is enabled and runs properly.
4.2.1.5 Service Account Creation in Openshift Environment
Problem
While deploying OCNWDAF in an Openshift environment, service account creation can result in Helm installation issues.
Solution
Add the service account manually in the namespace before deployment, run the following command to add the service account:
oc adm policy add-scc-to-user anyuid --serviceaccount=<namespace>-ocnwdaf-sa -n <namespace>
Where,
oc: OpenShift CLIadm: Adminscc: Security Context Constraint
4.2.1.6 Incorrect Values in Helm Chart
Problem
During Helm chart deployment, if instances of the command parameter <replace here> are not replaced with values or replaced with incorrect values, services are not deployed.
Error Code or Error Message
Sample error message:
Figure 4-2 Incorrect Values in Helm Chart
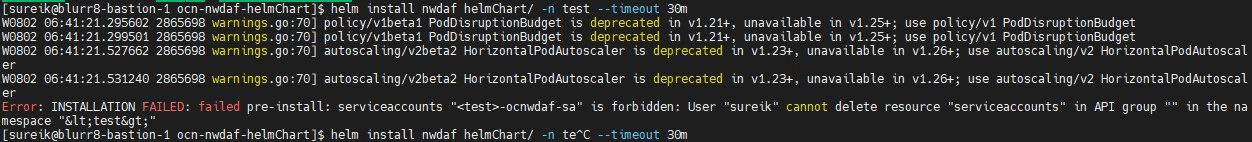
Solution
Uninstall the deployment and verify the values.yaml file in the Helm chart. Search for <replace here> instances and provide correct values.
4.2.1.7 Install Timeout Error
Problem
This error occurs when a hook restarts more than five times.
Error Code or Error Message
Sample error message:
Figure 4-3 Sample Error Message

Solution
Check whether the MySQL host or MySQL port is mentioned correctly in the values.yaml file of both the parent and the NRF client Helm charts. Verify the pod logs for more information.
Run the following command to verify the logs:
kubectl logs <name-of-pod/hook> -n <namespace>4.2.1.8 Pods Enter Pending State
Problem
Pods enter a pending state due to resource shortage in the setup.
Error Code or Error Message
Sample error message:
Figure 4-4 Sample Error Message
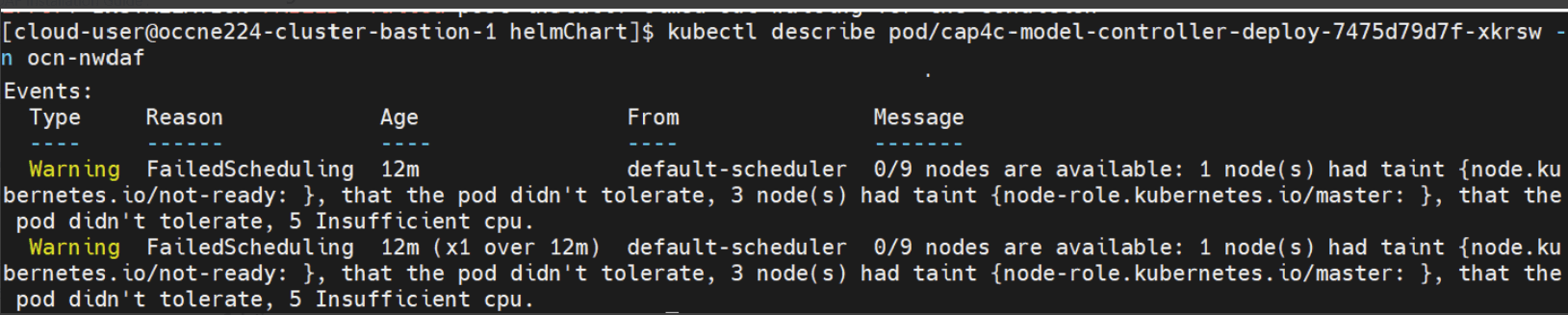
Solution
Free up all unnecessary resources present in the cluster that are consuming a lot of cluster resources.
4.2.1.9 Resource Creation Failure
Problem
The deployment namespace does not have appropriate permissions to create resources.
Error Code or Error Message
Sample error message:
Figure 4-5 Sample Error Message
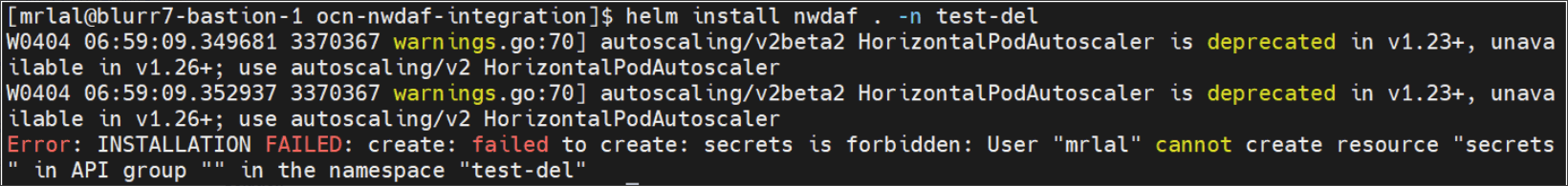
Solution
kubectl hns create <child-namespace> -n <parent-namespace> 4.2.1.10 Service Configuration or Parameter Mismatch
Problem
Service configuration or parameter mismatch might result in the service entering a CrashBackLoop off mode.
Solution
Update the properties in the corresponding services values.yaml file and perform a Helm install.
4.2.1.11 Service Nodeport Error
Problem
The service nodeport was previously assigned to other services running in the cluster.
Error Code or Error Message
Sample error message:
Figure 4-6 Sample Error Message

Solution
To resolve this error, edit the values.yaml file and provide a random port number to the service nodeport.
4.2.1.12 Common Services Gateway Service Name Mismatch
Problem
Suppose the service name of the common services gateway differs from "nwdaf-ingress-gateway-service" and "nwdaf-egress-gateway-service". This results in errors in the functioning of the gateways and forwarding of external requests to the respective services.
Solution
- Run the following command:
kubectl edit service <service-name> -n <namespace> - Edit the service names of the common services gateways to "nwdaf-ingress-gateway-service" for the Ingress Gateway and "nwdaf-egress-gateway-service" for the Egress Gateway respectively.
4.2.1.13 Run Only DB Creation Hook
Set the dbConfigStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmchart directory to dbonly to run only the DB creation hook. The Helm installation command will not deploy any other resource or make any other configuration change. Users can use different Helm installation names in the Helm install command to configure the latest database by updating the scripts ocnwdaf-db-config.yaml under /helmchart/templates directory and prehookconfig.yaml under /helmchart/charts/ocn-nwdaf-geo-redundancy-agent/templates directory.
4.2.1.14 Helm Chart Upgrade
helm upgrade <installation name> <path to the updated chart directory> -n $K8_NAMESPACE --timeout <timeout>hNote:
- Provide the correct installation name on which the installation was performed.
- The
timeoutvariable is optional. It is based on the speed of image pull from the nodes of the Bastion. The recommended timeout value is "4 h". - Helm upgrade must be performed only on the main Helm chart under /helmChart directory. It must not be performed on the subcharts under /charts directory. To update any subchart, make changes in the respective subchart and perform Helm upgrade on the main Helm chart under /helmChart directory.
- To enable DB creation hook or to prepare the dependencies hook, set the upgradeStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmChart directory to true before performing a Helm upgrade. To disable the hooks, set the upgradeStatus flag to false.
- Before performing a Helm upgrade on the ocn-nwdaf-communication, nwdaf-cap4c-zookeper-chart, nwdaf-cap4c-kafka-chart, ocn-nrf-simulator-service, and nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server-chart services, set the upgradeStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmChart directory to true. If there are no changes in the services, set the upgradeStatus flag to false.
- Use the prepare dependencies hook for Helm upgrade only when the upgradeStatus flag for nwdaf-cap4c-kafka-chart and nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server-chart microservices is set to false. To upgrade these microservices with the prepare dependencies hook, use the prepare dependencies hook in a separate Helm upgrade procedure, then perform an upgrade of the microservices.
Listed below are some use cases for performing a Helm upgrade:
- To update the fields such as image name, resources allotted, environment variables, and so on, make the required changes in the respective subcharts and run the Helm upgrade command on the updated chart.
- To enable or disable services, set the subcharts enable or disable flag in the centralized values.yaml file under the /helmchart directory to true or false (as required). The services with enable flag set to false are terminated.
- To reinstall the DB, enable the dbCreationHook upgradeStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmChart directory to true. The DB creation hook runs according to the configured dbConfigStatus flag in the file. For example, if the dbConfigStatus flag is set to nwdafdb, only the nwdafdb creation hook is run during upgrade.
- To transfer Spring Cloud config files from nwdaf-pre-installer.tar.gz to the spring-cloud-config-server microservice, and to create new Kafka topics in the Kafka microservice, use the prepare dependencies hook by updating prepareDependencyHook upgradeStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmChart directory to true. The Kafka pods and Spring Cloud Config server pods must be in Ready State before enabling upgradeStatus flag in values.yaml file under /helmChart directory to true.
4.2.1.15 Stream Transformation or Storage Not Working
Problem
Stream transformation or storage is not functioning correctly.
Solution
If stream transformation or storage is not functioning as expected, verify the consumer group list and lag for each topic as listed below:
-
To verify if stream storage is not storing data in the database, run the following script to verify the current number of records:
K8_NAMESPACE=... MYSQL_USER=... MYSQ_PASSWORD=... kubectl -n ${K8_NAMESPACE} exec -it mysql-pod -- mysql -u ${MYSQL_USER} -p${MYSQ_PASSWORD} -e "SELECT COUNT(*) FROM cap4c_kafka_ingestor_db.<replace-with-db>;" - Run the following script and verify the output to see if the topics are configured in Kafka:
K8_NAMESPACE=... KAFKA_POD=... kubectl -n ${K8_NAMESPACE} exec -it ${KAFKA_POD} -- kafka-consumer-groups.sh --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 - Run the following script and verify the output to see if the consumer group is consuming data from the requested topic:
K8_NAMESPACE=... KAFKA_POD=... KAFKA_CONSUMER_GROUP=... kubectl -n ${K8_NAMESPACE} exec -it ${KAFKA_POD} -- kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe --group ${KAFKA_CONSUMER_GROUP} - Run the following script and verify the output to see if data is produced in the expected format for the requested topic:
K8_NAMESPACE=... KAFKA_POD=... KAFKA_TOPIC=... kubectl -n ${K8_NAMESPACE} exec -it ${KAFKA_POD} -- kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic ${KAFKA_TOPIC} --max-messages 1 - Run the following script and verify the logs of the service which is not consuming the topic:
SERVICE_POD=... kubectl logs ${SERVICE_POD} -f
4.2.1.16 Slice Load and Geographical Data
Slice load and Geographical data is used for simulation. The cap4c_configuration_manager service database tables are populated with slice and cell data for the scripts to run correctly. This information is used as test data. Verify the tables if you face any issues during installation.
4.2.1.17 Data Director Integration - Certificates Not Working
Problem
The certificates generated by the gen_certs.sh script works only if a correct password is used and properties such as state, country, locality, organization, and so on are correctly configured.
Note:
The correct configuration of country, state, locality, organization and other fields are provided while generating the CA cert. The common name field can be any name other than the CA's common name.Solution
Use the OCNADD Kafka certificates and manually create the certificate config map for OCNWDAF Kafka. Run the following command:
kubectl create cm securityfiles --from-file=<truststore file name> --from-file=<keystore file name> -n <namespace>
Update the truststore and keystore filenames in the values.yaml file as below:
TRUSTSTORE_LOCATION: /var/security/<truststore file name>
KEYSTORE_LOCATION: /var/security/<keystore file name>4.2.1.18 Timeout Errors due to Inadequate Resources
Problem
Installation is susceptible timeout errors and potential failure if any of the scenarios listed below occur:
-
Insufficient Nodes to Deploy OCNWDAF
Sample command to verify nodes:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl top node NAME CPU(cores) CPU% MEMORY(bytes) MEMORY% qa-cluster-k8s-ctrl-1 909m 23% 2859Mi 86% qa-cluster-k8s-ctrl-2 248m 6% 2740Mi 82% qa-cluster-k8s-ctrl-3 233m 6% 2463Mi 74% qa-cluster-k8s-node-1 1605m 5% 18293Mi 14% qa-cluster-k8s-node-2 1717m 5% 30716Mi 23% qa-cluster-k8s-node-3 1277m 4% 14117Mi 10% qa-cluster-k8s-node-4 <unknown> <unknown> <unknown> <unknown> qa-cluster-k8s-node-5 <unknown> <unknown> <unknown> <unknown> qa-cluster-k8s-node-6 <unknown> <unknown> <unknown> <unknown> -
Insufficient PVC
Sample command to verify PVC:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl describe pod/nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-1 Name: nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-1 Priority: 0 Node: qa-cluster-k8s-node-6/192.168.200.80 Start Time: Tue, 12 Dec 2023 00:17:19 +0000 Labels: app.kubernetes.io/component=database ... ... ... Events: Type Reason Age From Message ---- ------ ---- ---- ------- Warning FailedScheduling 5m40s default-scheduler 0/9 nodes are available: 9 pod has unbound immediate PersistentVolumeClaims. -
Insufficient Storage
Sample command to verify storage:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ df -h Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on devtmpfs 32G 0 32G 0% /dev tmpfs 32G 168K 32G 1% /dev/shm tmpfs 32G 3.1G 29G 10% /run tmpfs 32G 0 32G 0% /sys/fs/cgroup /dev/mapper/vg_main-lv_root 96G 90G 7G 95% / /dev/vda1 495M 126M 370M 26% /boot tmpfs 6.3G 1.9M 6.3G 1% /run/user/1001
Timeout errors or installation failures are observed when there is a shortages of resources.
Sample Error Message
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl logs pod/cap4c-db-creation-hook-XXXXX
E1211 17:17:49.626634 7 memcache.go:238] couldn't get current server API group list: Get "https://10.233.0.1:443/api?timeout=32s": dial tcp 10.233.0.1:443: i/o timeout
E1211 17:18:19.628212 7 memcache.go:238] couldn't get current server API group list: Get "https://10.233.0.1:443/api?timeout=32s": dial tcp 10.233.0.1:443: i/o timeout
E1211 17:18:49.629644 7 memcache.go:238] couldn't get current server API group list: Get "https://10.233.0.1:443/api?timeout=32s": dial tcp 10.233.0.1:443: i/o timeout
E1211 17:19:19.630741 7 memcache.go:238] couldn't get current server API group list: Get "https://10.233.0.1:443/api?timeout=32s": dial tcp 10.233.0.1:443: i/o timeout
Unable to connect to the server: dial tcp 10.233.0.1:443: i/o timeoutWhen there is no connection between the OCNWDAF services and pods, the following error message is observed:
Sample Error Message
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl logs pod/nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-1 -c initconf
2023-12-11 17:24:59: Info: mysqlsh Ver 8.1.0-commercial for Linux on x86_64 - for MySQL 8.1.0 (MySQL Enterprise Server - Commercial) - build 11806512 - commit_id aa072a78647c21a540e40b8bdd04420e6efbe677
2023-12-11 17:24:59: Info: Using credential store helper: /usr/bin/mysql-secret-store-login-path
2023-12-11 17:24:59: Info: Loading startup files...
2023-12-11 17:24:59: Info: Loading plugins...
...
...
...
total 0
2023-12-11T17:27:13 - [WARNING] [urllib3.connectionpool] Retrying (Retry(total=2, connect=None, read=None, redirect=None, status=None)) after connection broken by 'NewConnectionError('<urllib3.connection.HTTPSConnection object at 0x7f1df49260d0>: Failed to establish a new connection: [Errno 110] Connection timed out')': /api/v1/namespaces/ocnwdaf-qa/pods/nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-1
Errors are also observed when there is no communication between MySQL InnoDB cluster components.
Solution
For a successful installation and operation ensure that the minimum and recommended CPU, memory, and storage requirements are met. For information on the resource requirements, see Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function Installation and Fault Recovery Guide.
4.2.2 Postinstallation
4.2.2.1 Helm Test Error Scenario
Following are the error scenarios that may be identified using Helm test.
- Run the following command to get the Helm Test pod name:
kubectl get pods -n <deployment-namespace> - When a Helm test is performed, a new Helm test pod is created. Check for the Helm Test pod that is in an error state.
- Get the logs using the following command:
kubectl logs <podname> -n <namespace>Example:kubectl get <helm_test_pod> -n ocnwdafFor further assistance, collect the logs and contact MOS.
4.2.2.2 Uninstall Helm Chart
Perform the following steps to uninstall the Helm chart:
- Run the following command to delete all jobs running in the cluster:
kubectl delete jobs --all -n <namespace> - Run the following command to delete resources like pods, deployments, services, and so on running in the cluster:
kubectl delete all --all -n <namespace> - Run the following Helm uninstall command:
helm uninstall <release-name> -n <namespace>
4.2.2.3 Purge Kafka Topics for New Installation
If in a previous OCNWDAF installation, Kafka topics contained messages, the topics should be retained in the new installation but not the messages. Follow the procedure below to prevent purge of Kafka topics:
- Connect to Kafka pod in your Kubernetes environment, run the command:
kubectl -n <namespace> exec -it <podname> -- bash - Change directory, move to the directory that contains the binary files:
cd kafka_2.13-3.1.0/bin/ - Obtain the list of topics, run the command:
kafka-topics.sh --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 - Delete each topic (repeat this step for each topic):
kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --delete --topic <topicname>
On completion of this procedure, the Kafka topics exist, but the messages do not exist.
Note:
After every installation is recommended to purge the topics before uninstalling them.4.3 Database Related Issues
This section describes the most common database related issues and their resolution steps. It is recommended to perform the resolution steps provided in this guide. If the issue still persists, then contact My Oracle Support.
4.3.1 Debugging MySQL DB Errors
If you are facing issues related to subscription creation, follow the procedure below to login to MySQL DB:
Note:
Once the MySQL cluster is created, the cndbtier_install container generates the password and stores it in the occne-mysqlndb-root-secret secret.- Retrieve the MySQL root password from occne-mysqlndb-root-secret secret.
Run the command:
$ kubectl -n occne-cndbtier get secret occne-mysqlndb-root-secret -o jsonpath='{.data}'map[mysql_root_password:TmV4dEdlbkNuZQ==] - Decode the encoded output received as an output of the previous step to get the actual password:
$ echo TmV4dEdlbkNuZQ== | base64 --decode NextGenCne - Login to MySQL pod, run the command:
$ kubectl -n occnepsa exec -it ndbmysqld-0 -- bashNote:
Default container name is:mysqlndbcluster.Run the command
kubectl describe pod/ndbmysqld-0 -n occnepsato see all the containers in this pod. - Login using MySQL client as the root user, run the command:
$ mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -uroot -p - Enter current root password for MySQL root user obtained from step 2.
- To debug each microservice, perform the following steps:
- For the ocn-nwdaf-subscription service, run the following SQL commands:
use <dbName>; use nwdaf_subscription; select * from nwdaf_subscription; select * from amf_ue_event_subscription select * from smf_ue_event_subscription - For the ocn-nrf-simulator service, run the following SQL commands:
use <dbName>; use nrf; select * from profile; - For the ocn-smf-simulator service, run the following SQL commands:
use <dbName>; use nrf; select * from smf_event_subscription; - For the ocn-amf-simulator service, run the following SQL commands:
use <dbName>; use nrf; select * from amf_event_subscription; - For the ocn-nwdaf-data-collection service, run the following SQL commands:
use <dbName>; use nwdaf_data_collection; select * from amf_event_notification_report_list; select * from amf_ue_event_report; select * from cap4c_ue_notification; select * from slice_load_level_notification; select * from smf_event_notification_report_list; select * from smf_ue_event_report; select * from ue_mobility_notification; - For the ocn-nwdaf-configuration-service service, run the following SQL commands:
use <dbName>; use nwdaf_configuration_service; select * from slice; select * from tracking_are; select * from slice_tracking_area; select * from cell;
- For the ocn-nwdaf-subscription service, run the following SQL commands:
4.3.2 Unable to Create Resources
Problem
Some errors may be observed during the first deployment of OCNWDAF with the MySQL Innodb cluster. The observed errors are listed below:
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: failed to install CRD crds/crd.yaml:
customresourcedefinitions.apiextensions.k8s.io is forbidden: User "user-xxxxx" cannot create resource "customresourcedefinitions" in API group "apiextensions.k8s.io" at the cluster scope
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: clusterkopfpeerings.zalando.org is forbidden:
User "user-xxxxx" cannot create resource "clusterkopfpeerings" in API group "zalando.org" at the cluster scope
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: clusterrolebindings.rbac.authorization.k8s.io is forbidden:
User "user-xxxxx" cannot create resource "clusterrolebindings" in API group "rbac.authorization.k8s.io" at the cluster scope
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: clusterroles.rbac.authorization.k8s.io is forbidden:
User "user-xxxxx" cannot create resource "clusterroles" in API group "rbac.authorization.k8s.io" at the cluster scope
Solution
kubectl describe clusterrole user-xxxxx-ns-admin-clusterFor example:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl describe clusterrole user-xxxxx-ns-admin-cluster
Name: user-xxxxx-admin-cluster
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
PolicyRule:
Resources Non-Resource URLs Resource Names Verbs
--------- ----------------- -------------- -----
clusterkopfpeerings.* [] [] [*]
clusterrolebindings.* [] [] [*]
clusterroles.* [] [] [*]
customresourcedefinitions.* [] [] [*]
kopfpeering.* [] [] [*]
mutatingwebhookconfigurations.* [] [] [*]
validatingwebhookconfigurations.* [] [] [*]
*.* [] [] [get list use]If the user does not have sufficient permissions, update the permissions as displayed in the above example.
4.3.3 Cluster Pod Forbidden during MySQL Innodb Deployment
Problem
Some errors may be observed during the first deployment of OCNWDAF with the MySQL Innodb cluster. The observed errors are listed below:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl describe statefulset.apps/mysql-innodb-cluster
Events:
Type Reason Age From Message
---- ------ ---- ---- -------
Normal SuccessfulCreate 40s statefulset-controller create Claim datadir-mysql-innodb-cluster-0 Pod mysql-innodb-cluster-0 in StatefulSet mysql-innodb-cluster success
Warning FailedCreate 20s (x13 over 40s) statefulset-controller create Pod mysql-innodb-cluster-0 in StatefulSet mysql-innodb-cluster failed error: pods "mysql-innodb-cluster-0" is forbidden: PodSecurityPolicy: unable to admit pod: [spec.initContainers[0].securityContext.runAsUser: Invalid value: 0: running with the root UID is forbidden spec.initContainers[0].securityContext.capabilities.add: Invalid value: "CHOWN": capability may not be added spec.initContainers[0].securityContext.capabilities.add: Invalid value: "FOWNER": capability may not be added]
Solution
The clusterrolebinding must use the context at the system:authenticated level instead of the Namespace level. For more information, see Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function Installation and Fault Recovery Guide.
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl edit clusterrolebinding user-xxxxx-ns-admin-cluster-role-binding- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: user-xxxxx-ns- apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Group
name: system:authenticated4.3.4 Cluster Pods in Terminating State
Problem
When Helm installation fails and the OCNWDAF is uninstalled, the pods remain in a "Terminating" state.
Run the following command:
kubectl get allSample output:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl get all
nwdaf-ns pod/nwdaf-innodb-cluster-0 0/2 Terminating 0 128m
nwdaf-ns pod/nwdaf-innodb-cluster-1 0/2 Terminating 0 128m
nwdaf-ns pod/nwdaf-innodb-cluster-2 0/2 Terminating 0 128mSolution
Delete and patch the pods in "Terminating" state.
For example:
kubectl delete pods nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-0 --grace-period=0 --force
kubectl delete pods nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-1 --grace-period=0 --force
kubectl delete pods nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-2 --grace-period=0 --force
....
kubectl patch pod nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-0 -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'
kubectl patch pod nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-1 -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'
kubectl patch pod nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster-2 -p '{"metadata":{"finalizers":null}}'4.3.5 Manually Delete Custom Resource Definition (CRD) of Innodb Cluster
Problem
When the OCNWDAF is deleted using the no-hooks option, the following error is observed:
helm.go:84: [debug] failed innodbclusters.mysql.oracle.com "nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster" already exists
INSTALLATION FAILEDRun the following command to verify if the Innodb cluster still exists:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl get innodbcluster
NAME STATUS ONLINE INSTANCES ROUTERS AGE
nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster OFFLINE 0 3 1 20hSolution
Ensure that the CRD of the Innodb cluster is deleted manually, run the following command:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl get innodbcluster nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster -o yaml > delete-innodb-cluster.yamlReplace the finalizers with an empty list, edit as displayed below:
vi delete-innodb-clusteryaml
apiVersion: mysql.oracle.com/v2
kind: InnoDBCluster
metadata:
annotations:
helm.sh/hook: pre-install
...
mysql.oracle.com/mysql-operator-version: 8.1.0-2.1.0
creationTimestamp: "2023-11-13T15:53:44Z"
finalizers: []
generation: 1
name: nwdaf-mysql-innodb-cluster
namespace: user-xxxxx
resourceVersion: "61716523"
uid: c69778c7-c866-4aa5-a393-c94c5c6b3b25
spec:
baseServerId: 1000
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
...
version: 8.1.0
status:
cluster:
lastProbeTime: "2023-11-13T16:10:36Z"
onlineInstances: 3
status: ONLINE
createTime: "2023-11-13T15:54:52Z"
kopf:
progress: {}Remove the CRD Innodb cluster and run the following command:
[user-xxxxx@kubernetes-cluster ~]$ kubectl apply -f delete-innodb-cluster.yamlRetry the OCNWDAF installation procedure. For the installation procedure, see Oracle Communications Networks Data Analytics Function Installation and Fault Recovery Guide.
4.4 Apache Kafka Related Issues
To debug issues related to Apache Kafka pipelines (such as, unable to read messages from the pipeline or write messages to the pipeline) perform the following steps:
- Get the Kafka pods, run the command:
kubectl -n <namespace> get pods -o wide | grep "kafka" - Select any pod and access the pod using the command:
kubectl -n <namespace> exec -it kafka-sts-0 -- bash - Move to the directory containing the binary files, run the command:
cd kafka_2.13-3.1.0/bin/ - Obtain the list of topics, run the command:
kafka-topics.sh --list --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 - For each topic, run the following command:
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server 127.0.0.1:9092 --topic <topic-name>
4.5 CAP4C Related Issues
- cap4c-model-controller
- cap4c-model-executor
- cap4c-kafka-ingestor
- cap4c-api-gateway
- cap4c-configuration-manager
- cap4c-stream-analytics
- cap4c-stream-transformer
- nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service
- nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service
To obtain more information on the service pods, follow the steps listed below:
-
Each of these services is deployed as pod in Kubernetes. To find the status of the pods in Kubernetes run the following command:
$ kubectl get pods -n <namespace>Sample output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cap4c-model-controller-deploy-779cbdcf8f-w2pfh 1/1 Running 0 4d8h cap4c-model-executor-deploy-f9c96db54-ttnhd 1/1 Running 0 4d5h cap4c-stream-analytics-deploy-744878569-5xr2w 1/1 Running 0 4d8h - To verify the pod information, print the detail of each pod to:
$ kubectl describe pod cap4c-model-controller-deploy-779cbdcf8f-w2pfh -n <namespace>Sample output:
Name: cap4c-model-controller-deploy-779cbdcf8f-w2pfh Namespace: performance-ns Priority: 0 Node: sunstreaker-k8s-node-2/192.168.200.197 Start Time: Fri, 26 Aug 2022 15:31:39 +0000 Labels: app=cap4c-model-controller pod-template-hash=779cbdcf8f Annotations: cni.projectcalico.org/containerID: 480ca581a828184ccf6fabf7ec7cfb68920624f48d57148f6d93db4512bc5335 cni.projectcalico.org/podIP: 10.233.76.134/32 cni.projectcalico.org/podIPs: 10.233.76.134/32 kubernetes.io/psp: restricted seccomp.security.alpha.kubernetes.io/pod: runtime/default Status: Running - List the service configuration for the pods, run the command:
$ kubectl get svc -n <namespace>Sample output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE cap4c-executor ClusterIP 10.233.5.218 <none> 8888:32767/TCP 4d8h
4.6 Service Related Issues
This section describes the most common service related issues and their resolution steps. It is recommended to perform the resolution steps provided in this guide. If the issue still persists, then contact My Oracle Support.
4.6.1 Errors from Microservices
The OCNWDAF microservices are listed below:
- ocn-nwdaf-analytics
- ocn-nwdaf-mtlf-service
- ocn-nwdaf-subscription-service
- ocn-amf-simulator-service
- ocn-smf-simulator-service
- ocn-nrf-simulator-service
- ocn-oam-simulator-service
- mesa-simulator
- cap4c-model-controller
- cap4c-model-executor
- cap4c-stream-analytics
- cap4c-kafka-ingestor
- nwdaf-cap4c-reporting-service
- nwdaf-cap4c-kafka
- nwdaf-cap4c-scheduler-service
- nwdaf-cap4c-spring-cloud-config-server
- nwdaf-portal
- nwdaf-portal-service
- nwdaf-cap4c-redis
- nwdaf-cap4c-zookeeper
- nwdaf-cap4c-initial-setup-script
- ocats-nwdaf
- ocats-nwdaf-notify
- ocats-nwdaf-notify-nginx
- nf-test
- ocn-nwdaf-geo-redundacy-agent
- ocingress_gateway
- ocegress_gateway
- oc-config-server
- oc-app-info
- oc-perf-info
- nrf-client
- ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-controller
- cap4c-configuration-manager-service
- cap4c-stream-transformer
- nwdaf-cap4c-nginx
- cap4c-api-gateway
To debug microservice related errors, obtain the logs in the pods that are facing issues, run the following commands for each microservice:
- To obtain the pod information, run the following command:
kubectl get pods -n <nameSpace> -o wide - To obtain the log information for the pods, run the following command:
kubectl logs <podName> -n <nameSpace>
kubectl logs ocn-nwdaf-subscription-84f8b74cc7-d7lk9 -n performance-nskubectl logs ocn-nwdaf-data-collection-57b948989c-xs7dq -n performance-nskubectl logs ocn-amf-simulator-584ccb8fd4-pcdn6 -n performance-ns